TE
-
 Prof. Seungbum Koo’s Team Receives Clinical Biomechanics Award at the 30th International Society of Biomechanics Conference
<(From Left) Ph.D candidate Jeongseok Oh from KAIST, Dr. Seungwoo Yoon from KAIST, Prof.Joon-Ho Wang from Samsung Medical Center, Prof.Seungbum Koo from KAIST>
Professor Seungbum Koo’s research team received the Clinical Biomechanics Award at the 30th International Society of Biomechanics (ISB) Conference, held in July 2025 in Stockholm, Sweden. The Plenary Lecture was delivered by first author and Ph.D. candidate Jeongseok Oh. This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Joon-Ho Wang’s team at Samsung Medical Center.
Residual Translational and Rotational Kinematics After Combined ACL and Anterolateral Ligament Reconstruction During Walking
Jeongseok Oh, Seungwoo Yoon, Joon-Ho Wang, Seungbum Koo
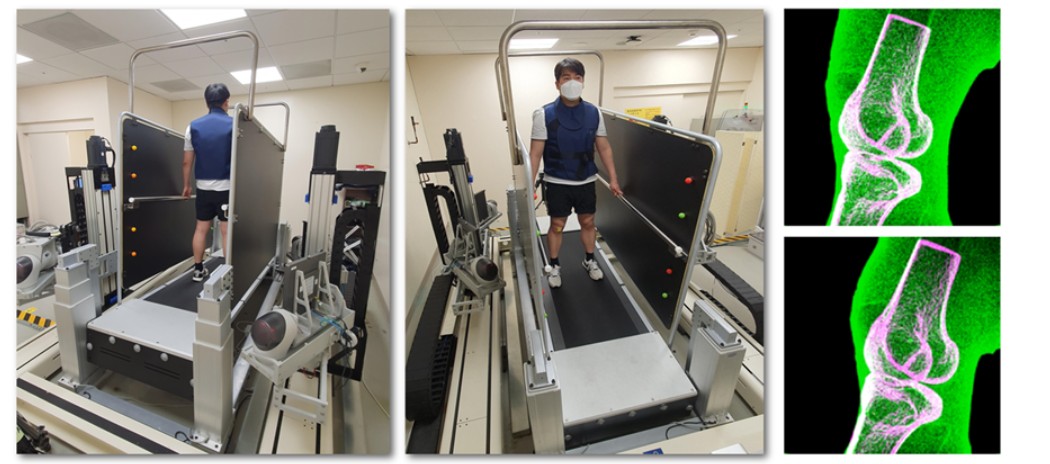
The study analyzed gait-related knee joint motion using high-speed biplane X-ray imaging and three-dimensional kinematic reconstruction in 10 healthy individuals and 10 patients who underwent ACL reconstruction with ALL augmentation. The patient group showed excessive anterior translation and internal rotation, suggesting incomplete restoration of normal joint kinematics post-surgery. These findings provide mechanistic insight into the early onset of knee osteoarthritis often reported in this population.'
The ISB conference, held biennially for over 60 years, is the largest international biomechanics meeting. This year, it hosted 1,600 researchers from 46 countries and featured over 1,400 presentations. The Clinical Biomechanics Award is given to one outstanding study selected from five top-rated abstracts invited for full manuscript review. The winning paper is published in Clinical Biomechanics, and the award includes a monetary prize and a Plenary Lecture opportunity.
From 2019 to 2023, Koo and Wang’s teams developed a system with support from the Samsung Future Technology Development Program to track knee motion in real time during treadmill walking, using high-speed biplane X-rays and custom three-dimensional reconstruction software. This system, along with proprietary software that precisely reconstructs the three-dimensional motion of joints, was approved for clinical trials by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety and installed at Samsung Medical Center. It is being used to quantitatively analyze abnormal joint motion patterns in patients with knee ligament injuries and those who have undergone knee surgery.
Additionally, Jeongseok Oh was named one of five finalists for the David Winter Young Investigator Award, presenting his work during the award session. This award recognizes promising young researchers in biomechanics worldwide.
2025.08.10 View 79
Prof. Seungbum Koo’s Team Receives Clinical Biomechanics Award at the 30th International Society of Biomechanics Conference
<(From Left) Ph.D candidate Jeongseok Oh from KAIST, Dr. Seungwoo Yoon from KAIST, Prof.Joon-Ho Wang from Samsung Medical Center, Prof.Seungbum Koo from KAIST>
Professor Seungbum Koo’s research team received the Clinical Biomechanics Award at the 30th International Society of Biomechanics (ISB) Conference, held in July 2025 in Stockholm, Sweden. The Plenary Lecture was delivered by first author and Ph.D. candidate Jeongseok Oh. This research was conducted in collaboration with Professor Joon-Ho Wang’s team at Samsung Medical Center.
Residual Translational and Rotational Kinematics After Combined ACL and Anterolateral Ligament Reconstruction During Walking
Jeongseok Oh, Seungwoo Yoon, Joon-Ho Wang, Seungbum Koo
The study analyzed gait-related knee joint motion using high-speed biplane X-ray imaging and three-dimensional kinematic reconstruction in 10 healthy individuals and 10 patients who underwent ACL reconstruction with ALL augmentation. The patient group showed excessive anterior translation and internal rotation, suggesting incomplete restoration of normal joint kinematics post-surgery. These findings provide mechanistic insight into the early onset of knee osteoarthritis often reported in this population.'
The ISB conference, held biennially for over 60 years, is the largest international biomechanics meeting. This year, it hosted 1,600 researchers from 46 countries and featured over 1,400 presentations. The Clinical Biomechanics Award is given to one outstanding study selected from five top-rated abstracts invited for full manuscript review. The winning paper is published in Clinical Biomechanics, and the award includes a monetary prize and a Plenary Lecture opportunity.
From 2019 to 2023, Koo and Wang’s teams developed a system with support from the Samsung Future Technology Development Program to track knee motion in real time during treadmill walking, using high-speed biplane X-rays and custom three-dimensional reconstruction software. This system, along with proprietary software that precisely reconstructs the three-dimensional motion of joints, was approved for clinical trials by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety and installed at Samsung Medical Center. It is being used to quantitatively analyze abnormal joint motion patterns in patients with knee ligament injuries and those who have undergone knee surgery.
Additionally, Jeongseok Oh was named one of five finalists for the David Winter Young Investigator Award, presenting his work during the award session. This award recognizes promising young researchers in biomechanics worldwide.
2025.08.10 View 79 -
 Material Innovation Realized with Robotic Arms and AI, Without Human Researchers
<(From Left) M.S candidate Dongwoo Kim from KAIST, Ph.D candidate Hyun-Gi Lee from KAIST, Intern Yeham Kang from KAIST, M.S candidate Seongjae Bae from KAIST, Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from KAIST, (From top right, from left) Senior Researcher Inchul Park from POSCO Holdings, Senior Researcher Jung Woo Park, senior researcher from POSCO Holdings>
A joint research team from industry and academia in Korea has successfully developed an autonomous lab that uses AI and automation to create new cathode materials for secondary batteries. This system operates without human intervention, drastically reducing researcher labor and cutting the material discovery period by 93%.
* Autonomous Lab: A platform that autonomously designs, conducts, and analyzes experiments to find the optimal material.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 3rd of August that the research team led by Professor Dong-Hwa Seo of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with the team of LIB Materials Research Center in Energy Materials R&D Laboratories at POSCO Holdings' POSCO N.EX.T Hub (Director Ki Soo Kim), built the lab to explore cathode materials using AI and automation technology.
Developing secondary battery cathode materials is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process for skilled researchers. It involves extensive exploration of various compositions and experimental variables through weighing, transporting, mixing, sintering*, and analyzing samples.
* Sintering: A process in which powder particles are heated to form a single solid mass through thermal activation.
The research team's autonomous lab combines an automated system with an AI model. The system handles all experimental steps—weighing, mixing, pelletizing, sintering, and analysis—without human interference. The AI model then interprets the data, learns from it, and selects the best candidates for the next experiment.
<Figure 1. Outline of the Anode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
To increase efficiency, the team designed the automation system with separate modules for each process, which are managed by a central robotic arm. This modular approach reduces the system's reliance on the robotic arm.
The team also significantly improved the synthesis speed by using a new high-speed sintering method, which is 50 times faster than the conventional low-speed method. This allows the autonomous lab to acquire 12 times more material data compared to traditional, researcher-led experiments.
<Figure 2. Synthesis of Cathode Material Using a High-Speed Sintering Device>
The vast amount of data collected is automatically interpreted by the AI model to extract information such as synthesized phases and impurity ratios. This data is systematically stored to create a high-quality database, which then serves as training data for an optimization AI model. This creates a closed-loop experimental system that recommends the next cathode composition and synthesis conditions for the automated system.
* Closed-loop experimental system: A system that independently performs all experimental processes without researcher intervention.
Operating this intelligent automation system 24 hours a day can secure more than 12 times the experimental data and shorten material discovery time by 93%. For a project requiring 500 experiments, the system can complete the work in about 6 days, whereas a traditional researcher-led approach would take 84 days.
During development, POSCO Holdings team managed the overall project planning, reviewed the platform design, and co-developed the partial module design and AI-based experimental model. The KAIST team, led by Professor Dong-hwa Seo, was responsible for the actual system implementation and operation, including platform design, module fabrication, algorithm creation, and system verification and improvement.
Professor Dong-Hwa Seo of KAIST stated that this system is a solution to the decrease in research personnel due to the low birth rate in Korea. He expects it will enhance global competitiveness by accelerating secondary battery material development through the acquisition of high-quality data.
<Figure 3. Exterior View (Side) of the Cathode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
POSCO N.EX.T Hub plans to apply an upgraded version of this autonomous lab to its own research facilities after 2026 to dramatically speed up next-generation secondary battery material development. They are planning further developments to enhance the system's stability and scalability, and hope this industry-academia collaboration will serve as a model for using innovative technology in real-world R&D.
<Figure 4. Exterior View (Front) of the Cathode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
The research was spearheaded by Ph.D. student Hyun-Gi Lee, along with master's students Seongjae Bae and Dongwoo Kim from Professor Dong-Hwa Seo’s lab at KAIST. Senior researchers Jung Woo Park and Inchul Park from LIB Materials Research Center of POSCO N.EX.T Hub's Energy Materials R&D Laboratories (Director Jeongjin Hong) also participated.
2025.08.06 View 83
Material Innovation Realized with Robotic Arms and AI, Without Human Researchers
<(From Left) M.S candidate Dongwoo Kim from KAIST, Ph.D candidate Hyun-Gi Lee from KAIST, Intern Yeham Kang from KAIST, M.S candidate Seongjae Bae from KAIST, Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from KAIST, (From top right, from left) Senior Researcher Inchul Park from POSCO Holdings, Senior Researcher Jung Woo Park, senior researcher from POSCO Holdings>
A joint research team from industry and academia in Korea has successfully developed an autonomous lab that uses AI and automation to create new cathode materials for secondary batteries. This system operates without human intervention, drastically reducing researcher labor and cutting the material discovery period by 93%.
* Autonomous Lab: A platform that autonomously designs, conducts, and analyzes experiments to find the optimal material.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 3rd of August that the research team led by Professor Dong-Hwa Seo of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with the team of LIB Materials Research Center in Energy Materials R&D Laboratories at POSCO Holdings' POSCO N.EX.T Hub (Director Ki Soo Kim), built the lab to explore cathode materials using AI and automation technology.
Developing secondary battery cathode materials is a labor-intensive and time-consuming process for skilled researchers. It involves extensive exploration of various compositions and experimental variables through weighing, transporting, mixing, sintering*, and analyzing samples.
* Sintering: A process in which powder particles are heated to form a single solid mass through thermal activation.
The research team's autonomous lab combines an automated system with an AI model. The system handles all experimental steps—weighing, mixing, pelletizing, sintering, and analysis—without human interference. The AI model then interprets the data, learns from it, and selects the best candidates for the next experiment.
<Figure 1. Outline of the Anode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
To increase efficiency, the team designed the automation system with separate modules for each process, which are managed by a central robotic arm. This modular approach reduces the system's reliance on the robotic arm.
The team also significantly improved the synthesis speed by using a new high-speed sintering method, which is 50 times faster than the conventional low-speed method. This allows the autonomous lab to acquire 12 times more material data compared to traditional, researcher-led experiments.
<Figure 2. Synthesis of Cathode Material Using a High-Speed Sintering Device>
The vast amount of data collected is automatically interpreted by the AI model to extract information such as synthesized phases and impurity ratios. This data is systematically stored to create a high-quality database, which then serves as training data for an optimization AI model. This creates a closed-loop experimental system that recommends the next cathode composition and synthesis conditions for the automated system.
* Closed-loop experimental system: A system that independently performs all experimental processes without researcher intervention.
Operating this intelligent automation system 24 hours a day can secure more than 12 times the experimental data and shorten material discovery time by 93%. For a project requiring 500 experiments, the system can complete the work in about 6 days, whereas a traditional researcher-led approach would take 84 days.
During development, POSCO Holdings team managed the overall project planning, reviewed the platform design, and co-developed the partial module design and AI-based experimental model. The KAIST team, led by Professor Dong-hwa Seo, was responsible for the actual system implementation and operation, including platform design, module fabrication, algorithm creation, and system verification and improvement.
Professor Dong-Hwa Seo of KAIST stated that this system is a solution to the decrease in research personnel due to the low birth rate in Korea. He expects it will enhance global competitiveness by accelerating secondary battery material development through the acquisition of high-quality data.
<Figure 3. Exterior View (Side) of the Cathode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
POSCO N.EX.T Hub plans to apply an upgraded version of this autonomous lab to its own research facilities after 2026 to dramatically speed up next-generation secondary battery material development. They are planning further developments to enhance the system's stability and scalability, and hope this industry-academia collaboration will serve as a model for using innovative technology in real-world R&D.
<Figure 4. Exterior View (Front) of the Cathode Material Autonomous Exploration Laboratory>
The research was spearheaded by Ph.D. student Hyun-Gi Lee, along with master's students Seongjae Bae and Dongwoo Kim from Professor Dong-Hwa Seo’s lab at KAIST. Senior researchers Jung Woo Park and Inchul Park from LIB Materials Research Center of POSCO N.EX.T Hub's Energy Materials R&D Laboratories (Director Jeongjin Hong) also participated.
2025.08.06 View 83 -
 KAIST Develops AI ‘MARIOH’ to Uncover and Reconstruct Hidden Multi-Entity Relationships
<(From Left) Professor Kijung Shin, Ph.D candidate Kyuhan Lee, and Ph.D candidate Geon Lee>
Just like when multiple people gather simultaneously in a meeting room, higher-order interactions—where many entities interact at once—occur across various fields and reflect the complexity of real-world relationships. However, due to technical limitations, in many fields, only low-order pairwise interactions between entities can be observed and collected, which results in the loss of full context and restricts practical use. KAIST researchers have developed the AI model “MARIOH,” which can accurately reconstruct* higher-order interactions from such low-order information, opening up innovative analytical possibilities in fields like social network analysis, neuroscience, and life sciences.
*Reconstruction: Estimating/reconstructing the original structure that has disappeared or was not observed.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that Professor Kijung Shin’s research team at the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI has developed an AI technology called “MARIOH” (Multiplicity-Aware Hypergraph Reconstruction), which can reconstruct higher-order interaction structures with high accuracy using only low-order interaction data.
Reconstructing higher-order interactions is challenging because a vast number of higher-order interactions can arise from the same low-order structure.
The key idea behind MARIOH, developed by the research team, is to utilize multiplicity information of low-order interactions to drastically reduce the number of candidate higher-order interactions that could stem from a given structure.
In addition, by employing efficient search techniques, MARIOH quickly identifies promising interaction candidates and uses multiplicity-based deep learning to accurately predict the likelihood that each candidate represents an actual higher-order interaction.
<Figure 1. An example of recovering high-dimensional relationships (right) from low-dimensional paper co-authorship relationships (left) with 100% accuracy, using MARIOH technology.>
Through experiments on ten diverse real-world datasets, the research team showed that MARIOH reconstructed higher-order interactions with up to 74% greater accuracy compared to existing methods.
For instance, in a dataset on co-authorship relations (source: DBLP), MARIOH achieved a reconstruction accuracy of over 98%, significantly outperforming existing methods, which reached only about 86%. Furthermore, leveraging the reconstructed higher-order structures led to improved performance in downstream tasks, including prediction and classification.
According to Kijung, “MARIOH moves beyond existing approaches that rely solely on simplified connection information, enabling precise analysis of the complex interconnections found in the real world.” Furthermore, “it has broad potential applications in fields such as social network analysis for group chats or collaborative networks, life sciences for studying protein complexes or gene interactions, and neuroscience for tracking simultaneous activity across multiple brain regions.”
The research was conducted by Kyuhan Lee (Integrated M.S.–Ph.D. program at the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST; currently a software engineer at GraphAI), Geon Lee (Integrated M.S.–Ph.D. program at KAIST), and Professor Kijung Shin. It was presented at the 41st IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (IEEE ICDE), held in Hong Kong this past May.
※ Paper title: MARIOH: Multiplicity-Aware Hypergraph Reconstruction ※ DOI: https://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/ICDE65448.2025.00233
<Figure 2. An example of the process of recovering high-dimensional relationships using MARIOH technology>
This research was supported by the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) through the project “EntireDB2AI: Foundational technologies and software for deep representation learning and prediction using complete relational databases,” as well as by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the project “Graph Foundation Model: Graph-based machine learning applicable across various modalities and domains.”
2025.08.05 View 207
KAIST Develops AI ‘MARIOH’ to Uncover and Reconstruct Hidden Multi-Entity Relationships
<(From Left) Professor Kijung Shin, Ph.D candidate Kyuhan Lee, and Ph.D candidate Geon Lee>
Just like when multiple people gather simultaneously in a meeting room, higher-order interactions—where many entities interact at once—occur across various fields and reflect the complexity of real-world relationships. However, due to technical limitations, in many fields, only low-order pairwise interactions between entities can be observed and collected, which results in the loss of full context and restricts practical use. KAIST researchers have developed the AI model “MARIOH,” which can accurately reconstruct* higher-order interactions from such low-order information, opening up innovative analytical possibilities in fields like social network analysis, neuroscience, and life sciences.
*Reconstruction: Estimating/reconstructing the original structure that has disappeared or was not observed.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that Professor Kijung Shin’s research team at the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI has developed an AI technology called “MARIOH” (Multiplicity-Aware Hypergraph Reconstruction), which can reconstruct higher-order interaction structures with high accuracy using only low-order interaction data.
Reconstructing higher-order interactions is challenging because a vast number of higher-order interactions can arise from the same low-order structure.
The key idea behind MARIOH, developed by the research team, is to utilize multiplicity information of low-order interactions to drastically reduce the number of candidate higher-order interactions that could stem from a given structure.
In addition, by employing efficient search techniques, MARIOH quickly identifies promising interaction candidates and uses multiplicity-based deep learning to accurately predict the likelihood that each candidate represents an actual higher-order interaction.
<Figure 1. An example of recovering high-dimensional relationships (right) from low-dimensional paper co-authorship relationships (left) with 100% accuracy, using MARIOH technology.>
Through experiments on ten diverse real-world datasets, the research team showed that MARIOH reconstructed higher-order interactions with up to 74% greater accuracy compared to existing methods.
For instance, in a dataset on co-authorship relations (source: DBLP), MARIOH achieved a reconstruction accuracy of over 98%, significantly outperforming existing methods, which reached only about 86%. Furthermore, leveraging the reconstructed higher-order structures led to improved performance in downstream tasks, including prediction and classification.
According to Kijung, “MARIOH moves beyond existing approaches that rely solely on simplified connection information, enabling precise analysis of the complex interconnections found in the real world.” Furthermore, “it has broad potential applications in fields such as social network analysis for group chats or collaborative networks, life sciences for studying protein complexes or gene interactions, and neuroscience for tracking simultaneous activity across multiple brain regions.”
The research was conducted by Kyuhan Lee (Integrated M.S.–Ph.D. program at the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST; currently a software engineer at GraphAI), Geon Lee (Integrated M.S.–Ph.D. program at KAIST), and Professor Kijung Shin. It was presented at the 41st IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (IEEE ICDE), held in Hong Kong this past May.
※ Paper title: MARIOH: Multiplicity-Aware Hypergraph Reconstruction ※ DOI: https://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/ICDE65448.2025.00233
<Figure 2. An example of the process of recovering high-dimensional relationships using MARIOH technology>
This research was supported by the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) through the project “EntireDB2AI: Foundational technologies and software for deep representation learning and prediction using complete relational databases,” as well as by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the project “Graph Foundation Model: Graph-based machine learning applicable across various modalities and domains.”
2025.08.05 View 207 -
 KAIST Successfully Presents the Future of AI Transformation and Physical AI Strategy at the 1st National Strategic Technology Forum
<(Front row, fourth from the right) President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST, (back row, fifth from the right) Forum co-host Representative Hyung-Doo Choi, (back row, sixth from the left) Forum co-host Representative Han-Kyu Kim, along with ruling and opposition party members of the Science, ICT, Broadcasting, and Communications Committee and the Trade, Industry, Energy, SMEs, and Startups Committee, as well as Professors Hoe-Jun Yoo and Jung Kim from KAIST)>
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on July that it had successfully held the “1st National Strategic Technology Forum” at the National Assembly Members' Office Building that day under the theme “The Future of Artificial Intelligence Transformation (AX): Physical AI.” This bipartisan policy forum aimed to discuss strategies for technology hegemony by leveraging Korea’s strengths in AI semiconductors and manufacturing.
The forum was hosted by KAIST and co-organized by Representative Hyung-Du Choi (People Power Party), the secretary of the National Assembly's Science, ICT, Broadcasting, and Communications Committee, and Representative Han-Kyu Kim (Democratic Party), a member of the Trade, Industry, Energy, SMEs, and Startups Committee. It marks the beginning of a five-part forum series, scheduled monthly through the rest of the year except for October.
The overarching theme, “Artificial Intelligence Transformation (AX),” was designed to address the structural changes reshaping industry, the economy, and society due to the spread of generative AI.
< KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee delivering his remarks >
The first session focused on “Physical AI,” reflecting how AI innovation—sparked by the proliferation of large language models (LLMs)—is rapidly expanding into the physical realm through ultra-low-power, ultra-lightweight semiconductors. This includes applications in robotics, sensors, and edge devices. Physical AI refers to technologies that interact directly with the real world through AI integration with robotics, autonomous driving, and smart factories. It is drawing attention as a promising next-generation field where Korea can secure a strategic edge, given its strengths in semiconductors and manufacturing.
<Hoi-Jun Yoo, Dean of the KAIST Graduate School of AI Semiconductor>
Hoi-Jun Yoo, Dean of the KAIST Graduate School of AI Semiconductor, gave a presentation titled “The Second AI Innovation Enabled by Ultra-Low-Power AI Semiconductors and Lightweight AI Models,” covering semiconductor trends for implementing Physical AI, academic and industrial strategies for robotics and semiconductors, and Korea’s development direction for “K-Physical AI.”
<Professor Jung Kim, the head of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering>
Following that, Professor Jung Kim, the head of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering gave a talk on “Trends in Physical AI and Humanoid Robots,” predicting a new industrial paradigm shaped by AI-robot convergence. He presented global trends, Korea’s development trajectory, and survival strategies for humanoid robots that can supplement or replace human intellectual and physical functions.
During the open discussion that followed, participating lawmakers and experts engaged in in-depth conversations about the need for bipartisan strategies and collaboration.
Representative Hyung-Du Choi (People Power Party) stated, “Through this forum as a platform for public discourse, I will work to ensure that legislation and policy align with the direction of the science and technology field, and that necessary measures are taken promptly to strengthen national competitiveness.”
Representative Han-Kyu Kim (Democratic Party) emphasized, “As strategic planning in science and technology accelerates, it becomes more difficult to coordinate policies involving multiple ministries. Forums like this, which enable ongoing communication among stakeholders, are instrumental in finding effective solutions.”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee remarked, “Although Korea is a latecomer in the generative AI field, we have a unique opportunity to gain strategic superiority in Physical AI, thanks to our technological capabilities in manufacturing, semiconductors, and robotics.” He added, “I hope lawmakers from both the ruling and opposition parties, along with experts, will come together regularly to devise practical policies and contribute to the advancement of Korea’s science and technology.”
<Poster of National Strategic Technology Forum>
This forum series aims to explore policy and institutional solutions to help Korea gain technological leadership in a global context where strategic technologies—such as AI, semiconductors, biotechnology, and energy—directly influence national security and economic sovereignty. Lawmakers from both the Science, ICT, Broadcasting, and Communications Committee and the Trade, Industry, Energy, SMEs, and Startups Committee will continue to participate, fostering bipartisan dialogue. The forums are coordinated by the KAIST Policy Research Institute for National Strategic Technologies.
2025.07.31 View 180
KAIST Successfully Presents the Future of AI Transformation and Physical AI Strategy at the 1st National Strategic Technology Forum
<(Front row, fourth from the right) President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST, (back row, fifth from the right) Forum co-host Representative Hyung-Doo Choi, (back row, sixth from the left) Forum co-host Representative Han-Kyu Kim, along with ruling and opposition party members of the Science, ICT, Broadcasting, and Communications Committee and the Trade, Industry, Energy, SMEs, and Startups Committee, as well as Professors Hoe-Jun Yoo and Jung Kim from KAIST)>
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on July that it had successfully held the “1st National Strategic Technology Forum” at the National Assembly Members' Office Building that day under the theme “The Future of Artificial Intelligence Transformation (AX): Physical AI.” This bipartisan policy forum aimed to discuss strategies for technology hegemony by leveraging Korea’s strengths in AI semiconductors and manufacturing.
The forum was hosted by KAIST and co-organized by Representative Hyung-Du Choi (People Power Party), the secretary of the National Assembly's Science, ICT, Broadcasting, and Communications Committee, and Representative Han-Kyu Kim (Democratic Party), a member of the Trade, Industry, Energy, SMEs, and Startups Committee. It marks the beginning of a five-part forum series, scheduled monthly through the rest of the year except for October.
The overarching theme, “Artificial Intelligence Transformation (AX),” was designed to address the structural changes reshaping industry, the economy, and society due to the spread of generative AI.
< KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee delivering his remarks >
The first session focused on “Physical AI,” reflecting how AI innovation—sparked by the proliferation of large language models (LLMs)—is rapidly expanding into the physical realm through ultra-low-power, ultra-lightweight semiconductors. This includes applications in robotics, sensors, and edge devices. Physical AI refers to technologies that interact directly with the real world through AI integration with robotics, autonomous driving, and smart factories. It is drawing attention as a promising next-generation field where Korea can secure a strategic edge, given its strengths in semiconductors and manufacturing.
<Hoi-Jun Yoo, Dean of the KAIST Graduate School of AI Semiconductor>
Hoi-Jun Yoo, Dean of the KAIST Graduate School of AI Semiconductor, gave a presentation titled “The Second AI Innovation Enabled by Ultra-Low-Power AI Semiconductors and Lightweight AI Models,” covering semiconductor trends for implementing Physical AI, academic and industrial strategies for robotics and semiconductors, and Korea’s development direction for “K-Physical AI.”
<Professor Jung Kim, the head of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering>
Following that, Professor Jung Kim, the head of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering gave a talk on “Trends in Physical AI and Humanoid Robots,” predicting a new industrial paradigm shaped by AI-robot convergence. He presented global trends, Korea’s development trajectory, and survival strategies for humanoid robots that can supplement or replace human intellectual and physical functions.
During the open discussion that followed, participating lawmakers and experts engaged in in-depth conversations about the need for bipartisan strategies and collaboration.
Representative Hyung-Du Choi (People Power Party) stated, “Through this forum as a platform for public discourse, I will work to ensure that legislation and policy align with the direction of the science and technology field, and that necessary measures are taken promptly to strengthen national competitiveness.”
Representative Han-Kyu Kim (Democratic Party) emphasized, “As strategic planning in science and technology accelerates, it becomes more difficult to coordinate policies involving multiple ministries. Forums like this, which enable ongoing communication among stakeholders, are instrumental in finding effective solutions.”
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee remarked, “Although Korea is a latecomer in the generative AI field, we have a unique opportunity to gain strategic superiority in Physical AI, thanks to our technological capabilities in manufacturing, semiconductors, and robotics.” He added, “I hope lawmakers from both the ruling and opposition parties, along with experts, will come together regularly to devise practical policies and contribute to the advancement of Korea’s science and technology.”
<Poster of National Strategic Technology Forum>
This forum series aims to explore policy and institutional solutions to help Korea gain technological leadership in a global context where strategic technologies—such as AI, semiconductors, biotechnology, and energy—directly influence national security and economic sovereignty. Lawmakers from both the Science, ICT, Broadcasting, and Communications Committee and the Trade, Industry, Energy, SMEs, and Startups Committee will continue to participate, fostering bipartisan dialogue. The forums are coordinated by the KAIST Policy Research Institute for National Strategic Technologies.
2025.07.31 View 180 -
 KAIST GESS Team Awarded Honorable Mention at 2025 Entrepreneurship Olympiad
<Photo: eaureco team at the final pitch>
The KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (GESS) winning team, eaureco, earned an Honorable Mention at the 2025 Entrepreneurship Olympiad, held July 21–23 at Stanford Faculty Club and hosted by Techdev Academy. Competing in the college track, the team showcased their innovative solution among participants from top institutions including Stanford University, UC Berkeley, UCLA, and UC San Diego.
Team eaureco—comprising KAIST undergraduate and graduate students Jiwon Park(Semiconductor Systems Engineering), Si Li Sara (Julia) Aow, Lunar Sebastian Widjaja (both Civil & Environmental Engineering), Seoyeon Jang (Impact MBA), and Isabel Alexandra Cornejo Lima (BTM/Global Digital Innovation)—presented a B2B solution that upcycles discarded seaweed into biodegradable ice packs for cold-chain companies. Their business model was recognized for its alignment with sustainability, resource circulation, and social impact goals.
<Photo: eaureco team preparing for the final pitch>
The team’s ability to rapidly adapt their pitch based on mentor feedback and clearly communicate the value of their idea to judges contributed to their recognition. This accomplishment further highlights the impact of KAIST's GESS program, which supports students in building real-world entrepreneurial skills through immersive learning experiences in Silicon Valley.
“The GESS program helped us refine every aspect of our business idea—from identifying the problem to developing a go-to-market strategy,” said Si Li Sara (Julia) Aow, a member of the eaureco team. “We’re grateful for the opportunity to showcase our work on a global stage and hope to continue developing innovations that drive meaningful change.”
“This award reaffirms the creative potential and practical capabilities of KAIST students in global innovation ecosystems,” said Dr. Soyoung Kim, Vice President of International Office. “We will continue to invest in programs like GESS to empower our students as future leaders in entrepreneurship.”
The Entrepreneurship Olympiad is a global event designed to foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and collaboration among young change-makers. This year’s program featured keynote talks, panels, and workshops led by industry pioneers including Marc Tarpenning (Co-founder, Tesla Motors), Pat Brown (Founder, Impossible Foods), and other influential entrepreneurs from the biotech, fintech, and deeptech sectors.
The Honorable Mention recognition underscores KAIST’s commitment to global entrepreneurship education and the growing international visibility of the GESS program.
2025.07.29 View 414
KAIST GESS Team Awarded Honorable Mention at 2025 Entrepreneurship Olympiad
<Photo: eaureco team at the final pitch>
The KAIST Global Entrepreneurship Summer School (GESS) winning team, eaureco, earned an Honorable Mention at the 2025 Entrepreneurship Olympiad, held July 21–23 at Stanford Faculty Club and hosted by Techdev Academy. Competing in the college track, the team showcased their innovative solution among participants from top institutions including Stanford University, UC Berkeley, UCLA, and UC San Diego.
Team eaureco—comprising KAIST undergraduate and graduate students Jiwon Park(Semiconductor Systems Engineering), Si Li Sara (Julia) Aow, Lunar Sebastian Widjaja (both Civil & Environmental Engineering), Seoyeon Jang (Impact MBA), and Isabel Alexandra Cornejo Lima (BTM/Global Digital Innovation)—presented a B2B solution that upcycles discarded seaweed into biodegradable ice packs for cold-chain companies. Their business model was recognized for its alignment with sustainability, resource circulation, and social impact goals.
<Photo: eaureco team preparing for the final pitch>
The team’s ability to rapidly adapt their pitch based on mentor feedback and clearly communicate the value of their idea to judges contributed to their recognition. This accomplishment further highlights the impact of KAIST's GESS program, which supports students in building real-world entrepreneurial skills through immersive learning experiences in Silicon Valley.
“The GESS program helped us refine every aspect of our business idea—from identifying the problem to developing a go-to-market strategy,” said Si Li Sara (Julia) Aow, a member of the eaureco team. “We’re grateful for the opportunity to showcase our work on a global stage and hope to continue developing innovations that drive meaningful change.”
“This award reaffirms the creative potential and practical capabilities of KAIST students in global innovation ecosystems,” said Dr. Soyoung Kim, Vice President of International Office. “We will continue to invest in programs like GESS to empower our students as future leaders in entrepreneurship.”
The Entrepreneurship Olympiad is a global event designed to foster innovation, entrepreneurship, and collaboration among young change-makers. This year’s program featured keynote talks, panels, and workshops led by industry pioneers including Marc Tarpenning (Co-founder, Tesla Motors), Pat Brown (Founder, Impossible Foods), and other influential entrepreneurs from the biotech, fintech, and deeptech sectors.
The Honorable Mention recognition underscores KAIST’s commitment to global entrepreneurship education and the growing international visibility of the GESS program.
2025.07.29 View 414 -
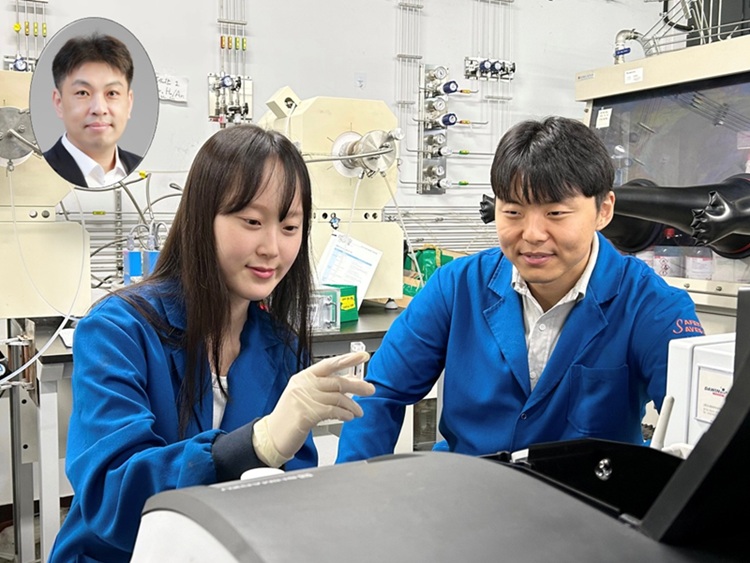 KAIST Enables On-Site Disease Diagnosis in Just 3 Minutes... Nanozyme Reaction Selectivity Improved 38-Fold
<(From Left) Professor Jinwoo Lee, Ph.D candidate Seonhye Park and Ph.D candidate Daeeun Choi from Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering>
To enable early diagnosis of acute illnesses and effective management of chronic conditions, point-of-care testing (POCT) technology—diagnostics conducted near the patient—is drawing global attention. The key to POCT lies in enzymes that recognize and react precisely with specific substances. However, traditional natural enzymes are expensive and unstable, and nanozymes (enzyme-mimicking catalysts) have suffered from low reaction selectivity. Now, a Korean research team has developed a high-sensitivity sensor platform that achieves 38 times higher selectivity than existing nanozymes and allows disease diagnostics visible to the naked eye within just 3 minutes.
On the 28th, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that Professor Jinwoo Lee’s research team from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, in collaboration with teams led by Professor Jeong Woo Han at Seoul National University and Professor Moon Il Kim at Gachon University, has developed a new single-atom catalyst that selectively performs only peroxidase-like reactions while maintaining high reaction efficiency.
Using bodily fluids such as blood, urine, or saliva, this diagnostic platform enables test results to be read within minutes even outside hospital settings—greatly improving medical accessibility and ensuring timely treatment. The key lies in the visual detection of biomarkers (disease indicators) through color changes triggered by enzyme reactions. However, natural enzymes are expensive and easily degraded in diagnostic environments, limiting their storage and distribution.
To address this, inorganic nanozyme materials have been developed as substitutes. Yet, they typically lack selectivity—when hydrogen peroxide is used as a substrate, the same catalyst triggers both peroxidase-like reactions (which cause color change) and catalase-like reactions (which remove the substrate), reducing diagnostic signal accuracy.
To control catalyst selectivity at the atomic level, the researchers used an innovative structural design: attaching chlorine (Cl) ligands in a three-dimensional configuration to the central ruthenium (Ru) atom to fine-tune its chemical properties. This enabled them to isolate only the desired diagnostic signal.
<Figure1. The catalyst in this study (ruthenium single-atom catalyst) exhibits peroxidase-like activity with selectivity akin to natural enzymes through three-dimensional directional ligand coordination. Due to the absence of competing catalase activity, selective peroxidase-like reactions proceed under biomimetic conditions. In contrast, conventional single-atom catalysts with active sites arranged on planar surfaces exhibit dual functionality depending on pH. Under neutral conditions, their catalase activity leads to hydrogen peroxide depletion, hindering accurate detection. The catalyst in this study eliminates such interference, enabling direct detection of biomarkers through coupled reactions with oxidases without the need for cumbersome steps like buffer replacement. The ability to simultaneously detect multiple target substances under biomimetic conditions demonstrates the practicality of ruthenium single-atom catalysts for on-site diagnostics>
Experimental results showed that the new catalyst achieved over 38-fold improvement in selectivity compared to existing nanozymes, with significantly increased sensitivity and speed in detecting hydrogen peroxide. Even in near-physiological conditions (pH 6.0), the catalyst maintained its performance, proving its applicability in real-world diagnostics.
By incorporating the catalyst and oxidase into a paper-based sensor, the team created a system that could simultaneously detect four key biomarkers related to health: glucose, lactate, cholesterol, and choline—all with a simple color change.
This platform is broadly applicable across various disease diagnostics and can deliver results within 3 minutes without complex instruments or pH adjustments. The findings show that diagnostic performance can be dramatically improved without changing the platform itself, but rather by engineering the catalyst structure.
<Figure 2.(a) Schematic diagram of the paper sensor (Zone 1: glucose oxidase immobilized; Zone 2: lactate oxidase immobilized; Zone 3: choline oxidase immobilized; Zone 4: cholesterol oxidase immobilized; Zone 5: no oxidase enzyme). (b) Single biomarker (single disease indicator) detection using the ruthenium single‑atom catalyst–based paper sensor.(c) Multiple biomarker (multiple disease indicator) detection using the ruthenium single‑atom catalyst–based paper sensor>
Professor Jinwoo Lee of KAIST commented, “This study is significant in that it simultaneously achieves enzyme-level selectivity and reactivity by structurally designing single-atom catalysts.” He added that “the structure–function-based catalyst design strategy can be extended to the development of various metal-based catalysts and other reaction domains where selectivity is critical.”
Seonhye Park and Daeeun Choi, both Ph.D. candidates at KAIST, are co-first authors. The research was published on July 6, 2025, in the prestigious journal Advanced Materials
-Title: Breaking the Selectivity Barrier of Single-Atom Nanozymes Through Out-of-Plane Ligand Coordinatio
- Authors: Seonhye Park (KAIST, co–first author), Daeeun Choi (KAIST, co–first author), Kyu In Shim (SNU, co–first author), Phuong Thy Nguyen (Gachon Univ., co–first author), Seongbeen Kim (KAIST), Seung Yeop Yi (KAIST), Moon Il Kim (Gachon Univ., corresponding author), Jeong Woo Han (SNU, corresponding author), Jinwoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author
-DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202506480
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
2025.07.29 View 320
KAIST Enables On-Site Disease Diagnosis in Just 3 Minutes... Nanozyme Reaction Selectivity Improved 38-Fold
<(From Left) Professor Jinwoo Lee, Ph.D candidate Seonhye Park and Ph.D candidate Daeeun Choi from Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering>
To enable early diagnosis of acute illnesses and effective management of chronic conditions, point-of-care testing (POCT) technology—diagnostics conducted near the patient—is drawing global attention. The key to POCT lies in enzymes that recognize and react precisely with specific substances. However, traditional natural enzymes are expensive and unstable, and nanozymes (enzyme-mimicking catalysts) have suffered from low reaction selectivity. Now, a Korean research team has developed a high-sensitivity sensor platform that achieves 38 times higher selectivity than existing nanozymes and allows disease diagnostics visible to the naked eye within just 3 minutes.
On the 28th, KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that Professor Jinwoo Lee’s research team from the Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering, in collaboration with teams led by Professor Jeong Woo Han at Seoul National University and Professor Moon Il Kim at Gachon University, has developed a new single-atom catalyst that selectively performs only peroxidase-like reactions while maintaining high reaction efficiency.
Using bodily fluids such as blood, urine, or saliva, this diagnostic platform enables test results to be read within minutes even outside hospital settings—greatly improving medical accessibility and ensuring timely treatment. The key lies in the visual detection of biomarkers (disease indicators) through color changes triggered by enzyme reactions. However, natural enzymes are expensive and easily degraded in diagnostic environments, limiting their storage and distribution.
To address this, inorganic nanozyme materials have been developed as substitutes. Yet, they typically lack selectivity—when hydrogen peroxide is used as a substrate, the same catalyst triggers both peroxidase-like reactions (which cause color change) and catalase-like reactions (which remove the substrate), reducing diagnostic signal accuracy.
To control catalyst selectivity at the atomic level, the researchers used an innovative structural design: attaching chlorine (Cl) ligands in a three-dimensional configuration to the central ruthenium (Ru) atom to fine-tune its chemical properties. This enabled them to isolate only the desired diagnostic signal.
<Figure1. The catalyst in this study (ruthenium single-atom catalyst) exhibits peroxidase-like activity with selectivity akin to natural enzymes through three-dimensional directional ligand coordination. Due to the absence of competing catalase activity, selective peroxidase-like reactions proceed under biomimetic conditions. In contrast, conventional single-atom catalysts with active sites arranged on planar surfaces exhibit dual functionality depending on pH. Under neutral conditions, their catalase activity leads to hydrogen peroxide depletion, hindering accurate detection. The catalyst in this study eliminates such interference, enabling direct detection of biomarkers through coupled reactions with oxidases without the need for cumbersome steps like buffer replacement. The ability to simultaneously detect multiple target substances under biomimetic conditions demonstrates the practicality of ruthenium single-atom catalysts for on-site diagnostics>
Experimental results showed that the new catalyst achieved over 38-fold improvement in selectivity compared to existing nanozymes, with significantly increased sensitivity and speed in detecting hydrogen peroxide. Even in near-physiological conditions (pH 6.0), the catalyst maintained its performance, proving its applicability in real-world diagnostics.
By incorporating the catalyst and oxidase into a paper-based sensor, the team created a system that could simultaneously detect four key biomarkers related to health: glucose, lactate, cholesterol, and choline—all with a simple color change.
This platform is broadly applicable across various disease diagnostics and can deliver results within 3 minutes without complex instruments or pH adjustments. The findings show that diagnostic performance can be dramatically improved without changing the platform itself, but rather by engineering the catalyst structure.
<Figure 2.(a) Schematic diagram of the paper sensor (Zone 1: glucose oxidase immobilized; Zone 2: lactate oxidase immobilized; Zone 3: choline oxidase immobilized; Zone 4: cholesterol oxidase immobilized; Zone 5: no oxidase enzyme). (b) Single biomarker (single disease indicator) detection using the ruthenium single‑atom catalyst–based paper sensor.(c) Multiple biomarker (multiple disease indicator) detection using the ruthenium single‑atom catalyst–based paper sensor>
Professor Jinwoo Lee of KAIST commented, “This study is significant in that it simultaneously achieves enzyme-level selectivity and reactivity by structurally designing single-atom catalysts.” He added that “the structure–function-based catalyst design strategy can be extended to the development of various metal-based catalysts and other reaction domains where selectivity is critical.”
Seonhye Park and Daeeun Choi, both Ph.D. candidates at KAIST, are co-first authors. The research was published on July 6, 2025, in the prestigious journal Advanced Materials
-Title: Breaking the Selectivity Barrier of Single-Atom Nanozymes Through Out-of-Plane Ligand Coordinatio
- Authors: Seonhye Park (KAIST, co–first author), Daeeun Choi (KAIST, co–first author), Kyu In Shim (SNU, co–first author), Phuong Thy Nguyen (Gachon Univ., co–first author), Seongbeen Kim (KAIST), Seung Yeop Yi (KAIST), Moon Il Kim (Gachon Univ., corresponding author), Jeong Woo Han (SNU, corresponding author), Jinwoo Lee (KAIST, corresponding author
-DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202506480
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
2025.07.29 View 320 -
 Better Sleep, Better Life — KAIST’s Sleep Algorithm Comes to Samsung Galaxy Watches
<Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of KAIST's Department of Mathematical Sciences>
Did you know that over 80% of people worldwide have irregular sleep habits? These sleep issues don’t just leave us feeling tired — they affect our health, focus, and quality of life. Now, a new sleep algorithm developed by a team of Korean researchers is aiming to change that. And it’s available on Samsung Galaxy smartwatches around the world, including the newly launched Galaxy Watch8 series.
The personalized sleep guide, created by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim’s research team at KAIST and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), doesn’t just tell you how long you slept. It actually recommends the best time for you to go to bed — helping you build healthy sleep habits and feel more refreshed every day.
What makes it special? Unlike most sleep features that focus only on the past (“You slept six hours last night”), this algorithm looks ahead. Using mathematical models and your body’s circadian rhythm, it suggests a personalized “sleep window” — like “Going to bed between 11:10 PM and 11:40 PM is ideal for you tonight.”
“It’s kind of like a weather forecast,” said Professor Kim. “Instead of just telling you what happened yesterday, it helps you prepare for tomorrow — so you can sleep better and feel better.”
<Conceptual Diagram of a Smart Sleep Algorithm>
The algorithm was developed over three years by a small team of mathematicians, not professional app developers. “We faced a lot of challenges trying to turn our research into a real product,” Kim admitted. “People kept asking us when they could try the algorithm, and we always felt bad that we couldn’t release it properly. Now, thanks to the support of KAIST’s Technology Commercialization Center and our partnership with Samsung, our work will finally reach people around the world.”
The academic world is paying attention, too. Professor Kim’s presentation on the algorithm was selected for the Hot Topics session at SLEEP 2025, the world’s largest sleep conference held in the U.S., and will also be featured at World Sleep 2025 in Singapore this fall.
Professor Kim is also working with Professor Eun Yeon Joo’s team at Samsung Medical Center to develop even more advanced sleep recommendation technology. Together, they created “SLEEPS,” an algorithm that predicts sleep disorders (available at sleep-math.com). Meanwhile, development continues on their own sleep app — with the hope of bringing math-powered sleep science into more people’s everyday lives.
Professor Kim is a world-renowned expert in mathematical biology. In 2025, he became the first Korean scientist to give a keynote speech at the SIAM Annual Meeting, and the first Korean to join the editorial board of SIAM Review, one of the most prestigious journals in applied mathematics. His work shows how basic science and mathematics can lead to real solutions that help people live healthier, better lives.
2025.07.28 View 401
Better Sleep, Better Life — KAIST’s Sleep Algorithm Comes to Samsung Galaxy Watches
<Professor Jae Kyoung Kim of KAIST's Department of Mathematical Sciences>
Did you know that over 80% of people worldwide have irregular sleep habits? These sleep issues don’t just leave us feeling tired — they affect our health, focus, and quality of life. Now, a new sleep algorithm developed by a team of Korean researchers is aiming to change that. And it’s available on Samsung Galaxy smartwatches around the world, including the newly launched Galaxy Watch8 series.
The personalized sleep guide, created by Professor Jae Kyoung Kim’s research team at KAIST and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), doesn’t just tell you how long you slept. It actually recommends the best time for you to go to bed — helping you build healthy sleep habits and feel more refreshed every day.
What makes it special? Unlike most sleep features that focus only on the past (“You slept six hours last night”), this algorithm looks ahead. Using mathematical models and your body’s circadian rhythm, it suggests a personalized “sleep window” — like “Going to bed between 11:10 PM and 11:40 PM is ideal for you tonight.”
“It’s kind of like a weather forecast,” said Professor Kim. “Instead of just telling you what happened yesterday, it helps you prepare for tomorrow — so you can sleep better and feel better.”
<Conceptual Diagram of a Smart Sleep Algorithm>
The algorithm was developed over three years by a small team of mathematicians, not professional app developers. “We faced a lot of challenges trying to turn our research into a real product,” Kim admitted. “People kept asking us when they could try the algorithm, and we always felt bad that we couldn’t release it properly. Now, thanks to the support of KAIST’s Technology Commercialization Center and our partnership with Samsung, our work will finally reach people around the world.”
The academic world is paying attention, too. Professor Kim’s presentation on the algorithm was selected for the Hot Topics session at SLEEP 2025, the world’s largest sleep conference held in the U.S., and will also be featured at World Sleep 2025 in Singapore this fall.
Professor Kim is also working with Professor Eun Yeon Joo’s team at Samsung Medical Center to develop even more advanced sleep recommendation technology. Together, they created “SLEEPS,” an algorithm that predicts sleep disorders (available at sleep-math.com). Meanwhile, development continues on their own sleep app — with the hope of bringing math-powered sleep science into more people’s everyday lives.
Professor Kim is a world-renowned expert in mathematical biology. In 2025, he became the first Korean scientist to give a keynote speech at the SIAM Annual Meeting, and the first Korean to join the editorial board of SIAM Review, one of the most prestigious journals in applied mathematics. His work shows how basic science and mathematics can lead to real solutions that help people live healthier, better lives.
2025.07.28 View 401 -
 Approaches to Human-Robot Interaction Using Biosignals
<(From left) Dr. Hwa-young Jeong, Professor Kyung-seo Park, Dr. Yoon-tae Jeong, Dr. Ji-hoon Seo, Professor Min-kyu Je, Professor Jung Kim >
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kim of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Min-kyu Je of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering recently published a review paper on the latest trends and advancements in intuitive Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) using bio-potential and bio-impedance in the internationally renowned academic journal 'Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering'.
This review paper is the result of a collaborative effort by Dr. Kyung-seo Park (DGIST, co-first author), Dr. Hwa-young Jeong (EPFL, co-first author), Dr. Yoon-tae Jeong (IMEC), and Dr. Ji-hoon Seo (UCSD), all doctoral graduates from the two laboratories. Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering is a review specialized journal in the field of electrical, electronic, and artificial intelligence technology, newly launched by Nature Publishing Group last year. It is known to invite world-renowned scholars in the field through strict selection criteria. Professor Jung Kim's research team's paper, titled "Using bio-potential and bio-impedance for intuitive human-robot interaction," was published on July 18, 2025. (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44287-025-00191-5)
This review paper explains how biosignals can be used to quickly and accurately detect movement intentions and introduces advancements in movement prediction technology based on neural signals and muscle activity. It also focuses on the crucial role of integrated circuits (ICs) in maximizing low-noise performance and energy efficiency in biosignal sensing, covering thelatest development trends in low-noise, low-power designs for accurately measuring bio-potential and impedance signals.
The review emphasizes the importance of hybrid and multi-modal sensing approaches, presenting the possibility of building robust, intuitive, and scalable HRI systems. The research team stressed that collaboration between sensor and IC design fields is essential for the practical application of biosignal-based HRI systems and stated that interdisciplinary collaboration will play a significant role in the development of next-generation HRI technology. Dr. Hwa-young Jeong, a co-first author of the paper, presented the potential of bio-potential and impedance signals to make human-robot interaction more intuitive and efficient, predicting that it will make significant contributions to the development of HRI technologies such as rehabilitation robots and robotic prostheses using biosignals in the future. This research was supported by several research projects, including the Human Plus Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.07.24 View 392
Approaches to Human-Robot Interaction Using Biosignals
<(From left) Dr. Hwa-young Jeong, Professor Kyung-seo Park, Dr. Yoon-tae Jeong, Dr. Ji-hoon Seo, Professor Min-kyu Je, Professor Jung Kim >
A joint research team led by Professor Jung Kim of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Min-kyu Je of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering recently published a review paper on the latest trends and advancements in intuitive Human-Robot Interaction (HRI) using bio-potential and bio-impedance in the internationally renowned academic journal 'Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering'.
This review paper is the result of a collaborative effort by Dr. Kyung-seo Park (DGIST, co-first author), Dr. Hwa-young Jeong (EPFL, co-first author), Dr. Yoon-tae Jeong (IMEC), and Dr. Ji-hoon Seo (UCSD), all doctoral graduates from the two laboratories. Nature Reviews Electrical Engineering is a review specialized journal in the field of electrical, electronic, and artificial intelligence technology, newly launched by Nature Publishing Group last year. It is known to invite world-renowned scholars in the field through strict selection criteria. Professor Jung Kim's research team's paper, titled "Using bio-potential and bio-impedance for intuitive human-robot interaction," was published on July 18, 2025. (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s44287-025-00191-5)
This review paper explains how biosignals can be used to quickly and accurately detect movement intentions and introduces advancements in movement prediction technology based on neural signals and muscle activity. It also focuses on the crucial role of integrated circuits (ICs) in maximizing low-noise performance and energy efficiency in biosignal sensing, covering thelatest development trends in low-noise, low-power designs for accurately measuring bio-potential and impedance signals.
The review emphasizes the importance of hybrid and multi-modal sensing approaches, presenting the possibility of building robust, intuitive, and scalable HRI systems. The research team stressed that collaboration between sensor and IC design fields is essential for the practical application of biosignal-based HRI systems and stated that interdisciplinary collaboration will play a significant role in the development of next-generation HRI technology. Dr. Hwa-young Jeong, a co-first author of the paper, presented the potential of bio-potential and impedance signals to make human-robot interaction more intuitive and efficient, predicting that it will make significant contributions to the development of HRI technologies such as rehabilitation robots and robotic prostheses using biosignals in the future. This research was supported by several research projects, including the Human Plus Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.07.24 View 392 -
 KAIST School of Transdisciplinary Studies Is Driving Innovation in Korean Education
<(From Left) Professor Jaeseung Jeong, haed of the School of Transdiciplinary Studies, Dr, Albert Chau, Vice President of Hong Kong Baptist University>
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th of July that its School of Transdisciplinary Studies has been consistently showcasing the results of its experiments and practices for educational innovation both domestically and abroad.
On June 27, Professor Jaeseung Jeong, head of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies, was invited to speak at the “Pacific Asia Summit on Transdisciplinary Education 2025 (PASTE 2025)” held at Hong Kong Baptist University. He presented the Korean model of transdisciplinary education under the title “The Philosophy and Achievements of the KAIST School of Transdisciplinary Studies.”
In his talk, Professor Jeong pointed out the limitations of conventional education systems that rely on answer-centered evaluation, perfectionism, and competitiveness, claiming that they hinder creativity and integrative thinking. He then introduced the philosophy and operational practices of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies, which was established in 2019 to overcome these issues.
Professor Jeong outlined five key principles that define the school's educational philosophy: ①a broad and integrative academic foundation, ②student-driven and customized education, ③creativity and execution, ④a sense of social responsibility and global citizenship, and ⑤learning driven by intrinsic motivation and curiosity. He explained that students are admitted without a declared major, allowed to design their own learning plans, and evaluated under a P/NR system* that focuses on growth rather than competition.
*P/NR system: A non-competitive grading system led by KAIST’s School of Transdisciplinary Studies. Instead of traditional letter grades (A/B/C/Fail), students receive Pass (P) or No Record (NR), with the latter not appearing as a failure and not affecting GPA.
Professor Jeong emphasized, “This experiment at KAIST represents a new educational paradigm that values questions over knowledge, culture over structure, and inquiry over competition. Students are bridging academic learning and real-world practice by addressing societal challenges through technology, which could lead to a fundamental shift in global higher education.”
His presentation provided an opportunity to spotlight how KAIST’s experimental approach to nurturing transdisciplinary talent is pointing to new directions for the global education community beyond Korea.
< Hyungjoon Jang, a student at the School of Transdisciplinary Studies>
The achievements of KAIST’s transdisciplinary education model are also reflected in students’ academic accomplishments. Hyungjoon Jang, a student at the School of Transdisciplinary Studies, participated in a collaborative study led by his mentor, Professor Jaekyung Kim in the Department of Mathematical Sciences, along with researchers from Chungnam National University and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). Their groundbreaking analytical method enables the accurate estimation of inhibition constants using only a single inhibitor concentration. The paper was published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications in June, with Jang listed as co–first author.
Jang played a leading role throughout the research process by developing the experimental methodology, creating a software package to support the method, drafting the manuscript, and engaging in peer review. He also effectively communicated mathematical and statistical models to pharmaceutical experts by mastering presentation techniques and visual explanation strategies, thereby setting a strong example of interdisciplinary collaboration.
He emphasized that “the School of Transdisciplinary Studies’ mentor system allowed regular research feedback and the systematic acquisition of essential knowledge and analytical skills through courses in biochemistry and computational neuroscience.”
This example demonstrates how undergraduate students at the School of Transdisciplinary Studies can take leading roles in cutting-edge interdisciplinary research.
The school’s educational philosophy is also reflected in students’ practical actions. Inseo Jeong, a current student and founder of the startup MPAge Inc., made a meaningful donation to help establish a creative makerspace in the school.
<Inseo Jeong, founder of MPAG>
Inseo Jeong explained that the decision was made to express gratitude for the knowledge gained and the mentorship received from professors, saying that at the School of Transdisciplinary Studies, she learned not only how to solve problems with technology but also how to view society, and that learning has helped her grow. She added, “The deep understanding of humanity and the world emphasized by Professor Jaeseung Jeong will be a great asset not only to entrepreneurs but to all students pursuing diverse paths,” expressing support for her fellow students.
Inseo Jeong collaborated for over two years with Professor Hyunwook Ka of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies on software research for individuals with hearing impairments. After numerous algorithm designs and experimental iterations, their work, which considered the social scalability of technology, was presented at the world-renowned CSUN Assistive Technology Conference held at California State University, Northridge. The project has filed for a patent under KAIST’s name.
※ Presentation title: Evidence-Based Adaptive Transcription for Sign Language Users
KAIST is now working to complete the makerspace on the third floor of the Administrative Annex (N2) in Room 314 with a size of approximately 33 m2 during the summer. The makerspace is expected to serve as a hands-on, integrative learning environment where various ideas can be realized and implemented, playing a key role in fostering students’ creative problem-solving and integrative thinking skills.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee stated, “The School of Transdisciplinary Studies is both an experimental ground and a practical field for overcoming the limitations of traditional education and nurturing global talents with creative problem-solving skills and integrative thinking, which are essential for the future.” He added, “KAIST will continue to lead efforts to cultivate question-asking, inquiry-driven, transdisciplinary talents and propose new paradigms for education and research.”
2025.07.24 View 316
KAIST School of Transdisciplinary Studies Is Driving Innovation in Korean Education
<(From Left) Professor Jaeseung Jeong, haed of the School of Transdiciplinary Studies, Dr, Albert Chau, Vice President of Hong Kong Baptist University>
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 24th of July that its School of Transdisciplinary Studies has been consistently showcasing the results of its experiments and practices for educational innovation both domestically and abroad.
On June 27, Professor Jaeseung Jeong, head of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies, was invited to speak at the “Pacific Asia Summit on Transdisciplinary Education 2025 (PASTE 2025)” held at Hong Kong Baptist University. He presented the Korean model of transdisciplinary education under the title “The Philosophy and Achievements of the KAIST School of Transdisciplinary Studies.”
In his talk, Professor Jeong pointed out the limitations of conventional education systems that rely on answer-centered evaluation, perfectionism, and competitiveness, claiming that they hinder creativity and integrative thinking. He then introduced the philosophy and operational practices of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies, which was established in 2019 to overcome these issues.
Professor Jeong outlined five key principles that define the school's educational philosophy: ①a broad and integrative academic foundation, ②student-driven and customized education, ③creativity and execution, ④a sense of social responsibility and global citizenship, and ⑤learning driven by intrinsic motivation and curiosity. He explained that students are admitted without a declared major, allowed to design their own learning plans, and evaluated under a P/NR system* that focuses on growth rather than competition.
*P/NR system: A non-competitive grading system led by KAIST’s School of Transdisciplinary Studies. Instead of traditional letter grades (A/B/C/Fail), students receive Pass (P) or No Record (NR), with the latter not appearing as a failure and not affecting GPA.
Professor Jeong emphasized, “This experiment at KAIST represents a new educational paradigm that values questions over knowledge, culture over structure, and inquiry over competition. Students are bridging academic learning and real-world practice by addressing societal challenges through technology, which could lead to a fundamental shift in global higher education.”
His presentation provided an opportunity to spotlight how KAIST’s experimental approach to nurturing transdisciplinary talent is pointing to new directions for the global education community beyond Korea.
< Hyungjoon Jang, a student at the School of Transdisciplinary Studies>
The achievements of KAIST’s transdisciplinary education model are also reflected in students’ academic accomplishments. Hyungjoon Jang, a student at the School of Transdisciplinary Studies, participated in a collaborative study led by his mentor, Professor Jaekyung Kim in the Department of Mathematical Sciences, along with researchers from Chungnam National University and the Institute for Basic Science (IBS). Their groundbreaking analytical method enables the accurate estimation of inhibition constants using only a single inhibitor concentration. The paper was published in the prestigious journal Nature Communications in June, with Jang listed as co–first author.
Jang played a leading role throughout the research process by developing the experimental methodology, creating a software package to support the method, drafting the manuscript, and engaging in peer review. He also effectively communicated mathematical and statistical models to pharmaceutical experts by mastering presentation techniques and visual explanation strategies, thereby setting a strong example of interdisciplinary collaboration.
He emphasized that “the School of Transdisciplinary Studies’ mentor system allowed regular research feedback and the systematic acquisition of essential knowledge and analytical skills through courses in biochemistry and computational neuroscience.”
This example demonstrates how undergraduate students at the School of Transdisciplinary Studies can take leading roles in cutting-edge interdisciplinary research.
The school’s educational philosophy is also reflected in students’ practical actions. Inseo Jeong, a current student and founder of the startup MPAge Inc., made a meaningful donation to help establish a creative makerspace in the school.
<Inseo Jeong, founder of MPAG>
Inseo Jeong explained that the decision was made to express gratitude for the knowledge gained and the mentorship received from professors, saying that at the School of Transdisciplinary Studies, she learned not only how to solve problems with technology but also how to view society, and that learning has helped her grow. She added, “The deep understanding of humanity and the world emphasized by Professor Jaeseung Jeong will be a great asset not only to entrepreneurs but to all students pursuing diverse paths,” expressing support for her fellow students.
Inseo Jeong collaborated for over two years with Professor Hyunwook Ka of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies on software research for individuals with hearing impairments. After numerous algorithm designs and experimental iterations, their work, which considered the social scalability of technology, was presented at the world-renowned CSUN Assistive Technology Conference held at California State University, Northridge. The project has filed for a patent under KAIST’s name.
※ Presentation title: Evidence-Based Adaptive Transcription for Sign Language Users
KAIST is now working to complete the makerspace on the third floor of the Administrative Annex (N2) in Room 314 with a size of approximately 33 m2 during the summer. The makerspace is expected to serve as a hands-on, integrative learning environment where various ideas can be realized and implemented, playing a key role in fostering students’ creative problem-solving and integrative thinking skills.
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee stated, “The School of Transdisciplinary Studies is both an experimental ground and a practical field for overcoming the limitations of traditional education and nurturing global talents with creative problem-solving skills and integrative thinking, which are essential for the future.” He added, “KAIST will continue to lead efforts to cultivate question-asking, inquiry-driven, transdisciplinary talents and propose new paradigms for education and research.”
2025.07.24 View 316 -
 KAIST Team Develops Optogenetic Platform for Spatiotemporal Control of Protein and mRNA Storage and Release
<Dr. Chaeyeon Lee, Professor Won Do Heo from Department of Biological Sciences>
A KAIST research team led by Professor Won Do Heo (Department of Biological Sciences) has developed an optogenetic platform, RELISR (REversible LIght-induced Store and Release), that enables precise spatiotemporal control over the storage and release of proteins and mRNAs in living cells and animals.
Traditional optogenetic condensate systems have been limited by their reliance on non-specific multivalent interactions, which can lead to unintended sequestration or release of endogenous molecules. RELISR overcomes these limitations by employing highly specific protein–protein (nanobody–antigen) and protein–RNA (MCP–MS2) interactions, enabling the selective and reversible compartmentalization of target proteins or mRNAs within engineered, membrane-less condensates.
In the dark, RELISR stably sequesters target molecules within condensates, physically isolating them from the cellular environment. Upon blue light stimulation, the condensates rapidly dissolve, releasing the stored proteins or mRNAs, which immediately regain their cellular functions or translational competency. This allows for reversible and rapid modulation of molecular activities in response to optical cues.
< Figure 1. Overview of the Artificial Condensate System (RELISR). The artificial condensate system, RELISR, includes "Protein-RELISR" for storing proteins and "mRNA-RELISR" for storing mRNA. These artificial condensates can be disassembled by blue light irradiation and reassembled in a dark state>
The research team demonstrated that RELISR enables temporal and spatial regulation of protein activity and mRNA translation in various cell types, including cultured neurons and mouse liver tissue. Comparative studies showed that RELISR provides more robust and reversible control of translation than previous systems based on spatial translocation.
While previous optogenetic systems such as LARIAT (Lee et al., Nature Methods, 2014) and mRNA-LARIAT (Kim et al., Nat. Cell Biol., 2019) enabled the selective sequestration of proteins or mRNAs into membrane-less condensates in response to light, they were primarily limited to the trapping phase. The RELISR platform introduced in this study establishes a new paradigm by enabling both the targeted storage of proteins and mRNAs and their rapid, light-triggered release. This approach allows researchers to not only confine molecular function on demand, but also to restore activity with precise temporal control.
< Figure 2. Cell shape change using the artificial condensate system (RELISR). A target protein, Vav2, which contributes to cell shape, was stored within the artificial condensate and then released after light irradiation. This release activated the target protein Vav2, causing a change in cell shape. It was confirmed that the storage, release, and activation of various proteins were effectively achieved>
Professor Heo stated, “RELISR is a versatile optogenetic tool that enables the precise control of protein and mRNA function at defined times and locations in living systems. We anticipate this platform will be broadly applicable for studies of cell signaling, neural circuits, and therapeutic development. Furthermore, the combination of RELISR with genome editing or tissue-targeted delivery could further expand its utility for molecular medicine.”
< Figure 3. Expression of a target mRNA using the artificial condensate system (RELISR) in mice. The genetic material for the artificial condensate system, RELISR, was injected into a living mouse. Using this system, a target mRNA was stored within the mouse's liver. Upon light irradiation, the mRNA was released, which induced the translation of a luminescent protein>
This research was conducted by first author Dr. Chaeyeon Lee, under the supervision of Professor Heo, with contributions from Dr. Daseuli Yu (co-corresponding author) and Professor YongKeun Park (co-corresponding author, Department of Physics), whose group performed quantitative imaging analyses of biophysical changes induced by RELISR in cells.
The findings were published in Nature Communications (July 7, 2025; DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61322-y). This work was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Foundation and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.07.23 View 262
KAIST Team Develops Optogenetic Platform for Spatiotemporal Control of Protein and mRNA Storage and Release
<Dr. Chaeyeon Lee, Professor Won Do Heo from Department of Biological Sciences>
A KAIST research team led by Professor Won Do Heo (Department of Biological Sciences) has developed an optogenetic platform, RELISR (REversible LIght-induced Store and Release), that enables precise spatiotemporal control over the storage and release of proteins and mRNAs in living cells and animals.
Traditional optogenetic condensate systems have been limited by their reliance on non-specific multivalent interactions, which can lead to unintended sequestration or release of endogenous molecules. RELISR overcomes these limitations by employing highly specific protein–protein (nanobody–antigen) and protein–RNA (MCP–MS2) interactions, enabling the selective and reversible compartmentalization of target proteins or mRNAs within engineered, membrane-less condensates.
In the dark, RELISR stably sequesters target molecules within condensates, physically isolating them from the cellular environment. Upon blue light stimulation, the condensates rapidly dissolve, releasing the stored proteins or mRNAs, which immediately regain their cellular functions or translational competency. This allows for reversible and rapid modulation of molecular activities in response to optical cues.
< Figure 1. Overview of the Artificial Condensate System (RELISR). The artificial condensate system, RELISR, includes "Protein-RELISR" for storing proteins and "mRNA-RELISR" for storing mRNA. These artificial condensates can be disassembled by blue light irradiation and reassembled in a dark state>
The research team demonstrated that RELISR enables temporal and spatial regulation of protein activity and mRNA translation in various cell types, including cultured neurons and mouse liver tissue. Comparative studies showed that RELISR provides more robust and reversible control of translation than previous systems based on spatial translocation.
While previous optogenetic systems such as LARIAT (Lee et al., Nature Methods, 2014) and mRNA-LARIAT (Kim et al., Nat. Cell Biol., 2019) enabled the selective sequestration of proteins or mRNAs into membrane-less condensates in response to light, they were primarily limited to the trapping phase. The RELISR platform introduced in this study establishes a new paradigm by enabling both the targeted storage of proteins and mRNAs and their rapid, light-triggered release. This approach allows researchers to not only confine molecular function on demand, but also to restore activity with precise temporal control.
< Figure 2. Cell shape change using the artificial condensate system (RELISR). A target protein, Vav2, which contributes to cell shape, was stored within the artificial condensate and then released after light irradiation. This release activated the target protein Vav2, causing a change in cell shape. It was confirmed that the storage, release, and activation of various proteins were effectively achieved>
Professor Heo stated, “RELISR is a versatile optogenetic tool that enables the precise control of protein and mRNA function at defined times and locations in living systems. We anticipate this platform will be broadly applicable for studies of cell signaling, neural circuits, and therapeutic development. Furthermore, the combination of RELISR with genome editing or tissue-targeted delivery could further expand its utility for molecular medicine.”
< Figure 3. Expression of a target mRNA using the artificial condensate system (RELISR) in mice. The genetic material for the artificial condensate system, RELISR, was injected into a living mouse. Using this system, a target mRNA was stored within the mouse's liver. Upon light irradiation, the mRNA was released, which induced the translation of a luminescent protein>
This research was conducted by first author Dr. Chaeyeon Lee, under the supervision of Professor Heo, with contributions from Dr. Daseuli Yu (co-corresponding author) and Professor YongKeun Park (co-corresponding author, Department of Physics), whose group performed quantitative imaging analyses of biophysical changes induced by RELISR in cells.
The findings were published in Nature Communications (July 7, 2025; DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-61322-y). This work was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Foundation and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.07.23 View 262 -
 Why Do Plants Attack Themselves? The Secret of Genetic Conflict Revealed
<Professor Ji-Joon Song of the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences>
Plants, with their unique immune systems, sometimes launch 'autoimmune responses' by mistakenly identifying their own protein structures as pathogens. In particular, 'hybrid necrosis,' a phenomenon where descendant plants fail to grow healthily and perish after cross-breeding different varieties, has long been a difficult challenge for botanists and agricultural researchers. In response, an international research team has successfully elucidated the mechanism inducing plant autoimmune responses and proposed a novel strategy for cultivar improvement that can predict and avoid these reactions.
Professor Ji-Joon Song's research team at KAIST, in collaboration with teams from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and the University of Oxford, announced on the 21st of July that they have elucidated the structure and function of the 'DM3' protein complex, which triggers plant autoimmune responses, using cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) technology.
This research is drawing attention because it identifies defects in protein structure as the cause of hybrid necrosis, which occurs due to an abnormal reaction of immune receptors during cross-breeding between plant hybrids.
This protein (DM3) is originally an enzyme involved in the plant's immune response, but problems arise when the structure of the DM3 protein is damaged in a specific protein combination called 'DANGEROUS MIX (DM)'.
Notably, one variant of DM3, the 'DM3Col-0' variant, forms a stable complex with six proteins and is recognized as normal, thus not triggering an immune response. In contrast, another 'DM3Hh-0' variant has improper binding between its six proteins, causing the plant to recognize it as an 'abnormal state' and trigger an immune alarm, leading to autoimmunity.
The research team visualized this structure using atomic-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) and revealed that the immune-inducing ability is not due to the enzymatic function of the DM3 protein, but rather to 'differences in protein binding affinity.'
<Figure 1. Mechanism of Plant Autoimmunity Triggered by the Collapse of the DM3 Protein Complex>
This demonstrates that plants can initiate an immune response by recognizing not only 'external pathogens' but also 'internal protein structures' when they undergo abnormal changes, treating them as if they were pathogens.
The study shows how sensitively the plant immune system changes and triggers autoimmune responses when genes are mixed and protein structures change during the cross-breeding of different plant varieties. It significantly advanced the understanding of genetic incompatibility that can occur during natural cross-breeding and cultivar improvement processes.
Dr. Gijeong Kim, the co-first author, stated, "Through international research collaboration, we presented a new perspective on understanding the plant immune system by leveraging the autoimmune phenomenon, completing a high-quality study that encompasses structural biochemistry, genetics, and cell biological experiments."
Professor Ji-Joon Song of the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, who led the research, said, "The fact that the immune system can detect not only external pathogens but also structural abnormalities in its own proteins will set a new standard for plant biotechnology and crop breeding strategies. Cryo-electron microscopy-based structural analysis will be an important tool for understanding the essence of gene interactions."
This research, with Professor Ji-Joon Song and Professor Eunyoung Chae of the University of Oxford as co-corresponding authors, Dr. Gijeong Kim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Zurich) and Dr. Wei-Lin Wan of the National University of Singapore as co-first authors, and Ph.D candidate Nayun Kim, as the second author, was published on July 17th in Molecular Cell, a sister journal of the international academic journal Cell.
This research was supported by the KAIST Grand Challenge 30 project.
Article Title: Structural determinants of DANGEROUS MIX 3, an alpha/beta hydrolase that triggers NLR-mediated genetic incompatibility in plants DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2025.06.021
2025.07.21 View 411
Why Do Plants Attack Themselves? The Secret of Genetic Conflict Revealed
<Professor Ji-Joon Song of the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences>
Plants, with their unique immune systems, sometimes launch 'autoimmune responses' by mistakenly identifying their own protein structures as pathogens. In particular, 'hybrid necrosis,' a phenomenon where descendant plants fail to grow healthily and perish after cross-breeding different varieties, has long been a difficult challenge for botanists and agricultural researchers. In response, an international research team has successfully elucidated the mechanism inducing plant autoimmune responses and proposed a novel strategy for cultivar improvement that can predict and avoid these reactions.
Professor Ji-Joon Song's research team at KAIST, in collaboration with teams from the National University of Singapore (NUS) and the University of Oxford, announced on the 21st of July that they have elucidated the structure and function of the 'DM3' protein complex, which triggers plant autoimmune responses, using cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) technology.
This research is drawing attention because it identifies defects in protein structure as the cause of hybrid necrosis, which occurs due to an abnormal reaction of immune receptors during cross-breeding between plant hybrids.
This protein (DM3) is originally an enzyme involved in the plant's immune response, but problems arise when the structure of the DM3 protein is damaged in a specific protein combination called 'DANGEROUS MIX (DM)'.
Notably, one variant of DM3, the 'DM3Col-0' variant, forms a stable complex with six proteins and is recognized as normal, thus not triggering an immune response. In contrast, another 'DM3Hh-0' variant has improper binding between its six proteins, causing the plant to recognize it as an 'abnormal state' and trigger an immune alarm, leading to autoimmunity.
The research team visualized this structure using atomic-resolution cryo-electron microscopy (Cryo-EM) and revealed that the immune-inducing ability is not due to the enzymatic function of the DM3 protein, but rather to 'differences in protein binding affinity.'
<Figure 1. Mechanism of Plant Autoimmunity Triggered by the Collapse of the DM3 Protein Complex>
This demonstrates that plants can initiate an immune response by recognizing not only 'external pathogens' but also 'internal protein structures' when they undergo abnormal changes, treating them as if they were pathogens.
The study shows how sensitively the plant immune system changes and triggers autoimmune responses when genes are mixed and protein structures change during the cross-breeding of different plant varieties. It significantly advanced the understanding of genetic incompatibility that can occur during natural cross-breeding and cultivar improvement processes.
Dr. Gijeong Kim, the co-first author, stated, "Through international research collaboration, we presented a new perspective on understanding the plant immune system by leveraging the autoimmune phenomenon, completing a high-quality study that encompasses structural biochemistry, genetics, and cell biological experiments."
Professor Ji-Joon Song of the KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, who led the research, said, "The fact that the immune system can detect not only external pathogens but also structural abnormalities in its own proteins will set a new standard for plant biotechnology and crop breeding strategies. Cryo-electron microscopy-based structural analysis will be an important tool for understanding the essence of gene interactions."
This research, with Professor Ji-Joon Song and Professor Eunyoung Chae of the University of Oxford as co-corresponding authors, Dr. Gijeong Kim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at the University of Zurich) and Dr. Wei-Lin Wan of the National University of Singapore as co-first authors, and Ph.D candidate Nayun Kim, as the second author, was published on July 17th in Molecular Cell, a sister journal of the international academic journal Cell.
This research was supported by the KAIST Grand Challenge 30 project.
Article Title: Structural determinants of DANGEROUS MIX 3, an alpha/beta hydrolase that triggers NLR-mediated genetic incompatibility in plants DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2025.06.021
2025.07.21 View 411 -
 KAIST Holds '2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp' for Multicultural Youth
<2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp Activities>
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of July that it hosted the '2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp' for multicultural youth from the 15th for three days and two nights at the Creative Learning Building on its main campus in Daejeon.
This event was organized in accordance with the 'Multicultural Talent Nurturing Agreement' signed by KAIST and GS Caltex in 2024. It marks the first year of a mid-to-long-term project in which 100 million KRW in development funds will be contributed annually for four years. The Global Institute for Talented Education organized the camp, and approximately 30 middle school students from multicultural families affiliated with the 'Hanmaum Educational Volunteer Group' (Director, Honorary Professor Byung Kyu Choi), a mentoring and volunteer organization for multicultural students, participated.
The camp participants enjoyed developing their scientific thinking skills and problem-solving abilities, and broadening their understanding of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) career paths through a variety of science activity programs, including: △'Black Box: Record the Egg's Last Moment!' △'Find the Best Strategy! Heuristic Algorithm Challenge' △'Future Society and AI, Finding Career Directions' △'Distance Dominates the World!' and △'Career Talk Concert.'
During the opening ceremony, Director Byung Kyu Choi delivered a congratulatory speech. Additionally, Yong Hyun Kim, Dean of Admissions at KAIST, gave a special lecture titled 'La La Land KAIST – A Story of Chasing the Dream of a Young Scientist,' sharing honest stories about careers and dreams as a scientist.
Gi Jung Yoo, a freshman from the Division of Undeclared Majors who participated in the camp as a student mentor, shared that he had a very meaningful time mentoring the participating students, who are future STEM hopefuls, sharing vivid experiences as well as insights on metric functions. He added his hope that more students would be given such opportunities.
< Students Actively Taking Part in the Camp Activities>
Si Jong Kwak, Director of the Global Institute for Talented Education, stated, "We hope this will be a practical way to help students foster their interest in science, learn the joy of discussion and communication, and design their future."
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee remarked, "This camp was a valuable opportunity for students from diverse cultural backgrounds to gain confidence through science and envision their future." He added, "KAIST will continue to dedicate efforts to nurturing multicultural talent and contribute to creating a sustainable society."
Since 2024, KAIST has introduced and selected multicultural students through its Equal Opportunity Admission track. Utilizing the development funds from GS Caltex, KAIST also established the 'GS Caltex Multicultural Excellence Scholarship Program.' Through this scholarship program, undergraduate students from multicultural families receive living expenses each semester, allowing them to focus more stably on their studies. As the number of applicants for the Equal Opportunity Admission track is increasing every year, more multicultural students are expected to benefit from scholarships in the future.
Additionally, in May, both organizations invited Ms. Si Si Wu Fong, a foreign employee at GS Caltex, to give a special lecture titled 'Working Life for Foreigners in Korea' to support foreign students' career exploration. Foreign students who attended the lecture reported positive feedback, stating that they gained practical career information and were motivated to pursue employment in STEM fields in Korea.
KAIST plans to continue strengthening its efforts to nurture multicultural talent, increase understanding of the upcoming multicultural society, and help spread social values.
<At the 2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp>
2025.07.18 View 469
KAIST Holds '2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp' for Multicultural Youth
<2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp Activities>
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of July that it hosted the '2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp' for multicultural youth from the 15th for three days and two nights at the Creative Learning Building on its main campus in Daejeon.
This event was organized in accordance with the 'Multicultural Talent Nurturing Agreement' signed by KAIST and GS Caltex in 2024. It marks the first year of a mid-to-long-term project in which 100 million KRW in development funds will be contributed annually for four years. The Global Institute for Talented Education organized the camp, and approximately 30 middle school students from multicultural families affiliated with the 'Hanmaum Educational Volunteer Group' (Director, Honorary Professor Byung Kyu Choi), a mentoring and volunteer organization for multicultural students, participated.
The camp participants enjoyed developing their scientific thinking skills and problem-solving abilities, and broadening their understanding of STEM (Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics) career paths through a variety of science activity programs, including: △'Black Box: Record the Egg's Last Moment!' △'Find the Best Strategy! Heuristic Algorithm Challenge' △'Future Society and AI, Finding Career Directions' △'Distance Dominates the World!' and △'Career Talk Concert.'
During the opening ceremony, Director Byung Kyu Choi delivered a congratulatory speech. Additionally, Yong Hyun Kim, Dean of Admissions at KAIST, gave a special lecture titled 'La La Land KAIST – A Story of Chasing the Dream of a Young Scientist,' sharing honest stories about careers and dreams as a scientist.
Gi Jung Yoo, a freshman from the Division of Undeclared Majors who participated in the camp as a student mentor, shared that he had a very meaningful time mentoring the participating students, who are future STEM hopefuls, sharing vivid experiences as well as insights on metric functions. He added his hope that more students would be given such opportunities.
< Students Actively Taking Part in the Camp Activities>
Si Jong Kwak, Director of the Global Institute for Talented Education, stated, "We hope this will be a practical way to help students foster their interest in science, learn the joy of discussion and communication, and design their future."
KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee remarked, "This camp was a valuable opportunity for students from diverse cultural backgrounds to gain confidence through science and envision their future." He added, "KAIST will continue to dedicate efforts to nurturing multicultural talent and contribute to creating a sustainable society."
Since 2024, KAIST has introduced and selected multicultural students through its Equal Opportunity Admission track. Utilizing the development funds from GS Caltex, KAIST also established the 'GS Caltex Multicultural Excellence Scholarship Program.' Through this scholarship program, undergraduate students from multicultural families receive living expenses each semester, allowing them to focus more stably on their studies. As the number of applicants for the Equal Opportunity Admission track is increasing every year, more multicultural students are expected to benefit from scholarships in the future.
Additionally, in May, both organizations invited Ms. Si Si Wu Fong, a foreign employee at GS Caltex, to give a special lecture titled 'Working Life for Foreigners in Korea' to support foreign students' career exploration. Foreign students who attended the lecture reported positive feedback, stating that they gained practical career information and were motivated to pursue employment in STEM fields in Korea.
KAIST plans to continue strengthening its efforts to nurture multicultural talent, increase understanding of the upcoming multicultural society, and help spread social values.
<At the 2025 KAIST Science Frontier Camp>
2025.07.18 View 469