research
-
 Expanding Gas Storage Capacity of Nanoporous Materials
A KAIST research team led by Professor Jihan Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has successfully proposed a rational defect engineering methodology that can greatly enhance the gas storage capacity of nanoporous materials. The team conducted a high-throughput computational screening of a large experimental metal-organic framework database to identify 13 candidate materials that could experience significant methane uptake enhancement with only a small proportion of linker vacancy defects.
This research was published online on November 16 in Nature Communications, with M.S. candidate Sanggyu Chong from KAIST as the first author and post-doctorate researcher Günther Thiele from the Department of Chemistry at UC Berkeley as a contributing author.
Metal-organic frameworks, hereinafter MOF, are crystalline nanoporous materials that are comprised of metal clusters and organic linkers continuously bound together by coordination bonds. Due to their ultrahigh surface areas and pore volumes, they have been widely studied for various energy and environment applications.
Similar to other crystalline materials, MOFs are never perfectly crystalline and are likely to contain several different types of defects within their crystalline structures. Among these defects, linker vacancy defects, or the random absence of linker vacancies in their designated bonding positions, are known to be controllable by practicing careful control over the synthesis conditions.
The research team combined the concepts of rational defect engineering over the linker vacancy defects and the potential presence of inaccessible pores within MOFs to propose a methodology where controlled the introduction of linker vacancy defects could lead to a dramatic enhancement in gas adsorption and storage capacities.
The study utilized a Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) code developed by Professor Kim in a high-throughput computational screening of 12,000 experimentally synthesized MOFs to identify the structures with significant amounts of pores that were inaccessible for methane. In determining the presence of inaccessible pores, a flood-fill algorithm was performed over the energy-low regions of the structure, which is the same algorithm used for filling an area with color in Microsoft Paint.
For the MOFs with significant amounts of inaccessible pores, as determined from the screening, the research team emulated linker vacancy defects in their crystalline structures so that the previously inaccessible pores would be newly merged into the main adsorption channel with the introduction of defects for additional surface area and pore volume available for adsorption. The research team successfully identified 13 structures that would experience up to a 55.56% increase in their methane uptake with less than 8.33% of the linker vacancy defects.
The research team believes that this rational defect engineering scheme can be further utilized for many other applications in areas such as selective adsorption of an adsorbate from a gas mixture and the semi-permanent capture of gas molecules.
This research was conducted with the support of the Mid-career Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure1. A diagram for flood fill algorithm and example of identification of inaccessible regions within the MOFs, using the flood fill algorithm
Figure2. Methane energy contours before and after detect introduction
2017.12.04 View 8663
Expanding Gas Storage Capacity of Nanoporous Materials
A KAIST research team led by Professor Jihan Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has successfully proposed a rational defect engineering methodology that can greatly enhance the gas storage capacity of nanoporous materials. The team conducted a high-throughput computational screening of a large experimental metal-organic framework database to identify 13 candidate materials that could experience significant methane uptake enhancement with only a small proportion of linker vacancy defects.
This research was published online on November 16 in Nature Communications, with M.S. candidate Sanggyu Chong from KAIST as the first author and post-doctorate researcher Günther Thiele from the Department of Chemistry at UC Berkeley as a contributing author.
Metal-organic frameworks, hereinafter MOF, are crystalline nanoporous materials that are comprised of metal clusters and organic linkers continuously bound together by coordination bonds. Due to their ultrahigh surface areas and pore volumes, they have been widely studied for various energy and environment applications.
Similar to other crystalline materials, MOFs are never perfectly crystalline and are likely to contain several different types of defects within their crystalline structures. Among these defects, linker vacancy defects, or the random absence of linker vacancies in their designated bonding positions, are known to be controllable by practicing careful control over the synthesis conditions.
The research team combined the concepts of rational defect engineering over the linker vacancy defects and the potential presence of inaccessible pores within MOFs to propose a methodology where controlled the introduction of linker vacancy defects could lead to a dramatic enhancement in gas adsorption and storage capacities.
The study utilized a Graphic Processing Unit (GPU) code developed by Professor Kim in a high-throughput computational screening of 12,000 experimentally synthesized MOFs to identify the structures with significant amounts of pores that were inaccessible for methane. In determining the presence of inaccessible pores, a flood-fill algorithm was performed over the energy-low regions of the structure, which is the same algorithm used for filling an area with color in Microsoft Paint.
For the MOFs with significant amounts of inaccessible pores, as determined from the screening, the research team emulated linker vacancy defects in their crystalline structures so that the previously inaccessible pores would be newly merged into the main adsorption channel with the introduction of defects for additional surface area and pore volume available for adsorption. The research team successfully identified 13 structures that would experience up to a 55.56% increase in their methane uptake with less than 8.33% of the linker vacancy defects.
The research team believes that this rational defect engineering scheme can be further utilized for many other applications in areas such as selective adsorption of an adsorbate from a gas mixture and the semi-permanent capture of gas molecules.
This research was conducted with the support of the Mid-career Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure1. A diagram for flood fill algorithm and example of identification of inaccessible regions within the MOFs, using the flood fill algorithm
Figure2. Methane energy contours before and after detect introduction
2017.12.04 View 8663 -
 Technology Detecting RNase Activity
(Ph.D. candidate Chang Yeol Lee)
A KAIST research team of Professor Hyun Gyu Park at Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering developed a new technology to detect the activity of RNase H, a RNA degrading enzyme. The team used highly efficient signal amplification reaction termed catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) to effectively analyze the RNase H activity. Considering that RNase H is required in the proliferation of retroviruses such as HIV, this research finding could contribute to AIDS treatments in the future, researchers say.
This study led by Ph.D. candidates Chang Yeol Lee and Hyowon Jang was chosen as the cover for Nanoscale (Issue 42, 2017) published in 14 November.
The existing techniques to detect RNase H require expensive fluorophore and quencher, and involve complex implementation. Further, there is no way to amplify the signal, leading to low detection efficiency overall. The team utilized CHA technology to overcome these limitations. CHA amplifies detection signal to allow more sensitive RNase H activity assay.
The team designed the reaction system so that the product of CHA reaction has G-quadruplex structures, which is suitable to generate fluorescence. By using fluorescent molecules that bind to G-quadruplexes to generate strong fluorescence, the team could develop high performance RNase H detection method that overcomes the limitations of existing techniques. Further, this technology could screen inhibitors of RNase H activity.
The team expects that the research finding could contribute to AIDS treatment. AIDS is disease caused by HIV, a retrovirus that utilizes reverse transcription, during which RNA is converted to DNA. RNase H is essential for reverse transcription in HIV, and thus inhibition of RNase H could in turn inhibit transcription of HIV DNA.
Professor Park said, “This technology is applicable to detect various enzyme activities, as well as RNase H activity.” He continued, “I hope this technology could be widely used in research on enzyme related diseases.”
This study was funded by Global Frontier project and Mid-career Researcher Support project of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2017.11.28 View 7334
Technology Detecting RNase Activity
(Ph.D. candidate Chang Yeol Lee)
A KAIST research team of Professor Hyun Gyu Park at Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering developed a new technology to detect the activity of RNase H, a RNA degrading enzyme. The team used highly efficient signal amplification reaction termed catalytic hairpin assembly (CHA) to effectively analyze the RNase H activity. Considering that RNase H is required in the proliferation of retroviruses such as HIV, this research finding could contribute to AIDS treatments in the future, researchers say.
This study led by Ph.D. candidates Chang Yeol Lee and Hyowon Jang was chosen as the cover for Nanoscale (Issue 42, 2017) published in 14 November.
The existing techniques to detect RNase H require expensive fluorophore and quencher, and involve complex implementation. Further, there is no way to amplify the signal, leading to low detection efficiency overall. The team utilized CHA technology to overcome these limitations. CHA amplifies detection signal to allow more sensitive RNase H activity assay.
The team designed the reaction system so that the product of CHA reaction has G-quadruplex structures, which is suitable to generate fluorescence. By using fluorescent molecules that bind to G-quadruplexes to generate strong fluorescence, the team could develop high performance RNase H detection method that overcomes the limitations of existing techniques. Further, this technology could screen inhibitors of RNase H activity.
The team expects that the research finding could contribute to AIDS treatment. AIDS is disease caused by HIV, a retrovirus that utilizes reverse transcription, during which RNA is converted to DNA. RNase H is essential for reverse transcription in HIV, and thus inhibition of RNase H could in turn inhibit transcription of HIV DNA.
Professor Park said, “This technology is applicable to detect various enzyme activities, as well as RNase H activity.” He continued, “I hope this technology could be widely used in research on enzyme related diseases.”
This study was funded by Global Frontier project and Mid-career Researcher Support project of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2017.11.28 View 7334 -
 New Photocatalyst Converts Carbon Dioxide to 99% Pure Fuel
(Professor Song, Ph.D. candidates Kim, and Lim (from left))
A KAIST research team led by Professor Hyunjoon Song of the Department of Chemistry developed a metal oxide nanocatalyst that converts carbon dioxide to 99% pure methane. This technology directly uses sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into methane, which is more efficient in terms of energy storage capacity, compared to the conventional way of storing the electricity produced by solar cells in batteries. The research team used cheap catalytic materials to significantly enhance the reaction efficiency and selectivity of the chemical energy storage method.
This research was conducted as a joint research project with Professor Ki Min Nam at Mokpo National University with co-first authors Dr. Kyung-Lyul Bae and Ph.D. candidates Jinmo Kim and Chan Kyu Lim. The study was published in Nature Communications on November 7.
Although there is growing interest in sunlight as an energy resource, its usage has been limited to daytime and the power output varies with the weather. If sunlight could be directly converted to chemical energy, such as fuel, the limitations of energy storage and its usage could be overcome. In particular, the usage of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide, a main cause of the greenhouse effect in our atmosphere, is of great interest since both energy and environmental issues can be addressed. However, the stability of carbon dioxide made it difficult to convert it to other molecules. Thus, there was a need for a catalyst with enhanced efficiency and selectivity.
Professor Song’s team synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles, often used in sun cream. The nanoparticles were then bound to copper oxide as single particles, forming a colloidal form of zinc oxide-copper oxide nanoparticles. Zinc oxides produce high energy electrons using light, and this energy is used to convert carbon dioxide into methane. Further, zinc oxide can also produce electrons with light and transfer the electrons to copper oxide. Similar to the principles of photosynthesis in leaves, the electron transfer reaction could be maintained for a long time. As a consequence, although the reaction was conducted in aqueous solution, methane of 99% purity could be obtained from carbon dioxide.
Conventional heterogeneous photocatalysts were in solid powder form with irregular structures and were not dispersed in water. Professor Song’s team used a nanochemical synthesis method to control the structure of the catalyst particles to be regular and maintained over a large surface area. This led to increasing carbon dioxide conversion activity by hundreds of fold in solution compared to existing catalysts.
Professor Song said, “A long time will be needed for the commercialization of the direct conversion reaction of carbon dioxide using sunlight. However, the precise control of catalyst structures at nanoscale would enhance the efficiency of photocatalyst reactions.” He continued, “Applying this method to various phtocatalysts will maximize the catalysts performance.”
(Figure 1. Scheme for carbon dioxide conversion reaction using nano photocatalyst in aqueous solution)
(Figure 2. Structure, photocatalytic CO2 conversion, and stability of ZnO-Cu2O nanocatalyst )
2017.11.13 View 9174
New Photocatalyst Converts Carbon Dioxide to 99% Pure Fuel
(Professor Song, Ph.D. candidates Kim, and Lim (from left))
A KAIST research team led by Professor Hyunjoon Song of the Department of Chemistry developed a metal oxide nanocatalyst that converts carbon dioxide to 99% pure methane. This technology directly uses sunlight to convert carbon dioxide into methane, which is more efficient in terms of energy storage capacity, compared to the conventional way of storing the electricity produced by solar cells in batteries. The research team used cheap catalytic materials to significantly enhance the reaction efficiency and selectivity of the chemical energy storage method.
This research was conducted as a joint research project with Professor Ki Min Nam at Mokpo National University with co-first authors Dr. Kyung-Lyul Bae and Ph.D. candidates Jinmo Kim and Chan Kyu Lim. The study was published in Nature Communications on November 7.
Although there is growing interest in sunlight as an energy resource, its usage has been limited to daytime and the power output varies with the weather. If sunlight could be directly converted to chemical energy, such as fuel, the limitations of energy storage and its usage could be overcome. In particular, the usage of sunlight to convert carbon dioxide, a main cause of the greenhouse effect in our atmosphere, is of great interest since both energy and environmental issues can be addressed. However, the stability of carbon dioxide made it difficult to convert it to other molecules. Thus, there was a need for a catalyst with enhanced efficiency and selectivity.
Professor Song’s team synthesized zinc oxide nanoparticles, often used in sun cream. The nanoparticles were then bound to copper oxide as single particles, forming a colloidal form of zinc oxide-copper oxide nanoparticles. Zinc oxides produce high energy electrons using light, and this energy is used to convert carbon dioxide into methane. Further, zinc oxide can also produce electrons with light and transfer the electrons to copper oxide. Similar to the principles of photosynthesis in leaves, the electron transfer reaction could be maintained for a long time. As a consequence, although the reaction was conducted in aqueous solution, methane of 99% purity could be obtained from carbon dioxide.
Conventional heterogeneous photocatalysts were in solid powder form with irregular structures and were not dispersed in water. Professor Song’s team used a nanochemical synthesis method to control the structure of the catalyst particles to be regular and maintained over a large surface area. This led to increasing carbon dioxide conversion activity by hundreds of fold in solution compared to existing catalysts.
Professor Song said, “A long time will be needed for the commercialization of the direct conversion reaction of carbon dioxide using sunlight. However, the precise control of catalyst structures at nanoscale would enhance the efficiency of photocatalyst reactions.” He continued, “Applying this method to various phtocatalysts will maximize the catalysts performance.”
(Figure 1. Scheme for carbon dioxide conversion reaction using nano photocatalyst in aqueous solution)
(Figure 2. Structure, photocatalytic CO2 conversion, and stability of ZnO-Cu2O nanocatalyst )
2017.11.13 View 9174 -
 Mutant Gene Network in Colon Cancer Identified
The principles of the gene network for colon tumorigenesis have been identified by a KAIST research team. The principles will be used to find the molecular target for effective anti-cancer drugs in the future. Further, this research gained attention for using a systems biology approach, which is an integrated research area of IT and BT.
The KAIST research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho for the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in the identification. Conducted by Dr. Dongkwan Shin and student researchers Jonghoon Lee and Jeong-Ryeol Gong, the research was published in Nature Communications online on November 2.
Human cancer is caused by genetic mutations. The frequency of the mutations differs by the type of cancer; for example, only around 10 mutations are found in leukemia and childhood cancer, but an average of 50 mutations are found in adult solid cancers and even hundreds of mutations are found in cancers due to external factors, such as with lung cancer.
Cancer researchers around the world are working to identify frequently found genetic mutations in patients, and in turn identify important cancer-inducing genes (called ‘driver genes’) to develop targets for anti-cancer drugs. However, gene mutations not only affect their own functions but also affect other genes through interactions. Therefore, there are limitations in current treatments targeting a few cancer-inducing genes without further knowledge on gene networks, hence current drugs are only effective in a few patients and often induce drug resistance.
Professor Cho’s team used large-scale genomic data from cancer patients to construct a mathematical model on the cooperative effects of multiple genetic mutations found in gene interaction networks. The basis of the model construction was The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) presented at the International Cancer Genome Consortium. The team successfully quantified the effects of mutations in gene networks to group colon cancer patients by clinical characteristics.
Further, the critical transition phenomenon that occurs in tumorigenesis was identified using large-scale computer simulation analysis, which was the first hidden gene network principle to be identified. Critical transition is the phenomenon in which the state of matter is suddenly changed through phase transition. It was not possible to identify the presence of transition phenomenon in the past, as it was difficult to track the sequence of gene mutations during tumorigenesis.
The research team used a systems biology-based research method to find that colon cancer tumorigenesis shows a critical transition phenomenon if the known driver gene mutations follow sequentially. Using the developed mathematical model, it can be possible to develop a new anti-cancer targeting drug that most effectively inhibits the effects of many gene mutations found in cancer patients. In particular, not only driver genes, but also other passenger genes affected by the gene mutations, could be evaluated to find the most effective drug targets.
Professor Cho said, “Little was known about the contribution of many gene mutations during tumorigenesis.” He continued, “In this research, a systems biology approach identified the principle of gene networks for the first time to suggest the possibility of anti-cancer drug target identification from a new perspective.”
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure1. Formation of giant clusters via mutation propagation
Figure2. Critical transition phenomenon by cooperative effect of mutations in tumorigenesis
2017.11.10 View 8612
Mutant Gene Network in Colon Cancer Identified
The principles of the gene network for colon tumorigenesis have been identified by a KAIST research team. The principles will be used to find the molecular target for effective anti-cancer drugs in the future. Further, this research gained attention for using a systems biology approach, which is an integrated research area of IT and BT.
The KAIST research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho for the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering succeeded in the identification. Conducted by Dr. Dongkwan Shin and student researchers Jonghoon Lee and Jeong-Ryeol Gong, the research was published in Nature Communications online on November 2.
Human cancer is caused by genetic mutations. The frequency of the mutations differs by the type of cancer; for example, only around 10 mutations are found in leukemia and childhood cancer, but an average of 50 mutations are found in adult solid cancers and even hundreds of mutations are found in cancers due to external factors, such as with lung cancer.
Cancer researchers around the world are working to identify frequently found genetic mutations in patients, and in turn identify important cancer-inducing genes (called ‘driver genes’) to develop targets for anti-cancer drugs. However, gene mutations not only affect their own functions but also affect other genes through interactions. Therefore, there are limitations in current treatments targeting a few cancer-inducing genes without further knowledge on gene networks, hence current drugs are only effective in a few patients and often induce drug resistance.
Professor Cho’s team used large-scale genomic data from cancer patients to construct a mathematical model on the cooperative effects of multiple genetic mutations found in gene interaction networks. The basis of the model construction was The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) presented at the International Cancer Genome Consortium. The team successfully quantified the effects of mutations in gene networks to group colon cancer patients by clinical characteristics.
Further, the critical transition phenomenon that occurs in tumorigenesis was identified using large-scale computer simulation analysis, which was the first hidden gene network principle to be identified. Critical transition is the phenomenon in which the state of matter is suddenly changed through phase transition. It was not possible to identify the presence of transition phenomenon in the past, as it was difficult to track the sequence of gene mutations during tumorigenesis.
The research team used a systems biology-based research method to find that colon cancer tumorigenesis shows a critical transition phenomenon if the known driver gene mutations follow sequentially. Using the developed mathematical model, it can be possible to develop a new anti-cancer targeting drug that most effectively inhibits the effects of many gene mutations found in cancer patients. In particular, not only driver genes, but also other passenger genes affected by the gene mutations, could be evaluated to find the most effective drug targets.
Professor Cho said, “Little was known about the contribution of many gene mutations during tumorigenesis.” He continued, “In this research, a systems biology approach identified the principle of gene networks for the first time to suggest the possibility of anti-cancer drug target identification from a new perspective.”
This research was funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Figure1. Formation of giant clusters via mutation propagation
Figure2. Critical transition phenomenon by cooperative effect of mutations in tumorigenesis
2017.11.10 View 8612 -
 Highly Flexible Organic Flash Memory for Foldable and Disposable Electronics
A KAIST team reported ultra-flexible organic flash memory that is bendable down to a radius of 300μm. The memory exhibits a significantly-long projected retention rate with a programming voltage on par with the present industrial standards.
A joint research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sung Gap Im of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering said that their memory technology can be applied to non-conventional substrates, such as plastics and papers, to demonstrate its feasibility over a wide range of applications.
With Dr. Seungwon Lee and Dr. Hanul Moon playing the role of leading authors, the research was published in Nature Communications on September 28.
Flash memory is a non-volatile, transistor-based data-storage device that has become essential in most electronic systems in daily life. With straightforward operation mechanisms and easy integration into NAND or NOR array architecture, flash memory has been established as the most successful and dominant non-volatile memory technology by far.
Despite promising demonstrations in the early stages of organic electronics, the overall progress in this field has been far slower than that of thin-film transistors (TFTs) or other devices based on flexible materials. It has been challenging, in particular, to develop flash memory that simultaneously exhibits a significant level of flexibility and performance. This is mainly due to the scarcity of flexible dielectric layers, which are responsible for the tunneling and blocking of charges.
The solution processing used for the preparation of most of the polymeric dielectric layers also makes it difficult to use them in flash memory due to the complexity involved in the formation of the bilayer dielectric structure, which is the key to flash memory operations.
The research team tried to overcome these hurdles and realize highly flexible flash memory by employing thin polymeric insulators grown with initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD), a vapor-phase growth technique for polymers that was previously shown to be promising for the fabrication of flexible TFTs. It was further shown that these iCVD-based polymeric insulators, when coupled with rational device design and material choice, can make a significant contribution to flash memory as well.
Memory using conventional polymer insulating films has often required a voltage as high as 100 V (volt) in order to attain long memory retention. If the device is made to operate at a low voltage, the short retention period of less than a month was problematic.
The KAIST team produced flash memory with programming voltages around 10 V and a projected data retention time of over 10 years, while maintaining its memory performance even at a mechanical strain of 2.8%. This is a significant improvement over the existing inorganic insulation layer-based flash memory that allowed only a 1% strain.
The team demonstrated the virtually foldable memory devices by fabricating the proposed flash memory on a 6-micrometer-thick ultrathin plastic film. In addition, it succeeded in producing them on printing paper, opening a way for disposable smart electronic products such as electronic paper and electronic business card.
Professor Yoo said, " This study well illustrates that even highly flexible flash memory can be made to have a practically viable level of performance, so that it contributes to full-fledged wearable electronic devices and smart electronic paper."
(Figure 1. Structure of flexible flash memory )
(Figure 2. Foldable flash memory)
2017.11.06 View 9575
Highly Flexible Organic Flash Memory for Foldable and Disposable Electronics
A KAIST team reported ultra-flexible organic flash memory that is bendable down to a radius of 300μm. The memory exhibits a significantly-long projected retention rate with a programming voltage on par with the present industrial standards.
A joint research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sung Gap Im of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering said that their memory technology can be applied to non-conventional substrates, such as plastics and papers, to demonstrate its feasibility over a wide range of applications.
With Dr. Seungwon Lee and Dr. Hanul Moon playing the role of leading authors, the research was published in Nature Communications on September 28.
Flash memory is a non-volatile, transistor-based data-storage device that has become essential in most electronic systems in daily life. With straightforward operation mechanisms and easy integration into NAND or NOR array architecture, flash memory has been established as the most successful and dominant non-volatile memory technology by far.
Despite promising demonstrations in the early stages of organic electronics, the overall progress in this field has been far slower than that of thin-film transistors (TFTs) or other devices based on flexible materials. It has been challenging, in particular, to develop flash memory that simultaneously exhibits a significant level of flexibility and performance. This is mainly due to the scarcity of flexible dielectric layers, which are responsible for the tunneling and blocking of charges.
The solution processing used for the preparation of most of the polymeric dielectric layers also makes it difficult to use them in flash memory due to the complexity involved in the formation of the bilayer dielectric structure, which is the key to flash memory operations.
The research team tried to overcome these hurdles and realize highly flexible flash memory by employing thin polymeric insulators grown with initiated chemical vapor deposition (iCVD), a vapor-phase growth technique for polymers that was previously shown to be promising for the fabrication of flexible TFTs. It was further shown that these iCVD-based polymeric insulators, when coupled with rational device design and material choice, can make a significant contribution to flash memory as well.
Memory using conventional polymer insulating films has often required a voltage as high as 100 V (volt) in order to attain long memory retention. If the device is made to operate at a low voltage, the short retention period of less than a month was problematic.
The KAIST team produced flash memory with programming voltages around 10 V and a projected data retention time of over 10 years, while maintaining its memory performance even at a mechanical strain of 2.8%. This is a significant improvement over the existing inorganic insulation layer-based flash memory that allowed only a 1% strain.
The team demonstrated the virtually foldable memory devices by fabricating the proposed flash memory on a 6-micrometer-thick ultrathin plastic film. In addition, it succeeded in producing them on printing paper, opening a way for disposable smart electronic products such as electronic paper and electronic business card.
Professor Yoo said, " This study well illustrates that even highly flexible flash memory can be made to have a practically viable level of performance, so that it contributes to full-fledged wearable electronic devices and smart electronic paper."
(Figure 1. Structure of flexible flash memory )
(Figure 2. Foldable flash memory)
2017.11.06 View 9575 -
 Highly Sensitive and Fast Indoor GNSS Signal Acquisition Technology
(Professor Seung-Hyun Kong (right) and Research Fellow Tae-Sun Kim)
A research team led by Professor Seung-Hyun Kong at the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation, KAIST, developed high-speed, high-sensitivity Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signal acquisition (search and detection) technology that can produce GNSS positioning fixes indoors.
Using the team’s new technology, GNSS signals will be sufficient to identify locations anywhere in the world, both indoors and outdoors. This new research finding was published in the international journal IEEE Signal Processing Magazine (IEEE SPM) this September.
Global Positioning System (GPS) developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1990s is the most widely-used satellite-based navigation system, and GNSS is a terminology to indicate conventional satellite based navigation systems, such as GPS and Russian GLONASS, as well as new satellite-based navigation systems under development, such as European GALILEO, Chinese COMPASS, and other regional satellite-based navigation systems.
In general, GNSS signals are transmitted all over the globe from 20,000 km above the Earth and thus a GNSS signal received by a small antennae in an outdoor environment has weak signal power. In addition, GNSS signals penetrating building walls become extremely weak so the signal can be less than 1/1000th of the signal power received outside.
Using conventional acquisition techniques including the frequency-domain correlation technique to acquire an extremely weak GNSS signal causes the computational cost to increase by over a million times and the processing time for acquisition also increases tremendously. Because of this, indoor measurement techniques using GNSS signals were considered practically impossible for the last 20 years.
To resolve such limitations, the research team developed a Synthesized Doppler-frequency Hypothesis Testing (SDHT) technique to dramatically reduce the acquisition time and computational load for extremely weak GNSS signals indoors.
In general, GNSS signal acquisition is a search process in which the instantaneous accurate code phase and Doppler frequency of the incoming GNSS signal are identified. However, the number of Doppler frequency hypotheses grows proportionally to the coherent correlation time that should be necessarily increased to detect weak signals. In practice, the coherent correlation time should be more than 1000 times longer for extremely weak GNSS signals so the number of Doppler frequency hypotheses is greater than 20,000. On the other hand, the SDHT algorithm indirectly tests the Doppler frequency hypothesis utilizing the coherent correlation results of neighboring hypotheses.
Therefore, using SDHT, only around 20 hypotheses are tested using conventional correlation techniques and the remaining 19,980 hypotheses are calculated with simple mathematical operations. As a result, SDHT achieves a huge computational cost reduction (by about 1000 times) and is 800 times faster for signal acquisition compared to conventional techniques. This means only about 15 seconds is required to detect extremely weak GNSS signals in buildings using a personal computer.
The team predicts further studies for strengthening SDHT technology and developing positioning systems robust enough to multipath in indoor environments will allow indoor GNSS measurements within several seconds inside most buildings using GNSS alone.
Professor Kong said, “This development made us the leader in indoor GNSS positioning technology in the world.” He continued, “We hope to commercialize indoor GNSS systems to create a new market.” The research team is currently registering a patent in Korea and applying for patents overseas, as well as planning to commercialize the technology with the help of the Institute for Startup KAIST.
(Figure1. Positioning Results for the GPS Indoor Positioning System using SDHT Technology)
2017.11.02 View 7574
Highly Sensitive and Fast Indoor GNSS Signal Acquisition Technology
(Professor Seung-Hyun Kong (right) and Research Fellow Tae-Sun Kim)
A research team led by Professor Seung-Hyun Kong at the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation, KAIST, developed high-speed, high-sensitivity Global Navigation Satellite System (GNSS) signal acquisition (search and detection) technology that can produce GNSS positioning fixes indoors.
Using the team’s new technology, GNSS signals will be sufficient to identify locations anywhere in the world, both indoors and outdoors. This new research finding was published in the international journal IEEE Signal Processing Magazine (IEEE SPM) this September.
Global Positioning System (GPS) developed by the U.S. Department of Defense in the 1990s is the most widely-used satellite-based navigation system, and GNSS is a terminology to indicate conventional satellite based navigation systems, such as GPS and Russian GLONASS, as well as new satellite-based navigation systems under development, such as European GALILEO, Chinese COMPASS, and other regional satellite-based navigation systems.
In general, GNSS signals are transmitted all over the globe from 20,000 km above the Earth and thus a GNSS signal received by a small antennae in an outdoor environment has weak signal power. In addition, GNSS signals penetrating building walls become extremely weak so the signal can be less than 1/1000th of the signal power received outside.
Using conventional acquisition techniques including the frequency-domain correlation technique to acquire an extremely weak GNSS signal causes the computational cost to increase by over a million times and the processing time for acquisition also increases tremendously. Because of this, indoor measurement techniques using GNSS signals were considered practically impossible for the last 20 years.
To resolve such limitations, the research team developed a Synthesized Doppler-frequency Hypothesis Testing (SDHT) technique to dramatically reduce the acquisition time and computational load for extremely weak GNSS signals indoors.
In general, GNSS signal acquisition is a search process in which the instantaneous accurate code phase and Doppler frequency of the incoming GNSS signal are identified. However, the number of Doppler frequency hypotheses grows proportionally to the coherent correlation time that should be necessarily increased to detect weak signals. In practice, the coherent correlation time should be more than 1000 times longer for extremely weak GNSS signals so the number of Doppler frequency hypotheses is greater than 20,000. On the other hand, the SDHT algorithm indirectly tests the Doppler frequency hypothesis utilizing the coherent correlation results of neighboring hypotheses.
Therefore, using SDHT, only around 20 hypotheses are tested using conventional correlation techniques and the remaining 19,980 hypotheses are calculated with simple mathematical operations. As a result, SDHT achieves a huge computational cost reduction (by about 1000 times) and is 800 times faster for signal acquisition compared to conventional techniques. This means only about 15 seconds is required to detect extremely weak GNSS signals in buildings using a personal computer.
The team predicts further studies for strengthening SDHT technology and developing positioning systems robust enough to multipath in indoor environments will allow indoor GNSS measurements within several seconds inside most buildings using GNSS alone.
Professor Kong said, “This development made us the leader in indoor GNSS positioning technology in the world.” He continued, “We hope to commercialize indoor GNSS systems to create a new market.” The research team is currently registering a patent in Korea and applying for patents overseas, as well as planning to commercialize the technology with the help of the Institute for Startup KAIST.
(Figure1. Positioning Results for the GPS Indoor Positioning System using SDHT Technology)
2017.11.02 View 7574 -
 Platinum Single Atom Catalysts for 'Direct Formic Acid Fuel Cells'
(Professor Hyunjoo Lee (left) and Ph.D. candidate Jiwhan Kim)
A research team co-led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST and Professor Jeong Woo Han from the University of Seoul synthesized highly stable high-Pt-content single atom catalysts for direct formic acid fuel cells. The amount of platinum can be reduced to 1/10 of that of conventional platinum nanoparticle catalysts.
Platinum (Pt) catalysts have been used in various catalytic reactions due to their high activity and stability. However, because Pt is rare and expensive, it is important to reduce the amount of Pt used. Pt single atom catalysts can reduce the size of the Pt particles to the size of an atom. Thus, the cost of Pt catalysts can be minimized because all of the Pt atoms can participate in the catalytic reactions. Additionally, single atom catalysts have no ensemble site in which two or more atoms are attached, and thus, the reaction selectivity is different from that of nanoparticle catalysts.
Despite these advantages, single atom catalysts are easily aggregated and less stable due to their low coordination number and high surface free energy. It is difficult to develop a single atom catalyst with high content and high stability, and thus, its application in practical devices is limited.
Direct formic acid fuel cells can be an energy source for next-generation portable devices because liquid formic acid as a fuel is safer and easier to store and transport than high-pressure hydrogen gas.
To improve the stability of Pt single atom catalysts, Professor Lee’s group developed a Pt-Sn single atom alloy structure on an antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO) support. This structure has been proven by computational calculations which show that Pt single atoms substitute antimony sites in the antimony-tin alloy structure and are thermodynamically stable. This catalyst has been shown to have a higher activity up to 50 times per weight of Pt than that of the commercial catalyst, Pt/C, in the oxidation of formic acid, and the stability of the catalyst was also remarkably high.
Professor Lee’s group also used a single atomic catalyst in a 'direct formic acid fuel cell’ consisting of membranes and electrodes. It is the first attempt to apply a single atomic catalyst to a full cell. In this case, an output similar to that of the commercial catalyst could be obtained by using 1/10 of the platinum compared to the commercial Pt/C catalyst.
Ph.D. candidate Jiwhan Kim from KAIST was the first author of the research. This research was published online on September 11 in Advanced Energy Materials.
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Electronics Future Technology Development Center.
(Figure 1. Concept photograph for Pt single atom catalysts.)
(Figure 2. Pt single atom catalysts by HAADF-STEM analysis (bright white circles))
2017.10.31 View 8028
Platinum Single Atom Catalysts for 'Direct Formic Acid Fuel Cells'
(Professor Hyunjoo Lee (left) and Ph.D. candidate Jiwhan Kim)
A research team co-led by Professor Hyunjoo Lee at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST and Professor Jeong Woo Han from the University of Seoul synthesized highly stable high-Pt-content single atom catalysts for direct formic acid fuel cells. The amount of platinum can be reduced to 1/10 of that of conventional platinum nanoparticle catalysts.
Platinum (Pt) catalysts have been used in various catalytic reactions due to their high activity and stability. However, because Pt is rare and expensive, it is important to reduce the amount of Pt used. Pt single atom catalysts can reduce the size of the Pt particles to the size of an atom. Thus, the cost of Pt catalysts can be minimized because all of the Pt atoms can participate in the catalytic reactions. Additionally, single atom catalysts have no ensemble site in which two or more atoms are attached, and thus, the reaction selectivity is different from that of nanoparticle catalysts.
Despite these advantages, single atom catalysts are easily aggregated and less stable due to their low coordination number and high surface free energy. It is difficult to develop a single atom catalyst with high content and high stability, and thus, its application in practical devices is limited.
Direct formic acid fuel cells can be an energy source for next-generation portable devices because liquid formic acid as a fuel is safer and easier to store and transport than high-pressure hydrogen gas.
To improve the stability of Pt single atom catalysts, Professor Lee’s group developed a Pt-Sn single atom alloy structure on an antimony-doped tin oxide (ATO) support. This structure has been proven by computational calculations which show that Pt single atoms substitute antimony sites in the antimony-tin alloy structure and are thermodynamically stable. This catalyst has been shown to have a higher activity up to 50 times per weight of Pt than that of the commercial catalyst, Pt/C, in the oxidation of formic acid, and the stability of the catalyst was also remarkably high.
Professor Lee’s group also used a single atomic catalyst in a 'direct formic acid fuel cell’ consisting of membranes and electrodes. It is the first attempt to apply a single atomic catalyst to a full cell. In this case, an output similar to that of the commercial catalyst could be obtained by using 1/10 of the platinum compared to the commercial Pt/C catalyst.
Ph.D. candidate Jiwhan Kim from KAIST was the first author of the research. This research was published online on September 11 in Advanced Energy Materials.
This research was carried out with the support of the Samsung Electronics Future Technology Development Center.
(Figure 1. Concept photograph for Pt single atom catalysts.)
(Figure 2. Pt single atom catalysts by HAADF-STEM analysis (bright white circles))
2017.10.31 View 8028 -
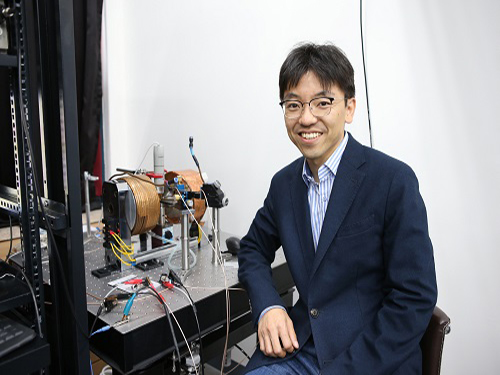 High-Speed Motion Core Technology for Magnetic Memory
(Professor Kab-Jin Kim of the Department of Physics)
A joint research team led by Professor Kab-Jin Kim of the Department of Physics, KAIST and Professor Kyung-Jin Lee at Korea University developed technology to dramatically enhance the speed of next generation domain wall-based magnetic memory. This research was published online in Nature Materials on September 25.
Currently-used memory materials, D-RAM and S-RAM, are fast but volatile, leading to memory loss when the power is switched off. Flash memory is non-volatile but slow, while hard disk drives (HDD) have greater storage but are high in energy usage and weak in physical shock tolerance.
To overcome the limitations of existing memory materials, ‘domain wall-based, magnetic memory’ is being researched. The core mechanism of domain wall magnetic memory is the movement of a domain wall by the current. Non-volatility is secured by using magnetic nanowires and the lack of mechanical rotation reduced power usage. This is a new form of high density, low power next-generation memory.
However, previous studies showed the speed limit of domain wall memory to be hundreds m/s at maximum due to the ‘Walker breakdown phenomenon’, which refers to velocity breakdown from the angular precession of a domain wall. Therefore, there was a need to develop core technology to remove the Walker breakdown phenomenon and increase the speed for the commercialization of domain wall memory.
Most domain wall memory studies used ferromagnetic bodies, which cannot overcome the Walker breakdown phenomenon. The team discovered that the use of ‘ferrimagnetic‘ GdFeCo at certain conditions could overcome the Walker breakdown phenomenon and using this mechanism they could increase domain wall speed to over 2Km/s at room temperature.
Domain wall memory is high-density, low-power, and non-volatile memory. The memory could be the leading next-generation memory with the addition of the high speed property discovered in this research.
Professor Kim said, “This research is significant in discovering a new physical phenomenon at the point at which the angular momentum of a ferrimagnetic body is 0 and it is expected to advance the implementation of next-generation memory in the future.”
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (MSIP) (No. 2017R1C1B2009686, NRF-2016R1A5A1008184) and by the DGIST R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (17-BT-02).
(Figure 1. Concept Map of Domain Wall Memory Material using Ferrimagnetic Body)
(Figure 2. Scheme and Experimental Results of Domain Wall Speed Measurements)
2017.10.30 View 9430
High-Speed Motion Core Technology for Magnetic Memory
(Professor Kab-Jin Kim of the Department of Physics)
A joint research team led by Professor Kab-Jin Kim of the Department of Physics, KAIST and Professor Kyung-Jin Lee at Korea University developed technology to dramatically enhance the speed of next generation domain wall-based magnetic memory. This research was published online in Nature Materials on September 25.
Currently-used memory materials, D-RAM and S-RAM, are fast but volatile, leading to memory loss when the power is switched off. Flash memory is non-volatile but slow, while hard disk drives (HDD) have greater storage but are high in energy usage and weak in physical shock tolerance.
To overcome the limitations of existing memory materials, ‘domain wall-based, magnetic memory’ is being researched. The core mechanism of domain wall magnetic memory is the movement of a domain wall by the current. Non-volatility is secured by using magnetic nanowires and the lack of mechanical rotation reduced power usage. This is a new form of high density, low power next-generation memory.
However, previous studies showed the speed limit of domain wall memory to be hundreds m/s at maximum due to the ‘Walker breakdown phenomenon’, which refers to velocity breakdown from the angular precession of a domain wall. Therefore, there was a need to develop core technology to remove the Walker breakdown phenomenon and increase the speed for the commercialization of domain wall memory.
Most domain wall memory studies used ferromagnetic bodies, which cannot overcome the Walker breakdown phenomenon. The team discovered that the use of ‘ferrimagnetic‘ GdFeCo at certain conditions could overcome the Walker breakdown phenomenon and using this mechanism they could increase domain wall speed to over 2Km/s at room temperature.
Domain wall memory is high-density, low-power, and non-volatile memory. The memory could be the leading next-generation memory with the addition of the high speed property discovered in this research.
Professor Kim said, “This research is significant in discovering a new physical phenomenon at the point at which the angular momentum of a ferrimagnetic body is 0 and it is expected to advance the implementation of next-generation memory in the future.”
This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea Government (MSIP) (No. 2017R1C1B2009686, NRF-2016R1A5A1008184) and by the DGIST R&D Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (17-BT-02).
(Figure 1. Concept Map of Domain Wall Memory Material using Ferrimagnetic Body)
(Figure 2. Scheme and Experimental Results of Domain Wall Speed Measurements)
2017.10.30 View 9430 -
 Development of a Highly-Accurate Computational Model of Human Metabolism
A research team from KAIST developed a computational framework that enables the reconstruction of a comprehensive computational model of human metabolism, which allows for an accurate prediction of personal metabolic features (or phenotypes).
Understanding personal metabolic phenotypes allows us to design effective therapeutic strategies for various chronic and infectious diseases. A human computational model called the genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) contains information on thousands of metabolic genes and their corresponding reactions and metabolites, and has played an important role in predicting metabolic phenotypes. Although several versions of human GEMs have been released, they had room for further development, especially as to incorporating biological information coming from a human genetics mechanism called “alternative splicing.” Alternative splicing is a genetic mechanism that allows a gene to give rise to multiple reactions, and is strongly associated with pathology.
To tackle this problem, Jae Yong Ryu (a Ph.D. student), Dr. Hyun Uk Kim (Research Fellow), and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, all from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, developed a computational framework that systematically generates metabolic reactions, and adds them to the human GEM. The resulting human GEM was demonstrated to accurately predict metabolic phenotypes under varied environmental conditions. The research results were published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on October 24, 2017, under the title “Framework and resource for more than 11,000 gene-transcript-protein-reaction associations in human metabolism.”
The research team first updated the biological contents of a previous version of the human GEM. The updated biological contents include metabolic genes and their corresponding metabolites and reactions. In particular, metabolic reactions catalyzed by already-known protein isoforms were additionally incorporated into the human GEM; protein isoforms are multiple variants of proteins generated from individual genes through the alternative splicing process. Each protein isoform is often responsible for the operation of a metabolic reaction. Although multiple protein isoforms generated from one gene can play different functions by having different sets of protein domains and/or subcellular localizations, such information was not properly considered in previous versions of human GEMs.
Upon the initial update of the human GEM, named Recon 2M.1, the research team subsequently implemented a computational framework that systematically generates information on Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA) in order to identify protein isoforms that were previously not identified. This framework was developed in this study. As a result of the implementation of the framework for GeTPRA, more than 11,000 GeTPRA were automatically predicted, and thoroughly validated. Additional metabolic reactions were then added to Recon 2M.1 based on the predicted GeTPRA for the previously uncharacterized protein isoforms; Recon 2M.1 was renamed Recon 2M.2 from this upgrade.
Finally, Recon 2M.2 was integrated with 446 sets of personal biological data (RNA-Seq data) in order to build patient-specific cancer models. These patient-specific cancer models were used to predict cancer metabolism activities and anticancer targets.
The development of a new version of human GEMs along with the computational framework for GeTPRA is expected to boost studies in fundamental human genetics and medicine. Model files of the human GEMs Recon 2M.1 and 2M.2, a full list of the GeTPRA and the source code for the computational framework to predict the GeTPRA are all available as part of the publication of this study.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “The predicted GeTPRA from the computational framework is expected to serve as a guideline for future experiments on human genetics and biochemistry, whereas the resulting Recon 2M.2 can be used to predict drug targets for various human diseases.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
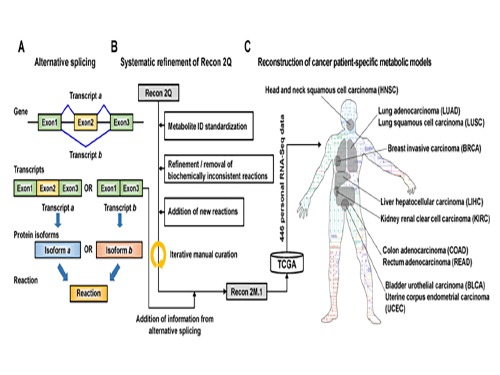
(Figure 1:A scheme of Recon 2M.1 development and its use in reconstructing personal genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs). (A) A concept of alternative splicing of human genes and its use in Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA) of Recon 2M.1. (B) A procedure of systematic refinement of the Recon 2Q. Recon 2Q is one of the previously released human GEMs. Biochemically inconsistent reactions include unbalanced, artificial, blocked, and/or redundant reactions. Iterative manual curation was conducted while validating the Recon 2M.1. (C) Reconstruction of cancer patient-specific GEMs using Recon 2M.1 for further simulation studies. In this study, personal biological data (RNA-Seq data) were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA; https://cancergenome.nih.gov/ ) across the ten cancer types.
(Figure 2: Computational framework for the systematic generation of Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA; red box in the flowchart). Peptide sequences of metabolic genes defined in Recon 2M.1 were retrieved from a database called Ensembl. EC numbers and subcellular localizations of all the protein isoforms of metabolic genes in Recon 2M.1 were predicted using software programs EFICAz2.5 and Wolf PSort, respectively. Information on the newly predicted GeTPRA was systematically incorporated into the Recon 2M.1, thereby resulting in Recon 2M.2.)
2017.10.25 View 10868
Development of a Highly-Accurate Computational Model of Human Metabolism
A research team from KAIST developed a computational framework that enables the reconstruction of a comprehensive computational model of human metabolism, which allows for an accurate prediction of personal metabolic features (or phenotypes).
Understanding personal metabolic phenotypes allows us to design effective therapeutic strategies for various chronic and infectious diseases. A human computational model called the genome-scale metabolic model (GEM) contains information on thousands of metabolic genes and their corresponding reactions and metabolites, and has played an important role in predicting metabolic phenotypes. Although several versions of human GEMs have been released, they had room for further development, especially as to incorporating biological information coming from a human genetics mechanism called “alternative splicing.” Alternative splicing is a genetic mechanism that allows a gene to give rise to multiple reactions, and is strongly associated with pathology.
To tackle this problem, Jae Yong Ryu (a Ph.D. student), Dr. Hyun Uk Kim (Research Fellow), and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, all from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, developed a computational framework that systematically generates metabolic reactions, and adds them to the human GEM. The resulting human GEM was demonstrated to accurately predict metabolic phenotypes under varied environmental conditions. The research results were published online in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) on October 24, 2017, under the title “Framework and resource for more than 11,000 gene-transcript-protein-reaction associations in human metabolism.”
The research team first updated the biological contents of a previous version of the human GEM. The updated biological contents include metabolic genes and their corresponding metabolites and reactions. In particular, metabolic reactions catalyzed by already-known protein isoforms were additionally incorporated into the human GEM; protein isoforms are multiple variants of proteins generated from individual genes through the alternative splicing process. Each protein isoform is often responsible for the operation of a metabolic reaction. Although multiple protein isoforms generated from one gene can play different functions by having different sets of protein domains and/or subcellular localizations, such information was not properly considered in previous versions of human GEMs.
Upon the initial update of the human GEM, named Recon 2M.1, the research team subsequently implemented a computational framework that systematically generates information on Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA) in order to identify protein isoforms that were previously not identified. This framework was developed in this study. As a result of the implementation of the framework for GeTPRA, more than 11,000 GeTPRA were automatically predicted, and thoroughly validated. Additional metabolic reactions were then added to Recon 2M.1 based on the predicted GeTPRA for the previously uncharacterized protein isoforms; Recon 2M.1 was renamed Recon 2M.2 from this upgrade.
Finally, Recon 2M.2 was integrated with 446 sets of personal biological data (RNA-Seq data) in order to build patient-specific cancer models. These patient-specific cancer models were used to predict cancer metabolism activities and anticancer targets.
The development of a new version of human GEMs along with the computational framework for GeTPRA is expected to boost studies in fundamental human genetics and medicine. Model files of the human GEMs Recon 2M.1 and 2M.2, a full list of the GeTPRA and the source code for the computational framework to predict the GeTPRA are all available as part of the publication of this study.
Distinguished Professor Lee said, “The predicted GeTPRA from the computational framework is expected to serve as a guideline for future experiments on human genetics and biochemistry, whereas the resulting Recon 2M.2 can be used to predict drug targets for various human diseases.”
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012M1A2A2026556 and NRF-2012M1A2A2026557) from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
(Figure 1:A scheme of Recon 2M.1 development and its use in reconstructing personal genome-scale metabolic models (GEMs). (A) A concept of alternative splicing of human genes and its use in Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA) of Recon 2M.1. (B) A procedure of systematic refinement of the Recon 2Q. Recon 2Q is one of the previously released human GEMs. Biochemically inconsistent reactions include unbalanced, artificial, blocked, and/or redundant reactions. Iterative manual curation was conducted while validating the Recon 2M.1. (C) Reconstruction of cancer patient-specific GEMs using Recon 2M.1 for further simulation studies. In this study, personal biological data (RNA-Seq data) were obtained from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA; https://cancergenome.nih.gov/ ) across the ten cancer types.
(Figure 2: Computational framework for the systematic generation of Gene-Transcript-Protein-Reaction Associations (GeTPRA; red box in the flowchart). Peptide sequences of metabolic genes defined in Recon 2M.1 were retrieved from a database called Ensembl. EC numbers and subcellular localizations of all the protein isoforms of metabolic genes in Recon 2M.1 were predicted using software programs EFICAz2.5 and Wolf PSort, respectively. Information on the newly predicted GeTPRA was systematically incorporated into the Recon 2M.1, thereby resulting in Recon 2M.2.)
2017.10.25 View 10868 -
 Ultra-Fast and Ultra-Sensitive Hydrogen Sensor
(From left: Professor Kim, Ph.D. candidate Koo, and Professor Penner)
A KAIST team made an ultra-fast hydrogen sensor that can detect hydrogen gas levels under 1% in less than seven seconds. The sensor also can detect hundreds of parts per million levels of hydrogen gas within 60 seconds at room temperature.
A research group under Professor Il-Doo Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, in collaboration with Professor Reginald M. Penner of the University of California-Irvine, has developed an ultra-fast hydrogen gas detection system based on a palladium (Pd) nanowire array coated with a metal-organic framework (MOF).
Hydrogen has been regarded as an eco-friendly next-generation energy source. However, it is a flammable gas that can explode even with a small spark. For safety, the lower explosion limit for hydrogen gas is 4 vol% so sensors should be able to detect the colorless and odorless hydrogen molecule quickly. The importance of sensors capable of rapidly detecting colorless and odorless hydrogen gas has been emphasized in recent guidelines issued by the U.S. Department of Energy. According to the guidelines, hydrogen sensors should detect 1 vol% of hydrogen in air in less than 60 seconds for adequate response and recovery times.
To overcome the limitations of Pd-based hydrogen sensors, the research team introduced a MOF layer on top of a Pd nanowire array. Lithographically patterned Pd nanowires were simply overcoated with a Zn-based zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) layer composed of Zn ions and organic ligands. ZIF-8 film is easily coated on Pd nanowires by simple dipping (for 2–6 hours) in a methanol solution including Zn (NO3)2·6H2O and 2-methylimidazole.
(This cover image depicts lithographically-patterned Pd nanowires overcoated with a Zn-based zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) layer.)
As synthesized ZIF-8 is a highly porous material composed of a number of micro-pores of 0.34 nm and 1.16 nm, hydrogen gas with a kinetic diameter of 0.289 nm can easily penetrate inside the ZIF-8 membrane, while large molecules (> 0.34 nm) are effectively screened by the MOF filter. Thus, the ZIF-8 filter on the Pd nanowires allows the predominant penetration of hydrogen molecules, leading to the acceleration of Pd-based H2 sensors with a 20-fold faster recovery and response speed compared to pristine Pd nanowires at room temperature.
Professor Kim expects that the ultra-fast hydrogen sensor can be useful for the prevention of explosion accidents caused by the leakage of hydrogen gas. In addition, he expects that other harmful gases in the air can be accurately detected through effective nano-filtration by using of a variety of MOF layers.
This study was carried out by Ph.D. candidate Won-Tae Koo (first author), Professor Kim (co-corresponding author), and Professor Penner (co-corresponding author). The study has been published in the online edition of ACS Nano, as the cover-featured image for the September issue.
Figure 1. Representative image for this paper published in ACS Nano, August, 18.
Figure 2. Images of Pd nanowire array-based hydrogen sensors, scanning electron microscopy image of a Pd nanowire covered by a metal-organic framework layer, and the hydrogen sensing properties of the sensors.
Figure 3. Schematic illustration of a metal-organic framework (MOF). The MOF, consisting of metal ions and organic ligands, is a highly porous material with an ultrahigh surface area. The various structures of MOFs can be synthesized depending on the kinds of metal ions and organic ligands.
2017.09.28 View 11569
Ultra-Fast and Ultra-Sensitive Hydrogen Sensor
(From left: Professor Kim, Ph.D. candidate Koo, and Professor Penner)
A KAIST team made an ultra-fast hydrogen sensor that can detect hydrogen gas levels under 1% in less than seven seconds. The sensor also can detect hundreds of parts per million levels of hydrogen gas within 60 seconds at room temperature.
A research group under Professor Il-Doo Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, in collaboration with Professor Reginald M. Penner of the University of California-Irvine, has developed an ultra-fast hydrogen gas detection system based on a palladium (Pd) nanowire array coated with a metal-organic framework (MOF).
Hydrogen has been regarded as an eco-friendly next-generation energy source. However, it is a flammable gas that can explode even with a small spark. For safety, the lower explosion limit for hydrogen gas is 4 vol% so sensors should be able to detect the colorless and odorless hydrogen molecule quickly. The importance of sensors capable of rapidly detecting colorless and odorless hydrogen gas has been emphasized in recent guidelines issued by the U.S. Department of Energy. According to the guidelines, hydrogen sensors should detect 1 vol% of hydrogen in air in less than 60 seconds for adequate response and recovery times.
To overcome the limitations of Pd-based hydrogen sensors, the research team introduced a MOF layer on top of a Pd nanowire array. Lithographically patterned Pd nanowires were simply overcoated with a Zn-based zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) layer composed of Zn ions and organic ligands. ZIF-8 film is easily coated on Pd nanowires by simple dipping (for 2–6 hours) in a methanol solution including Zn (NO3)2·6H2O and 2-methylimidazole.
(This cover image depicts lithographically-patterned Pd nanowires overcoated with a Zn-based zeolite imidazole framework (ZIF-8) layer.)
As synthesized ZIF-8 is a highly porous material composed of a number of micro-pores of 0.34 nm and 1.16 nm, hydrogen gas with a kinetic diameter of 0.289 nm can easily penetrate inside the ZIF-8 membrane, while large molecules (> 0.34 nm) are effectively screened by the MOF filter. Thus, the ZIF-8 filter on the Pd nanowires allows the predominant penetration of hydrogen molecules, leading to the acceleration of Pd-based H2 sensors with a 20-fold faster recovery and response speed compared to pristine Pd nanowires at room temperature.
Professor Kim expects that the ultra-fast hydrogen sensor can be useful for the prevention of explosion accidents caused by the leakage of hydrogen gas. In addition, he expects that other harmful gases in the air can be accurately detected through effective nano-filtration by using of a variety of MOF layers.
This study was carried out by Ph.D. candidate Won-Tae Koo (first author), Professor Kim (co-corresponding author), and Professor Penner (co-corresponding author). The study has been published in the online edition of ACS Nano, as the cover-featured image for the September issue.
Figure 1. Representative image for this paper published in ACS Nano, August, 18.
Figure 2. Images of Pd nanowire array-based hydrogen sensors, scanning electron microscopy image of a Pd nanowire covered by a metal-organic framework layer, and the hydrogen sensing properties of the sensors.
Figure 3. Schematic illustration of a metal-organic framework (MOF). The MOF, consisting of metal ions and organic ligands, is a highly porous material with an ultrahigh surface area. The various structures of MOFs can be synthesized depending on the kinds of metal ions and organic ligands.
2017.09.28 View 11569 -
 Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Cancer Therapy Using BR Nanoparticles
(Professor Sangyong Jon and PhD Candidate Dong Yun Lee)
Sangyong Jon, a professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and his team developed combined photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy for cancer by using Bilirubin (BR) nanoparticles.
The research team applied the properties of a bile pigment called BR, which exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, to this research.
The team expects this research, which shows high biocompatibility as well as outstanding photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy, to be an appropriate system in the field of treatment for cancer.
In the past, the research team developed a PEGylated bilirubin-based nanoparticle system by combining water-insoluble BR with water-soluble Polyethylene Glycol (PEG).
This technology facilitated BR exerting antioxidants yet prevented them from being accumulated in the body. Its efficiency and safety was identified in an animal disease model, for conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, islet cell transportation, and asthma.
Differing from previous research methods, this research applied the different physicochemical properties of BR to cancer treatment.
When the causative agent of jaundice, yellow BR, is exposed to a certain wavelength of blue light, the agent becomes a photonic nanomaterial as it responses to the light. This light-responsive nanomaterial can be used to cure jaundice because it allows for active excretion in infants.
Secondly, the team identified that BR is a major component of black pigment gallstones which can be often found in gall bladders or bile ducts under certain pathological conditions. The findings show that BR forms black pigment gallstones without the role of an intermediate or cation, such as calcium and copper. The research team combined cisplatin, a platinum metal-based anticancer drug, with BR so that BR nanoparticles changed the solution color from yellow to purple.
The team also examined the possibility of cisplatin-chelated BR nanoparticles as a probe for photoacoustic images. They found that considerable photoacoustic activity was shown when it was exposed to near infrared light. In fact, the photoacoustic signal was increased significantly in tumors of animals with colorectal cancer when the nanoparticles were administered to it intravenously. The team expects a more accurate diagnosis of tumors through this technology.
Moreover, the team assessed the photothermal effects of cisplatin-chelated BR nanoparticles. The research showed that the temperature of tumors increased by 25 degrees Celsius within five minutes when they were exposed to near infrared light, due to the photothermal effect. After two weeks, their size was reduced compared to that of other groups, and sometimes the tumors were even necrotized.
Professor Jon said, “Existing substances have a low biocompatibility and limitation for clinical therapy because they are artificially oriented; therefore, they might have toxicity. I am hoping that these cisplatin-chelated BR-based nanoparticles will provide a new platform for preclinical, translational research and clinical adaptation of the photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy.”
The paper (Dong Yun Lee as a first author) was published online in the renowned journal in the field of applied chemistry, Angewandte Chemi International Edition, on September 4. This research was sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
(Schematic diagram of the research)
(From left: Bilirubin nanoparticles, cisplatin-chelated Bilirubin nanoparticles)
2017.09.26 View 9639
Photoacoustic Imaging and Photothermal Cancer Therapy Using BR Nanoparticles
(Professor Sangyong Jon and PhD Candidate Dong Yun Lee)
Sangyong Jon, a professor in the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST, and his team developed combined photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy for cancer by using Bilirubin (BR) nanoparticles.
The research team applied the properties of a bile pigment called BR, which exerts potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, to this research.
The team expects this research, which shows high biocompatibility as well as outstanding photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy, to be an appropriate system in the field of treatment for cancer.
In the past, the research team developed a PEGylated bilirubin-based nanoparticle system by combining water-insoluble BR with water-soluble Polyethylene Glycol (PEG).
This technology facilitated BR exerting antioxidants yet prevented them from being accumulated in the body. Its efficiency and safety was identified in an animal disease model, for conditions such as inflammatory bowel disease, islet cell transportation, and asthma.
Differing from previous research methods, this research applied the different physicochemical properties of BR to cancer treatment.
When the causative agent of jaundice, yellow BR, is exposed to a certain wavelength of blue light, the agent becomes a photonic nanomaterial as it responses to the light. This light-responsive nanomaterial can be used to cure jaundice because it allows for active excretion in infants.
Secondly, the team identified that BR is a major component of black pigment gallstones which can be often found in gall bladders or bile ducts under certain pathological conditions. The findings show that BR forms black pigment gallstones without the role of an intermediate or cation, such as calcium and copper. The research team combined cisplatin, a platinum metal-based anticancer drug, with BR so that BR nanoparticles changed the solution color from yellow to purple.
The team also examined the possibility of cisplatin-chelated BR nanoparticles as a probe for photoacoustic images. They found that considerable photoacoustic activity was shown when it was exposed to near infrared light. In fact, the photoacoustic signal was increased significantly in tumors of animals with colorectal cancer when the nanoparticles were administered to it intravenously. The team expects a more accurate diagnosis of tumors through this technology.
Moreover, the team assessed the photothermal effects of cisplatin-chelated BR nanoparticles. The research showed that the temperature of tumors increased by 25 degrees Celsius within five minutes when they were exposed to near infrared light, due to the photothermal effect. After two weeks, their size was reduced compared to that of other groups, and sometimes the tumors were even necrotized.
Professor Jon said, “Existing substances have a low biocompatibility and limitation for clinical therapy because they are artificially oriented; therefore, they might have toxicity. I am hoping that these cisplatin-chelated BR-based nanoparticles will provide a new platform for preclinical, translational research and clinical adaptation of the photoacoustic imaging and photothermal therapy.”
The paper (Dong Yun Lee as a first author) was published online in the renowned journal in the field of applied chemistry, Angewandte Chemi International Edition, on September 4. This research was sponsored by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
(Schematic diagram of the research)
(From left: Bilirubin nanoparticles, cisplatin-chelated Bilirubin nanoparticles)
2017.09.26 View 9639 -
 Unlocking the Keys to Parkinson's Disease
A KAIST research team has identified a new mechanism that causes the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, namely tremors, rigidity, and loss of voluntary movement.
The discovery, made in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, presents a new perspective to three decades of conventional wisdom in Parkinson’s disease research. It also opens up new avenues that can help alleviate the motor problems suffered by patients of the disease, which reportedly number more than 10 million worldwide. The research was published in Neuron on August 30.
The research team was led by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Professor George Augustine from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at NTU. Dr. Jeongjin Kim, a former postdoctoral fellow at KAIST who now works at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), is the lead author.
It is known that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that transmits neural signals. However, it remains unknown how the disease causes the motor
Smooth, voluntary movements, such as reaching for a cup of coffee, are controlled by the basal ganglia, which issue instructions via neurons (nerve cells that process and transmit information in the brain) in the thalamus to the cortex. These instructions come in two types: one that triggers a response (excitatory signals) and the other that suppresses a response (inhibitory signals). Proper balance between the two controls movement.
A low level of dopamine causes the basal ganglia to severely inhibit target neurons in the thalamus, called an inhibition. Scientists have long assumed that this stronger inhibition causes the motor problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.
To test this assumption, the research team used optogenetic technology in an animal model to study the effects of this increased inhibition of the thalamus and ultimately movement. Optogenetics is the use of light to control the activity of specific types of neurons within the brain.
They found that when signals from the basal ganglia are more strongly activated by light, the target neurons in the thalamus paradoxically became hyperactive. Called rebound excitation, this hyperactivity produced abnormal muscular stiffness and tremor. Such motor problems are very similar to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease patients. When this hyperactivity of thalamic neurons is suppressed by light, mice show normal movments without Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Reducing the levels of activity back to normal caused the motor symptoms to stop, proving that the hyperactivity caused the motor problems experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Professor Kim at KAIST said, “This study overturns three decades of consensus on the provenance of Parkinsonian symptoms.” The lead author, Dr Jeongjin Kim said, “The therapeutic implications of this study for the treatment of Parkinsonian symptoms are profound. It may soon become possible to remedy movement disorders without using L-DOPA, a pre-cursor to dopamine.”
Professor Augustine at NTU added, “Our findings are a breakthrough, both for understanding how the brain normally controls the movement of our body and how this control goes awry during Parkinson’s disease and related dopamine-deficiency disorders.”
The study took five years to complete, and includes researchers from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering at KAIST.
The research team will move forward by investigating how hyperactivity in neurons in the thalamus leads to abnormal movement, as well as developing therapeutic strategies for the disease by targeting this neural mechanism.
Figure abstract: Inhibitory inputs from the basal ganglia inhibit thalamic neurons (upper). In low-dopamine states, like PD, rebound firing follows inhibition and causes movement disorders (middle). The inhibition of rebound firing alleviates PD-like symptoms in a mouse model of PD.
2017.09.22 View 11270
Unlocking the Keys to Parkinson's Disease
A KAIST research team has identified a new mechanism that causes the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s disease, namely tremors, rigidity, and loss of voluntary movement.
The discovery, made in collaboration with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, presents a new perspective to three decades of conventional wisdom in Parkinson’s disease research. It also opens up new avenues that can help alleviate the motor problems suffered by patients of the disease, which reportedly number more than 10 million worldwide. The research was published in Neuron on August 30.
The research team was led by Professor Daesoo Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST and Professor George Augustine from the Lee Kong Chian School of Medicine at NTU. Dr. Jeongjin Kim, a former postdoctoral fellow at KAIST who now works at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), is the lead author.
It is known that Parkinson’s disease is caused by a lack of dopamine, a chemical in the brain that transmits neural signals. However, it remains unknown how the disease causes the motor
Smooth, voluntary movements, such as reaching for a cup of coffee, are controlled by the basal ganglia, which issue instructions via neurons (nerve cells that process and transmit information in the brain) in the thalamus to the cortex. These instructions come in two types: one that triggers a response (excitatory signals) and the other that suppresses a response (inhibitory signals). Proper balance between the two controls movement.
A low level of dopamine causes the basal ganglia to severely inhibit target neurons in the thalamus, called an inhibition. Scientists have long assumed that this stronger inhibition causes the motor problems of Parkinson’s disease patients.
To test this assumption, the research team used optogenetic technology in an animal model to study the effects of this increased inhibition of the thalamus and ultimately movement. Optogenetics is the use of light to control the activity of specific types of neurons within the brain.
They found that when signals from the basal ganglia are more strongly activated by light, the target neurons in the thalamus paradoxically became hyperactive. Called rebound excitation, this hyperactivity produced abnormal muscular stiffness and tremor. Such motor problems are very similar to the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease patients. When this hyperactivity of thalamic neurons is suppressed by light, mice show normal movments without Parkinson’s disease symptoms. Reducing the levels of activity back to normal caused the motor symptoms to stop, proving that the hyperactivity caused the motor problems experienced by Parkinson’s disease patients.
Professor Kim at KAIST said, “This study overturns three decades of consensus on the provenance of Parkinsonian symptoms.” The lead author, Dr Jeongjin Kim said, “The therapeutic implications of this study for the treatment of Parkinsonian symptoms are profound. It may soon become possible to remedy movement disorders without using L-DOPA, a pre-cursor to dopamine.”
Professor Augustine at NTU added, “Our findings are a breakthrough, both for understanding how the brain normally controls the movement of our body and how this control goes awry during Parkinson’s disease and related dopamine-deficiency disorders.”
The study took five years to complete, and includes researchers from the Department of Bio & Brain Engineering at KAIST.
The research team will move forward by investigating how hyperactivity in neurons in the thalamus leads to abnormal movement, as well as developing therapeutic strategies for the disease by targeting this neural mechanism.
Figure abstract: Inhibitory inputs from the basal ganglia inhibit thalamic neurons (upper). In low-dopamine states, like PD, rebound firing follows inhibition and causes movement disorders (middle). The inhibition of rebound firing alleviates PD-like symptoms in a mouse model of PD.
2017.09.22 View 11270