ICA
-
 KAIST develops technology for selective RNA modification in living cells and animals
· A team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed a pioneering technology that selectively acetylates specific RNA molecules in living cells and tissues.
· The platform uses RNA-targeting CRISPR tools in combination with RNA-modifying enzymes to chemically modify only the intended RNA.
· The method opens new possibilities for gene therapy by enabling precise control of disease-related RNA without affecting the rest of the transcriptome.
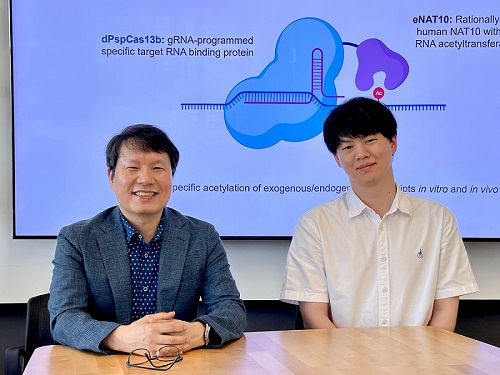
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Won Do Heo and Jihwan Yu, a Ph.D. Candidate of the Department of Biological Sciences >
CRISPR-Cas13, a powerful RNA-targeting technology is gaining increasing attention as a next-generation gene therapy platform due to its precision and reduced side effects. Utilizing this system, researchers at KAIST have now developed the world’s first technology capable of selectively acetylating (chemically modifying) specific RNA molecules among countless transcripts within living cells. This breakthrough enables precise, programmable control of RNA function and is expected to open new avenues in RNA-based therapeutic development.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Won Do Heo in the Department of Biological Sciences has recently developed a groundbreaking technology capable of selectively acetylating specific RNA molecules within the human body using the CRISPR-Cas13 system—an RNA-targeting platform gaining increasing attention in the fields of gene regulation and RNA-based therapeutics.
RNA molecules can undergo chemical modifications—the addition of specific chemical groups—which alter their function and behavior without changing the underlying nucleotide sequence. However, some of these modifications, a critical layer of post-transcriptional gene regulation, remain poorly understood. Among them, N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) has been particularly enigmatic, with ongoing debate about its existence and function in human messenger RNA (mRNA), the RNA that encodes proteins.
To address this gap, the KAIST research team developed a targeted RNA acetylation system, named dCas13-eNAT10. This platform combines a catalytically inactive Cas13 enzyme (dCas13) that guides the system to specific RNA targets, with a hyperactive variant of the NAT10 enzyme (eNAT10), which performs RNA acetylation. This approach enables precise acetylation of only the desired RNA molecules among the vast pool of transcripts within the cell.
< Figure 1. Development of hyperactive variant eNAT10 through NAT10 protein engineering. By engineering the NAT10 protein, which performs RNA acetylation in human cells, based on its domain and structure, eNAT10 was developed, showing approximately a 3-fold increase in RNA acetylation activity compared to the wild-type enzyme. >
Using this system, the researchers demonstrated that guide RNAs could direct the dCas13-eNAT10 complex to acetylate specific RNA targets, and acetylation significantly increased protein expression from the modified mRNA. Moreover, the study revealed, for the first time, that RNA acetylation plays a role in intracellular RNA localization, facilitating the export of RNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm—a critical step in gene expression regulation.
To validate its therapeutic potential, the team successfully delivered the targeted RNA acetylation system into the livers of live mice using adeno-associated virus (AAV), a commonly used gene therapy vector. This marks the first demonstration of in vivo RNA modification, extending the applicability of RNA chemical modification tools from cell culture models to living organisms.
< Figure 2. Acetylation of various RNA in cells using dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein. Utilizing the CRISPR-Cas13 system, which can precisely target specific RNA through guide RNA, a dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein was created, demonstrating its ability to specifically acetylate various endogenous RNA at different locations within cells. >
Professor Won Do Heo, who previously developed COVID-19 treatment technology using RNA gene scissors and technology to activate RNA gene scissors with light, stated, "Existing RNA chemical modification research faced difficulties in controlling specificity, temporality, and spatiality. However, this new technology allows selective acetylation of desired RNA, opening the door for accurate and detailed research into the functions of RNA acetylation." He added, "The RNA chemical modification technology developed in this study can be widely used as an RNA-based therapeutic agent and a tool for regulating RNA functions in living organisms in the future."
< Figure 3. In vivo delivery of targeted RNA acetylation system. The targeted RNA acetylation system was encoded in an AAV vector, commonly used in gene therapy, and delivered intravenously to adult mice, showing that target RNA in liver tissue was specifically acetylated according to the guide RNA. >
This research, with Ph.D. candidate Jihwan Yu from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST as the first author, was published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology on June 2, 2025. (Title: Programmable RNA acetylation with CRISPR-Cas13, Impact factor: 12.9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-025-01922-3)
This research was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Foundation and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.06.10 View 1904
KAIST develops technology for selective RNA modification in living cells and animals
· A team led by Professor Won Do Heo from the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed a pioneering technology that selectively acetylates specific RNA molecules in living cells and tissues.
· The platform uses RNA-targeting CRISPR tools in combination with RNA-modifying enzymes to chemically modify only the intended RNA.
· The method opens new possibilities for gene therapy by enabling precise control of disease-related RNA without affecting the rest of the transcriptome.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Won Do Heo and Jihwan Yu, a Ph.D. Candidate of the Department of Biological Sciences >
CRISPR-Cas13, a powerful RNA-targeting technology is gaining increasing attention as a next-generation gene therapy platform due to its precision and reduced side effects. Utilizing this system, researchers at KAIST have now developed the world’s first technology capable of selectively acetylating (chemically modifying) specific RNA molecules among countless transcripts within living cells. This breakthrough enables precise, programmable control of RNA function and is expected to open new avenues in RNA-based therapeutic development.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that a research team led by Professor Won Do Heo in the Department of Biological Sciences has recently developed a groundbreaking technology capable of selectively acetylating specific RNA molecules within the human body using the CRISPR-Cas13 system—an RNA-targeting platform gaining increasing attention in the fields of gene regulation and RNA-based therapeutics.
RNA molecules can undergo chemical modifications—the addition of specific chemical groups—which alter their function and behavior without changing the underlying nucleotide sequence. However, some of these modifications, a critical layer of post-transcriptional gene regulation, remain poorly understood. Among them, N4-acetylcytidine (ac4C) has been particularly enigmatic, with ongoing debate about its existence and function in human messenger RNA (mRNA), the RNA that encodes proteins.
To address this gap, the KAIST research team developed a targeted RNA acetylation system, named dCas13-eNAT10. This platform combines a catalytically inactive Cas13 enzyme (dCas13) that guides the system to specific RNA targets, with a hyperactive variant of the NAT10 enzyme (eNAT10), which performs RNA acetylation. This approach enables precise acetylation of only the desired RNA molecules among the vast pool of transcripts within the cell.
< Figure 1. Development of hyperactive variant eNAT10 through NAT10 protein engineering. By engineering the NAT10 protein, which performs RNA acetylation in human cells, based on its domain and structure, eNAT10 was developed, showing approximately a 3-fold increase in RNA acetylation activity compared to the wild-type enzyme. >
Using this system, the researchers demonstrated that guide RNAs could direct the dCas13-eNAT10 complex to acetylate specific RNA targets, and acetylation significantly increased protein expression from the modified mRNA. Moreover, the study revealed, for the first time, that RNA acetylation plays a role in intracellular RNA localization, facilitating the export of RNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm—a critical step in gene expression regulation.
To validate its therapeutic potential, the team successfully delivered the targeted RNA acetylation system into the livers of live mice using adeno-associated virus (AAV), a commonly used gene therapy vector. This marks the first demonstration of in vivo RNA modification, extending the applicability of RNA chemical modification tools from cell culture models to living organisms.
< Figure 2. Acetylation of various RNA in cells using dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein. Utilizing the CRISPR-Cas13 system, which can precisely target specific RNA through guide RNA, a dCas13-eNAT10 fusion protein was created, demonstrating its ability to specifically acetylate various endogenous RNA at different locations within cells. >
Professor Won Do Heo, who previously developed COVID-19 treatment technology using RNA gene scissors and technology to activate RNA gene scissors with light, stated, "Existing RNA chemical modification research faced difficulties in controlling specificity, temporality, and spatiality. However, this new technology allows selective acetylation of desired RNA, opening the door for accurate and detailed research into the functions of RNA acetylation." He added, "The RNA chemical modification technology developed in this study can be widely used as an RNA-based therapeutic agent and a tool for regulating RNA functions in living organisms in the future."
< Figure 3. In vivo delivery of targeted RNA acetylation system. The targeted RNA acetylation system was encoded in an AAV vector, commonly used in gene therapy, and delivered intravenously to adult mice, showing that target RNA in liver tissue was specifically acetylated according to the guide RNA. >
This research, with Ph.D. candidate Jihwan Yu from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST as the first author, was published in the journal Nature Chemical Biology on June 2, 2025. (Title: Programmable RNA acetylation with CRISPR-Cas13, Impact factor: 12.9, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-025-01922-3)
This research was supported by the Samsung Future Technology Foundation and the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.06.10 View 1904 -
 KAIST Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu Receives Global IEEE Robotics Journal Best Paper Award
- Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu of Civil and Environmental Engineering receives the Best Paper Award from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics Journal, officially presented at ICRA, a world-renowned robotics conference.
- This is the highest level of international recognition, awarded to only the top 5 papers out of approximately 1,500 published in 2024.
- Securing a new working channel technology for soft growing robots expands the practicality and application possibilities in the field of soft robotics.
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu (left), Nam Gyun Kim, Ph.D. Candidate (right) from the KAIST Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and KAIST Robotics Program >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering received the 2024 Best Paper Award from the Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), a premier journal under the IEEE, at the '2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)' held in Atlanta, USA, on May 22nd.
This Best Paper Award is a prestigious honor presented to only the top 5 papers out of approximately 1,500 published in 2024, boasting high international competition and authority.
The award-winning paper by Professor Ryu proposes a novel working channel securing mechanism that significantly expands the practicality and application possibilities of 'Soft Growing Robots,' which are based on soft materials that move or perform tasks through a growing motion similar to plant roots.
< IEEE Robotics Journal Award Ceremony >
Existing soft growing robots move by inflating or contracting their bodies through increasing or decreasing internal pressure, which can lead to blockages in their internal passages. In contrast, the newly developed soft growing robot achieves a growing function while maintaining the internal passage pressure equal to the external atmospheric pressure, thereby successfully securing an internal passage while retaining the robot's flexible and soft characteristics.
This structure allows various materials or tools to be freely delivered through the internal passage (working channel) within the robot and offers the advantage of performing multi-purpose tasks by flexibly replacing equipment according to the working environment.
The research team fabricated a prototype to prove the effectiveness of this technology and verified its performance through various experiments. Specifically, in the slide plate experiment, they confirmed whether materials or equipment could pass through the robot's internal channel without obstruction, and in the pipe pulling experiment, they verified if a long pipe-shaped tool could be pulled through the internal channel.
< Figure 1. Overall hardware structure of the proposed soft growing robot (left) and a cross-sectional view composing the inflatable structure (right) >
Experimental results demonstrated that the internal channel remained stable even while the robot was growing, serving as a key basis for supporting the technology's practicality and scalability.
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu stated, "This award is very meaningful as it signifies the global recognition of Korea's robotics technology and academic achievements. Especially, it holds great significance in achieving technical progress that can greatly expand the practicality and application fields of soft growing robots. This achievement was possible thanks to the dedication and collaboration of the research team, and I will continue to contribute to the development of robotics technology through innovative research."
< Figure 2. Material supplying mechanism of the Soft Growing Robot >
This research was co-authored by Dongoh Seo, Ph.D. Candidate in Civil and Environmental Engineering, and Nam Gyun Kim, Ph.D. Candidate in Robotics. It was published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters on September 1, 2024.
(Paper Title: Inflatable-Structure-Based Working-Channel Securing Mechanism for Soft Growing Robots, DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3426322)
This project was supported simultaneously by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Future Promising Convergence Technology Pioneer Research Project and Mid-career Researcher Project.
2025.06.09 View 2963
KAIST Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu Receives Global IEEE Robotics Journal Best Paper Award
- Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu of Civil and Environmental Engineering receives the Best Paper Award from the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics Journal, officially presented at ICRA, a world-renowned robotics conference.
- This is the highest level of international recognition, awarded to only the top 5 papers out of approximately 1,500 published in 2024.
- Securing a new working channel technology for soft growing robots expands the practicality and application possibilities in the field of soft robotics.
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu (left), Nam Gyun Kim, Ph.D. Candidate (right) from the KAIST Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering and KAIST Robotics Program >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th that Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering received the 2024 Best Paper Award from the Robotics and Automation Letters (RA-L), a premier journal under the IEEE, at the '2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)' held in Atlanta, USA, on May 22nd.
This Best Paper Award is a prestigious honor presented to only the top 5 papers out of approximately 1,500 published in 2024, boasting high international competition and authority.
The award-winning paper by Professor Ryu proposes a novel working channel securing mechanism that significantly expands the practicality and application possibilities of 'Soft Growing Robots,' which are based on soft materials that move or perform tasks through a growing motion similar to plant roots.
< IEEE Robotics Journal Award Ceremony >
Existing soft growing robots move by inflating or contracting their bodies through increasing or decreasing internal pressure, which can lead to blockages in their internal passages. In contrast, the newly developed soft growing robot achieves a growing function while maintaining the internal passage pressure equal to the external atmospheric pressure, thereby successfully securing an internal passage while retaining the robot's flexible and soft characteristics.
This structure allows various materials or tools to be freely delivered through the internal passage (working channel) within the robot and offers the advantage of performing multi-purpose tasks by flexibly replacing equipment according to the working environment.
The research team fabricated a prototype to prove the effectiveness of this technology and verified its performance through various experiments. Specifically, in the slide plate experiment, they confirmed whether materials or equipment could pass through the robot's internal channel without obstruction, and in the pipe pulling experiment, they verified if a long pipe-shaped tool could be pulled through the internal channel.
< Figure 1. Overall hardware structure of the proposed soft growing robot (left) and a cross-sectional view composing the inflatable structure (right) >
Experimental results demonstrated that the internal channel remained stable even while the robot was growing, serving as a key basis for supporting the technology's practicality and scalability.
Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu stated, "This award is very meaningful as it signifies the global recognition of Korea's robotics technology and academic achievements. Especially, it holds great significance in achieving technical progress that can greatly expand the practicality and application fields of soft growing robots. This achievement was possible thanks to the dedication and collaboration of the research team, and I will continue to contribute to the development of robotics technology through innovative research."
< Figure 2. Material supplying mechanism of the Soft Growing Robot >
This research was co-authored by Dongoh Seo, Ph.D. Candidate in Civil and Environmental Engineering, and Nam Gyun Kim, Ph.D. Candidate in Robotics. It was published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters on September 1, 2024.
(Paper Title: Inflatable-Structure-Based Working-Channel Securing Mechanism for Soft Growing Robots, DOI: 10.1109/LRA.2024.3426322)
This project was supported simultaneously by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Future Promising Convergence Technology Pioneer Research Project and Mid-career Researcher Project.
2025.06.09 View 2963 -
 KAIST Research Team Develops Electronic Ink for Room-Temperature Printing of High-Resolution, Variable-Stiffness Electronics
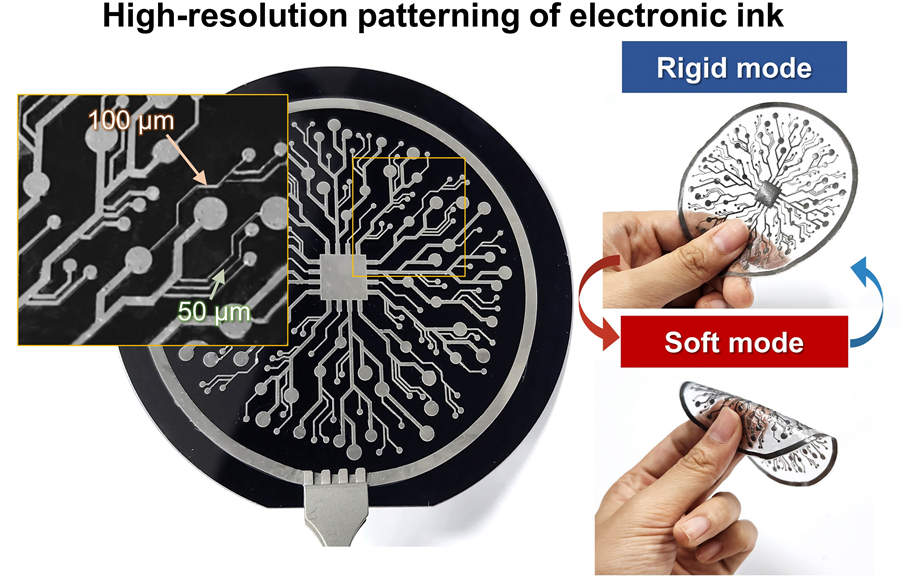
A team of researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University has developed a groundbreaking electronic ink that enables room-temperature printing of variable-stiffness circuits capable of switching between rigid and soft modes. This advancement marks a significant leap toward next-generation wearable, implantable, and robotic devices.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Jae-Woong Jeong and PhD candidate Simok Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering, (in separate bubbles, from left) Professor Gun-Hee Lee of Pusan National University, Professor Seongjun Park of Seoul National University, Professor Steve Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering>
Variable-stiffness electronics are at the forefront of adaptive technology, offering the ability for a single device to transition between rigid and soft modes depending on its use case. Gallium, a metal known for its high rigidity contrast between solid and liquid states, is a promising candidate for such applications. However, its use has been hindered by challenges including high surface tension, low viscosity, and undesirable phase transitions during manufacturing.
On June 4th, a research team led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, Professor Seongjun Park from the Digital Healthcare Major at Seoul National University, and Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST introduced a novel liquid metal electronic ink. This ink allows for micro-scale circuit printing – thinner than a human hair – at room temperature, with the ability to reversibly switch between rigid and soft modes depending on temperature.
The new ink combines printable viscosity with excellent electrical conductivity, enabling the creation of complex, high-resolution multilayer circuits comparable to commercial printed circuit boards (PCBs). These circuits can dynamically change stiffness in response to temperature, presenting new opportunities for multifunctional electronics, medical technologies, and robotics.
Conventional electronics typically have fixed form factors – either rigid for durability or soft for wearability. Rigid devices like smartphones and laptops offer robust performance but are uncomfortable when worn, while soft electronics are more comfortable but lack precise handling. As demand grows for devices that can adapt their stiffness to context, variable-stiffness electronics are becoming increasingly important.
< Figure 1. Fabrication process of stable, high-viscosity electronic ink by dispersing micro-sized gallium particles in a polymer matrix (left). High-resolution large-area circuit printing process through pH-controlled chemical sintering (right). >
To address this challenge, the researchers focused on gallium, which melts just below body temperature. Solid gallium is quite stiff, while its liquid form is fluid and soft. Despite its potential, gallium’s use in electronic printing has been limited by its high surface tension and instability when melted.
To overcome these issues, the team developed a pH-controlled liquid metal ink printing process. By dispersing micro-sized gallium particles into a hydrophilic polyurethane matrix using a neutral solvent (dimethyl sulfoxide, or DMSO), they created a stable, high-viscosity ink suitable for precision printing. During post-print heating, the DMSO decomposes to form an acidic environment, which removes the oxide layer on the gallium particles. This triggers the particles to coalesce into electrically conductive networks with tunable mechanical properties.
The resulting printed circuits exhibit fine feature sizes (~50 μm), high conductivity (2.27 × 10⁶ S/m), and a stiffness modulation ratio of up to 1,465 – allowing the material to shift from plastic-like rigidity to rubber-like softness. Furthermore, the ink is compatible with conventional printing techniques such as screen printing and dip coating, supporting large-area and 3D device fabrication.
< Figure 2. Key features of the electronic ink. (i) High-resolution printing and multilayer integration capability. (ii) Batch fabrication capability through large-area screen printing. (iii) Complex three-dimensional structure printing capability through dip coating. (iv) Excellent electrical conductivity and stiffness control capability.>
The team demonstrated this technology by developing a multi-functional device that operates as a rigid portable electronic under normal conditions but transforms into a soft wearable healthcare device when attached to the body. They also created a neural probe that remains stiff during surgical insertion for accurate positioning but softens once inside brain tissue to reduce inflammation – highlighting its potential for biomedical implants.
< Figure 3. Variable stiffness wearable electronics with high-resolution circuits and multilayer structure comparable to commercial printed circuit boards (PCBs). Functions as a rigid portable electronic device at room temperature, then transforms into a wearable healthcare device by softening at body temperature upon skin contact.>
“The core achievement of this research lies in overcoming the longstanding challenges of liquid metal printing through our innovative technology,” said Professor Jeong. “By controlling the ink’s acidity, we were able to electrically and mechanically connect printed gallium particles, enabling the room-temperature fabrication of high-resolution, large-area circuits with tunable stiffness. This opens up new possibilities for future personal electronics, medical devices, and robotics.”
< Figure 4. Body-temperature softening neural probe implemented by coating electronic ink on an optical waveguide structure. (Left) Remains rigid during surgery for precise manipulation and brain insertion, then softens after implantation to minimize mechanical stress on the brain and greatly enhance biocompatibility. (Right) >
This research was published in Science Advances under the title, “Phase-Change Metal Ink with pH-Controlled Chemical Sintering for Versatile and Scalable Fabrication of Variable Stiffness Electronics.” The work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Boston-Korea Project, and the BK21 FOUR Program.
2025.06.04 View 3381
KAIST Research Team Develops Electronic Ink for Room-Temperature Printing of High-Resolution, Variable-Stiffness Electronics
A team of researchers from KAIST and Seoul National University has developed a groundbreaking electronic ink that enables room-temperature printing of variable-stiffness circuits capable of switching between rigid and soft modes. This advancement marks a significant leap toward next-generation wearable, implantable, and robotic devices.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Jae-Woong Jeong and PhD candidate Simok Lee of the School of Electrical Engineering, (in separate bubbles, from left) Professor Gun-Hee Lee of Pusan National University, Professor Seongjun Park of Seoul National University, Professor Steve Park of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering>
Variable-stiffness electronics are at the forefront of adaptive technology, offering the ability for a single device to transition between rigid and soft modes depending on its use case. Gallium, a metal known for its high rigidity contrast between solid and liquid states, is a promising candidate for such applications. However, its use has been hindered by challenges including high surface tension, low viscosity, and undesirable phase transitions during manufacturing.
On June 4th, a research team led by Professor Jae-Woong Jeong from the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, Professor Seongjun Park from the Digital Healthcare Major at Seoul National University, and Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST introduced a novel liquid metal electronic ink. This ink allows for micro-scale circuit printing – thinner than a human hair – at room temperature, with the ability to reversibly switch between rigid and soft modes depending on temperature.
The new ink combines printable viscosity with excellent electrical conductivity, enabling the creation of complex, high-resolution multilayer circuits comparable to commercial printed circuit boards (PCBs). These circuits can dynamically change stiffness in response to temperature, presenting new opportunities for multifunctional electronics, medical technologies, and robotics.
Conventional electronics typically have fixed form factors – either rigid for durability or soft for wearability. Rigid devices like smartphones and laptops offer robust performance but are uncomfortable when worn, while soft electronics are more comfortable but lack precise handling. As demand grows for devices that can adapt their stiffness to context, variable-stiffness electronics are becoming increasingly important.
< Figure 1. Fabrication process of stable, high-viscosity electronic ink by dispersing micro-sized gallium particles in a polymer matrix (left). High-resolution large-area circuit printing process through pH-controlled chemical sintering (right). >
To address this challenge, the researchers focused on gallium, which melts just below body temperature. Solid gallium is quite stiff, while its liquid form is fluid and soft. Despite its potential, gallium’s use in electronic printing has been limited by its high surface tension and instability when melted.
To overcome these issues, the team developed a pH-controlled liquid metal ink printing process. By dispersing micro-sized gallium particles into a hydrophilic polyurethane matrix using a neutral solvent (dimethyl sulfoxide, or DMSO), they created a stable, high-viscosity ink suitable for precision printing. During post-print heating, the DMSO decomposes to form an acidic environment, which removes the oxide layer on the gallium particles. This triggers the particles to coalesce into electrically conductive networks with tunable mechanical properties.
The resulting printed circuits exhibit fine feature sizes (~50 μm), high conductivity (2.27 × 10⁶ S/m), and a stiffness modulation ratio of up to 1,465 – allowing the material to shift from plastic-like rigidity to rubber-like softness. Furthermore, the ink is compatible with conventional printing techniques such as screen printing and dip coating, supporting large-area and 3D device fabrication.
< Figure 2. Key features of the electronic ink. (i) High-resolution printing and multilayer integration capability. (ii) Batch fabrication capability through large-area screen printing. (iii) Complex three-dimensional structure printing capability through dip coating. (iv) Excellent electrical conductivity and stiffness control capability.>
The team demonstrated this technology by developing a multi-functional device that operates as a rigid portable electronic under normal conditions but transforms into a soft wearable healthcare device when attached to the body. They also created a neural probe that remains stiff during surgical insertion for accurate positioning but softens once inside brain tissue to reduce inflammation – highlighting its potential for biomedical implants.
< Figure 3. Variable stiffness wearable electronics with high-resolution circuits and multilayer structure comparable to commercial printed circuit boards (PCBs). Functions as a rigid portable electronic device at room temperature, then transforms into a wearable healthcare device by softening at body temperature upon skin contact.>
“The core achievement of this research lies in overcoming the longstanding challenges of liquid metal printing through our innovative technology,” said Professor Jeong. “By controlling the ink’s acidity, we were able to electrically and mechanically connect printed gallium particles, enabling the room-temperature fabrication of high-resolution, large-area circuits with tunable stiffness. This opens up new possibilities for future personal electronics, medical devices, and robotics.”
< Figure 4. Body-temperature softening neural probe implemented by coating electronic ink on an optical waveguide structure. (Left) Remains rigid during surgery for precise manipulation and brain insertion, then softens after implantation to minimize mechanical stress on the brain and greatly enhance biocompatibility. (Right) >
This research was published in Science Advances under the title, “Phase-Change Metal Ink with pH-Controlled Chemical Sintering for Versatile and Scalable Fabrication of Variable Stiffness Electronics.” The work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Boston-Korea Project, and the BK21 FOUR Program.
2025.06.04 View 3381 -
 Professor Hyun Myung's Team Wins First Place in a Challenge at ICRA by IEEE
< Photo 1. (From left) Daebeom Kim (Team Leader, Ph.D. student), Seungjae Lee (Ph.D. student), Seoyeon Jang (Ph.D. student), Jei Kong (Master's student), Professor Hyun Myung >
A team of the Urban Robotics Lab, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering, achieved a remarkable first-place overall victory in the Nothing Stands Still Challenge (NSS Challenge) 2025, held at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), the world's most prestigious robotics conference, from May 19 to 23 in Atlanta, USA.
The NSS Challenge was co-hosted by HILTI, a global construction company based in Liechtenstein, and Stanford University's Gradient Spaces Group. It is an expanded version of the HILTI SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)* Challenge, which has been held since 2021, and is considered one of the most prominent challenges at 2025 IEEE ICRA.*SLAM: Refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, a technology where robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, etc., determine their own position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings.
< Photo 2. A scene from the oral presentation on the winning team's technology (Speakers: Seungjae Lee and Seoyeon Jang, Ph.D. candidates of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering) >
This challenge primarily evaluates how accurately and robustly LiDAR scan data, collected at various times, can be registered in situations with frequent structural changes, such as construction and industrial environments. In particular, it is regarded as a highly technical competition because it deals with multi-session localization and mapping (Multi-session SLAM) technology that responds to structural changes occurring over multiple timeframes, rather than just single-point registration accuracy.
The Urban Robotics Lab team secured first place overall, surpassing National Taiwan University (3rd place) and Northwestern Polytechnical University of China (2nd place) by a significant margin, with their unique localization and mapping technology that solves the problem of registering LiDAR data collected across multiple times and spaces. The winning team will be awarded a prize of $4,000.
< Figure 1. Example of Multiway-Registration for Registering Multiple Scans >
The Urban Robotics Lab team independently developed a multiway-registration framework that can robustly register multiple scans even without prior connection information. This framework consists of an algorithm for summarizing feature points within scans and finding correspondences (CubicFeat), an algorithm for performing global registration based on the found correspondences (Quatro), and an algorithm for refining results based on change detection (Chamelion). This combination of technologies ensures stable registration performance based on fixed structures, even in highly dynamic industrial environments.
< Figure 2. Example of Change Detection Using the Chamelion Algorithm>
LiDAR scan registration technology is a core component of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) in various autonomous systems such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous robots, autonomous walking systems, and autonomous flying vehicles.
Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering stated, "This award-winning technology is evaluated as a case that simultaneously proves both academic value and industrial applicability by maximizing the performance of precisely estimating the relative positions between different scans even in complex environments. I am grateful to the students who challenged themselves and never gave up, even when many teams abandoned due to the high difficulty."
< Figure 3. Competition Result Board, Lower RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) Indicates Higher Score (Unit: meters)>
The Urban Robotics Lab team first participated in the SLAM Challenge in 2022, winning second place among academic teams, and in 2023, they secured first place overall in the LiDAR category and first place among academic teams in the vision category.
2025.05.30 View 4084
Professor Hyun Myung's Team Wins First Place in a Challenge at ICRA by IEEE
< Photo 1. (From left) Daebeom Kim (Team Leader, Ph.D. student), Seungjae Lee (Ph.D. student), Seoyeon Jang (Ph.D. student), Jei Kong (Master's student), Professor Hyun Myung >
A team of the Urban Robotics Lab, led by Professor Hyun Myung from the KAIST School of Electrical Engineering, achieved a remarkable first-place overall victory in the Nothing Stands Still Challenge (NSS Challenge) 2025, held at the 2025 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), the world's most prestigious robotics conference, from May 19 to 23 in Atlanta, USA.
The NSS Challenge was co-hosted by HILTI, a global construction company based in Liechtenstein, and Stanford University's Gradient Spaces Group. It is an expanded version of the HILTI SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping)* Challenge, which has been held since 2021, and is considered one of the most prominent challenges at 2025 IEEE ICRA.*SLAM: Refers to Simultaneous Localization and Mapping, a technology where robots, drones, autonomous vehicles, etc., determine their own position and simultaneously create a map of their surroundings.
< Photo 2. A scene from the oral presentation on the winning team's technology (Speakers: Seungjae Lee and Seoyeon Jang, Ph.D. candidates of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering) >
This challenge primarily evaluates how accurately and robustly LiDAR scan data, collected at various times, can be registered in situations with frequent structural changes, such as construction and industrial environments. In particular, it is regarded as a highly technical competition because it deals with multi-session localization and mapping (Multi-session SLAM) technology that responds to structural changes occurring over multiple timeframes, rather than just single-point registration accuracy.
The Urban Robotics Lab team secured first place overall, surpassing National Taiwan University (3rd place) and Northwestern Polytechnical University of China (2nd place) by a significant margin, with their unique localization and mapping technology that solves the problem of registering LiDAR data collected across multiple times and spaces. The winning team will be awarded a prize of $4,000.
< Figure 1. Example of Multiway-Registration for Registering Multiple Scans >
The Urban Robotics Lab team independently developed a multiway-registration framework that can robustly register multiple scans even without prior connection information. This framework consists of an algorithm for summarizing feature points within scans and finding correspondences (CubicFeat), an algorithm for performing global registration based on the found correspondences (Quatro), and an algorithm for refining results based on change detection (Chamelion). This combination of technologies ensures stable registration performance based on fixed structures, even in highly dynamic industrial environments.
< Figure 2. Example of Change Detection Using the Chamelion Algorithm>
LiDAR scan registration technology is a core component of SLAM (Simultaneous Localization And Mapping) in various autonomous systems such as autonomous vehicles, autonomous robots, autonomous walking systems, and autonomous flying vehicles.
Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering stated, "This award-winning technology is evaluated as a case that simultaneously proves both academic value and industrial applicability by maximizing the performance of precisely estimating the relative positions between different scans even in complex environments. I am grateful to the students who challenged themselves and never gave up, even when many teams abandoned due to the high difficulty."
< Figure 3. Competition Result Board, Lower RMSE (Root Mean Squared Error) Indicates Higher Score (Unit: meters)>
The Urban Robotics Lab team first participated in the SLAM Challenge in 2022, winning second place among academic teams, and in 2023, they secured first place overall in the LiDAR category and first place among academic teams in the vision category.
2025.05.30 View 4084 -
 KAIST Develops Virtual Staining Technology for 3D Histopathology
Moving beyond traditional methods of observing thinly sliced and stained cancer tissues, a collaborative international research team led by KAIST has successfully developed a groundbreaking technology. This innovation uses advanced optical techniques combined with an artificial intelligence-based deep learning algorithm to create realistic, virtually stained 3D images of cancer tissue without the need for serial sectioning nor staining. This breakthrough is anticipated to pave the way for next-generation non-invasive pathological diagnosis.
< Photo 1. (From left) Juyeon Park (Ph.D. Candidate, Department of Physics), Professor YongKeun Park (Department of Physics) (Top left) Professor Su-Jin Shin (Gangnam Severance Hospital), Professor Tae Hyun Hwang (Vanderbilt University School of Medicine) >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Professor Su-Jin Shin's team at Yonsei University Gangnam Severance Hospital, Professor Tae Hyun Hwang's team at Mayo Clinic, and Tomocube's AI research team, has developed an innovative technology capable of vividly displaying the 3D structure of cancer tissues without separate staining.
For over 200 years, conventional pathology has relied on observing cancer tissues under a microscope, a method that only shows specific cross-sections of the 3D cancer tissue. This has limited the ability to understand the three-dimensional connections and spatial arrangements between cells.
To overcome this, the research team utilized holotomography (HT), an advanced optical technology, to measure the 3D refractive index information of tissues. They then integrated an AI-based deep learning algorithm to successfully generate virtual H&E* images.* H&E (Hematoxylin & Eosin): The most widely used staining method for observing pathological tissues. Hematoxylin stains cell nuclei blue, and eosin stains cytoplasm pink.
The research team quantitatively demonstrated that the images generated by this technology are highly similar to actual stained tissue images. Furthermore, the technology exhibited consistent performance across various organs and tissues, proving its versatility and reliability as a next-generation pathological analysis tool.
< Figure 1. Comparison of conventional 3D tissue pathology procedure and the 3D virtual H&E staining technology proposed in this study. The traditional method requires preparing and staining dozens of tissue slides, while the proposed technology can reduce the number of slides by up to 10 times and quickly generate H&E images without the staining process. >
Moreover, by validating the feasibility of this technology through joint research with hospitals and research institutions in Korea and the United States, utilizing Tomocube's holotomography equipment, the team demonstrated its potential for full-scale adoption in real-world pathological research settings.
Professor YongKeun Park stated, "This research marks a major advancement by transitioning pathological analysis from conventional 2D methods to comprehensive 3D imaging. It will greatly enhance biomedical research and clinical diagnostics, particularly in understanding cancer tumor boundaries and the intricate spatial arrangements of cells within tumor microenvironments."
< Figure 2. Results of AI-based 3D virtual H&E staining and quantitative analysis of pathological tissue. The virtually stained images enabled 3D reconstruction of key pathological features such as cell nuclei and glandular lumens. Based on this, various quantitative indicators, including cell nuclear distribution, volume, and surface area, could be extracted. >
This research, with Juyeon Park, a student of the Integrated Master’s and Ph.D. Program at KAIST, as the first author, was published online in the prestigious journal Nature Communications on May 22.
(Paper title: Revealing 3D microanatomical structures of unlabeled thick cancer tissues using holotomography and virtual H&E staining.
[https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59820-0]
This study was supported by the Leader Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Global Industry Technology Cooperation Center Project of the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology, and the Korea Health Industry Development Institute.
2025.05.26 View 3987
KAIST Develops Virtual Staining Technology for 3D Histopathology
Moving beyond traditional methods of observing thinly sliced and stained cancer tissues, a collaborative international research team led by KAIST has successfully developed a groundbreaking technology. This innovation uses advanced optical techniques combined with an artificial intelligence-based deep learning algorithm to create realistic, virtually stained 3D images of cancer tissue without the need for serial sectioning nor staining. This breakthrough is anticipated to pave the way for next-generation non-invasive pathological diagnosis.
< Photo 1. (From left) Juyeon Park (Ph.D. Candidate, Department of Physics), Professor YongKeun Park (Department of Physics) (Top left) Professor Su-Jin Shin (Gangnam Severance Hospital), Professor Tae Hyun Hwang (Vanderbilt University School of Medicine) >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th that a research team led by Professor YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Professor Su-Jin Shin's team at Yonsei University Gangnam Severance Hospital, Professor Tae Hyun Hwang's team at Mayo Clinic, and Tomocube's AI research team, has developed an innovative technology capable of vividly displaying the 3D structure of cancer tissues without separate staining.
For over 200 years, conventional pathology has relied on observing cancer tissues under a microscope, a method that only shows specific cross-sections of the 3D cancer tissue. This has limited the ability to understand the three-dimensional connections and spatial arrangements between cells.
To overcome this, the research team utilized holotomography (HT), an advanced optical technology, to measure the 3D refractive index information of tissues. They then integrated an AI-based deep learning algorithm to successfully generate virtual H&E* images.* H&E (Hematoxylin & Eosin): The most widely used staining method for observing pathological tissues. Hematoxylin stains cell nuclei blue, and eosin stains cytoplasm pink.
The research team quantitatively demonstrated that the images generated by this technology are highly similar to actual stained tissue images. Furthermore, the technology exhibited consistent performance across various organs and tissues, proving its versatility and reliability as a next-generation pathological analysis tool.
< Figure 1. Comparison of conventional 3D tissue pathology procedure and the 3D virtual H&E staining technology proposed in this study. The traditional method requires preparing and staining dozens of tissue slides, while the proposed technology can reduce the number of slides by up to 10 times and quickly generate H&E images without the staining process. >
Moreover, by validating the feasibility of this technology through joint research with hospitals and research institutions in Korea and the United States, utilizing Tomocube's holotomography equipment, the team demonstrated its potential for full-scale adoption in real-world pathological research settings.
Professor YongKeun Park stated, "This research marks a major advancement by transitioning pathological analysis from conventional 2D methods to comprehensive 3D imaging. It will greatly enhance biomedical research and clinical diagnostics, particularly in understanding cancer tumor boundaries and the intricate spatial arrangements of cells within tumor microenvironments."
< Figure 2. Results of AI-based 3D virtual H&E staining and quantitative analysis of pathological tissue. The virtually stained images enabled 3D reconstruction of key pathological features such as cell nuclei and glandular lumens. Based on this, various quantitative indicators, including cell nuclear distribution, volume, and surface area, could be extracted. >
This research, with Juyeon Park, a student of the Integrated Master’s and Ph.D. Program at KAIST, as the first author, was published online in the prestigious journal Nature Communications on May 22.
(Paper title: Revealing 3D microanatomical structures of unlabeled thick cancer tissues using holotomography and virtual H&E staining.
[https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-59820-0]
This study was supported by the Leader Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Global Industry Technology Cooperation Center Project of the Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology, and the Korea Health Industry Development Institute.
2025.05.26 View 3987 -
 KAIST to Develop a Korean-style ChatGPT Platform Specifically Geared Toward Medical Diagnosis and Drug Discovery
On May 23rd, KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that its Digital Bio-Health AI Research Center (Director: Professor JongChul Ye of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI) has been selected for the Ministry of Science and ICT's 'AI Top-Tier Young Researcher Support Program (AI Star Fellowship Project).' With a total investment of ₩11.5 billion from May 2025 to December 2030, the center will embark on the full-scale development of AI technology and a platform capable of independently inferring and determining the kinds of diseases, and discovering new drugs.
< Photo. On May 20th, a kick-off meeting for the AI Star Fellowship Project was held at KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI’s Yangjae Research Center with the KAIST research team and participating organizations of Samsung Medical Center, NAVER Cloud, and HITS. [From left to right in the front row] Professor Jaegul Joo (KAIST), Professor Yoonjae Choi (KAIST), Professor Woo Youn Kim (KAIST/HITS), Professor JongChul Ye (KAIST), Professor Sungsoo Ahn (KAIST), Dr. Haanju Yoo (NAVER Cloud), Yoonho Lee (KAIST), HyeYoon Moon (Samsung Medical Center), Dr. Su Min Kim (Samsung Medical Center) >
This project aims to foster an innovative AI research ecosystem centered on young researchers and develop an inferential AI agent that can utilize and automatically expand specialized knowledge systems in the bio and medical fields.
Professor JongChul Ye of the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI will serve as the lead researcher, with young researchers from KAIST including Professors Yoonjae Choi, Kimin Lee, Sungsoo Ahn, and Chanyoung Park, along with mid-career researchers like Professors Jaegul Joo and Woo Youn Kim, jointly undertaking the project. They will collaborate with various laboratories within KAIST to conduct comprehensive research covering the entire cycle from the theoretical foundations of AI inference to its practical application.
Specifically, the main goals include: - Building high-performance inference models that integrate diverse medical knowledge systems to enhance the precision and reliability of diagnosis and treatment. - Developing a convergence inference platform that efficiently combines symbol-based inference with neural network models. - Securing AI technology for new drug development and biomarker discovery based on 'cell ontology.'
Furthermore, through close collaboration with industry and medical institutions such as Samsung Medical Center, NAVER Cloud, and HITS Co., Ltd., the project aims to achieve: - Clinical diagnostic AI utilizing medical knowledge systems. - AI-based molecular target exploration for new drug development. - Commercialization of an extendible AI inference platform.
Professor JongChul Ye, Director of KAIST's Digital Bio-Health AI Research Center, stated, "At a time when competition in AI inference model development is intensifying, it is a great honor for KAIST to lead the development of AI technology specialized in the bio and medical fields with world-class young researchers." He added, "We will do our best to ensure that the participating young researchers reach a world-leading level in terms of research achievements after the completion of this seven-year project starting in 2025."
The AI Star Fellowship is a newly established program where post-doctoral researchers and faculty members within seven years of appointment participate as project leaders (PLs) to independently lead research. Multiple laboratories within a university and demand-side companies form a consortium to operate the program.
Through this initiative, KAIST plans to nurture bio-medical convergence AI talent and simultaneously promote the commercialization of core technologies in collaboration with Samsung Medical Center, NAVER Cloud, and HITS.
2025.05.26 View 4639
KAIST to Develop a Korean-style ChatGPT Platform Specifically Geared Toward Medical Diagnosis and Drug Discovery
On May 23rd, KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that its Digital Bio-Health AI Research Center (Director: Professor JongChul Ye of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI) has been selected for the Ministry of Science and ICT's 'AI Top-Tier Young Researcher Support Program (AI Star Fellowship Project).' With a total investment of ₩11.5 billion from May 2025 to December 2030, the center will embark on the full-scale development of AI technology and a platform capable of independently inferring and determining the kinds of diseases, and discovering new drugs.
< Photo. On May 20th, a kick-off meeting for the AI Star Fellowship Project was held at KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI’s Yangjae Research Center with the KAIST research team and participating organizations of Samsung Medical Center, NAVER Cloud, and HITS. [From left to right in the front row] Professor Jaegul Joo (KAIST), Professor Yoonjae Choi (KAIST), Professor Woo Youn Kim (KAIST/HITS), Professor JongChul Ye (KAIST), Professor Sungsoo Ahn (KAIST), Dr. Haanju Yoo (NAVER Cloud), Yoonho Lee (KAIST), HyeYoon Moon (Samsung Medical Center), Dr. Su Min Kim (Samsung Medical Center) >
This project aims to foster an innovative AI research ecosystem centered on young researchers and develop an inferential AI agent that can utilize and automatically expand specialized knowledge systems in the bio and medical fields.
Professor JongChul Ye of the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI will serve as the lead researcher, with young researchers from KAIST including Professors Yoonjae Choi, Kimin Lee, Sungsoo Ahn, and Chanyoung Park, along with mid-career researchers like Professors Jaegul Joo and Woo Youn Kim, jointly undertaking the project. They will collaborate with various laboratories within KAIST to conduct comprehensive research covering the entire cycle from the theoretical foundations of AI inference to its practical application.
Specifically, the main goals include: - Building high-performance inference models that integrate diverse medical knowledge systems to enhance the precision and reliability of diagnosis and treatment. - Developing a convergence inference platform that efficiently combines symbol-based inference with neural network models. - Securing AI technology for new drug development and biomarker discovery based on 'cell ontology.'
Furthermore, through close collaboration with industry and medical institutions such as Samsung Medical Center, NAVER Cloud, and HITS Co., Ltd., the project aims to achieve: - Clinical diagnostic AI utilizing medical knowledge systems. - AI-based molecular target exploration for new drug development. - Commercialization of an extendible AI inference platform.
Professor JongChul Ye, Director of KAIST's Digital Bio-Health AI Research Center, stated, "At a time when competition in AI inference model development is intensifying, it is a great honor for KAIST to lead the development of AI technology specialized in the bio and medical fields with world-class young researchers." He added, "We will do our best to ensure that the participating young researchers reach a world-leading level in terms of research achievements after the completion of this seven-year project starting in 2025."
The AI Star Fellowship is a newly established program where post-doctoral researchers and faculty members within seven years of appointment participate as project leaders (PLs) to independently lead research. Multiple laboratories within a university and demand-side companies form a consortium to operate the program.
Through this initiative, KAIST plans to nurture bio-medical convergence AI talent and simultaneously promote the commercialization of core technologies in collaboration with Samsung Medical Center, NAVER Cloud, and HITS.
2025.05.26 View 4639 -
 KAIST and Mainz Researchers Unveil 3D Magnon Control, Charting a New Course for Neuromorphic and Quantum Technologies
< Professor Se Kwon Kim of the Department of Physics (left), Dr. Zarzuela of the University of Mainz, Germany (right) >
What if the magnon Hall effect, which processes information using magnons (spin waves) capable of current-free information transfer with magnets, could overcome its current limitation of being possible only on a 2D plane? If magnons could be utilized in 3D space, they would enable flexible design, including 3D circuits, and be applicable in various fields such as next-generation neuromorphic (brain-mimicking) computing structures, similar to human brain information processing. KAIST and an international joint research team have, for the first time in the world, predicted a 3D magnon Hall effect, demonstrating that magnons can move freely and complexly in 3D space, transcending the conventional concept of magnons.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on May 22nd that Professor Se Kwon Kim of the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Dr. Ricardo Zarzuela of the University of Mainz, Germany, has revealed that the interaction between magnons (spin waves) and solitons (spin vortices) within complex magnetic structures (topologically textured frustrated magnets) is not simple, but complex in a way that enables novel functionalities.
Magnons (spin waves), which can transmit information like electron movement, are garnering attention as a next-generation information processing technology that transmits information without using current, thus generating no heat. Until now, magnon research has focused on simple magnets where spins are neatly aligned in one direction, and the mathematics describing this was a relatively simple 'Abelian gauge theory.'
The research team demonstrated, for the first time in the world, that in complex spin structures like frustrated magnets, magnons interact and become entangled in complex ways from various directions. They applied an advanced mathematical framework, 'non-Abelian gauge theory,' to describe this movement, which is a groundbreaking achievement.
This research presents the possibility of future applications in low-power logic devices using magnons and topology-based quantum information processing technologies, indicating a potential paradigm shift in future information technology.
In conventional linear magnetic materials, the value representing the magnetic state (order parameter) is given as a vector. In magnonics research based on this, it has been interpreted that a U(1) Abelian gauge field is induced when magnons move in soliton structures like skyrmions. This means that the interaction between solitons and magnons has a structure similar to quantum electrodynamics (QED), which has successfully explained various experimental results such as the magnon Hall effect in 2D magnets.
< Figure. Schematic diagram of non-Abelian magnon quantum chromodynamics describing the dynamics of three types of magnons discovered for the first time in this study.>
However, through this research, the team theoretically revealed that in frustrated magnets, the order parameter must be expressed not as a simple vector but as a quaternion. As a result, the gauge field experienced by magnons resembles an SU(3) non-Abelian gauge field, rather than a simple U(1) Abelian gauge field.
This implies that within frustrated magnets, there are not one or two types of magnons seen in conventional magnets, but three distinct types of magnons, each interacting and intricately entangled with solitons. This structure is highly significant as it resembles quantum chromodynamics (QCD) that describes the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons rather than quantum electrodynamics (QED) that describes electromagnetic forces.
Professor Se Kwon Kim stated, "This research presents a powerful theoretical framework to explain the dynamics of magnons occurring within the complex order of frustrated magnets," adding, "By pioneering non-Abelian magnonics, it will be a conceptual turning point that can influence quantum magnetism research as a whole."
The research results, with Dr. Ricardo Zarzuela of the University of Mainz, Germany, as the first author, were published in the world-renowned physics journal Physical Review Letters on May 6th.※ Paper title: "Non-Abelian Gauge Theory for Magnons in Topologically Textured Frustrated Magnets," Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 186701 (2025)DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.186701
This research was supported by the Brain Pool Plus program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.05.22 View 3625
KAIST and Mainz Researchers Unveil 3D Magnon Control, Charting a New Course for Neuromorphic and Quantum Technologies
< Professor Se Kwon Kim of the Department of Physics (left), Dr. Zarzuela of the University of Mainz, Germany (right) >
What if the magnon Hall effect, which processes information using magnons (spin waves) capable of current-free information transfer with magnets, could overcome its current limitation of being possible only on a 2D plane? If magnons could be utilized in 3D space, they would enable flexible design, including 3D circuits, and be applicable in various fields such as next-generation neuromorphic (brain-mimicking) computing structures, similar to human brain information processing. KAIST and an international joint research team have, for the first time in the world, predicted a 3D magnon Hall effect, demonstrating that magnons can move freely and complexly in 3D space, transcending the conventional concept of magnons.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on May 22nd that Professor Se Kwon Kim of the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Dr. Ricardo Zarzuela of the University of Mainz, Germany, has revealed that the interaction between magnons (spin waves) and solitons (spin vortices) within complex magnetic structures (topologically textured frustrated magnets) is not simple, but complex in a way that enables novel functionalities.
Magnons (spin waves), which can transmit information like electron movement, are garnering attention as a next-generation information processing technology that transmits information without using current, thus generating no heat. Until now, magnon research has focused on simple magnets where spins are neatly aligned in one direction, and the mathematics describing this was a relatively simple 'Abelian gauge theory.'
The research team demonstrated, for the first time in the world, that in complex spin structures like frustrated magnets, magnons interact and become entangled in complex ways from various directions. They applied an advanced mathematical framework, 'non-Abelian gauge theory,' to describe this movement, which is a groundbreaking achievement.
This research presents the possibility of future applications in low-power logic devices using magnons and topology-based quantum information processing technologies, indicating a potential paradigm shift in future information technology.
In conventional linear magnetic materials, the value representing the magnetic state (order parameter) is given as a vector. In magnonics research based on this, it has been interpreted that a U(1) Abelian gauge field is induced when magnons move in soliton structures like skyrmions. This means that the interaction between solitons and magnons has a structure similar to quantum electrodynamics (QED), which has successfully explained various experimental results such as the magnon Hall effect in 2D magnets.
< Figure. Schematic diagram of non-Abelian magnon quantum chromodynamics describing the dynamics of three types of magnons discovered for the first time in this study.>
However, through this research, the team theoretically revealed that in frustrated magnets, the order parameter must be expressed not as a simple vector but as a quaternion. As a result, the gauge field experienced by magnons resembles an SU(3) non-Abelian gauge field, rather than a simple U(1) Abelian gauge field.
This implies that within frustrated magnets, there are not one or two types of magnons seen in conventional magnets, but three distinct types of magnons, each interacting and intricately entangled with solitons. This structure is highly significant as it resembles quantum chromodynamics (QCD) that describes the strong interaction between quarks mediated by gluons rather than quantum electrodynamics (QED) that describes electromagnetic forces.
Professor Se Kwon Kim stated, "This research presents a powerful theoretical framework to explain the dynamics of magnons occurring within the complex order of frustrated magnets," adding, "By pioneering non-Abelian magnonics, it will be a conceptual turning point that can influence quantum magnetism research as a whole."
The research results, with Dr. Ricardo Zarzuela of the University of Mainz, Germany, as the first author, were published in the world-renowned physics journal Physical Review Letters on May 6th.※ Paper title: "Non-Abelian Gauge Theory for Magnons in Topologically Textured Frustrated Magnets," Phys. Rev. Lett. 134, 186701 (2025)DOI: https://doi.org/10.1103/PhysRevLett.134.186701
This research was supported by the Brain Pool Plus program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.05.22 View 3625 -
 “For the First Time, We Shared a Meaningful Exchange”: KAIST Develops an AI App for Parents and Minimally Verbal Autistic Children Connect
• KAIST team up with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center Develop ‘AAcessTalk’, an AI-driven Communication Tool bridging the gap Between Children with Autism and their Parents
• The project earned the prestigious Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025, the Premier International Conference in Human-Computer Interaction
• Families share heartwarming stories of breakthrough communication and newfound understanding.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hwajung Hong and Doctoral candidate Dasom Choi of the Department of Industrial Design with SoHyun Park and Young-Ho Kim of Naver Cloud AI Lab >
For many families of minimally verbal autistic (MVA) children, communication often feels like an uphill battle. But now, thanks to a new AI-powered app developed by researchers at KAIST in collaboration with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center, parents are finally experiencing moments of genuine connection with their children.
On the 16th, the KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) research team, led by Professor Hwajung Hong of the Department of Industrial Design, announced the development of ‘AAcessTalk,’ an artificial intelligence (AI)-based communication tool that enables genuine communication between children with autism and their parents.
This research was recognized for its human-centered AI approach and received international attention, earning the Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025*, an international conference held in Yokohama, Japan.*ACM CHI (ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2025: One of the world's most prestigious academic conference in the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI).
This year, approximately 1,200 papers were selected out of about 5,000 submissions, with the Best Paper Award given to only the top 1%. The conference, which drew over 5,000 researchers, was the largest in its history, reflecting the growing interest in ‘Human-AI Interaction.’
Called AACessTalk, the app offers personalized vocabulary cards tailored to each child’s interests and context, while guiding parents through conversations with customized prompts. This creates a space where children’s voices can finally be heard—and where parents and children can connect on a deeper level.
Traditional augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) tools have relied heavily on fixed card systems that often fail to capture the subtle emotions and shifting interests of children with autism. AACessTalk breaks new ground by integrating AI technology that adapts in real time to the child’s mood and environment.
< Figure. Schematics of AACessTalk system. It provides personalized vocabulary cards for children with autism and context-based conversation guides for parents to focus on practical communication. Large ‘Turn Pass Button’ is placed at the child’s side to allow the child to lead the conversation. >
Among its standout features is a large ‘Turn Pass Button’ that gives children control over when to start or end conversations—allowing them to lead with agency. Another feature, the “What about Mom/Dad?” button, encourages children to ask about their parents’ thoughts, fostering mutual engagement in dialogue, something many children had never done before.
One parent shared, “For the first time, we shared a meaningful exchange.” Such stories were common among the 11 families who participated in a two-week pilot study, where children used the app to take more initiative in conversations and parents discovered new layers of their children’s language abilities.
Parents also reported moments of surprise and joy when their children used unexpected words or took the lead in conversations, breaking free from repetitive patterns. “I was amazed when my child used a word I hadn’t heard before. It helped me understand them in a whole new way,” recalled one caregiver.
Professor Hwajung Hong, who led the research at KAIST’s Department of Industrial Design, emphasized the importance of empowering children to express their own voices. “This study shows that AI can be more than a communication aid—it can be a bridge to genuine connection and understanding within families,” she said.
Looking ahead, the team plans to refine and expand human-centered AI technologies that honor neurodiversity, with a focus on bringing practical solutions to socially vulnerable groups and enriching user experiences.
This research is the result of KAIST Department of Industrial Design doctoral student Dasom Choi's internship at NAVER AI Lab.* Thesis Title: AACessTalk: Fostering Communication between Minimally Verbal Autistic Children and Parents with Contextual Guidance and Card Recommendation* DOI: 10.1145/3706598.3713792* Main Author Information: Dasom Choi (KAIST, NAVER AI Lab, First Author), SoHyun Park (NAVER AI Lab) , Kyungah Lee (Dodakim Child Development Center), Hwajung Hong (KAIST), and Young-Ho Kim (NAVER AI Lab, Corresponding Author)
This research was supported by the NAVER AI Lab internship program and grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea: the Doctoral Student Research Encouragement Grant (NRF-2024S1A5B5A19043580) and the Mid-Career Researcher Support Program for the Development of a Generative AI-Based Augmentative and Alternative Communication System for Autism Spectrum Disorder (RS-2024-00458557).
2025.05.19 View 4845
“For the First Time, We Shared a Meaningful Exchange”: KAIST Develops an AI App for Parents and Minimally Verbal Autistic Children Connect
• KAIST team up with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center Develop ‘AAcessTalk’, an AI-driven Communication Tool bridging the gap Between Children with Autism and their Parents
• The project earned the prestigious Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025, the Premier International Conference in Human-Computer Interaction
• Families share heartwarming stories of breakthrough communication and newfound understanding.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hwajung Hong and Doctoral candidate Dasom Choi of the Department of Industrial Design with SoHyun Park and Young-Ho Kim of Naver Cloud AI Lab >
For many families of minimally verbal autistic (MVA) children, communication often feels like an uphill battle. But now, thanks to a new AI-powered app developed by researchers at KAIST in collaboration with NAVER AI Lab and Dodakim Child Development Center, parents are finally experiencing moments of genuine connection with their children.
On the 16th, the KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) research team, led by Professor Hwajung Hong of the Department of Industrial Design, announced the development of ‘AAcessTalk,’ an artificial intelligence (AI)-based communication tool that enables genuine communication between children with autism and their parents.
This research was recognized for its human-centered AI approach and received international attention, earning the Best Paper Award at the ACM CHI 2025*, an international conference held in Yokohama, Japan.*ACM CHI (ACM Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2025: One of the world's most prestigious academic conference in the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI).
This year, approximately 1,200 papers were selected out of about 5,000 submissions, with the Best Paper Award given to only the top 1%. The conference, which drew over 5,000 researchers, was the largest in its history, reflecting the growing interest in ‘Human-AI Interaction.’
Called AACessTalk, the app offers personalized vocabulary cards tailored to each child’s interests and context, while guiding parents through conversations with customized prompts. This creates a space where children’s voices can finally be heard—and where parents and children can connect on a deeper level.
Traditional augmentative and alternative communication (AAC) tools have relied heavily on fixed card systems that often fail to capture the subtle emotions and shifting interests of children with autism. AACessTalk breaks new ground by integrating AI technology that adapts in real time to the child’s mood and environment.
< Figure. Schematics of AACessTalk system. It provides personalized vocabulary cards for children with autism and context-based conversation guides for parents to focus on practical communication. Large ‘Turn Pass Button’ is placed at the child’s side to allow the child to lead the conversation. >
Among its standout features is a large ‘Turn Pass Button’ that gives children control over when to start or end conversations—allowing them to lead with agency. Another feature, the “What about Mom/Dad?” button, encourages children to ask about their parents’ thoughts, fostering mutual engagement in dialogue, something many children had never done before.
One parent shared, “For the first time, we shared a meaningful exchange.” Such stories were common among the 11 families who participated in a two-week pilot study, where children used the app to take more initiative in conversations and parents discovered new layers of their children’s language abilities.
Parents also reported moments of surprise and joy when their children used unexpected words or took the lead in conversations, breaking free from repetitive patterns. “I was amazed when my child used a word I hadn’t heard before. It helped me understand them in a whole new way,” recalled one caregiver.
Professor Hwajung Hong, who led the research at KAIST’s Department of Industrial Design, emphasized the importance of empowering children to express their own voices. “This study shows that AI can be more than a communication aid—it can be a bridge to genuine connection and understanding within families,” she said.
Looking ahead, the team plans to refine and expand human-centered AI technologies that honor neurodiversity, with a focus on bringing practical solutions to socially vulnerable groups and enriching user experiences.
This research is the result of KAIST Department of Industrial Design doctoral student Dasom Choi's internship at NAVER AI Lab.* Thesis Title: AACessTalk: Fostering Communication between Minimally Verbal Autistic Children and Parents with Contextual Guidance and Card Recommendation* DOI: 10.1145/3706598.3713792* Main Author Information: Dasom Choi (KAIST, NAVER AI Lab, First Author), SoHyun Park (NAVER AI Lab) , Kyungah Lee (Dodakim Child Development Center), Hwajung Hong (KAIST), and Young-Ho Kim (NAVER AI Lab, Corresponding Author)
This research was supported by the NAVER AI Lab internship program and grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea: the Doctoral Student Research Encouragement Grant (NRF-2024S1A5B5A19043580) and the Mid-Career Researcher Support Program for the Development of a Generative AI-Based Augmentative and Alternative Communication System for Autism Spectrum Disorder (RS-2024-00458557).
2025.05.19 View 4845 -
 Decoding Fear: KAIST Identifies An Affective Brain Circuit Crucial for Fear Memory Formation by Non-nociceptive Threat Stimulus
Fear memories can form in the brain following exposure to threatening situations such as natural disasters, accidents, or violence. When these memories become excessive or distorted, they can lead to severe mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying fear memory formation triggered by affective pain rather than direct physical pain have remained largely unexplored – until now.
A KAIST research team has identified, for the first time, a brain circuit specifically responsible for forming fear memories in the absence of physical pain, marking a significant advance in understanding how psychological distress is processed and drives fear memory formation in the brain. This discovery opens the door to the development of targeted treatments for trauma-related conditions by addressing the underlying neural pathways.
< Photo 1. (from left) Professor Jin-Hee Han, Dr. Junho Han and Ph.D. Candidate Boin Suh of the Department of Biological Sciences >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 15th that the research team led by Professor Jin-Hee Han in the Department of Biological Sciences has identified the pIC-PBN circuit*, a key neural pathway involved in forming fear memories triggered by psychological threats in the absence of sensory pain. This groundbreaking work was conducted through experiments with mice.*pIC–PBN circuit: A newly identified descending neural pathway from the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to the parabrachial nucleus (PBN), specialized for transmitting psychological threat information.
Traditionally, the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) has been recognized as a critical part of the ascending pain pathway, receiving pain signals from the spinal cord. However, this study reveals a previously unknown role for the PBN in processing fear induced by non-painful psychological stimuli, fundamentally changing our understanding of its function in the brain.
This work is considered the first experimental evidence that 'emotional distress' and 'physical pain' are processed through different neural circuits to form fear memories, making it a significant contribution to the field of neuroscience. It clearly demonstrates the existence of a dedicated pathway (pIC-PBN) for transmitting emotional distress.
The study's first author, Dr. Junho Han, shared the personal motivation behind this research: “Our dog, Lego, is afraid of motorcycles. He never actually crashed into one, but ever since having a traumatizing event of having a motorbike almost run into him, just hearing the sound now triggers a fearful response. Humans react similarly – even if you didn’t have a personal experience of being involved in an accident, a near-miss or exposure to alarming media can create lasting fear memories, which may eventually lead to PTSD.”
He continued, “Until now, fear memory research has mainly relied on experimental models involving physical pain. However, much of real-world human fears arise from psychological threats, rather than from direct physical harm. Despite this, little was known about the brain circuits responsible for processing these psychological threats that can drive fear memory formation.”
To investigate this, the research team developed a novel fear conditioning model that utilizes visual threat stimuli instead of electrical shocks. In this model, mice were exposed to a rapidly expanding visual disk on a ceiling screen, simulating the threat of an approaching predator. This approach allowed the team to demonstrate that fear memories can form in response to a non-nociceptive, psychological threat alone, without the need for physical pain.
< Figure 1. Artificial activation of the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) neural circuit induces anxiety-like behaviors and fear memory formation in mice. >
Using advanced chemogenetic and optogenetic techniques, the team precisely controlled neuronal activity, revealing that the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) is essential to form fear memories in response to visual threats. They further traced the origin of these signals to the posterior insular cortex (pIC), a region known to process negative emotions and pain, confirming a direct connection between the two areas.
The study also showed that inhibiting the pIC–PBN circuit significantly reduced fear memory formation in response to visual threats, without affecting innate fear responses or physical pain-based learning. Conversely, artificially activating this circuit alone was sufficient to drive fear memory formation, confirming its role as a key pathway for processing psychological threat information.
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram of brain neural circuits transmitting emotional & physical pain threat signals. Visual threat stimuli do not involve physical pain but can create an anxious state and form fear memory through the affective pain signaling pathway. >
Professor Jin-Hee Han commented, “This study lays an important foundation for understanding how emotional distress-based mental disorders, such as PTSD, panic disorder, and anxiety disorder, develop, and opens new possibilities for targeted treatment approaches.”
The findings, authored by Dr. Junho Han (first author), Ph.D. candidate Boin Suh (second author), and Dr. Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author) of the Department of Biological Sciences, were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 9, 2025.※ Paper Title: A top-down insular cortex circuit crucial for non-nociceptive fear learning. Science Advances (https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.14.618356)※ Author Information: Junho Han (first author), Boin Suh (second author), and Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author)
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022M3E5E8081183 and NRF-2017M3C7A1031322).
2025.05.15 View 3896
Decoding Fear: KAIST Identifies An Affective Brain Circuit Crucial for Fear Memory Formation by Non-nociceptive Threat Stimulus
Fear memories can form in the brain following exposure to threatening situations such as natural disasters, accidents, or violence. When these memories become excessive or distorted, they can lead to severe mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying fear memory formation triggered by affective pain rather than direct physical pain have remained largely unexplored – until now.
A KAIST research team has identified, for the first time, a brain circuit specifically responsible for forming fear memories in the absence of physical pain, marking a significant advance in understanding how psychological distress is processed and drives fear memory formation in the brain. This discovery opens the door to the development of targeted treatments for trauma-related conditions by addressing the underlying neural pathways.
< Photo 1. (from left) Professor Jin-Hee Han, Dr. Junho Han and Ph.D. Candidate Boin Suh of the Department of Biological Sciences >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 15th that the research team led by Professor Jin-Hee Han in the Department of Biological Sciences has identified the pIC-PBN circuit*, a key neural pathway involved in forming fear memories triggered by psychological threats in the absence of sensory pain. This groundbreaking work was conducted through experiments with mice.*pIC–PBN circuit: A newly identified descending neural pathway from the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to the parabrachial nucleus (PBN), specialized for transmitting psychological threat information.
Traditionally, the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) has been recognized as a critical part of the ascending pain pathway, receiving pain signals from the spinal cord. However, this study reveals a previously unknown role for the PBN in processing fear induced by non-painful psychological stimuli, fundamentally changing our understanding of its function in the brain.
This work is considered the first experimental evidence that 'emotional distress' and 'physical pain' are processed through different neural circuits to form fear memories, making it a significant contribution to the field of neuroscience. It clearly demonstrates the existence of a dedicated pathway (pIC-PBN) for transmitting emotional distress.
The study's first author, Dr. Junho Han, shared the personal motivation behind this research: “Our dog, Lego, is afraid of motorcycles. He never actually crashed into one, but ever since having a traumatizing event of having a motorbike almost run into him, just hearing the sound now triggers a fearful response. Humans react similarly – even if you didn’t have a personal experience of being involved in an accident, a near-miss or exposure to alarming media can create lasting fear memories, which may eventually lead to PTSD.”
He continued, “Until now, fear memory research has mainly relied on experimental models involving physical pain. However, much of real-world human fears arise from psychological threats, rather than from direct physical harm. Despite this, little was known about the brain circuits responsible for processing these psychological threats that can drive fear memory formation.”
To investigate this, the research team developed a novel fear conditioning model that utilizes visual threat stimuli instead of electrical shocks. In this model, mice were exposed to a rapidly expanding visual disk on a ceiling screen, simulating the threat of an approaching predator. This approach allowed the team to demonstrate that fear memories can form in response to a non-nociceptive, psychological threat alone, without the need for physical pain.
< Figure 1. Artificial activation of the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) neural circuit induces anxiety-like behaviors and fear memory formation in mice. >
Using advanced chemogenetic and optogenetic techniques, the team precisely controlled neuronal activity, revealing that the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) is essential to form fear memories in response to visual threats. They further traced the origin of these signals to the posterior insular cortex (pIC), a region known to process negative emotions and pain, confirming a direct connection between the two areas.
The study also showed that inhibiting the pIC–PBN circuit significantly reduced fear memory formation in response to visual threats, without affecting innate fear responses or physical pain-based learning. Conversely, artificially activating this circuit alone was sufficient to drive fear memory formation, confirming its role as a key pathway for processing psychological threat information.
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram of brain neural circuits transmitting emotional & physical pain threat signals. Visual threat stimuli do not involve physical pain but can create an anxious state and form fear memory through the affective pain signaling pathway. >
Professor Jin-Hee Han commented, “This study lays an important foundation for understanding how emotional distress-based mental disorders, such as PTSD, panic disorder, and anxiety disorder, develop, and opens new possibilities for targeted treatment approaches.”
The findings, authored by Dr. Junho Han (first author), Ph.D. candidate Boin Suh (second author), and Dr. Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author) of the Department of Biological Sciences, were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 9, 2025.※ Paper Title: A top-down insular cortex circuit crucial for non-nociceptive fear learning. Science Advances (https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.14.618356)※ Author Information: Junho Han (first author), Boin Suh (second author), and Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author)
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022M3E5E8081183 and NRF-2017M3C7A1031322).
2025.05.15 View 3896 -
 KAIST Develops Novel Catalyst With 100-Fold Platinum Efficiency
Propylene, a key building block used in producing plastics, textiles, automotive components, and electronics, is essential to the petrochemical industry. A KAIST research team has developed a novel catalyst that dramatically enhances the efficiency of propylene production while significantly reducing costs.
< Photo. Professor Minkee Choi (left), and Ph.D. Candidate Susung Lee (right) of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of May that a research group led by Professor Minkee Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has successfully developed a new catalyst using inexpensive metals—gallium (Ga) and alumina (Al₂O₃)—with only a trace amount of platinum (100 ppm, or 0.01%). Remarkably, this new catalyst outperforms conventional industrial catalysts that use high concentrations of platinum (10,000 ppm).
Propylene is commonly produced through the propane dehydrogenation (PDH) process, which removes hydrogen from propane. Platinum has long been used as a catalyst in PDH due to its high efficiency in breaking carbon-hydrogen bonds and facilitating hydrogen removal. However, platinum is costly and suffers from performance degradation over repeated use.
To address this, the KAIST team engineered a catalyst that incorporates only a minimal amount of platinum, relying on gallium and alumina as the primary components.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram showing the catalytic cooperation between gallium (Ga) and platinum (Pt) >
The core mechanism of the catalyst involves a cooperative function between the metals: gallium activates the C–H bond in propane to produce propylene, while platinum bonds the residual hydrogen atoms on the surface to form hydrogen gas (H₂), which is then released. This division of roles allows for high catalytic efficiency despite the drastic reduction in platinum content.
The researchers identified an optimal platinum-to-gallium ratio that delivered peak performance and provided a scientific rationale and quantitative metrics to predict this ideal composition.
Additionally, the team addressed a major limitation of traditional platinum catalysts: sintering—the agglomeration of platinum particles during repeated use, which causes performance loss. By adding a small amount of cerium (Ce), the researchers successfully suppressed this aggregation. As a result, the new catalyst maintained stable performance even after more than 20 reaction-regeneration cycles.
< Figure 2. Performance comparison of KAIST's newly developed catalyst (100 ppm platinum) and existing commercial platinum catalyst (10,000 ppm platinum) >
Professor Choi stated, “This research demonstrates the possibility of reducing platinum usage to 1/100th of current levels without compromising, and even enhancing, performance. It presents significant economic and environmental advantages, including lower catalyst costs, extended replacement intervals, and reduced catalyst waste.”
He added, “We are planning to evaluate this technology for large-scale process demonstration and commercialization. If adopted in industry, it could greatly improve the economic viability and efficiency of propylene production.”
The study was led by Professor Minkee Choi as corresponding author, with Ph.D. candidate Susung Lee as the first author. The findings were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), a leading journal in chemistry and chemical engineering, on February 13.※ Paper title: Ideal Bifunctional Catalysis for Propane Dehydrogenation over Pt-Promoted Gallia-Alumina and Minimized Use of Precious Elements※ DOI: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.4c13787
The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and Hanwha Solutions Corporation.
2025.05.12 View 2225
KAIST Develops Novel Catalyst With 100-Fold Platinum Efficiency
Propylene, a key building block used in producing plastics, textiles, automotive components, and electronics, is essential to the petrochemical industry. A KAIST research team has developed a novel catalyst that dramatically enhances the efficiency of propylene production while significantly reducing costs.
< Photo. Professor Minkee Choi (left), and Ph.D. Candidate Susung Lee (right) of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 12th of May that a research group led by Professor Minkee Choi from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has successfully developed a new catalyst using inexpensive metals—gallium (Ga) and alumina (Al₂O₃)—with only a trace amount of platinum (100 ppm, or 0.01%). Remarkably, this new catalyst outperforms conventional industrial catalysts that use high concentrations of platinum (10,000 ppm).
Propylene is commonly produced through the propane dehydrogenation (PDH) process, which removes hydrogen from propane. Platinum has long been used as a catalyst in PDH due to its high efficiency in breaking carbon-hydrogen bonds and facilitating hydrogen removal. However, platinum is costly and suffers from performance degradation over repeated use.
To address this, the KAIST team engineered a catalyst that incorporates only a minimal amount of platinum, relying on gallium and alumina as the primary components.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram showing the catalytic cooperation between gallium (Ga) and platinum (Pt) >
The core mechanism of the catalyst involves a cooperative function between the metals: gallium activates the C–H bond in propane to produce propylene, while platinum bonds the residual hydrogen atoms on the surface to form hydrogen gas (H₂), which is then released. This division of roles allows for high catalytic efficiency despite the drastic reduction in platinum content.
The researchers identified an optimal platinum-to-gallium ratio that delivered peak performance and provided a scientific rationale and quantitative metrics to predict this ideal composition.
Additionally, the team addressed a major limitation of traditional platinum catalysts: sintering—the agglomeration of platinum particles during repeated use, which causes performance loss. By adding a small amount of cerium (Ce), the researchers successfully suppressed this aggregation. As a result, the new catalyst maintained stable performance even after more than 20 reaction-regeneration cycles.
< Figure 2. Performance comparison of KAIST's newly developed catalyst (100 ppm platinum) and existing commercial platinum catalyst (10,000 ppm platinum) >
Professor Choi stated, “This research demonstrates the possibility of reducing platinum usage to 1/100th of current levels without compromising, and even enhancing, performance. It presents significant economic and environmental advantages, including lower catalyst costs, extended replacement intervals, and reduced catalyst waste.”
He added, “We are planning to evaluate this technology for large-scale process demonstration and commercialization. If adopted in industry, it could greatly improve the economic viability and efficiency of propylene production.”
The study was led by Professor Minkee Choi as corresponding author, with Ph.D. candidate Susung Lee as the first author. The findings were published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), a leading journal in chemistry and chemical engineering, on February 13.※ Paper title: Ideal Bifunctional Catalysis for Propane Dehydrogenation over Pt-Promoted Gallia-Alumina and Minimized Use of Precious Elements※ DOI: https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/jacs.4c13787
The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea and Hanwha Solutions Corporation.
2025.05.12 View 2225 -
 KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of immunotherapies that help immune cells attack cancer more effectively, have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, fewer than 20% of patients respond to these treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new strategies tailored to both responders and non-responders.
KAIST researchers have discovered that 'DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)', a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment. This breakthrough technology has been transferred to faculty startup BioRevert Inc., where it is currently being developed as a companion therapeutic and is expected to enter clinical trials by 2028.
< Photo 1. (From left) Researcher Jungeun Lee, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and Postdoctoral Researcher Jeong-Ryeol Gong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 8 that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had identified DDX54 as a critical factor that determines the immune evasion capacity of lung cancer cells. They demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 enhances immune cell infiltration into tumors and significantly improves the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy using anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies is considered a powerful approach in cancer treatment. However, its low response rate limits the number of patients who actually benefit.
To identify likely responders, tumor mutational burden (TMB) has recently been approved by the FDA as a key biomarker for immunotherapy. Cancers with high mutation rates are thought to be more responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, even tumors with high TMB can display an “immune-desert” phenotype—where immune cell infiltration is severely limited—resulting in poor treatment responses.
< Figure 1. DDX54 was identified as the master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy by orchestrating suppression of immune cell infiltration through cancer tissues as lung cancer cells become immune-evasive >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team compared transcriptome and genome data of lung cancer patients with immune evasion capabilities through gene regulatory network analysis (A) and discovered DDX54, a master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy (B-F).
This study is especially significant in that it successfully demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 in immune-desert lung tumors can overcome immunotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
The team used transcriptomic and genomic data from immune-evasive lung cancer patients and employed systems biology techniques to infer gene regulatory networks. Through this analysis, they identified DDX54 as a central regulator in the immune evasion of lung cancer cells.
In a syngeneic mouse model, the suppression of DDX54 led to significant increases in the infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells such as T cells and NK cells, and greatly improved the response to immunotherapy.
Single-cell transcriptomic and spatial transcriptomic analyses further showed that combination therapy targeting DDX54 promoted the differentiation of T cells and memory T cells that suppress tumors, while reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells and exhausted T cells that support tumor growth.
< Figure 2. In the syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells, it was confirmed that inhibiting DDX54 reversed the immune-evasion ability of cancer cells and enhanced the sensitivity to anti-PD-1 therapy >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells exhibiting immunotherapy resistance, the treatment applied after DDX54 inhibition resulted in statistically significant inhibition of lung cancer growth (B-D) and a significant increase in immune cell infiltration into the tumor tissue (E, F).
The mechanism is believed to involve DDX54 suppression inactivating signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT, MYC, and NF-κB, thereby downregulating immune-evasive proteins CD38 and CD47. This also reduced the infiltration of circulating monocytes—which promote tumor development—and promoted the differentiation of M1 macrophages that play anti-tumor roles.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho stated, “We have, for the first time, identified a master regulatory factor that enables immune evasion in lung cancer cells. By targeting this factor, we developed a new therapeutic strategy that can induce responsiveness to immunotherapy in previously resistant cancers.”
He added, “The discovery of DDX54—hidden within the complex molecular networks of cancer cells—was made possible through the systematic integration of systems biology, combining IT and BT.”
The study, led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 2, 2025, with Jeong-Ryeol Gong being the first author, Jungeun Lee, a co-first author, and Younghyun Han, a co-author of the article.
< Figure 3. Single-cell transcriptome and spatial transcriptome analysis confirmed that knockdown of DDX54 increased immune cell infiltration into cancer tissues >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells that underwent immunotherapy in combination with DDX54 inhibition, single-cell transcriptome (H-L) and spatial transcriptome (A-G) analysis of immune cells infiltrating inside cancer tissues were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that anticancer immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells actively infiltrated the core of lung cancer tissues when DDX54 inhibition and immunotherapy were concurrently administered.
(Paper title: “DDX54 downregulation enhances anti-PD1 therapy in immune-desert lung tumors with high tumor mutational burden,” DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2412310122)
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Research Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program.
< Figure 4. The identified master regulator DDX54 was confirmed to induce CD38 and CD47 expression through Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB activation. >
DDX54 activates the Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB pathways in lung cancer cells to increase CD38 and CD47 expression (A-G). This creates a cancer microenvironment that contributes to cancer development (H) and ultimately induces immune anticancer treatment resistance.
< Figure 5. It was confirmed that an immune-inflamed environment can be created by combining DDX54 inhibition and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. >
When DDX54 inhibition and ICI therapy are simultaneously administered, the cancer cell characteristics change, the immune evasion ability is restored, and the environment is transformed into an ‘immune-activated’ environment in which immune cells easily infiltrate cancer tissues. This strengthens the anticancer immune response, thereby increasing the sensitivity of immunotherapy even in lung cancer tissues that previously had low responsiveness to immunotherapy.
2025.04.08 View 6452
KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of immunotherapies that help immune cells attack cancer more effectively, have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, fewer than 20% of patients respond to these treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new strategies tailored to both responders and non-responders.
KAIST researchers have discovered that 'DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)', a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment. This breakthrough technology has been transferred to faculty startup BioRevert Inc., where it is currently being developed as a companion therapeutic and is expected to enter clinical trials by 2028.
< Photo 1. (From left) Researcher Jungeun Lee, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and Postdoctoral Researcher Jeong-Ryeol Gong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 8 that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had identified DDX54 as a critical factor that determines the immune evasion capacity of lung cancer cells. They demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 enhances immune cell infiltration into tumors and significantly improves the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy using anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies is considered a powerful approach in cancer treatment. However, its low response rate limits the number of patients who actually benefit.
To identify likely responders, tumor mutational burden (TMB) has recently been approved by the FDA as a key biomarker for immunotherapy. Cancers with high mutation rates are thought to be more responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, even tumors with high TMB can display an “immune-desert” phenotype—where immune cell infiltration is severely limited—resulting in poor treatment responses.
< Figure 1. DDX54 was identified as the master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy by orchestrating suppression of immune cell infiltration through cancer tissues as lung cancer cells become immune-evasive >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team compared transcriptome and genome data of lung cancer patients with immune evasion capabilities through gene regulatory network analysis (A) and discovered DDX54, a master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy (B-F).
This study is especially significant in that it successfully demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 in immune-desert lung tumors can overcome immunotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
The team used transcriptomic and genomic data from immune-evasive lung cancer patients and employed systems biology techniques to infer gene regulatory networks. Through this analysis, they identified DDX54 as a central regulator in the immune evasion of lung cancer cells.
In a syngeneic mouse model, the suppression of DDX54 led to significant increases in the infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells such as T cells and NK cells, and greatly improved the response to immunotherapy.
Single-cell transcriptomic and spatial transcriptomic analyses further showed that combination therapy targeting DDX54 promoted the differentiation of T cells and memory T cells that suppress tumors, while reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells and exhausted T cells that support tumor growth.
< Figure 2. In the syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells, it was confirmed that inhibiting DDX54 reversed the immune-evasion ability of cancer cells and enhanced the sensitivity to anti-PD-1 therapy >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells exhibiting immunotherapy resistance, the treatment applied after DDX54 inhibition resulted in statistically significant inhibition of lung cancer growth (B-D) and a significant increase in immune cell infiltration into the tumor tissue (E, F).
The mechanism is believed to involve DDX54 suppression inactivating signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT, MYC, and NF-κB, thereby downregulating immune-evasive proteins CD38 and CD47. This also reduced the infiltration of circulating monocytes—which promote tumor development—and promoted the differentiation of M1 macrophages that play anti-tumor roles.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho stated, “We have, for the first time, identified a master regulatory factor that enables immune evasion in lung cancer cells. By targeting this factor, we developed a new therapeutic strategy that can induce responsiveness to immunotherapy in previously resistant cancers.”
He added, “The discovery of DDX54—hidden within the complex molecular networks of cancer cells—was made possible through the systematic integration of systems biology, combining IT and BT.”
The study, led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 2, 2025, with Jeong-Ryeol Gong being the first author, Jungeun Lee, a co-first author, and Younghyun Han, a co-author of the article.
< Figure 3. Single-cell transcriptome and spatial transcriptome analysis confirmed that knockdown of DDX54 increased immune cell infiltration into cancer tissues >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells that underwent immunotherapy in combination with DDX54 inhibition, single-cell transcriptome (H-L) and spatial transcriptome (A-G) analysis of immune cells infiltrating inside cancer tissues were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that anticancer immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells actively infiltrated the core of lung cancer tissues when DDX54 inhibition and immunotherapy were concurrently administered.
(Paper title: “DDX54 downregulation enhances anti-PD1 therapy in immune-desert lung tumors with high tumor mutational burden,” DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2412310122)
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Research Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program.
< Figure 4. The identified master regulator DDX54 was confirmed to induce CD38 and CD47 expression through Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB activation. >
DDX54 activates the Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB pathways in lung cancer cells to increase CD38 and CD47 expression (A-G). This creates a cancer microenvironment that contributes to cancer development (H) and ultimately induces immune anticancer treatment resistance.
< Figure 5. It was confirmed that an immune-inflamed environment can be created by combining DDX54 inhibition and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. >
When DDX54 inhibition and ICI therapy are simultaneously administered, the cancer cell characteristics change, the immune evasion ability is restored, and the environment is transformed into an ‘immune-activated’ environment in which immune cells easily infiltrate cancer tissues. This strengthens the anticancer immune response, thereby increasing the sensitivity of immunotherapy even in lung cancer tissues that previously had low responsiveness to immunotherapy.
2025.04.08 View 6452 -
 KAIST Innovates Mid-Infrared Photodetectors for Exoplanet Detection, Expanding Applications to Environmental and Medical Fields
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) utilizes mid-infrared spectroscopy to precisely analyze molecular components such as water vapor and sulfur dioxide in exoplanet atmospheres. The key to this analysis, where each molecule exhibits a unique spectral "fingerprint," lies in highly sensitive photodetector technology capable of measuring extremely weak light intensities. Recently, KAIST researchers have developed an innovative photodetector capable of detecting a broad range of mid-infrared spectra, garnering significant attention.
< Photo 1. (from the left) Ph.D. candidate Inki Kim (co-author), Professor SangHyeon Kim (corresponding author), Dr. Joonsup Shim (first author), and Dr. Jinha Lim (co-author) of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering. >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th of March that a research team led by Professor SangHyeon Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a mid-infrared photodetector that operates stably at room temperature, marking a major turning point for the commercialization of ultra-compact optical sensors.
The newly developed photodetector utilizes conventional silicon-based CMOS processes, enabling low-cost mass production while maintaining stable operation at room temperature. Notably, the research team successfully demonstrated the real-time detection of carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas using ultra-compact and ultra-thin optical sensors equipped with this photodetector, proving its potential for environmental monitoring and hazardous gas analysis.
Existing mid-infrared photodetectors generally require cooling systems due to high thermal noise at room temperature. These cooling systems increase the size and cost of equipment, making miniaturization and integration into portable devices challenging. Furthermore, conventional mid-infrared photodetectors are incompatible with silicon-based CMOS processes, limiting large-scale production and commercialization.
To address these limitations, the research team developed a waveguide-integrated photodetector using germanium (Ge), a Group IV element like silicon. This approach enables broad-spectrum mid-infrared detection while ensuring stable operation at room temperature.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a room-temperature mid-infrared waveguide-integrated photodetector based on the Ge-on-insulator optical platform proposed in this study (top). Optical microscope image of the integrated photodetector connected with the sensing unit (bottom). >
A waveguide is a structure designed to efficiently guide light along a specific path with minimal loss. To implement various optical functions on a chip (on-chip), the development of waveguide-integrated photodetectors and waveguide-based optical components is essential.
Unlike conventional photodetectors that primarily rely on bandgap absorption principles, this new technology leverages the bolometric effect*, allowing it to detect the entire mid-infrared spectral range. As a result, it can be widely applied to the real-time sensing of various molecular species.
*Bolometric effect: A principle in which light absorption leads to an increase in temperature, causing electrical signals to change accordingly.
The waveguide-integrated mid-infrared photodetector developed by the research team is considered a groundbreaking innovation that overcomes the limitations of existing mid-infrared sensor technologies, including the need for cooling, difficulties in mass production, and high costs.
< Figure 2. Room temperature photoresponse characteristics of the mid-infrared waveguide photodetector proposed in this study (left) and real-time carbon dioxide (CO2) gas sensing results using the photodetector (right). >
This breakthrough technology is expected to be applicable across diverse fields, including environmental monitoring, medical diagnostics, industrial process management, national defense and security, and smart devices. It also paves the way for next-generation mid-infrared sensor advancements.
Professor SangHyeon Kim from KAIST stated, "This research represents a novel approach that overcomes the limitations of existing mid-infrared photodetector technologies and has great potential for practical applications in various fields." He further emphasized, "Since this sensor technology is compatible with CMOS processes, it enables low-cost mass production, making it highly suitable for next-generation environmental monitoring systems and smart manufacturing sites."
< Figure 3. Performance comparison image of a room-temperature mid-infrared waveguide photodetector fabricated with the technology proposed in this study. It achieves the world’s highest performance compared to existing technologies utilizing the Bolometric effect, and is the only solution compatible with CMOS processes. The technology proposed by our research team is characterized by its ability to respond to a wide spectrum of the mid-infrared band without limitations. >
The study, with Dr. Joonsup Shim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard University) as the first author, was published on March 19, 2025 in the internationally renowned journal Light: Science & Applications (JCR 2.9%, IF=20.6).
(Paper title: “Room-temperature waveguide-integrated photodetector using bolometric effect for mid-infrared spectroscopy applications,” https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-025-01803-3)
2025.03.27 View 3893
KAIST Innovates Mid-Infrared Photodetectors for Exoplanet Detection, Expanding Applications to Environmental and Medical Fields
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) utilizes mid-infrared spectroscopy to precisely analyze molecular components such as water vapor and sulfur dioxide in exoplanet atmospheres. The key to this analysis, where each molecule exhibits a unique spectral "fingerprint," lies in highly sensitive photodetector technology capable of measuring extremely weak light intensities. Recently, KAIST researchers have developed an innovative photodetector capable of detecting a broad range of mid-infrared spectra, garnering significant attention.
< Photo 1. (from the left) Ph.D. candidate Inki Kim (co-author), Professor SangHyeon Kim (corresponding author), Dr. Joonsup Shim (first author), and Dr. Jinha Lim (co-author) of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering. >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th of March that a research team led by Professor SangHyeon Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a mid-infrared photodetector that operates stably at room temperature, marking a major turning point for the commercialization of ultra-compact optical sensors.
The newly developed photodetector utilizes conventional silicon-based CMOS processes, enabling low-cost mass production while maintaining stable operation at room temperature. Notably, the research team successfully demonstrated the real-time detection of carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas using ultra-compact and ultra-thin optical sensors equipped with this photodetector, proving its potential for environmental monitoring and hazardous gas analysis.
Existing mid-infrared photodetectors generally require cooling systems due to high thermal noise at room temperature. These cooling systems increase the size and cost of equipment, making miniaturization and integration into portable devices challenging. Furthermore, conventional mid-infrared photodetectors are incompatible with silicon-based CMOS processes, limiting large-scale production and commercialization.
To address these limitations, the research team developed a waveguide-integrated photodetector using germanium (Ge), a Group IV element like silicon. This approach enables broad-spectrum mid-infrared detection while ensuring stable operation at room temperature.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a room-temperature mid-infrared waveguide-integrated photodetector based on the Ge-on-insulator optical platform proposed in this study (top). Optical microscope image of the integrated photodetector connected with the sensing unit (bottom). >
A waveguide is a structure designed to efficiently guide light along a specific path with minimal loss. To implement various optical functions on a chip (on-chip), the development of waveguide-integrated photodetectors and waveguide-based optical components is essential.
Unlike conventional photodetectors that primarily rely on bandgap absorption principles, this new technology leverages the bolometric effect*, allowing it to detect the entire mid-infrared spectral range. As a result, it can be widely applied to the real-time sensing of various molecular species.
*Bolometric effect: A principle in which light absorption leads to an increase in temperature, causing electrical signals to change accordingly.
The waveguide-integrated mid-infrared photodetector developed by the research team is considered a groundbreaking innovation that overcomes the limitations of existing mid-infrared sensor technologies, including the need for cooling, difficulties in mass production, and high costs.
< Figure 2. Room temperature photoresponse characteristics of the mid-infrared waveguide photodetector proposed in this study (left) and real-time carbon dioxide (CO2) gas sensing results using the photodetector (right). >
This breakthrough technology is expected to be applicable across diverse fields, including environmental monitoring, medical diagnostics, industrial process management, national defense and security, and smart devices. It also paves the way for next-generation mid-infrared sensor advancements.
Professor SangHyeon Kim from KAIST stated, "This research represents a novel approach that overcomes the limitations of existing mid-infrared photodetector technologies and has great potential for practical applications in various fields." He further emphasized, "Since this sensor technology is compatible with CMOS processes, it enables low-cost mass production, making it highly suitable for next-generation environmental monitoring systems and smart manufacturing sites."
< Figure 3. Performance comparison image of a room-temperature mid-infrared waveguide photodetector fabricated with the technology proposed in this study. It achieves the world’s highest performance compared to existing technologies utilizing the Bolometric effect, and is the only solution compatible with CMOS processes. The technology proposed by our research team is characterized by its ability to respond to a wide spectrum of the mid-infrared band without limitations. >
The study, with Dr. Joonsup Shim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard University) as the first author, was published on March 19, 2025 in the internationally renowned journal Light: Science & Applications (JCR 2.9%, IF=20.6).
(Paper title: “Room-temperature waveguide-integrated photodetector using bolometric effect for mid-infrared spectroscopy applications,” https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-025-01803-3)
2025.03.27 View 3893