exchange
-
 KAIST's Partnership Agreement with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, UK
KAIST signed an agreement on academic and research cooperation with the Imperial College of Science, Technology (Imperial College London) and Medicine in the United Kingdom (UK) on November 6th, 2013 in London.
The two universities have been implementing collaboration programs at the department level in the areas of plastic electronics since September 2012 and systems engineering and molecular simulation since February 2013, but have never had a formal partnership agreement.
President Steve Kang from KAIST and Provost James Stirling from Imperial College London signed the comprehensive cooperation agreement which will not only strengthen the existing collaborations between the two institutions but also explore areas of mutual interest in the interdisciplinary study of big data, as well as in the fields of mechanical engineering, synthetic biology, and quantum physics.
Workshops, seminars, lectures, and conferences will be jointly organized and held to facilitate the exchange of research staff and faculty and to promote collaborations in research assignments. The universities will also look into the possibility of exchange programs for undergraduate and graduate students.
The partnership agreement will be effective for five years.
Minister Moon-Gi Choi from the Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Science, Information and Communications Technology (ICT) & Future Planning attended the signing ceremony as well and congratulated the establishment of the partnership, saying:
“We are living in the age of highly advanced science and technology that requires us to have a new economic development paradigm for sustainable growth. Through convergence research based on the application of ICT and technology innovation, we will have new opportunities for development. I hope KAIST and the Imperial College London will be at the forefront of such endeavors in coming years.”With its history spanning over 100 years, the Imperial College London is a public research university located in London, UK, specializing in science, engineering, medicine, and business. The university is regarded as being one of the most prestigious universities in the world, having eminent alumni such as Thomas Henry Huxley (biologist), H.G. Wells (author), and Sir Alexander Fleming (pharmacologist).
From left to right: Provost James Stirling, Minister Moon-Gi Choi, and President Steve Kang
2013.11.12 View 9874
KAIST's Partnership Agreement with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, UK
KAIST signed an agreement on academic and research cooperation with the Imperial College of Science, Technology (Imperial College London) and Medicine in the United Kingdom (UK) on November 6th, 2013 in London.
The two universities have been implementing collaboration programs at the department level in the areas of plastic electronics since September 2012 and systems engineering and molecular simulation since February 2013, but have never had a formal partnership agreement.
President Steve Kang from KAIST and Provost James Stirling from Imperial College London signed the comprehensive cooperation agreement which will not only strengthen the existing collaborations between the two institutions but also explore areas of mutual interest in the interdisciplinary study of big data, as well as in the fields of mechanical engineering, synthetic biology, and quantum physics.
Workshops, seminars, lectures, and conferences will be jointly organized and held to facilitate the exchange of research staff and faculty and to promote collaborations in research assignments. The universities will also look into the possibility of exchange programs for undergraduate and graduate students.
The partnership agreement will be effective for five years.
Minister Moon-Gi Choi from the Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Science, Information and Communications Technology (ICT) & Future Planning attended the signing ceremony as well and congratulated the establishment of the partnership, saying:
“We are living in the age of highly advanced science and technology that requires us to have a new economic development paradigm for sustainable growth. Through convergence research based on the application of ICT and technology innovation, we will have new opportunities for development. I hope KAIST and the Imperial College London will be at the forefront of such endeavors in coming years.”With its history spanning over 100 years, the Imperial College London is a public research university located in London, UK, specializing in science, engineering, medicine, and business. The university is regarded as being one of the most prestigious universities in the world, having eminent alumni such as Thomas Henry Huxley (biologist), H.G. Wells (author), and Sir Alexander Fleming (pharmacologist).
From left to right: Provost James Stirling, Minister Moon-Gi Choi, and President Steve Kang
2013.11.12 View 9874 -
 Artist in residence program at KAIST
A new and innovative program to support artists’ creative activities was launched by KAIST for the first time in Korean college history.
The artist in residence program is an unusual collaboration between engineers and artists. Out of hundreds of applicants for the program, three writers were selected: a novelist, web-based cartoonist, and screen writer. In late October, they became the residents of KAIST.
Housing and an office are provided for the writers in addition to a monthly cash stipend of 800,000 won for up to six months. A variety of programs will be available as well including a tour of laboratories to help the writers get ideas and inspiration.
KAIST’s Vice President Jun-Ho Oh, the founder of the program, said, “Artists can freshen their imagination, and KAIST members can benefit from them to promote creative and innovative ideas through exchange and collaboration.”
2013.11.04 View 6943
Artist in residence program at KAIST
A new and innovative program to support artists’ creative activities was launched by KAIST for the first time in Korean college history.
The artist in residence program is an unusual collaboration between engineers and artists. Out of hundreds of applicants for the program, three writers were selected: a novelist, web-based cartoonist, and screen writer. In late October, they became the residents of KAIST.
Housing and an office are provided for the writers in addition to a monthly cash stipend of 800,000 won for up to six months. A variety of programs will be available as well including a tour of laboratories to help the writers get ideas and inspiration.
KAIST’s Vice President Jun-Ho Oh, the founder of the program, said, “Artists can freshen their imagination, and KAIST members can benefit from them to promote creative and innovative ideas through exchange and collaboration.”
2013.11.04 View 6943 -
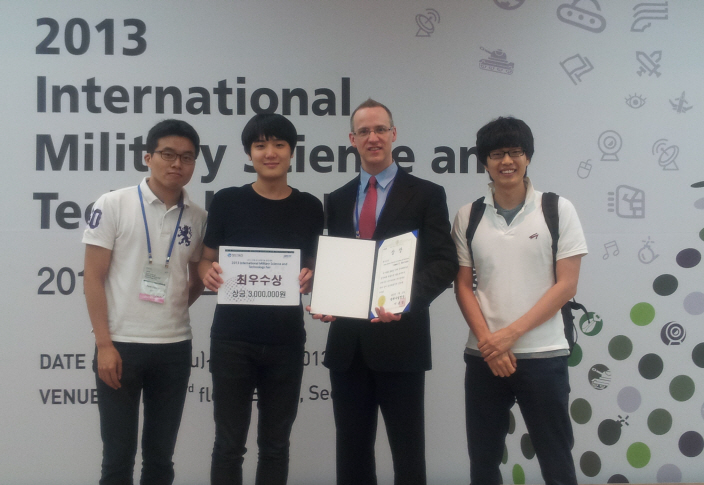 First Prize in the 2013 International Military Science and Technology Contest
Professor James R. Morrison and his students of the Industrial and Systems Engineering Department at KAIST were awarded the first prize in the 2013 International Military Science and Technology Contest organized by the Defense Acquisition Program Administration held in COEX from July 11 to 14.
The research group, Byungduk Song (Ph.D candidate), Jonghoe Kim (Ph.D candidate), Hyolin Park (MS candidate) and Professor James R. Morrison, received the first prize with their paper entitled “Automated and persistent UAV system for a complementary method for border patrol and target tracking.”
The Defense Acquisition Program Administration is the host of the annual contest which aims to contribute to the future of the defense industry and to expand technology exchange between private institutes and the military through the coordination of defense technology and advanced technology from industrial and educational cooperation.Professor Morrison’s team received the honor of the first-place prize out of 56 competitors from within Korea and 7 from overseas in the field of Synthetic New Technology/Academic Thesis.
2013.10.31 View 9786
First Prize in the 2013 International Military Science and Technology Contest
Professor James R. Morrison and his students of the Industrial and Systems Engineering Department at KAIST were awarded the first prize in the 2013 International Military Science and Technology Contest organized by the Defense Acquisition Program Administration held in COEX from July 11 to 14.
The research group, Byungduk Song (Ph.D candidate), Jonghoe Kim (Ph.D candidate), Hyolin Park (MS candidate) and Professor James R. Morrison, received the first prize with their paper entitled “Automated and persistent UAV system for a complementary method for border patrol and target tracking.”
The Defense Acquisition Program Administration is the host of the annual contest which aims to contribute to the future of the defense industry and to expand technology exchange between private institutes and the military through the coordination of defense technology and advanced technology from industrial and educational cooperation.Professor Morrison’s team received the honor of the first-place prize out of 56 competitors from within Korea and 7 from overseas in the field of Synthetic New Technology/Academic Thesis.
2013.10.31 View 9786 -
 2013 International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST (ICISTS-KAIST)
The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST (ICISTS-KAIST) is a global forum organized by KAIST undergraduate students to promote the exchange of ideas and facilitate the discussion of issues that are important to science, technology, society, and higher education. The ICISTS-KAIST conference has been held annually every summer since 2005, inviting distinguished speakers and guests from all around the world to share their insights and expertise with students gathered from Korea and abroad. Last year alone, more than 300 students from 22 nations and 40 speakers participated in the event.
Originally, the ICISTS-KAIST was established by KAIST students who were inspired by the Harvard Project for Asian and International Relations (HPAIR), which is one of the Harvard’s largest annual student conferences in Asia.
This year, 335 students from 103 universities in 22 countries joined the conference that was held on August 5th-9th in Daejeon, making the 2013 ICISTS-KAIST the biggest science and engineering gathering hosted by university students in Asia. About 36% of the participants were international students.
The theme of the conference was “Perfect Alliance: Coexistence for Human Society,” in which students and speakers addressed issues on how to harmonize the speed of scientific progress with the development of important values in society, as well as to explore solutions to overcome the chasm, if any, between the boundaries of science and society.
In his opening remarks, President Steve Kang said, “Creativity and innovation are born out of openness. Therefore, it is essential for young scientists and engineers to communicate with people from different cultural and political backgrounds. Through this kind of global interaction and exchange of ideas and views, students will have an opportunity to deepen their understanding of the world and to better examine the purpose of their intellectual exploration in science and technology.” At the 2013 ICISTS-KAIST, 25 distinguished speakers participated including Walter Bender, a former director of the Media Lab at MIT and David Christian, a professor of Macquarie University in Australia.
2013.08.08 View 11377
2013 International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST (ICISTS-KAIST)
The International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society at KAIST (ICISTS-KAIST) is a global forum organized by KAIST undergraduate students to promote the exchange of ideas and facilitate the discussion of issues that are important to science, technology, society, and higher education. The ICISTS-KAIST conference has been held annually every summer since 2005, inviting distinguished speakers and guests from all around the world to share their insights and expertise with students gathered from Korea and abroad. Last year alone, more than 300 students from 22 nations and 40 speakers participated in the event.
Originally, the ICISTS-KAIST was established by KAIST students who were inspired by the Harvard Project for Asian and International Relations (HPAIR), which is one of the Harvard’s largest annual student conferences in Asia.
This year, 335 students from 103 universities in 22 countries joined the conference that was held on August 5th-9th in Daejeon, making the 2013 ICISTS-KAIST the biggest science and engineering gathering hosted by university students in Asia. About 36% of the participants were international students.
The theme of the conference was “Perfect Alliance: Coexistence for Human Society,” in which students and speakers addressed issues on how to harmonize the speed of scientific progress with the development of important values in society, as well as to explore solutions to overcome the chasm, if any, between the boundaries of science and society.
In his opening remarks, President Steve Kang said, “Creativity and innovation are born out of openness. Therefore, it is essential for young scientists and engineers to communicate with people from different cultural and political backgrounds. Through this kind of global interaction and exchange of ideas and views, students will have an opportunity to deepen their understanding of the world and to better examine the purpose of their intellectual exploration in science and technology.” At the 2013 ICISTS-KAIST, 25 distinguished speakers participated including Walter Bender, a former director of the Media Lab at MIT and David Christian, a professor of Macquarie University in Australia.
2013.08.08 View 11377 -
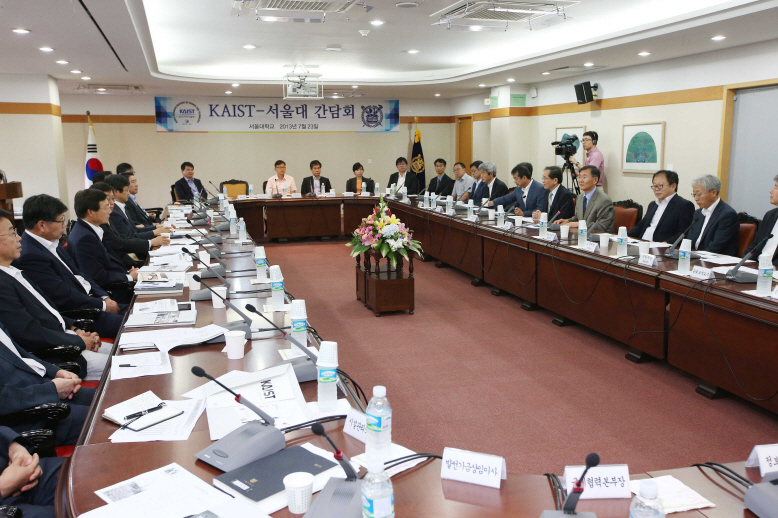 KAIST and Seoul National University Agree to Expand Cooperation in Education and Research
The presidents of two top-notch universities in Korea, KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU), met on July 23rd at the SNU campus and agreed to expand their academic cooperation to promote the univresities" mutual development.
To start, President Yeon-Cheon Oh of SNU proposed a student exchange program through which SNU students can take courses at KAIST for six months.
In return, President Steve Kang suggested that KAIST establish a liaison office on the SNU campus to facilitate better communication between two universities, thereby developing more exchange programs for research and education.Additionally, the two public universities will set up a task force to implement the agreement, conduct joint research programs, and hold regular meetings between their faculty members.President Kang said, “SNU has superb academic and research programs not only in the fields of science and technology but also in the humanities, arts, and social sciences. KAIST will surely benefit from SNU’s excellence in a broad range of academic disciplines, and SNU will have an opportunity to capitalize on KAIST’s expertise in science, engineering, and technology to enhance its growth.”At the conclusion of their consultation, the presidents expressed the hope that the agreement will strengthen the two institutions" capacity for competitiveness and globalization, preparing them to compete with leading universities in the world.
2013.07.25 View 8419
KAIST and Seoul National University Agree to Expand Cooperation in Education and Research
The presidents of two top-notch universities in Korea, KAIST and Seoul National University (SNU), met on July 23rd at the SNU campus and agreed to expand their academic cooperation to promote the univresities" mutual development.
To start, President Yeon-Cheon Oh of SNU proposed a student exchange program through which SNU students can take courses at KAIST for six months.
In return, President Steve Kang suggested that KAIST establish a liaison office on the SNU campus to facilitate better communication between two universities, thereby developing more exchange programs for research and education.Additionally, the two public universities will set up a task force to implement the agreement, conduct joint research programs, and hold regular meetings between their faculty members.President Kang said, “SNU has superb academic and research programs not only in the fields of science and technology but also in the humanities, arts, and social sciences. KAIST will surely benefit from SNU’s excellence in a broad range of academic disciplines, and SNU will have an opportunity to capitalize on KAIST’s expertise in science, engineering, and technology to enhance its growth.”At the conclusion of their consultation, the presidents expressed the hope that the agreement will strengthen the two institutions" capacity for competitiveness and globalization, preparing them to compete with leading universities in the world.
2013.07.25 View 8419 -
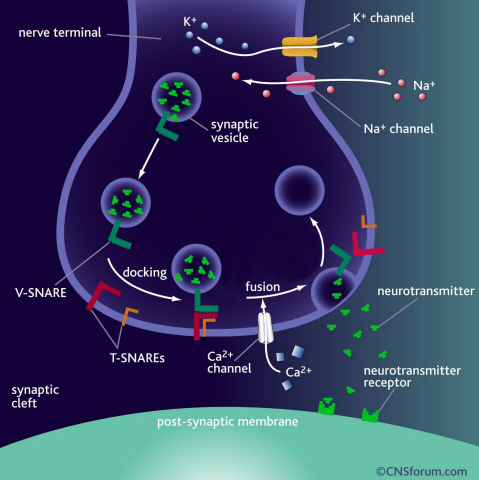 Neurotransmitter protein structure and operation principle identified
Professor Tae-Young Yoon
- Real-time measurement of structural change of bio-membrane fusion protein
- A new clue to degenerative brain diseases research
KAIST Physics Department’s Professor Tae-Young Yoon has successfully identified the hidden structure and operation mechanism of the SNARE protein, which has a central role in transporting neurotransmitters between neurons, using magnetic nanotweezers. SNARE protein’s cell membrane fusion function is closely related to degenerative brain diseases or neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s. Hence, this research may provide a clue to the disease’s prevention and treatment.
Neurotransmission occurs when vesicles containing neurotransmitters fuse with cell membranes in neuron synapses. The SNARE protein is a cell-membrane fusion protein with a core role of releasing neurotransmitters. The academia speculated the SNARE protein would regulate the exchange of neurotransmitters, but its precise function and structure has been unknown. Professor Yoon’s research team developed an experimental technique using nanotweezers to measure physical changes to nanometer level by pulling and releasing each protein with force of 1 pN (piconewton). The research identified the existence of hidden SNARE protein"s intermediate structure. The process of withstanding and maintaining repulsive forces between bio-membranes in the hidden intermediate structure of SNARE to regulate the exchange of neurotransmitters has also been identified.
Professor Yoon’s research team developed an experimental technique using magnetic nanotweezers to measure physical changes of proteins to nanometer level by pulling and releasing each protein with force of 1 pN. The research identified the existence of hidden SNARE protein"s intermediate structure and its formation. The process of withstanding and maintaining repulsive forces between bio-membranes in the hidden intermediate structure of SNARE to regulate the exchange of neurotransmitters has also been discovered.
Professor Yoon said, “Ground breaking research results have been produced. A simple experimental technique of applying the smallest possible forces to proteins (with tweezers) to see their hidden structure and formation process can produce the same result as real observation has been developed.” He continued, “This technique will be very important in researching biological object with physical experimental technique. It will be a vital foundation to consilient research of different academia in the future.”
This research was a joint project of Physics Department’s Professor Tae-Young Yoon, KAIST, and Biomedical Engineering Institute’s Professor Yeon-Kyun Shin at KIST. KAIST Physics Department’s Professor Yong-Hoon Cho, Ph.D. candidate Do-Yong Lee and KIAS Computational Sciences Department’s Professor Chang-Bong Hyun participated. The research was published on Nature Communications on April 16th.
a) Neurotransmission occurs when vesicles containing neurotransmitters fuse with cell membranes in neuron synapses. A SNARE protein is a cell-membrane fusion protein with a core role of releasing neurotransmitters.
b) A schematic diagram using magnetic nanotweezers to measure protein structure changes on molecular level. The nanotweezers exert an exquisite pull and release of each protein with a force of 1 pN to measure physical changes to nanometer level in real-time to observe the hidden intermediate structure and operation principles of bio-membrane fusion protein.
2013.05.25 View 9874
Neurotransmitter protein structure and operation principle identified
Professor Tae-Young Yoon
- Real-time measurement of structural change of bio-membrane fusion protein
- A new clue to degenerative brain diseases research
KAIST Physics Department’s Professor Tae-Young Yoon has successfully identified the hidden structure and operation mechanism of the SNARE protein, which has a central role in transporting neurotransmitters between neurons, using magnetic nanotweezers. SNARE protein’s cell membrane fusion function is closely related to degenerative brain diseases or neurological disorders such as Alzheimer’s. Hence, this research may provide a clue to the disease’s prevention and treatment.
Neurotransmission occurs when vesicles containing neurotransmitters fuse with cell membranes in neuron synapses. The SNARE protein is a cell-membrane fusion protein with a core role of releasing neurotransmitters. The academia speculated the SNARE protein would regulate the exchange of neurotransmitters, but its precise function and structure has been unknown. Professor Yoon’s research team developed an experimental technique using nanotweezers to measure physical changes to nanometer level by pulling and releasing each protein with force of 1 pN (piconewton). The research identified the existence of hidden SNARE protein"s intermediate structure. The process of withstanding and maintaining repulsive forces between bio-membranes in the hidden intermediate structure of SNARE to regulate the exchange of neurotransmitters has also been identified.
Professor Yoon’s research team developed an experimental technique using magnetic nanotweezers to measure physical changes of proteins to nanometer level by pulling and releasing each protein with force of 1 pN. The research identified the existence of hidden SNARE protein"s intermediate structure and its formation. The process of withstanding and maintaining repulsive forces between bio-membranes in the hidden intermediate structure of SNARE to regulate the exchange of neurotransmitters has also been discovered.
Professor Yoon said, “Ground breaking research results have been produced. A simple experimental technique of applying the smallest possible forces to proteins (with tweezers) to see their hidden structure and formation process can produce the same result as real observation has been developed.” He continued, “This technique will be very important in researching biological object with physical experimental technique. It will be a vital foundation to consilient research of different academia in the future.”
This research was a joint project of Physics Department’s Professor Tae-Young Yoon, KAIST, and Biomedical Engineering Institute’s Professor Yeon-Kyun Shin at KIST. KAIST Physics Department’s Professor Yong-Hoon Cho, Ph.D. candidate Do-Yong Lee and KIAS Computational Sciences Department’s Professor Chang-Bong Hyun participated. The research was published on Nature Communications on April 16th.
a) Neurotransmission occurs when vesicles containing neurotransmitters fuse with cell membranes in neuron synapses. A SNARE protein is a cell-membrane fusion protein with a core role of releasing neurotransmitters.
b) A schematic diagram using magnetic nanotweezers to measure protein structure changes on molecular level. The nanotweezers exert an exquisite pull and release of each protein with a force of 1 pN to measure physical changes to nanometer level in real-time to observe the hidden intermediate structure and operation principles of bio-membrane fusion protein.
2013.05.25 View 9874 -
 Cooperation Agreement signed between KAIST and University of Oxford
On April 6th, a Cooperation Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), including the exchange of students between two universities, was signed by KAIST and University of Oxford on April 6th.
In the MOU, KAIST and Oxford agreed to achieve mutual development through cooperation, such as joint research programs and the exchange of professors and students.
President Sung-Mo Kang stated, “This agreement will be the start of close cooperation between the two universities, and I will continue to endeavor to expand the relationship.”
Andrew Hamilton, the president of Oxford University replied, “I am well aware of the excellent quality of teaching and research of Korean students and KAIST. I hope the cooperation between KAIST and Oxford will achieve exchange at diverse levels.”
President Hamilton taught chemistry at the University of Pittsburgh and Princeton University and also served as the vice-president of Yale University. Having experience of teaching a KAIST student before, he has high praise for the ability of KAIST students.
The President of the University of Oxford, Andrew Hamilton (left), and the President of KAIST, Sung-Mo "Steve" Kang, shake hands in acknowledgement of signing the Cooperation MOU.
2013.05.20 View 7179
Cooperation Agreement signed between KAIST and University of Oxford
On April 6th, a Cooperation Memorandum of Understanding (MOU), including the exchange of students between two universities, was signed by KAIST and University of Oxford on April 6th.
In the MOU, KAIST and Oxford agreed to achieve mutual development through cooperation, such as joint research programs and the exchange of professors and students.
President Sung-Mo Kang stated, “This agreement will be the start of close cooperation between the two universities, and I will continue to endeavor to expand the relationship.”
Andrew Hamilton, the president of Oxford University replied, “I am well aware of the excellent quality of teaching and research of Korean students and KAIST. I hope the cooperation between KAIST and Oxford will achieve exchange at diverse levels.”
President Hamilton taught chemistry at the University of Pittsburgh and Princeton University and also served as the vice-president of Yale University. Having experience of teaching a KAIST student before, he has high praise for the ability of KAIST students.
The President of the University of Oxford, Andrew Hamilton (left), and the President of KAIST, Sung-Mo "Steve" Kang, shake hands in acknowledgement of signing the Cooperation MOU.
2013.05.20 View 7179 -
 KAIST signs a Cooperation Agreement with University of California, Irvine
On April 6th, KAIST signed a cooperation memorandum of understanding (MOU) establishing academic exchanges of faculty and students with the University of California, Irvine (UC Irvine).
The MOU states that the collaboration between both universities will promote the exchange of faculty and students, as well as joint research.
Following UC Los Angeles (UCLA), Irvine became the second UC campus to make the exchange agreement with KAIST.
UC Irvine was founded in 1965, and is known as a prestigious public university composed of 13 departments, including colleges of arts, biological sciences, engineering, and humanities.
The ceremony was attended by KAIST President, Sung-Mo Kang, and UC Irvine President, Michael V. Drake, as well as Suk-Hee Kang, the former Mayor of Irvine.
KAIST President Sung-Mo "Steve" Kang (left) and President of UC Irvine Michael Drake (right) shake hands after signing the Cooperation MOU.
2013.05.20 View 7019
KAIST signs a Cooperation Agreement with University of California, Irvine
On April 6th, KAIST signed a cooperation memorandum of understanding (MOU) establishing academic exchanges of faculty and students with the University of California, Irvine (UC Irvine).
The MOU states that the collaboration between both universities will promote the exchange of faculty and students, as well as joint research.
Following UC Los Angeles (UCLA), Irvine became the second UC campus to make the exchange agreement with KAIST.
UC Irvine was founded in 1965, and is known as a prestigious public university composed of 13 departments, including colleges of arts, biological sciences, engineering, and humanities.
The ceremony was attended by KAIST President, Sung-Mo Kang, and UC Irvine President, Michael V. Drake, as well as Suk-Hee Kang, the former Mayor of Irvine.
KAIST President Sung-Mo "Steve" Kang (left) and President of UC Irvine Michael Drake (right) shake hands after signing the Cooperation MOU.
2013.05.20 View 7019 -
 KAIST develops a low-power 60 GHz radio frequency chip for mobile devices
As the capacity of handheld devices increases to accommodate a greater number of functions, these devices have more memory, larger display screens, and the ability to play higher definition video files. If the users of mobile devices, including smartphones, tablet PCs, and notebooks, want to share or transfer data on one device with that of another device, a great deal of time and effort are needed.
As a possible method for the speedy transmission of large data, researchers are studying the adoption of gigabits per second (Gbps) wireless communications operating over the 60 gigahertz (GHz) frequency band. Some commercial approaches have been introduced for full-HD video streaming from a fixed source to a display by using the 60 GHz band. But mobile applications have not been developed yet because the 60 GHz radio frequency (RF) circuit consumes hundreds of milliwatts (mW) of DC power.
Professor Chul Soon Park from the Department of Electrical Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and his research team recently developed a low-power version of the 60 GHz radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC). Inside the circuit are an energy-efficient modulator performing amplification as well as modulation and a sensitivity-improved receiver employing a gain boosting demodulator.
The research team said that their RFIC draws as little as 67 mW of power in the 60 GHz frequency band, consuming 31mW to send and 36mW to receive large volumes of data. RFIC is also small enough to be mounted on smartphones or notebooks, requiring only one chip (its width, length, and height are about 1 mm) and one antenna (4x5x1 mm3) for sending and receiving data with an integrated switch.
Professor Park, Director of the Intelligent Radio Engineering Center at KAIST, gave an upbeat assessment of the potential of RFIC for future applications. What we have developed is a low-power 60-GHz RF chip with a transmission speed of 10.7 gigabits per second. In tests, we were able to stream uncompressed full-HD videos from a smartphone or notebook to a display without a cable connection (Youtube Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6PVSLBhMymc). Our chip can be installed on mobile devices or even on cameras so that the devices are virtually connected to other devices and able to exchange large data with each other."
2013.04.02 View 9132
KAIST develops a low-power 60 GHz radio frequency chip for mobile devices
As the capacity of handheld devices increases to accommodate a greater number of functions, these devices have more memory, larger display screens, and the ability to play higher definition video files. If the users of mobile devices, including smartphones, tablet PCs, and notebooks, want to share or transfer data on one device with that of another device, a great deal of time and effort are needed.
As a possible method for the speedy transmission of large data, researchers are studying the adoption of gigabits per second (Gbps) wireless communications operating over the 60 gigahertz (GHz) frequency band. Some commercial approaches have been introduced for full-HD video streaming from a fixed source to a display by using the 60 GHz band. But mobile applications have not been developed yet because the 60 GHz radio frequency (RF) circuit consumes hundreds of milliwatts (mW) of DC power.
Professor Chul Soon Park from the Department of Electrical Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and his research team recently developed a low-power version of the 60 GHz radio frequency integrated circuit (RFIC). Inside the circuit are an energy-efficient modulator performing amplification as well as modulation and a sensitivity-improved receiver employing a gain boosting demodulator.
The research team said that their RFIC draws as little as 67 mW of power in the 60 GHz frequency band, consuming 31mW to send and 36mW to receive large volumes of data. RFIC is also small enough to be mounted on smartphones or notebooks, requiring only one chip (its width, length, and height are about 1 mm) and one antenna (4x5x1 mm3) for sending and receiving data with an integrated switch.
Professor Park, Director of the Intelligent Radio Engineering Center at KAIST, gave an upbeat assessment of the potential of RFIC for future applications. What we have developed is a low-power 60-GHz RF chip with a transmission speed of 10.7 gigabits per second. In tests, we were able to stream uncompressed full-HD videos from a smartphone or notebook to a display without a cable connection (Youtube Link: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6PVSLBhMymc). Our chip can be installed on mobile devices or even on cameras so that the devices are virtually connected to other devices and able to exchange large data with each other."
2013.04.02 View 9132 -
 KAIST and Saudi Aramco agreed to establish a joint CO2 research center in Korea
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Saudi Aramco, a global energy and petrochemicals enterprise, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on January 6, 2013 in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia and pledged to jointly collaborate in research and development of innovative technologies and solutions to address the world"s energy challenges.
Under the MOU, the two entities agreed to establish a research center, Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Research Center, near KAIST"s main campus in Daejeon, Korea. The research center, to be jointly managed by KAIST and Saudi Aramco, will foster and facilitate research collaborations in areas such as tackling carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by removal or capture of CO2, conversing CO2 into useful products, developing efficiency improvements in energy production, sharing carbon management technologies, establishing exchange programs, and conducting joint projects.
According to Saudi Aramco, the company"s collaboration with KAIST is the first partnership established in Asia. Khalid A. Al-Falih, President and CEO of Saudi Aramco, said,
"The CO2 Research Center represents a major step in Saudi Aramco"s research and technology strategy to partner with top global institutions to help address and find sustainable solutions to the world’s energy challenge both domestically and internationally."
2013.03.19 View 10796
KAIST and Saudi Aramco agreed to establish a joint CO2 research center in Korea
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Saudi Aramco, a global energy and petrochemicals enterprise, signed a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on January 6, 2013 in Dhahran, Saudi Arabia and pledged to jointly collaborate in research and development of innovative technologies and solutions to address the world"s energy challenges.
Under the MOU, the two entities agreed to establish a research center, Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Research Center, near KAIST"s main campus in Daejeon, Korea. The research center, to be jointly managed by KAIST and Saudi Aramco, will foster and facilitate research collaborations in areas such as tackling carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions by removal or capture of CO2, conversing CO2 into useful products, developing efficiency improvements in energy production, sharing carbon management technologies, establishing exchange programs, and conducting joint projects.
According to Saudi Aramco, the company"s collaboration with KAIST is the first partnership established in Asia. Khalid A. Al-Falih, President and CEO of Saudi Aramco, said,
"The CO2 Research Center represents a major step in Saudi Aramco"s research and technology strategy to partner with top global institutions to help address and find sustainable solutions to the world’s energy challenge both domestically and internationally."
2013.03.19 View 10796 -
 Launched the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a global energy and petrochemicals enterprise, signed on February 20, 2013 the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement (the Agreement) on joint collaborations in research and development of carbon management between the two entities.
The Agreement was subsequently concluded upon the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between KAIST and Saudi Aramco, dated January 7th, 2013. In the Agreement, the two organizations specified terms and conditions necessary to conduct joint research projects and stipulated governing body for the operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a national oil company for Saudi Arabia, entered into the MOU, in which the two parties shared a common interest in addressing the issue of CO2 capture, CO2storage, CO2 avoidance using efficiency improvements, and converting CO2 into useful chemicals and other materials, and agreed to “create a major research center for CO2” in Korea.
As envisioned by the MOU and its subsequent agreement, KAIST and Saudi Aramco decided to operate an interim office of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center at KAIST campus in Daejeon, Korea, pending the establishment of the research center. The full-fledged, independent research facility will be built at a location and during a period to be agreed between the two parties.
Following the signing of the Agreement, there was a celebration event taken place, including a signboard hanging ceremony for the interim research office. A 10-member delegation from Saudi Aramco, which was headed by Vice President of Engineering Services Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Dr. Nam-Pyo Suh, former president of KAIST, Vice President of Research at KAIST Kyung-Wook Paik, and senior representatives from Korean oil and petrochemical companies such as S-Oil, Lotte Chemicals, SK Innovation, and STX attended the event.
Kyung-Wook Paik, Vice President of Research at KAIST, said,
“In order to help find solutions to carbon management, KAIST and Saudi Aramco will facilitate to exchange each party’s complementary technical expertise, gain insight into new research fields, and have access to key sources of talent, while promoting innovation for technology solutions and contributing to the lifelong learning agenda of both organizations.”
Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Vice President of Engineering Services at Saudi Aramco, added that “As a world-leading oil and gas company, Saudi Aramco’s mission is to promote the continued use of safe, environmentally-friendly petroleum products with a vision to becoming a global leader in research and technology. Building a strong and cooperative relationship with KAIST in our endeavor to search for alternative ways to better utilization of fossil fuels will expedite the creation of opportunities to make the world environmentally safer and sustainable.”
KAIST and Saudi Aramco will each chip in a maximum of USD 5 million annually for the establishment and operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center during the initial term of the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement, which starts in 2013 and continues through 2018.
2013.03.19 View 14784
Launched the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center in Korea
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a global energy and petrochemicals enterprise, signed on February 20, 2013 the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement (the Agreement) on joint collaborations in research and development of carbon management between the two entities.
The Agreement was subsequently concluded upon the signing of the Memorandum of Understanding (MOU) between KAIST and Saudi Aramco, dated January 7th, 2013. In the Agreement, the two organizations specified terms and conditions necessary to conduct joint research projects and stipulated governing body for the operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
KAIST and Saudi Aramco, a national oil company for Saudi Arabia, entered into the MOU, in which the two parties shared a common interest in addressing the issue of CO2 capture, CO2storage, CO2 avoidance using efficiency improvements, and converting CO2 into useful chemicals and other materials, and agreed to “create a major research center for CO2” in Korea.
As envisioned by the MOU and its subsequent agreement, KAIST and Saudi Aramco decided to operate an interim office of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center at KAIST campus in Daejeon, Korea, pending the establishment of the research center. The full-fledged, independent research facility will be built at a location and during a period to be agreed between the two parties.
Following the signing of the Agreement, there was a celebration event taken place, including a signboard hanging ceremony for the interim research office. A 10-member delegation from Saudi Aramco, which was headed by Vice President of Engineering Services Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Dr. Nam-Pyo Suh, former president of KAIST, Vice President of Research at KAIST Kyung-Wook Paik, and senior representatives from Korean oil and petrochemical companies such as S-Oil, Lotte Chemicals, SK Innovation, and STX attended the event.
Kyung-Wook Paik, Vice President of Research at KAIST, said,
“In order to help find solutions to carbon management, KAIST and Saudi Aramco will facilitate to exchange each party’s complementary technical expertise, gain insight into new research fields, and have access to key sources of talent, while promoting innovation for technology solutions and contributing to the lifelong learning agenda of both organizations.”
Samir Al-Tubayyeb, Vice President of Engineering Services at Saudi Aramco, added that “As a world-leading oil and gas company, Saudi Aramco’s mission is to promote the continued use of safe, environmentally-friendly petroleum products with a vision to becoming a global leader in research and technology. Building a strong and cooperative relationship with KAIST in our endeavor to search for alternative ways to better utilization of fossil fuels will expedite the creation of opportunities to make the world environmentally safer and sustainable.”
KAIST and Saudi Aramco will each chip in a maximum of USD 5 million annually for the establishment and operation of the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center during the initial term of the Master Research and Collaboration Agreement, which starts in 2013 and continues through 2018.
2013.03.19 View 14784 -
 KAIST International Students Organize KAIST ONE Program
International Students at KAIST are running a program called “KAIST ONE” (Overseas Networking Exchange) in order to promote an active exchange between students and to present their cultures.
Originally an international cultural activity at the ICU (then the Information and Communications University) in 2007, the program changed its name to “KAIST ONE” and was continued after the merging of the university with KAIST. Students of about 40 different countries have participated to date, and each annual event attracts more than 150 students.
Over 700 international students from 70 different countries around the world spontaneously organize and manage the KAIST ONE program, which is run five times this semester, every other Thursday from 7p.m. to 9p.m. at the KAIST International Center.
The 11th of last month and the 1st of this month witnessed an enthusiastic response from about 150 participants who joined the Columbian and the Saudi Arabian students in introducing their cultures, presenting traditional cultural performances, and sharing traditional foods.
The next in line are Danish, Ugandan, and Cameroonian students who are set to have their turns on this month’s 15th, 29th, and next month’s 6th, respectively.
Also notable is the active attention and support from foreign embassies such as the participation of Tunisian, Brazilian, Pakistani, Azerbaijani, Thai, and German ambassadors in the program since last year to provide food and introductory guides to cultures.
The director of this year’s program, Karim Charfi (Tunisian, 3rd year Electrical Engineering) said, “During the selection stage of each semester, everyone competes for the chance to present their country,” and “KAIST ONE has established itself as a unique and exotic cultural event at KAIST since it networks about 40 of the relatively less known countries such as Uganda, Cameroon, Tunisia, and Chile and the people with diverse cultures.”
The supervisor of the program, Chang Dong Yoo of the Office of Special Projects and Institutional Relations said, “KAIST ONE is an opportunity for international students to acquaint people with their cultures, and it is also a site of cultural exchange and of building friendships among KAIST students and international students,” and “we plan to extend the event such that not only the KAIST members but also the local residents can join in.”
The program welcomes KAIST students as well as the general public.
2012.12.21 View 8423
KAIST International Students Organize KAIST ONE Program
International Students at KAIST are running a program called “KAIST ONE” (Overseas Networking Exchange) in order to promote an active exchange between students and to present their cultures.
Originally an international cultural activity at the ICU (then the Information and Communications University) in 2007, the program changed its name to “KAIST ONE” and was continued after the merging of the university with KAIST. Students of about 40 different countries have participated to date, and each annual event attracts more than 150 students.
Over 700 international students from 70 different countries around the world spontaneously organize and manage the KAIST ONE program, which is run five times this semester, every other Thursday from 7p.m. to 9p.m. at the KAIST International Center.
The 11th of last month and the 1st of this month witnessed an enthusiastic response from about 150 participants who joined the Columbian and the Saudi Arabian students in introducing their cultures, presenting traditional cultural performances, and sharing traditional foods.
The next in line are Danish, Ugandan, and Cameroonian students who are set to have their turns on this month’s 15th, 29th, and next month’s 6th, respectively.
Also notable is the active attention and support from foreign embassies such as the participation of Tunisian, Brazilian, Pakistani, Azerbaijani, Thai, and German ambassadors in the program since last year to provide food and introductory guides to cultures.
The director of this year’s program, Karim Charfi (Tunisian, 3rd year Electrical Engineering) said, “During the selection stage of each semester, everyone competes for the chance to present their country,” and “KAIST ONE has established itself as a unique and exotic cultural event at KAIST since it networks about 40 of the relatively less known countries such as Uganda, Cameroon, Tunisia, and Chile and the people with diverse cultures.”
The supervisor of the program, Chang Dong Yoo of the Office of Special Projects and Institutional Relations said, “KAIST ONE is an opportunity for international students to acquaint people with their cultures, and it is also a site of cultural exchange and of building friendships among KAIST students and international students,” and “we plan to extend the event such that not only the KAIST members but also the local residents can join in.”
The program welcomes KAIST students as well as the general public.
2012.12.21 View 8423