research
< Researcher Yang-Sun Hwang (left), Researcher You-Hyang Song (center), and Professor Seung-Hee Lee (right) >,_Researcher_You-Hyang_Song_(center),_and_Professor_Seung-Hee_Lee_(r.jpg)
Researchers have confirmed that neuropeptide somatostatin can improve cognitive function in the brain. A research group of Professor Seung-Hee Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST found that the application of neuropeptide somatostatin improves visual processing and cognitive behaviors by reducing excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the cortex.
This study, reported at Science Advances on April 22nd (EST), sheds a new light on the therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. According to a recent study in Korea, one in ten seniors over 65 is experiencing dementia-related symptoms in their daily lives such like memory loss, cognitive decline, and motion function disorders. Professor Lee believes that somatostatin treatment can be directly applied to the recovery of cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s disease patients.
Professor Lee started this study noting the fact that the level of somatostatin expression was dramatically decreased in the cerebral cortex and cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients
Somatostatin-expressing neurons in the cortex are known to exert the dendritic inhibition of pyramidal neurons via GABAergic transmission. Previous studies focused on their inhibitory effects on cortical circuits, but somatostatin-expressing neurons can co-release somatostatin upon activation. Despite the abundant expression of somatostatin and its receptors in the cerebral cortex, it was not known if somatostatin could modulate cognitive processing in the cortex.
The research team demonstrated that the somatostatin treatment into the cerebral cortex could enhance visual processing and cognitive behaviors in mice. The research team combined behaviors, in vivo and in vitro electrophysiology, and electron microscopy techniques to reveal how the activation of somatostatin receptors in vivo enhanced the ability of visual recognition in animals. Interestingly, somatostatin release can reduce excitatory synaptic transmission to another subtype of GABAergic interneurons, parvalbumin (PV)-expressing neurons.
As somatostatin is a stable and safe neuropeptide expressed naturally in the mammalian brain, it was safe to be injected into the cortex and cerebrospinal fluid, showing a potential application to drug development for curing cognitive disorders in humans.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed the key role of the neuropeptide SST in modulating cortical function and enhancing cognitive ability in the mammalian brain. I hope new drugs can be developed based on the function of somatostatin to treat cognitive disabilities in many patients suffering from neurological disorders.”
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
< Figure 1. Effects of SST and cyclo-SST injections on the visual discrimination performance of mice. >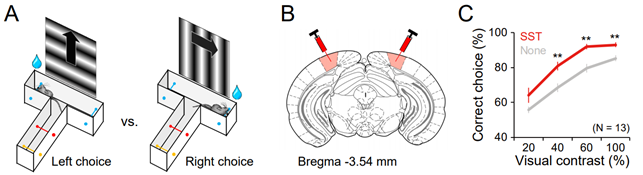
< Figure. 2 SST increases the orientation selectivity and visual-evoked activity in the V1 of anesthetized mice. >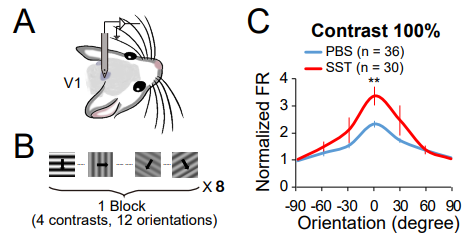
< Figure 3. PV+ neurons receive perisomatic excitatory synaptic inputs that are innervated by axons of SST neurons. >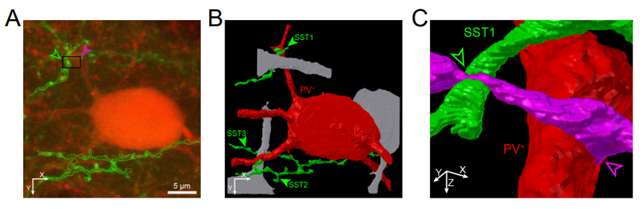
Publication:
Song, Y. H et al. (2020) ‘Somatostatin enhances visual processing and perception by suppressing excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-positive interneurons in V1’, Science Advances, 6(17). Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz0517
Profile:
Seung-Hee Lee
Associate Professor
shlee1@kaist.ac.kr
https://sites.google.com/site/leelab2013/
Sensory Processing Lab (SPL)
Department of Biological Sciences (BIO)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Profile:
You-Hyang Song
Researcher (Ph.D.)
dbgidtm17@kaist.ac.kr
SPL, KAIST BIO
Profile:
Yang-Sun Hwang
Researcher (M.S.)
hys940129@kaist.ac.kr
SPL, KAIST BIO
(END)
-
research The World’s First Hacking-preventing Cryptographic Semiconductor Chip
With the dramatic increase in the amount of information exchanged between components or devices in the 5G/6G era, such as for the Internet of Things (IoT) and autonomous driving, hacking attacks are becoming more sophisticated. Consequently, enhancing security functions is essential for safely transmitting data between and among devices. On February 29th, a KAIST research team led by Professors Yang-gyu Choi and Seung-tak Ryu from the School of Electrical Engineering announced the successful
2024-03-07 -
research KAIST Research Team Develops Sweat-Resistant Wearable Robot Sensor
New electromyography (EMG) sensor technology that allows the long-term stable control of wearable robots and is not affected by the wearer’s sweat and dead skin has gained attention recently. Wearable robots are devices used across a variety of rehabilitation treatments for the elderly and patients recovering from stroke or trauma. A joint research team led by Professor Jae-Woong Jung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering (EE) and Professor Jung Kim from the KAIST Department of
2024-01-30 -
research KAIST develops an artificial muscle device that produces force 34 times its weight
- Professor IlKwon Oh’s research team in KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a soft fluidic switch using an ionic polymer artificial muscle that runs with ultra-low power to lift objects 34 times greater than its weight. - Its light weight and small size make it applicable to various industrial fields such as soft electronics, smart textiles, and biomedical devices by controlling fluid flow with high precision, even in narrow spaces. Soft robots, medical devic
2024-01-11 -
research KAIST Research Team Proves How a Neurotransmitter may be the Key in Controlling Alzheimer’s Toxicity
With nearly 50 million dementia patients worldwide, and Alzheimers’s disease is the most common neurodegenerative disease. Its main symptom is the impairment of general cognitive abilities, including the ability to speak or to remember. The importance of finding a cure is widely understood with increasingly aging population and the life expectancy being ever-extended. However, even the cause of the grim disease is yet to be given a clear definition. A KAIST research team in the Departme
2022-07-29 -
research Tinkering with Roundworm Proteins Offers Hope for Anti-aging Drugs
- The somatic nuclear protein kinase VRK-1 increases the worm’s lifespan through AMPK activation, and this mechanism can be applied to promoting human longevity, the study reveals. - KAIST researchers have been able to dial up and down creatures’ lifespans by altering the activity of proteins found in roundworm cells that tell them to convert sugar into energy when their cellular energy is running low. Humans also have these proteins, offering up the intriguing possibilities for d
2020-07-31