best+paper
-
 Sound-based Touch Input Technology for Smart Tables and Mirrors
(from left: MS candidate Anish Byanjankar, Research Assistant Professor Hyosu Kim and Professor Insik Shin)
Time passes so quickly, especially in the morning. Your hands are so busy brushing your teeth and checking the weather on your smartphone. You might wish that your mirror could turn into a touch screen and free up your hands. That wish can be achieved very soon. A KAIST team has developed a smartphone-based touch sound localization technology to facilitate ubiquitous interactions, turning objects like furniture and mirrors into touch input tools.
This technology analyzes touch sounds generated from a user’s touch on a surface and identifies the location of the touch input. For instance, users can turn surrounding tables or walls into virtual keyboards and write lengthy e-mails much more conveniently by using only the built-in microphone on their smartphones or tablets. Moreover, family members can enjoy a virtual chessboard or enjoy board games on their dining tables.
Additionally, traditional smart devices such as smart TVs or mirrors, which only provide simple screen display functions, can play a smarter role by adding touch input function support (see the image below).
Figure 1.Examples of using touch input technology: By using only smartphone, you can use surrounding objects as a touch screen anytime and anywhere.
The most important aspect of enabling the sound-based touch input method is to identify the location of touch inputs in a precise manner (within about 1cm error). However, it is challenging to meet these requirements, mainly because this technology can be used in diverse and dynamically changing environments. Users may use objects like desks, walls, or mirrors as touch input tools and the surrounding environments (e.g. location of nearby objects or ambient noise level) can be varied. These environmental changes can affect the characteristics of touch sounds.
To address this challenge, Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing and his team focused on analyzing the fundamental properties of touch sounds, especially how they are transmitted through solid surfaces.
On solid surfaces, sound experiences a dispersion phenomenon that makes different frequency components travel at different speeds. Based on this phenomenon, the team observed that the arrival time difference (TDoA) between frequency components increases in proportion to the sound transmission distance, and this linear relationship is not affected by the variations of surround environments.
Based on these observations, Research Assistant Professor Hyosu Kim proposed a novel sound-based touch input technology that records touch sounds transmitted through solid surfaces, then conducts a simple calibration process to identify the relationship between TDoA and the sound transmission distance, finally achieving accurate touch input localization.
The accuracy of the proposed system was then measured. The average localization error was lower than about 0.4 cm on a 17-inch touch screen. Particularly, it provided a measurement error of less than 1cm, even with a variety of objects such as wooden desks, glass mirrors, and acrylic boards and when the position of nearby objects and noise levels changed dynamically. Experiments with practical users have also shown positive responses to all measurement factors, including user experience and accuracy.
Professor Shin said, “This is novel touch interface technology that allows a touch input system just by installing three to four microphones, so it can easily turn nearby objects into touch screens.”
The proposed system was presented at ACM SenSys, a top-tier conference in the field of mobile computing and sensing, and was selected as a best paper runner-up in November 2018.
(The demonstration video of the sound-based touch input technology)
2018.12.26 View 10502
Sound-based Touch Input Technology for Smart Tables and Mirrors
(from left: MS candidate Anish Byanjankar, Research Assistant Professor Hyosu Kim and Professor Insik Shin)
Time passes so quickly, especially in the morning. Your hands are so busy brushing your teeth and checking the weather on your smartphone. You might wish that your mirror could turn into a touch screen and free up your hands. That wish can be achieved very soon. A KAIST team has developed a smartphone-based touch sound localization technology to facilitate ubiquitous interactions, turning objects like furniture and mirrors into touch input tools.
This technology analyzes touch sounds generated from a user’s touch on a surface and identifies the location of the touch input. For instance, users can turn surrounding tables or walls into virtual keyboards and write lengthy e-mails much more conveniently by using only the built-in microphone on their smartphones or tablets. Moreover, family members can enjoy a virtual chessboard or enjoy board games on their dining tables.
Additionally, traditional smart devices such as smart TVs or mirrors, which only provide simple screen display functions, can play a smarter role by adding touch input function support (see the image below).
Figure 1.Examples of using touch input technology: By using only smartphone, you can use surrounding objects as a touch screen anytime and anywhere.
The most important aspect of enabling the sound-based touch input method is to identify the location of touch inputs in a precise manner (within about 1cm error). However, it is challenging to meet these requirements, mainly because this technology can be used in diverse and dynamically changing environments. Users may use objects like desks, walls, or mirrors as touch input tools and the surrounding environments (e.g. location of nearby objects or ambient noise level) can be varied. These environmental changes can affect the characteristics of touch sounds.
To address this challenge, Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing and his team focused on analyzing the fundamental properties of touch sounds, especially how they are transmitted through solid surfaces.
On solid surfaces, sound experiences a dispersion phenomenon that makes different frequency components travel at different speeds. Based on this phenomenon, the team observed that the arrival time difference (TDoA) between frequency components increases in proportion to the sound transmission distance, and this linear relationship is not affected by the variations of surround environments.
Based on these observations, Research Assistant Professor Hyosu Kim proposed a novel sound-based touch input technology that records touch sounds transmitted through solid surfaces, then conducts a simple calibration process to identify the relationship between TDoA and the sound transmission distance, finally achieving accurate touch input localization.
The accuracy of the proposed system was then measured. The average localization error was lower than about 0.4 cm on a 17-inch touch screen. Particularly, it provided a measurement error of less than 1cm, even with a variety of objects such as wooden desks, glass mirrors, and acrylic boards and when the position of nearby objects and noise levels changed dynamically. Experiments with practical users have also shown positive responses to all measurement factors, including user experience and accuracy.
Professor Shin said, “This is novel touch interface technology that allows a touch input system just by installing three to four microphones, so it can easily turn nearby objects into touch screens.”
The proposed system was presented at ACM SenSys, a top-tier conference in the field of mobile computing and sensing, and was selected as a best paper runner-up in November 2018.
(The demonstration video of the sound-based touch input technology)
2018.12.26 View 10502 -
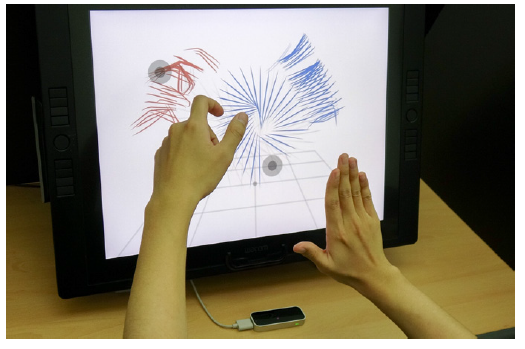 It's Time to 3D Sketch with Air Scaffolding
People often use their hands when describing an object, while pens are great tools for describing objects in detail. Taking this idea, a KAIST team introduced a new 3D sketching workflow, combining the strengths of hand and pen input. This technique will ease the way for ideation in three dimensions, leading to efficient product design in terms of time and cost.
For a designer's drawing to become a product in reality, one has to transform a designer's 2D drawing into a 3D shape; however, it is difficult to infer accurate 3D shapes that match the original intention from an inaccurate 2D drawing made by hand. When creating a 3D shape from a planar 2D drawing, unobtainable information is required. On the other hand, loss of depth information occurs when a 3D shape is expressed as a 2D drawing using perspective drawing techniques.
To fill in these “missing links” during the conversion, "3D sketching" techniques have been actively studied. Their main purpose is to help designers naturally provide missing 3D shape information in a 2D drawing. For example, if a designer draws two symmetric curves from a single point of view or draws the same curves from different points of view, the geometric clues that are left in this process are collected and mathematically interpreted to define the proper 3D curve. As a result, designers can use 3D sketching to directly draw a 3D shape as if using pen and paper.
Among 3D sketching tools, sketching with hand motions, in VR environments in particular, has drawn attention because it is easy and quick. But the biggest limitation is that they cannot articulate the design solely using rough hand motions, hence they are difficult to be applied to product designs. Moreover, users may feel tired after raising their hands in the air during the entire drawing process.
Using hand motions but to elaborate designs, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae and his team from the Department of Industrial Design integrated hand motions and pen-based sketching, allocating roles according to their strengths. This new technique is called Agile 3D Sketching with Air Scaffolding. Designers use their hand motions in the air to create rough 3D shapes which will be used as scaffolds, and then they can add details with pen-based 3D sketching on a tablet (Figure 1).
Figure 1. In the agile 3D sketching workflow with air scaffolding, the user (a) makes unconstrained hand movements in the air to quickly generate rough shapes to be used as scaffolds, (b) uses the scaffolds as references and draws finer details with them, (c) produces a high-fidelity 3D concept sketch of a steering wheel in an iterative and progressive manner.
The team came up with an algorithm to identify descriptive hand motions from transitory hand motions and extract only the intended shapes from unconstrained hand motions, based on air scaffolds from the identified motions.
Through user tests, the team identified that this technique is easy to learn and use, and demonstrates good applicability. Most importantly, the users can reduce time, yet enhance the accuracy of defining the proportion and scale of products.
Eventually, this tool will be able to be applied to various fields including the automobile industry, home appliances, animations and the movie making industry, and robotics. It also can be linked to smart production technology, such as 3D printing, to make manufacturing process faster and more flexible.
PhD candidate Yongkwan Kim, who led the research project, said, “I believe the system will enhance product quality and work efficiency because designers can express their 3D ideas quickly yet accurately without using complex 3D CAD modeling software. I will make it into a product that every designer wants to use in various fields.”
“There have been many attempts to encourage creative activities in various fields by using advanced computer technology. Based on in-depth understanding of designers, we will take the lead in innovating the design process by applying cutting-edge technology,” Professor Bae added.
Professor Bae and his team from the Department of Industrial Design has been delving into developing better 3D sketching tools. They started with a 3D curve sketching system for professional designers called ILoveSketch and moved on to SketchingWithHands for designing a handheld product with first-person hand postures captured by a hand-tracking sensor. They then took their project to the next level and introduced Agile 3D Sketching with Air Scaffolding, a new 3D sketching workflow combining hand motion and pen drawing which was chosen as one of the CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2018 Best Papers by the Association for Computing Machinery.
- Click the link to watch video clip of SketchingWithHands
2018.07.25 View 10621
It's Time to 3D Sketch with Air Scaffolding
People often use their hands when describing an object, while pens are great tools for describing objects in detail. Taking this idea, a KAIST team introduced a new 3D sketching workflow, combining the strengths of hand and pen input. This technique will ease the way for ideation in three dimensions, leading to efficient product design in terms of time and cost.
For a designer's drawing to become a product in reality, one has to transform a designer's 2D drawing into a 3D shape; however, it is difficult to infer accurate 3D shapes that match the original intention from an inaccurate 2D drawing made by hand. When creating a 3D shape from a planar 2D drawing, unobtainable information is required. On the other hand, loss of depth information occurs when a 3D shape is expressed as a 2D drawing using perspective drawing techniques.
To fill in these “missing links” during the conversion, "3D sketching" techniques have been actively studied. Their main purpose is to help designers naturally provide missing 3D shape information in a 2D drawing. For example, if a designer draws two symmetric curves from a single point of view or draws the same curves from different points of view, the geometric clues that are left in this process are collected and mathematically interpreted to define the proper 3D curve. As a result, designers can use 3D sketching to directly draw a 3D shape as if using pen and paper.
Among 3D sketching tools, sketching with hand motions, in VR environments in particular, has drawn attention because it is easy and quick. But the biggest limitation is that they cannot articulate the design solely using rough hand motions, hence they are difficult to be applied to product designs. Moreover, users may feel tired after raising their hands in the air during the entire drawing process.
Using hand motions but to elaborate designs, Professor Seok-Hyung Bae and his team from the Department of Industrial Design integrated hand motions and pen-based sketching, allocating roles according to their strengths. This new technique is called Agile 3D Sketching with Air Scaffolding. Designers use their hand motions in the air to create rough 3D shapes which will be used as scaffolds, and then they can add details with pen-based 3D sketching on a tablet (Figure 1).
Figure 1. In the agile 3D sketching workflow with air scaffolding, the user (a) makes unconstrained hand movements in the air to quickly generate rough shapes to be used as scaffolds, (b) uses the scaffolds as references and draws finer details with them, (c) produces a high-fidelity 3D concept sketch of a steering wheel in an iterative and progressive manner.
The team came up with an algorithm to identify descriptive hand motions from transitory hand motions and extract only the intended shapes from unconstrained hand motions, based on air scaffolds from the identified motions.
Through user tests, the team identified that this technique is easy to learn and use, and demonstrates good applicability. Most importantly, the users can reduce time, yet enhance the accuracy of defining the proportion and scale of products.
Eventually, this tool will be able to be applied to various fields including the automobile industry, home appliances, animations and the movie making industry, and robotics. It also can be linked to smart production technology, such as 3D printing, to make manufacturing process faster and more flexible.
PhD candidate Yongkwan Kim, who led the research project, said, “I believe the system will enhance product quality and work efficiency because designers can express their 3D ideas quickly yet accurately without using complex 3D CAD modeling software. I will make it into a product that every designer wants to use in various fields.”
“There have been many attempts to encourage creative activities in various fields by using advanced computer technology. Based on in-depth understanding of designers, we will take the lead in innovating the design process by applying cutting-edge technology,” Professor Bae added.
Professor Bae and his team from the Department of Industrial Design has been delving into developing better 3D sketching tools. They started with a 3D curve sketching system for professional designers called ILoveSketch and moved on to SketchingWithHands for designing a handheld product with first-person hand postures captured by a hand-tracking sensor. They then took their project to the next level and introduced Agile 3D Sketching with Air Scaffolding, a new 3D sketching workflow combining hand motion and pen drawing which was chosen as one of the CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems) 2018 Best Papers by the Association for Computing Machinery.
- Click the link to watch video clip of SketchingWithHands
2018.07.25 View 10621 -
 Yoon Ki Hong Named 2018 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(From left: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from ADD, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School)
Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from the Agency of Defense Development (ADD) was named the 2018 recipient of the Jong-Hoon Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient of this award receives a 25 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Hong has achieved outstanding work in the field of aerospace engineering. In particular, he conducted research on designing an air heating device which is the crucial component for ground experimental equipment. It is required for testing and evaluating supersonic vehicles’ structural strength tests using technology cannot be imported. In cooperation with his colleagues, he succeeded in developing an air heating device, a feat that has only been accomplished by developed countries. He also verified its operational performance.
Moreover, he received the best paper award from Korean Federation of Science and Minister of Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s Prize.
The award was endowed by the family of the late PhD candidate Jeong Hun Cho, who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In Cho’s memory, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship’. Since 2005, the scholarship annually selects three young scholars specializing in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
In addition to Dr. Hong, the Award Committee chose three students for scholarships: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School.
2018.05.11 View 12187
Yoon Ki Hong Named 2018 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(From left: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from ADD, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School)
Dr. Yoon Ki Hong from the Agency of Defense Development (ADD) was named the 2018 recipient of the Jong-Hoon Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient of this award receives a 25 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Hong has achieved outstanding work in the field of aerospace engineering. In particular, he conducted research on designing an air heating device which is the crucial component for ground experimental equipment. It is required for testing and evaluating supersonic vehicles’ structural strength tests using technology cannot be imported. In cooperation with his colleagues, he succeeded in developing an air heating device, a feat that has only been accomplished by developed countries. He also verified its operational performance.
Moreover, he received the best paper award from Korean Federation of Science and Minister of Defense Acquisition Program Administration’s Prize.
The award was endowed by the family of the late PhD candidate Jeong Hun Cho, who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In Cho’s memory, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship’. Since 2005, the scholarship annually selects three young scholars specializing in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
In addition to Dr. Hong, the Award Committee chose three students for scholarships: PhD candidate Seungkwan Baek from the Department of Aerospace Engineering, PhD candidate Wonhee Choi from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Jaehun Lee from Kongju National University High School.
2018.05.11 View 12187 -
 Seong-Tae Kim Wins Robert-Wagner All-Conference Best Paper Award
(Ph.D. candidate Seong-Tae Kim)
Ph.D. candidate Seong-Tae Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering won the Robert Wagner All-Conference Best Student Paper Award during the 2018 International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE) Medical Imaging Conference, which was held in Houston last month.
Kim, supervised by Professor Yong Man Ro, received the award for his paper in the category of computer-aided diagnosis. His paper, titled “ICADx: Interpretable Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Breast Masses”, was selected as the best paper out of 900 submissions. The conference selects the best paper in nine different categories. His research provides new insights on diagnostic technology to detect breast cancer powered by deep learning.
2018.03.15 View 13295
Seong-Tae Kim Wins Robert-Wagner All-Conference Best Paper Award
(Ph.D. candidate Seong-Tae Kim)
Ph.D. candidate Seong-Tae Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering won the Robert Wagner All-Conference Best Student Paper Award during the 2018 International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE) Medical Imaging Conference, which was held in Houston last month.
Kim, supervised by Professor Yong Man Ro, received the award for his paper in the category of computer-aided diagnosis. His paper, titled “ICADx: Interpretable Computer-Aided Diagnosis of Breast Masses”, was selected as the best paper out of 900 submissions. The conference selects the best paper in nine different categories. His research provides new insights on diagnostic technology to detect breast cancer powered by deep learning.
2018.03.15 View 13295 -
 Professor Hojong Chang Wins the Best Paper Award at ISIITA 2018
Professor Hojong Chang from the KAIST Institute won the best paper award at the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology and Application (ISIITA) 2018.
ISIITA is a global networking symposium in which leading researchers in the field of information technology and applications gather to exchange knowledge on technological convergence.
Professor Chang won the prize for his paper, titled ‘A Study on the Measurement of Aptamer in Urine Using SiPM’.
This paper proposes using aptamer to measure and analyze the density of sodium and potassium contained in urine, allowing diseases to be diagnosed in advance.
Professor Chang said, “With a point-of-care test system that facilitates a quick diagnosis without extra processes, such as centrifugation, it is possible to get an early diagnosis and check infection in real time. Through generalizing this crucial technology, we expect to develop adequate technology for enhancing quality of life.
2018.02.12 View 10394
Professor Hojong Chang Wins the Best Paper Award at ISIITA 2018
Professor Hojong Chang from the KAIST Institute won the best paper award at the International Symposium on Innovation in Information Technology and Application (ISIITA) 2018.
ISIITA is a global networking symposium in which leading researchers in the field of information technology and applications gather to exchange knowledge on technological convergence.
Professor Chang won the prize for his paper, titled ‘A Study on the Measurement of Aptamer in Urine Using SiPM’.
This paper proposes using aptamer to measure and analyze the density of sodium and potassium contained in urine, allowing diseases to be diagnosed in advance.
Professor Chang said, “With a point-of-care test system that facilitates a quick diagnosis without extra processes, such as centrifugation, it is possible to get an early diagnosis and check infection in real time. Through generalizing this crucial technology, we expect to develop adequate technology for enhancing quality of life.
2018.02.12 View 10394 -
 Professor Dai Gil Lee Recognized by the ICCS
Emeritus Professor Dai Gil Lee, from the School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, received a special achievement award from the 20th International Conference on Composite Structures (ICCS).
ICCS is a renowned conference in the field of applied composite structures, which highlights the practicality of composite structures. This year, the conference was held at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers (CNAM), Paris, France from September 4 to 7. Approximately 650 papers were presented from 45 countries.
Especially, the conference honored Emeritus Professor Lee, who has been engaged in ICCS since 1993 and received best paper award twice. The ICCS recognized him for serving with distinction in science and technology in the fields of composite materials and structures. As a member of the Editorial Board for many years, he gave significant support to the journal Composite Structures. At the conference, he gave a special lecture titled ‘Lightweight Carbon Composite Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells’.
Professor Lee said, “I will dedicate myself to innovate Vanadium Redox Flow Battery-ESS (VRFB) based on the research findings announced at the conference and related patents. I am hoping that these efforts will contribute to solving energy issues around the world.”
2017.10.19 View 10213
Professor Dai Gil Lee Recognized by the ICCS
Emeritus Professor Dai Gil Lee, from the School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, received a special achievement award from the 20th International Conference on Composite Structures (ICCS).
ICCS is a renowned conference in the field of applied composite structures, which highlights the practicality of composite structures. This year, the conference was held at the Conservatoire National des Arts et Métiers (CNAM), Paris, France from September 4 to 7. Approximately 650 papers were presented from 45 countries.
Especially, the conference honored Emeritus Professor Lee, who has been engaged in ICCS since 1993 and received best paper award twice. The ICCS recognized him for serving with distinction in science and technology in the fields of composite materials and structures. As a member of the Editorial Board for many years, he gave significant support to the journal Composite Structures. At the conference, he gave a special lecture titled ‘Lightweight Carbon Composite Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cells’.
Professor Lee said, “I will dedicate myself to innovate Vanadium Redox Flow Battery-ESS (VRFB) based on the research findings announced at the conference and related patents. I am hoping that these efforts will contribute to solving energy issues around the world.”
2017.10.19 View 10213 -
 Dr. Zi Jing Wong Named 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(Photo caption: The 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Scholarship recipients pose with President Shin (left photo) and Dr. Zi Jing Wong, the recipient of the 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Award)
Dr. Zi Jing Wong, a postdoctoral scholar at the University of California, Berkeley was named the 2017 recipient of the Jeong Hun Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient receives a 20 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Wong who earned his MS at KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering is a rising scholar in the fields of optic meta materials, photonics, imaging, among others. He has published five papers on the realization of a zero refractive index and the control of a refractive index, as well as the realization of a 3D invisibility cloak in Science and Nature Photonics in 2014 and 2015. Dr. Wong also swept the best paper awards from many international academic societies including the US Materials Research Society, IEEE, SPIE, and Metamaterials Congress in 2015. He finished his Ph.D. at the University of California, Berkeley.
The Award Committee also named three recipients of the Jeong Hun Cho Scholarship: Ph.D. candidate Hyon-Tak Kim of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Ph.D. candidate Ho-Song Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Hyong-Jin Choi of Kongju National University High School.
The award was endowed by the family of the late Ph.D. candidate Jeong Hun Cho who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In memory of Cho, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship.’ The scholarship annually selects three young scholars from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
2017.05.12 View 13855
Dr. Zi Jing Wong Named 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Awardee
(Photo caption: The 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Scholarship recipients pose with President Shin (left photo) and Dr. Zi Jing Wong, the recipient of the 2017 Jeong Hun Cho Award)
Dr. Zi Jing Wong, a postdoctoral scholar at the University of California, Berkeley was named the 2017 recipient of the Jeong Hun Cho Award. The award recognizes outstanding young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering annually. The recipient receives a 20 million KRW prize.
The Award Committee said that Dr. Wong who earned his MS at KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering is a rising scholar in the fields of optic meta materials, photonics, imaging, among others. He has published five papers on the realization of a zero refractive index and the control of a refractive index, as well as the realization of a 3D invisibility cloak in Science and Nature Photonics in 2014 and 2015. Dr. Wong also swept the best paper awards from many international academic societies including the US Materials Research Society, IEEE, SPIE, and Metamaterials Congress in 2015. He finished his Ph.D. at the University of California, Berkeley.
The Award Committee also named three recipients of the Jeong Hun Cho Scholarship: Ph.D. candidate Hyon-Tak Kim of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, Ph.D. candidate Ho-Song Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University, and Hyong-Jin Choi of Kongju National University High School.
The award was endowed by the family of the late Ph.D. candidate Jeong Hun Cho who died in a rocket lab accident in the Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2003. Cho was posthumously conferred an honorary doctorate degree.
In memory of Cho, his father established the ‘Jeong Hun Cho Award and Scholarship.’ The scholarship annually selects three young scholars from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
2017.05.12 View 13855 -
 Professor Lee Recognized by the KMS as Best Paper Awardee
Professor Ji Oon Lee of the Department of Mathematical Sciences was selected as the 2017 Best Paper Awardee by the Korean Mathematical Society. The award will be presented during the KMS spring meeting on April 29. Dr. Lee is being honored for proving a necessary and sufficient condition for the Tracy-Wisdom law of Wigner matrices. In a paper titled ‘A Necessary and Sufficient Condition for Edge Universality of Wigner Matrices,’ he proposed a solution for one of the many unanswered problems in the field of random matrix theory that have existed for decades. The paper, co-authored with Professor Jun Yin at the University of Wisconsin – Madison, was published in the Duke Mathematical Journal in 2014. Professor Lee joined KAIST in 2010 after finishing his Ph.D. at Harvard University. He was named a ‘POSCI Science Fellow’ and received the ‘Young Scientist Award’ from the KMS in 2014.
2017.04.27 View 11838
Professor Lee Recognized by the KMS as Best Paper Awardee
Professor Ji Oon Lee of the Department of Mathematical Sciences was selected as the 2017 Best Paper Awardee by the Korean Mathematical Society. The award will be presented during the KMS spring meeting on April 29. Dr. Lee is being honored for proving a necessary and sufficient condition for the Tracy-Wisdom law of Wigner matrices. In a paper titled ‘A Necessary and Sufficient Condition for Edge Universality of Wigner Matrices,’ he proposed a solution for one of the many unanswered problems in the field of random matrix theory that have existed for decades. The paper, co-authored with Professor Jun Yin at the University of Wisconsin – Madison, was published in the Duke Mathematical Journal in 2014. Professor Lee joined KAIST in 2010 after finishing his Ph.D. at Harvard University. He was named a ‘POSCI Science Fellow’ and received the ‘Young Scientist Award’ from the KMS in 2014.
2017.04.27 View 11838 -
 EEWS Graduate School Team Receives the S-Oil Best Paper Award
Professor Hyungjun Kim and Dr. He-Young Shin from the EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School at KAIST received the Best Paper Award in Chemistry from S-Oil, a Korean petroleum and refinery company, on November 29, 2016.
Established in 2011, the S-Oil Best Paper Awards are bestowed annually upon ten young scientists in the fields of five basic sciences: mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, and earth science. The scientists are selected at the recommendation of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology and the Association of Korean Universities. The awards grant a total of USD 230,000 for research funding.
Dr. Shin, the lead author of the awarded research paper, said, “My research interest has been catalyst studies based on theoretical chemistry. I am pleased to accept this award that will support my studies, and will continue to research catalyst design that can predict parameters and integrate them into catalytic systems.”
Professor Hyungjun Kim (left) and Dr. He-Young Shin (right)
2016.12.23 View 13068
EEWS Graduate School Team Receives the S-Oil Best Paper Award
Professor Hyungjun Kim and Dr. He-Young Shin from the EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability) Graduate School at KAIST received the Best Paper Award in Chemistry from S-Oil, a Korean petroleum and refinery company, on November 29, 2016.
Established in 2011, the S-Oil Best Paper Awards are bestowed annually upon ten young scientists in the fields of five basic sciences: mathematics, physics, chemistry, biology, and earth science. The scientists are selected at the recommendation of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology and the Association of Korean Universities. The awards grant a total of USD 230,000 for research funding.
Dr. Shin, the lead author of the awarded research paper, said, “My research interest has been catalyst studies based on theoretical chemistry. I am pleased to accept this award that will support my studies, and will continue to research catalyst design that can predict parameters and integrate them into catalytic systems.”
Professor Hyungjun Kim (left) and Dr. He-Young Shin (right)
2016.12.23 View 13068 -
 Professor Dongman Lee Wins the 2016 Korea Internet Award
Professor Dongman Lee of KAIST’s School of Computing received the 11th Korea Internet Award in the category of personal achievement on December 13 at the Creative Economy and Innovation Center in Gyeonggi province.
Hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, the Internet Award recognizes leaders in the Internet industry and their contributions.
Since 2010, Professor Lee has conducted research on the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, resulting in the publication of five research papers in Science Citation Index (SCI) journals, ten papers in Korean journals, 30 best papers nominations at international conferences, and the registration of eleven patents. He has also worked on the creation of an IoT ecosystem through his research on object interworking platforms that can provide diverse user-customized services in the IoT environment.
His research team built a test bed for applicable IoT platforms on the 8th floor of the IT Convergence Center on campus to implement experiments and collect various data, thereby creating a foundation to carry out research projects in this field.
Professor Lee has helped the advancement of an Internet governance system in Korea by researching Internet governance policies, holding important posts in related academic societies including the Chairman of the Korea Internet Governance Alliance (KIGA) Council, and hosting major conferences such as the Asia Pacific Regional Internet Governance Forum (APrIGF).
2016.12.20 View 10601
Professor Dongman Lee Wins the 2016 Korea Internet Award
Professor Dongman Lee of KAIST’s School of Computing received the 11th Korea Internet Award in the category of personal achievement on December 13 at the Creative Economy and Innovation Center in Gyeonggi province.
Hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea, the Internet Award recognizes leaders in the Internet industry and their contributions.
Since 2010, Professor Lee has conducted research on the Internet of Things (IoT) platforms, resulting in the publication of five research papers in Science Citation Index (SCI) journals, ten papers in Korean journals, 30 best papers nominations at international conferences, and the registration of eleven patents. He has also worked on the creation of an IoT ecosystem through his research on object interworking platforms that can provide diverse user-customized services in the IoT environment.
His research team built a test bed for applicable IoT platforms on the 8th floor of the IT Convergence Center on campus to implement experiments and collect various data, thereby creating a foundation to carry out research projects in this field.
Professor Lee has helped the advancement of an Internet governance system in Korea by researching Internet governance policies, holding important posts in related academic societies including the Chairman of the Korea Internet Governance Alliance (KIGA) Council, and hosting major conferences such as the Asia Pacific Regional Internet Governance Forum (APrIGF).
2016.12.20 View 10601 -
 Mobile Software Platform Research Center Recognized by the MSIP
The Mobile Software Platform Research Center (MSPRC) at KAIST received an award from the Minister of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea on November 29, 2016, at Coex in Seoul. The award was presented at the Conference of Software R&D Annual Report 2016 hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MISP) and the Institute for Information and Communications Technology Promotion (IITP).
The research center developed user experience (UX)-oriented mobile software platforms that support the invention of next-generation UX service technologies. The center has filed 37 patents and registered 15 technologies. Its researchers received ten Best Paper Awards and published a total of 133 papers in Korean and international journals.
Research teams at MSPRC expect that their software platforms will offer training programs for software engineers and new UX services. They also said that their extensive event processing platforms would reduce energy consumption on mobile devices.
Professor Seungryoul Maeng of the School of Computing, the Director of MSPRC, said, “This is a great honor for us. I am greatly thankful for the teamwork of participating departments--Computer Science, Industrial Design, and Industrial and Systems Engineering. We will continue to introduce our research outcomes and to work towards commercializing these results.”
Members of the Mobile Software Platform Research Center, KAIST
2016.12.07 View 8541
Mobile Software Platform Research Center Recognized by the MSIP
The Mobile Software Platform Research Center (MSPRC) at KAIST received an award from the Minister of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea on November 29, 2016, at Coex in Seoul. The award was presented at the Conference of Software R&D Annual Report 2016 hosted by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MISP) and the Institute for Information and Communications Technology Promotion (IITP).
The research center developed user experience (UX)-oriented mobile software platforms that support the invention of next-generation UX service technologies. The center has filed 37 patents and registered 15 technologies. Its researchers received ten Best Paper Awards and published a total of 133 papers in Korean and international journals.
Research teams at MSPRC expect that their software platforms will offer training programs for software engineers and new UX services. They also said that their extensive event processing platforms would reduce energy consumption on mobile devices.
Professor Seungryoul Maeng of the School of Computing, the Director of MSPRC, said, “This is a great honor for us. I am greatly thankful for the teamwork of participating departments--Computer Science, Industrial Design, and Industrial and Systems Engineering. We will continue to introduce our research outcomes and to work towards commercializing these results.”
Members of the Mobile Software Platform Research Center, KAIST
2016.12.07 View 8541 -
 Doctoral Student Receives the Best Paper Award from the International Metabolic Engineering Conference 2016
So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, received the Student and Young Investigator Poster Award at the 11th International Metabolic Engineering Conference held in Awaji, Japan on June 26-30.
Choi received the award for her research on one-step fermentative production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli, which was published in the April 2016 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
In her paper, she presented a novel technology to synthesize PLGA, a non-natural copolymer, through a biological production process. Because of its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility, PLGA is widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications, including surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Employing a metabolic engineering approach, Choi manipulated the metabolic pathway of an Escherichia coli bacterium to convert glucose and xylose into the biosynthesis of PLGA within the cell. Previously, PLGA could be obtained only through chemical synthesis.
Choi said, “I’m thrilled to receive an award from a flagship conference of my research field. Mindful of this recognition, I will continue my research to produce meaningful results, thereby contributing to the development of science and technology in Korea.”
The International Metabolic Engineering Conference is a leading professional gathering where state-of-the-art developments and achievements made in the field of metabolic engineering are shared. With the participation of about 400 professionals from all around the world, the conference participants discussed this year’s theme of “Design, Synthesis and System Integration for Metabolic Engineering.”
2016.07.07 View 12643
Doctoral Student Receives the Best Paper Award from the International Metabolic Engineering Conference 2016
So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, received the Student and Young Investigator Poster Award at the 11th International Metabolic Engineering Conference held in Awaji, Japan on June 26-30.
Choi received the award for her research on one-step fermentative production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli, which was published in the April 2016 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
In her paper, she presented a novel technology to synthesize PLGA, a non-natural copolymer, through a biological production process. Because of its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility, PLGA is widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications, including surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Employing a metabolic engineering approach, Choi manipulated the metabolic pathway of an Escherichia coli bacterium to convert glucose and xylose into the biosynthesis of PLGA within the cell. Previously, PLGA could be obtained only through chemical synthesis.
Choi said, “I’m thrilled to receive an award from a flagship conference of my research field. Mindful of this recognition, I will continue my research to produce meaningful results, thereby contributing to the development of science and technology in Korea.”
The International Metabolic Engineering Conference is a leading professional gathering where state-of-the-art developments and achievements made in the field of metabolic engineering are shared. With the participation of about 400 professionals from all around the world, the conference participants discussed this year’s theme of “Design, Synthesis and System Integration for Metabolic Engineering.”
2016.07.07 View 12643