Atom
-
 KAIST Develops Analog Memristive Synapses for Neuromorphic Chips
(Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering)
A KAIST research team developed a technology that makes a transition of the operation mode of flexible memristors to synaptic analog switching by reducing the size of the formed filament. Through this technology, memristors can extend their role to memristive synapses for neuromorphic chips, which will lead to developing soft neuromorphic intelligent systems.
Brain-inspired neuromorphic chips have been gaining a great deal of attention for reducing the power consumption and integrating data processing, compared to conventional semiconductor chips. Similarly, memristors are known to be the most suitable candidate for making a crossbar array which is the most efficient architecture for realizing hardware-based artificial neural network (ANN) inside a neuromorphic chip.
A hardware-based ANN consists of a neuron circuit and synapse elements, the connecting pieces. In the neuromorphic system, the synaptic weight, which represents the connection strength between neurons, should be stored and updated as the type of analog data at each synapse.
However, most memristors have digital characteristics suitable for nonvolatile memory. These characteristics put a limitation on the analog operation of the memristors, which makes it difficult to apply them to synaptic devices.
Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team fabricated a flexible polymer memristor on a plastic substrate, and found that changing the size of the conductive metal filaments formed inside the device on the scale of metal atoms can make a transition of the memristor behavior from digital to analog.
Using this phenomenon, the team developed flexible memristor-based electronic synapses, which can continuously and linearly update synaptic weight, and operate under mechanical deformations such as bending.
The team confirmed that the ANN based on these memristor synapses can effectively classify person’s facial images even when they were damaged. This research demonstrated the possibility of a neuromorphic chip that can efficiently recognize faces, numbers, and objects.
Professor Choi said, “We found the principles underlying the transition from digital to analog operation of the memristors. I believe that this research paves the way for applying various memristors to either digital memory or electronic synapses, and will accelerate the development of a high-performing neuromorphic chip.”
In a joint research project with Professor Sung Gap Im (KAIST) and Professor V. P. Dravid (Northwestern University), this study was led by Dr. Byung Chul Jang (Samsung Electronics), Dr. Sungkyu Kim (Northwestern University) and Dr. Sang Yoon Yang (KAIST), and was published online in Nano Letters (10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04023) on January 4, 2019.
Figure 1. a) Schematic illustration of a flexible pV3D3 memristor-based electronic synapse array. b) Cross-sectional TEM image of the flexible pV3D3 memristor
2019.02.28 View 11335
KAIST Develops Analog Memristive Synapses for Neuromorphic Chips
(Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering)
A KAIST research team developed a technology that makes a transition of the operation mode of flexible memristors to synaptic analog switching by reducing the size of the formed filament. Through this technology, memristors can extend their role to memristive synapses for neuromorphic chips, which will lead to developing soft neuromorphic intelligent systems.
Brain-inspired neuromorphic chips have been gaining a great deal of attention for reducing the power consumption and integrating data processing, compared to conventional semiconductor chips. Similarly, memristors are known to be the most suitable candidate for making a crossbar array which is the most efficient architecture for realizing hardware-based artificial neural network (ANN) inside a neuromorphic chip.
A hardware-based ANN consists of a neuron circuit and synapse elements, the connecting pieces. In the neuromorphic system, the synaptic weight, which represents the connection strength between neurons, should be stored and updated as the type of analog data at each synapse.
However, most memristors have digital characteristics suitable for nonvolatile memory. These characteristics put a limitation on the analog operation of the memristors, which makes it difficult to apply them to synaptic devices.
Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team fabricated a flexible polymer memristor on a plastic substrate, and found that changing the size of the conductive metal filaments formed inside the device on the scale of metal atoms can make a transition of the memristor behavior from digital to analog.
Using this phenomenon, the team developed flexible memristor-based electronic synapses, which can continuously and linearly update synaptic weight, and operate under mechanical deformations such as bending.
The team confirmed that the ANN based on these memristor synapses can effectively classify person’s facial images even when they were damaged. This research demonstrated the possibility of a neuromorphic chip that can efficiently recognize faces, numbers, and objects.
Professor Choi said, “We found the principles underlying the transition from digital to analog operation of the memristors. I believe that this research paves the way for applying various memristors to either digital memory or electronic synapses, and will accelerate the development of a high-performing neuromorphic chip.”
In a joint research project with Professor Sung Gap Im (KAIST) and Professor V. P. Dravid (Northwestern University), this study was led by Dr. Byung Chul Jang (Samsung Electronics), Dr. Sungkyu Kim (Northwestern University) and Dr. Sang Yoon Yang (KAIST), and was published online in Nano Letters (10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04023) on January 4, 2019.
Figure 1. a) Schematic illustration of a flexible pV3D3 memristor-based electronic synapse array. b) Cross-sectional TEM image of the flexible pV3D3 memristor
2019.02.28 View 11335 -
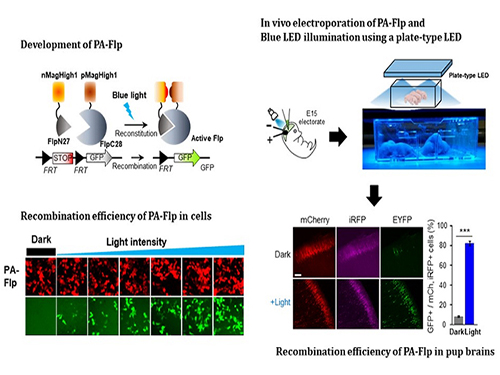 Noninvasive Light-Sensitive Recombinase for Deep Brain Genetic Manipulation
A KAIST team presented a noninvasive light-sensitive photoactivatable recombinase suitable for genetic manipulation in vivo. The highly light-sensitive property of photoactivatable Flp recombinase will be ideal for controlling genetic manipulation in deep mouse brain regions by illumination with a noninvasive light-emitting diode. This easy-to-use optogenetic module made by Professor Won Do Heo and his team will provide a side-effect free and expandable genetic manipulation tool for neuroscience research.
Spatiotemporal control of gene expression has been acclaimed as a valuable strategy for identifying functions of genes with complex neural circuits. Studies of complex brain functions require highly sophisticated and robust technologies that enable specific labeling and rapid genetic modification in live animals. A number of approaches for controlling the activity of proteins or expression of genes in a spatiotemporal manner using light, small molecules, hormones, and peptides have been developed for manipulating intact circuits or functions.
Among them, recombination-employing, chemically inducible systems are the most commonly used in vivo gene-modification systems. Other approaches include selective or conditional Cre-activation systems within subsets of green fluorescent protein-expressing cells or dual-promoter-driven intersectional populations of cells.
However, these methods are limited by the considerable time and effort required to establish knock-in mouse lines and by constraints on spatiotemporal control, which relies on a limited set of available genetic promoters and transgenic mouse resources.
Beyond these constraints, optogenetic approaches allow the activity of genetically defined neurons in the mouse brain to be controlled with high spatiotemporal resolution. However, an optogenetic module for gene-manipulation capable of revealing the spatiotemporal functions of specific target genes in the mouse brain has remained a challenge.
In the study published at Nature Communication on Jan. 18, the team featured photoactivatable Flp recombinase by searching out split sites of Flp recombinase that were not previously identified, being capable of reconstitution to be active. The team validated the highly light-sensitive, efficient performance of photoactivatable Flp recombinase through precise light targeting by showing transgene expression within anatomically confined mouse brain regions.
The concept of local genetic labeling presented here suggests a new approach for genetically identifying subpopulations of cells defined by the spatial and temporal characteristics of light delivery. To date, an optogenetic module for gene-manipulation capable of revealing spatiotemporal functions of specific target genes in the mouse brain has remained out of reach and no such light-inducible Flp system has been developed. Accordingly, the team sought to develop a photoactivatable Flp recombinase that takes full advantage of the high spatiotemporal control offered by light stimulation.
This activation through noninvasive light illumination deep inside the brain is advantageous in that it avoids chemical or optic fiber implantation-mediated side effects, such as off-target cytotoxicity or physical lesions that might influence animal physiology or behaviors. The technique provides expandable utilities for transgene expression systems upon Flp recombinase activity in vivo, by designing a viral vector for minimal leaky expression influenced by viral nascent promoters.
The team demonstrated the utility of PA-Flp as a noninvasive in vivo optogenetic manipulation tool for use in the mouse brain, even applicable for deep brain structures as it can reach the hippocampus or medial septum using external LED light illumination.
The study is the result of five years of research by Professor Heo, who has led the bio-imaging and optogenetics fields by developing his own bio-imaging and optogenetics technologies. “It will be a great advantage to control specific gene expression desired by LEDs with little physical and chemical stimulation that can affect the physiological phenomenon in living animals,” he explained.
2019.01.22 View 8494
Noninvasive Light-Sensitive Recombinase for Deep Brain Genetic Manipulation
A KAIST team presented a noninvasive light-sensitive photoactivatable recombinase suitable for genetic manipulation in vivo. The highly light-sensitive property of photoactivatable Flp recombinase will be ideal for controlling genetic manipulation in deep mouse brain regions by illumination with a noninvasive light-emitting diode. This easy-to-use optogenetic module made by Professor Won Do Heo and his team will provide a side-effect free and expandable genetic manipulation tool for neuroscience research.
Spatiotemporal control of gene expression has been acclaimed as a valuable strategy for identifying functions of genes with complex neural circuits. Studies of complex brain functions require highly sophisticated and robust technologies that enable specific labeling and rapid genetic modification in live animals. A number of approaches for controlling the activity of proteins or expression of genes in a spatiotemporal manner using light, small molecules, hormones, and peptides have been developed for manipulating intact circuits or functions.
Among them, recombination-employing, chemically inducible systems are the most commonly used in vivo gene-modification systems. Other approaches include selective or conditional Cre-activation systems within subsets of green fluorescent protein-expressing cells or dual-promoter-driven intersectional populations of cells.
However, these methods are limited by the considerable time and effort required to establish knock-in mouse lines and by constraints on spatiotemporal control, which relies on a limited set of available genetic promoters and transgenic mouse resources.
Beyond these constraints, optogenetic approaches allow the activity of genetically defined neurons in the mouse brain to be controlled with high spatiotemporal resolution. However, an optogenetic module for gene-manipulation capable of revealing the spatiotemporal functions of specific target genes in the mouse brain has remained a challenge.
In the study published at Nature Communication on Jan. 18, the team featured photoactivatable Flp recombinase by searching out split sites of Flp recombinase that were not previously identified, being capable of reconstitution to be active. The team validated the highly light-sensitive, efficient performance of photoactivatable Flp recombinase through precise light targeting by showing transgene expression within anatomically confined mouse brain regions.
The concept of local genetic labeling presented here suggests a new approach for genetically identifying subpopulations of cells defined by the spatial and temporal characteristics of light delivery. To date, an optogenetic module for gene-manipulation capable of revealing spatiotemporal functions of specific target genes in the mouse brain has remained out of reach and no such light-inducible Flp system has been developed. Accordingly, the team sought to develop a photoactivatable Flp recombinase that takes full advantage of the high spatiotemporal control offered by light stimulation.
This activation through noninvasive light illumination deep inside the brain is advantageous in that it avoids chemical or optic fiber implantation-mediated side effects, such as off-target cytotoxicity or physical lesions that might influence animal physiology or behaviors. The technique provides expandable utilities for transgene expression systems upon Flp recombinase activity in vivo, by designing a viral vector for minimal leaky expression influenced by viral nascent promoters.
The team demonstrated the utility of PA-Flp as a noninvasive in vivo optogenetic manipulation tool for use in the mouse brain, even applicable for deep brain structures as it can reach the hippocampus or medial septum using external LED light illumination.
The study is the result of five years of research by Professor Heo, who has led the bio-imaging and optogenetics fields by developing his own bio-imaging and optogenetics technologies. “It will be a great advantage to control specific gene expression desired by LEDs with little physical and chemical stimulation that can affect the physiological phenomenon in living animals,” he explained.
2019.01.22 View 8494 -
 From Concept to Reality: Changing Color of Light Using a Spatiotemporal Boundary
(from left: Professor Bumki Min, PhD candidate Jaehyeon Son and PhD Kanghee Lee)
A KAIST team developed an optical technique to change the color (frequency) of light using a spatiotemporal boundary. The research focuses on realizing a spatiotemporal boundary with a much higher degree of freedom than the results of previous studies by fabricating a thin metal structure on a semiconductor surface. Such a spatiotemporal boundary is expected to be applicable to an ultra-thin film type optical device capable of changing the color of light.
The optical frequency conversion device plays a key role in precision measurement and communication technology, and the device has been developed mainly based on optical nonlinearity.
If the intensity of light is very strong, the optical medium responds nonlinearly so the nonlinear optical phenomena, such as frequency doubling or frequency mixing, can be observed. Such optical nonlinear phenomena are realized usually by the interaction between a high-intensity laser and a nonlinear medium.
As an alternative method frequency conversion is observed by temporally modifying the optical properties of the medium through which light travels using an external stimulus. Since frequency conversion in this way can be observed even in weak light, such a technique could be particularly useful in communication technology.
However, rapid optical property modification of the medium by an external stimulus and subsequent light frequency conversion techniques have been researched only in the pertubative regime, and it has been difficult to realize these theoretical results in practical applications.
To realize such a conceptual idea, Professor Bumki Min from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his team collaborated with Professor Wonju Jeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Fabian Rotermund from the Department of Physics. They developed an artificial optical material (metamaterial) by arranging a metal microstructure that mimics an atomic structure and succeeded in creating a spatiotemporal boundary by changing the optical property of the artificial material abruptly.
While previous studies only slightly modified the refractive index of the medium, this study provided a spatiotemporal boundary as a platform for freely designing and changing the spectral properties of the medium. Using this, the research team developed a device that can control the frequency of light to a large degree.
The research team said a spatiotemporal boundary, which was only conceptually considered in previous research and realized in the pertubative regime, was developed as a step that can be realized and applied.
Professor Min said, “The frequency conversion of light becomes designable and predictable, so our research could be applied in many optical applications. This research will present a new direction for time-variant media research projects in the field of optics.”
This research, led by PhD Kanghee Lee and PhD candidate Jaehyeon Son, was published online in Nature Photonics on October 8, 2018.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the government of Korea. The work was also supported by the Center for Advanced Meta-Materials (CAMM) funded by the Korea Government (MSIP) as the Global Frontier Project (NRF-2014M3A6B3063709).
Figure 1. The frequency conversion process of light using a spatiotemporal boundary.
Figure 2. The complex amplitude of light at the converted frequency with the variation of a spatiotemporal boundary.
2018.11.29 View 9399
From Concept to Reality: Changing Color of Light Using a Spatiotemporal Boundary
(from left: Professor Bumki Min, PhD candidate Jaehyeon Son and PhD Kanghee Lee)
A KAIST team developed an optical technique to change the color (frequency) of light using a spatiotemporal boundary. The research focuses on realizing a spatiotemporal boundary with a much higher degree of freedom than the results of previous studies by fabricating a thin metal structure on a semiconductor surface. Such a spatiotemporal boundary is expected to be applicable to an ultra-thin film type optical device capable of changing the color of light.
The optical frequency conversion device plays a key role in precision measurement and communication technology, and the device has been developed mainly based on optical nonlinearity.
If the intensity of light is very strong, the optical medium responds nonlinearly so the nonlinear optical phenomena, such as frequency doubling or frequency mixing, can be observed. Such optical nonlinear phenomena are realized usually by the interaction between a high-intensity laser and a nonlinear medium.
As an alternative method frequency conversion is observed by temporally modifying the optical properties of the medium through which light travels using an external stimulus. Since frequency conversion in this way can be observed even in weak light, such a technique could be particularly useful in communication technology.
However, rapid optical property modification of the medium by an external stimulus and subsequent light frequency conversion techniques have been researched only in the pertubative regime, and it has been difficult to realize these theoretical results in practical applications.
To realize such a conceptual idea, Professor Bumki Min from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and his team collaborated with Professor Wonju Jeon from the Department of Mechanical Engineering and Professor Fabian Rotermund from the Department of Physics. They developed an artificial optical material (metamaterial) by arranging a metal microstructure that mimics an atomic structure and succeeded in creating a spatiotemporal boundary by changing the optical property of the artificial material abruptly.
While previous studies only slightly modified the refractive index of the medium, this study provided a spatiotemporal boundary as a platform for freely designing and changing the spectral properties of the medium. Using this, the research team developed a device that can control the frequency of light to a large degree.
The research team said a spatiotemporal boundary, which was only conceptually considered in previous research and realized in the pertubative regime, was developed as a step that can be realized and applied.
Professor Min said, “The frequency conversion of light becomes designable and predictable, so our research could be applied in many optical applications. This research will present a new direction for time-variant media research projects in the field of optics.”
This research, led by PhD Kanghee Lee and PhD candidate Jaehyeon Son, was published online in Nature Photonics on October 8, 2018.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the government of Korea. The work was also supported by the Center for Advanced Meta-Materials (CAMM) funded by the Korea Government (MSIP) as the Global Frontier Project (NRF-2014M3A6B3063709).
Figure 1. The frequency conversion process of light using a spatiotemporal boundary.
Figure 2. The complex amplitude of light at the converted frequency with the variation of a spatiotemporal boundary.
2018.11.29 View 9399 -
 Rh Ensemble Catalyst for Effective Automobile Exhaust Treatment
(from left: Professor Hyunjoo Lee and PhD candidate Hojin Jeong)
A KAIST research team has developed a fully dispersed Rh ensemble catalyst (ENS) that shows better performance than commercial diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). This newly developed ENSs could improve low-temperature automobile exhaust treatment.
Precious metals have been used for various heterogeneous reactions, but it is crucial to maximize efficiency of catalysts due to their high cost. Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have received much attention because it is possible for all of the metal atoms to be used for reactions, yet they do not show catalytic activity for reactions that require ensemble sites.
Meanwhile, hydrocarbons, such as propylene (C3H6) and propane (C3H8) are typical automobile exhaust gas pollutants and must be converted to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) before they are released as exhaust. Since the hydrocarbon oxidation reaction proceeds only during carbon-carbon (C-C) or carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond cleavage, it is essential to secure the metal ensemble site for the catalytic reaction. Therefore, precious metal catalysts with high dispersion and ensemble sites are greatly needed.
To solve this issue, Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Professor Jeong Woo Han from POSTECH developed an Rh ensemble catalyst with 100% dispersion, and applied it to automobile after-treatment. Having a 100% dispersion means that every metal atom is used for the reaction since it is exposed on the surface.
SACs also have 100% dispersion, but the difference is that ENSs have the unique advantage of having an ensemble site with two or more atoms.
As a result of the experiment, the ENSs showed excellent catalytic performance in CO, NO, propylene, and propane oxidation at low temperatures. This complements the disadvantage of nanoparticle catalyst (NPs) that perform catalysis poorly at low temperatures due to low metal dispersion, or SACs without hydrocarbon oxidation.
In particular, the ENSs have superior low-temperature activity even better than commercial DOC, hence they are expected to be applied to automobile exhaust treatment.
Professor Lee said, “I believe that the ENSs have given academic contribution for proposing a new concept of metal catalysts, differentiating from conventional SACs and NPs. At the same time, they are of great value in the industry of exhaust treatment catalysts.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Hojin Jeong, was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 5.
Figure 1. Concept of Rh ensemble catalyst for automobile exhaust treatment
Figure 2. Structure and performance comparison of single-atom catalyst and ensemble catalyst
Figure 3. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) mapping images for SAC, ENS, and NP, respectively (green, Eh; red, Ce)
2018.08.29 View 8239
Rh Ensemble Catalyst for Effective Automobile Exhaust Treatment
(from left: Professor Hyunjoo Lee and PhD candidate Hojin Jeong)
A KAIST research team has developed a fully dispersed Rh ensemble catalyst (ENS) that shows better performance than commercial diesel oxidation catalyst (DOC). This newly developed ENSs could improve low-temperature automobile exhaust treatment.
Precious metals have been used for various heterogeneous reactions, but it is crucial to maximize efficiency of catalysts due to their high cost. Single-atom catalysts (SACs) have received much attention because it is possible for all of the metal atoms to be used for reactions, yet they do not show catalytic activity for reactions that require ensemble sites.
Meanwhile, hydrocarbons, such as propylene (C3H6) and propane (C3H8) are typical automobile exhaust gas pollutants and must be converted to carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O) before they are released as exhaust. Since the hydrocarbon oxidation reaction proceeds only during carbon-carbon (C-C) or carbon-hydrogen (C-H) bond cleavage, it is essential to secure the metal ensemble site for the catalytic reaction. Therefore, precious metal catalysts with high dispersion and ensemble sites are greatly needed.
To solve this issue, Professor Hyunjoo Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and Professor Jeong Woo Han from POSTECH developed an Rh ensemble catalyst with 100% dispersion, and applied it to automobile after-treatment. Having a 100% dispersion means that every metal atom is used for the reaction since it is exposed on the surface.
SACs also have 100% dispersion, but the difference is that ENSs have the unique advantage of having an ensemble site with two or more atoms.
As a result of the experiment, the ENSs showed excellent catalytic performance in CO, NO, propylene, and propane oxidation at low temperatures. This complements the disadvantage of nanoparticle catalyst (NPs) that perform catalysis poorly at low temperatures due to low metal dispersion, or SACs without hydrocarbon oxidation.
In particular, the ENSs have superior low-temperature activity even better than commercial DOC, hence they are expected to be applied to automobile exhaust treatment.
Professor Lee said, “I believe that the ENSs have given academic contribution for proposing a new concept of metal catalysts, differentiating from conventional SACs and NPs. At the same time, they are of great value in the industry of exhaust treatment catalysts.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Hojin Jeong, was published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on July 5.
Figure 1. Concept of Rh ensemble catalyst for automobile exhaust treatment
Figure 2. Structure and performance comparison of single-atom catalyst and ensemble catalyst
Figure 3. Energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDS) mapping images for SAC, ENS, and NP, respectively (green, Eh; red, Ce)
2018.08.29 View 8239 -
 Levitating 2D Semiconductor for Better Performance
(from top: Professor Yeon Sik Jung and PhD candidate Soomin Yim)
Atomically thin 2D semiconductors have been drawing attention for their superior physical properties over silicon semiconductors; nevertheless, they are not the most appealing materials due to their structural instability and costly manufacturing process. To shed some light on these limitations, a KAIST research team suspended a 2D semiconductor on a dome-shaped nanostructure to produce a highly efficient semiconductor at a low cost.
2D semiconducting materials have emerged as alternatives for silicon-based semiconductors because of their inherent flexibility, high transparency, and excellent carrier transport properties, which are the important characteristics for flexible electronics.
Despite their outstanding physical and chemical properties, they are oversensitive to their environment due to their extremely thin nature. Hence, any irregularities in the supporting surface can affect the properties of 2D semiconductors and make it more difficult to produce reliable and well performing devices. In particular, it can result in serious degradation of charge-carrier mobility or light-emission yield.
To solve this problem, there have been continued efforts to fundamentally block the substrate effects. One way is to suspend a 2D semiconductor; however, this method will degrade mechanical durability due to the absence of a supporter underneath the 2D semiconducting materials.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and his team came up with a new strategy based on the insertion of high-density topographic patterns as a nanogap-containing supporter between 2D materials and the substrate in order to mitigate their contact and to block the substrate-induced unwanted effects.
More than 90% of the dome-shaped supporter is simply an empty space because of its nanometer scale size. Placing a 2D semiconductor on this structure creates a similar effect to levitating the layer. Hence, this method secures the mechanical durability of the device while minimizing the undesired effects from the substrate. By applying this method to the 2D semiconductor, the charge-carrier mobility was more than doubled, showing a significant improvement of the performance of the 2D semiconductor.
Additionally, the team reduced the price of manufacturing the semiconductor. In general, constructing an ultra-fine dome structure on a surface generally involves costly equipment to create individual patterns on the surface. However, the team employed a method of self-assembling nanopatterns in which molecules assemble themselves to form a nanostructure. This method led to reducing production costs and showed good compatibility with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Professor Jung said, “This research can be applied to improve devices using various 2D semiconducting materials as well as devices using graphene, a metallic 2D material. It will be useful in a broad range of applications, such as the material for the high speed transistor channels for next-generation flexible displays or for the active layer in light detectors.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Soomin Yim, was published in Nano Letters in April.
Figure 1. Image of a 2D semiconductor using dome structures
2018.08.28 View 7524
Levitating 2D Semiconductor for Better Performance
(from top: Professor Yeon Sik Jung and PhD candidate Soomin Yim)
Atomically thin 2D semiconductors have been drawing attention for their superior physical properties over silicon semiconductors; nevertheless, they are not the most appealing materials due to their structural instability and costly manufacturing process. To shed some light on these limitations, a KAIST research team suspended a 2D semiconductor on a dome-shaped nanostructure to produce a highly efficient semiconductor at a low cost.
2D semiconducting materials have emerged as alternatives for silicon-based semiconductors because of their inherent flexibility, high transparency, and excellent carrier transport properties, which are the important characteristics for flexible electronics.
Despite their outstanding physical and chemical properties, they are oversensitive to their environment due to their extremely thin nature. Hence, any irregularities in the supporting surface can affect the properties of 2D semiconductors and make it more difficult to produce reliable and well performing devices. In particular, it can result in serious degradation of charge-carrier mobility or light-emission yield.
To solve this problem, there have been continued efforts to fundamentally block the substrate effects. One way is to suspend a 2D semiconductor; however, this method will degrade mechanical durability due to the absence of a supporter underneath the 2D semiconducting materials.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and his team came up with a new strategy based on the insertion of high-density topographic patterns as a nanogap-containing supporter between 2D materials and the substrate in order to mitigate their contact and to block the substrate-induced unwanted effects.
More than 90% of the dome-shaped supporter is simply an empty space because of its nanometer scale size. Placing a 2D semiconductor on this structure creates a similar effect to levitating the layer. Hence, this method secures the mechanical durability of the device while minimizing the undesired effects from the substrate. By applying this method to the 2D semiconductor, the charge-carrier mobility was more than doubled, showing a significant improvement of the performance of the 2D semiconductor.
Additionally, the team reduced the price of manufacturing the semiconductor. In general, constructing an ultra-fine dome structure on a surface generally involves costly equipment to create individual patterns on the surface. However, the team employed a method of self-assembling nanopatterns in which molecules assemble themselves to form a nanostructure. This method led to reducing production costs and showed good compatibility with conventional semiconductor manufacturing processes.
Professor Jung said, “This research can be applied to improve devices using various 2D semiconducting materials as well as devices using graphene, a metallic 2D material. It will be useful in a broad range of applications, such as the material for the high speed transistor channels for next-generation flexible displays or for the active layer in light detectors.”
This research, led by PhD candidate Soomin Yim, was published in Nano Letters in April.
Figure 1. Image of a 2D semiconductor using dome structures
2018.08.28 View 7524 -
 Computer Simulation Identifies a Key Principle for Next-generation Carbon Fibers
(from left: Professor Yong-Hoon Kim and PhD candidate Juho Lee)
Performing state-of-the-art computer simulations, a KAIST research team identified an atomistic design principle to produce high-quality, next-generation carbon fibers.
Carbon fibers are light-weight yet excellent in mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Boasting these properties, they can be diversely applied in high-technology sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and nuclear engineering.
They are produced from a polymer precursor through a series of spinning, stabilization, and carbonization processes. However, there is a major obstacle to producing high-quality carbon fibers. That is, when there exist ill-defined regions within the polymer matrixes, they result in disorder and defects within the produced carbon fibers.
As a solution to this problem, it was proposed that the introduction of carbon nanotubes (CNT) could enhance polymer orientation and crystallization. However, although the alignment geometry of the CNT-polymer interface apparently affects the quality of produced fibers, the atomistic understanding of the CNT-polymer interface has been so far lacking, hindering further developments.
To clarify the nature of CNT-polymer interactions, Professor Yong-Hoon Kim from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team employed a multiscale approach that combines first-principles density functional theory (DFT) calculations and force-fields molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and revealed the unique structural and electronic characteristics of polymer-CNT interfaces.
Here, they studied polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-CNT hybrid structures as a representative case of polymer-CNT composites. PAN is the most common polymer precursor, taking more than 90% of carbon fiber production.
Based on their DFT calculations, the team showed that the lying-down PAN configurations give a larger PAN-CNT binding energy than their standing-up counterparts. Moreover, maximizing the lying-down PAN configuration was shown to allow linear alignments of PANs on CNT, enabling the desirable ordered long-range PAN-PAN packing.
They also identified the CNT curvature as another significant factor, giving the largest PAN-CNT binding energy in the zero-curvature graphene limit. Conducting large-scale MD simulations, they then demonstrated that graphene nanoribbons are a promising carbon nano-reinforcement candidate by explicitly showing its strong propensity to induce linear alignments of PANs adsorbed on them.
Professor Kim said, “This research can be an exemplary case where the quantum mechanical simulations identify basic principles for developing advanced materials. Computer simulation studies will play an increasingly greater role thanks to the advances in the simulation theory and computer performance.”
This research, carried out by the PhD candidate Juho Lee, was published in the inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials on April 11.
Figure 1. Inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials
Figure 2. Research outline
2018.08.03 View 9087
Computer Simulation Identifies a Key Principle for Next-generation Carbon Fibers
(from left: Professor Yong-Hoon Kim and PhD candidate Juho Lee)
Performing state-of-the-art computer simulations, a KAIST research team identified an atomistic design principle to produce high-quality, next-generation carbon fibers.
Carbon fibers are light-weight yet excellent in mechanical strength and thermal resistance. Boasting these properties, they can be diversely applied in high-technology sectors, including automotive, aerospace, and nuclear engineering.
They are produced from a polymer precursor through a series of spinning, stabilization, and carbonization processes. However, there is a major obstacle to producing high-quality carbon fibers. That is, when there exist ill-defined regions within the polymer matrixes, they result in disorder and defects within the produced carbon fibers.
As a solution to this problem, it was proposed that the introduction of carbon nanotubes (CNT) could enhance polymer orientation and crystallization. However, although the alignment geometry of the CNT-polymer interface apparently affects the quality of produced fibers, the atomistic understanding of the CNT-polymer interface has been so far lacking, hindering further developments.
To clarify the nature of CNT-polymer interactions, Professor Yong-Hoon Kim from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability and his team employed a multiscale approach that combines first-principles density functional theory (DFT) calculations and force-fields molecular dynamics (MD) simulations and revealed the unique structural and electronic characteristics of polymer-CNT interfaces.
Here, they studied polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-CNT hybrid structures as a representative case of polymer-CNT composites. PAN is the most common polymer precursor, taking more than 90% of carbon fiber production.
Based on their DFT calculations, the team showed that the lying-down PAN configurations give a larger PAN-CNT binding energy than their standing-up counterparts. Moreover, maximizing the lying-down PAN configuration was shown to allow linear alignments of PANs on CNT, enabling the desirable ordered long-range PAN-PAN packing.
They also identified the CNT curvature as another significant factor, giving the largest PAN-CNT binding energy in the zero-curvature graphene limit. Conducting large-scale MD simulations, they then demonstrated that graphene nanoribbons are a promising carbon nano-reinforcement candidate by explicitly showing its strong propensity to induce linear alignments of PANs adsorbed on them.
Professor Kim said, “This research can be an exemplary case where the quantum mechanical simulations identify basic principles for developing advanced materials. Computer simulation studies will play an increasingly greater role thanks to the advances in the simulation theory and computer performance.”
This research, carried out by the PhD candidate Juho Lee, was published in the inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials on April 11.
Figure 1. Inside back cover of Advanced Functional Materials
Figure 2. Research outline
2018.08.03 View 9087 -
 Visualizing Chemical Reaction on Bimetal Surfaces
Catalysts are the result of many chemists searching to unravel the beauty of molecules and the mystery of chemical reactions. Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, whose research focuses on catalytic chemical reactions, is no exception. His research team recently made breakthroughs in addressing long-standing questions for understanding reaction mechanisms on bimetal catalysts.
During the studies reported in Science Advances, following a publication in Nature Communications this month, Professor Park’s research team identified that the formation of metal–oxide interfaces is the key factor responsible for the synergistic catalytic effect in bimetal catalysts. The team confirmed this fundamental reaction mechanism through in situ imaging of reaction conditions. This is the first visualization of bimetal surfaces under reaction conditions, signifying the role of metal–oxide interfaces in heterogeneous catalysis.
Bimetallic materials have outstanding catalytic performance, which opens a new pathway for controlling electronic structures and binding energy in catalysts. Despite considerable research on various catalytic reaction efficiencies, there are yet unanswered questions on the underlying principles behind the improved performance. Even more, it was very hard to figure out what led to the efficiency because the structure, chemical composition, and oxidation state of bimetallic materials change according to reaction conditions.
Recently, some research groups suggested that oxide–metal interfacial sites formed by the surface segregation of bimetallic nanoparticles might be responsible for the increased catalytic performance. However, they failed to present any definitive evidence illustrating the physical nature or the fundamental role of the oxide–metal interfaces leading to the improved performance.
To specifically address this challenge, the research team carried out in situ observations of structural modulation on platinum–nickel bimetal catalysts under carbon monoxide oxidation conditions with ambient pressure scanning tunneling microscopy and ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
The team observed that platinum–nickel bimetal catalysts exhibited a variety of different structures depending on the gas conditions. Under ultrahigh vacuum conditions, the surface exhibited a platinum skin layer on the platinum–nickel alloyed surface, selective nickel segregation followed by the formation of nickel oxide clusters using oxygen gas, and finally the coexistence of nickel oxide clusters on the platinum skin during carbon monoxide oxidation. The research team found that the formation of interfacial platinum–nickel oxide nanostructures is responsible for a highly efficient step in the carbon monoxide oxidation reaction.
These findings illustrate that the enhancement of the catalytic activity on the bimetallic catalyst surface originates from the thermodynamically efficient reaction pathways at the metal–metal oxide interface, which demonstrates a straightforward process for the strong metal–support interaction effect. The formation of these interfacial metal–metal oxide nanostructures increases catalytic activity while providing a thermodynamically efficient reaction pathway by lowering the heat of the reactions on the surface. [J. Kim et al. Adsorbate-driven reactive interfacial Pt-NiO1-x nanostructure formation on the Pt3Ni(111) alloy surface, Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aat3151 ]
Professor Park said that one way to monitor catalysts is to detect hot electrons associated with energy dissipation and conversion processes during surface reactions. His team led the real-time detection of hot electrons generated on bimetallic PtCo nanoparticles during exothermic hydrogen oxidation. The team successfully clarified the origin of the synergistic catalytic activity of PtCo nanoparticles with corresponding chemicurrent values.
By estimating the chemicurrent yield, the research team conclude that the catalytic properties of the bimetallic nanoparticles are strongly governed by the oxide–metal interface, which facilitates hot electron transfer. [H. Lee et al. Boosting hot electron flux and catalytic activity at metal–oxide interfaces of PtCo bimetallic nanoparticles, Nature Comm, 9, 2235 (2018)].
Professor Park explained, “We feel that the precise measurement of hot electrons on catalysts gives insight into the mechanism for heterogeneous catalysis, which can help with the smart design of highly reactive materials. The control of catalytic activity via electronic engineering of catalysts is a promising prospect that may open the door to the new field of combining catalysis with electronics, called “catalytronics.” He added that the study also establishes a strategy for improving catalytic activity for catalytic reactions in industrial chemical reactors.
Professors Park and Yousung Jung from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the Graduate School of EEWS conducted this research in collaboration with Professor Bongjin Mun from the Department of Physics at GIST.
Figure 1. Evolution of surface structures of PtNi bimetal surfaces under various ambient conditions.
Figure 2. Formation of Pt-CoO interface leads to the catalytic enhancement of PtCo bimetal catalysts.
2018.07.25 View 11401
Visualizing Chemical Reaction on Bimetal Surfaces
Catalysts are the result of many chemists searching to unravel the beauty of molecules and the mystery of chemical reactions. Professor Jeong Young Park from the Department of Chemistry, whose research focuses on catalytic chemical reactions, is no exception. His research team recently made breakthroughs in addressing long-standing questions for understanding reaction mechanisms on bimetal catalysts.
During the studies reported in Science Advances, following a publication in Nature Communications this month, Professor Park’s research team identified that the formation of metal–oxide interfaces is the key factor responsible for the synergistic catalytic effect in bimetal catalysts. The team confirmed this fundamental reaction mechanism through in situ imaging of reaction conditions. This is the first visualization of bimetal surfaces under reaction conditions, signifying the role of metal–oxide interfaces in heterogeneous catalysis.
Bimetallic materials have outstanding catalytic performance, which opens a new pathway for controlling electronic structures and binding energy in catalysts. Despite considerable research on various catalytic reaction efficiencies, there are yet unanswered questions on the underlying principles behind the improved performance. Even more, it was very hard to figure out what led to the efficiency because the structure, chemical composition, and oxidation state of bimetallic materials change according to reaction conditions.
Recently, some research groups suggested that oxide–metal interfacial sites formed by the surface segregation of bimetallic nanoparticles might be responsible for the increased catalytic performance. However, they failed to present any definitive evidence illustrating the physical nature or the fundamental role of the oxide–metal interfaces leading to the improved performance.
To specifically address this challenge, the research team carried out in situ observations of structural modulation on platinum–nickel bimetal catalysts under carbon monoxide oxidation conditions with ambient pressure scanning tunneling microscopy and ambient pressure X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy.
The team observed that platinum–nickel bimetal catalysts exhibited a variety of different structures depending on the gas conditions. Under ultrahigh vacuum conditions, the surface exhibited a platinum skin layer on the platinum–nickel alloyed surface, selective nickel segregation followed by the formation of nickel oxide clusters using oxygen gas, and finally the coexistence of nickel oxide clusters on the platinum skin during carbon monoxide oxidation. The research team found that the formation of interfacial platinum–nickel oxide nanostructures is responsible for a highly efficient step in the carbon monoxide oxidation reaction.
These findings illustrate that the enhancement of the catalytic activity on the bimetallic catalyst surface originates from the thermodynamically efficient reaction pathways at the metal–metal oxide interface, which demonstrates a straightforward process for the strong metal–support interaction effect. The formation of these interfacial metal–metal oxide nanostructures increases catalytic activity while providing a thermodynamically efficient reaction pathway by lowering the heat of the reactions on the surface. [J. Kim et al. Adsorbate-driven reactive interfacial Pt-NiO1-x nanostructure formation on the Pt3Ni(111) alloy surface, Science Advances (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aat3151 ]
Professor Park said that one way to monitor catalysts is to detect hot electrons associated with energy dissipation and conversion processes during surface reactions. His team led the real-time detection of hot electrons generated on bimetallic PtCo nanoparticles during exothermic hydrogen oxidation. The team successfully clarified the origin of the synergistic catalytic activity of PtCo nanoparticles with corresponding chemicurrent values.
By estimating the chemicurrent yield, the research team conclude that the catalytic properties of the bimetallic nanoparticles are strongly governed by the oxide–metal interface, which facilitates hot electron transfer. [H. Lee et al. Boosting hot electron flux and catalytic activity at metal–oxide interfaces of PtCo bimetallic nanoparticles, Nature Comm, 9, 2235 (2018)].
Professor Park explained, “We feel that the precise measurement of hot electrons on catalysts gives insight into the mechanism for heterogeneous catalysis, which can help with the smart design of highly reactive materials. The control of catalytic activity via electronic engineering of catalysts is a promising prospect that may open the door to the new field of combining catalysis with electronics, called “catalytronics.” He added that the study also establishes a strategy for improving catalytic activity for catalytic reactions in industrial chemical reactors.
Professors Park and Yousung Jung from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and the Graduate School of EEWS conducted this research in collaboration with Professor Bongjin Mun from the Department of Physics at GIST.
Figure 1. Evolution of surface structures of PtNi bimetal surfaces under various ambient conditions.
Figure 2. Formation of Pt-CoO interface leads to the catalytic enhancement of PtCo bimetal catalysts.
2018.07.25 View 11401 -
 Lead-free, Efficient Perovskite for Photovoltaic Cells
(Clockwise from left: Post-doc Researcher Lamjed Debbichi, Master’s Candidate Songju Lee, Professor Min Seok Jang and Professor Hyungjun Kim)
A KAIST research team has proposed a perovskite material, Cs2Au2I6 that serves as a potential active material for highly efficient lead-free thin-film photovoltaic devices. This material is expected to lay the foundation to overcome previously known limitations of perovskite including its stability and toxicity issues.
As strong candidates for next-generation high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, perovskite photovoltaic cells have a maximum photoconversion efficiency of 22%, comparable to high-performance crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells. In addition, perovskite-based cells can be fabricated at low temperatures, thereby bringing about dramatic cost reductions.
However, it has been noted that conventional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite materials exhibit low stability, eventually degrading their performance and making them unfit for continued use. Moreover, their inclusion of lead has undermined their environmental friendliness.
In light of this, a joint team led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering has analyzed a previously discovered perovskite material, Cs2Au2I6, consisting of only inorganic substances and investigated its suitability for application in thin-film photovoltaic devices. Theoretical investigations suggests that this new perovskite material is not only as efficient but also more stable and environment friendly compared to the conventional perovskite materials. For this analysis, the team developed multiscale multiphysics simulation frameworks. Atomic-scale first-principle quantum calculations were carried out to study the optical properties of the proposed material, and device-scale electromagnetic simulations were conducted to suggest that the material could indeed serve as a promising photovoltaic substance at the device level.
From this point onward, the research team plans to extend the study in two directions: an empirical study to apply the perovskite material in real-world photovoltaic cells and a theoretical analysis to find the optimal and highly stable material for photovoltaic cells. The team said, “Perovskite materials are highly efficient, but in order to completely replace the conventional solar cells, their stability and toxicity issues must first be resolved.” They added that this research is expected to accelerate related studies in pursuit of high-efficiency, environment-friendly perovskite materials.
This research, led by post-doc researcher Lamjed Debbichi and master’s candidate Songju Lee, was selected as the front cover article of Advanced Materials on March 22.
Figure 1. Cover of Advanced Materials
Figure 2. Schematic of full solar cell device structure
2018.06.08 View 10579
Lead-free, Efficient Perovskite for Photovoltaic Cells
(Clockwise from left: Post-doc Researcher Lamjed Debbichi, Master’s Candidate Songju Lee, Professor Min Seok Jang and Professor Hyungjun Kim)
A KAIST research team has proposed a perovskite material, Cs2Au2I6 that serves as a potential active material for highly efficient lead-free thin-film photovoltaic devices. This material is expected to lay the foundation to overcome previously known limitations of perovskite including its stability and toxicity issues.
As strong candidates for next-generation high-efficiency photovoltaic cells, perovskite photovoltaic cells have a maximum photoconversion efficiency of 22%, comparable to high-performance crystalline silicon photovoltaic cells. In addition, perovskite-based cells can be fabricated at low temperatures, thereby bringing about dramatic cost reductions.
However, it has been noted that conventional organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite materials exhibit low stability, eventually degrading their performance and making them unfit for continued use. Moreover, their inclusion of lead has undermined their environmental friendliness.
In light of this, a joint team led by Professor Hyungjun Kim from the KAIST Department of Chemistry and Professor Min Seok Jang from the School of Electrical Engineering has analyzed a previously discovered perovskite material, Cs2Au2I6, consisting of only inorganic substances and investigated its suitability for application in thin-film photovoltaic devices. Theoretical investigations suggests that this new perovskite material is not only as efficient but also more stable and environment friendly compared to the conventional perovskite materials. For this analysis, the team developed multiscale multiphysics simulation frameworks. Atomic-scale first-principle quantum calculations were carried out to study the optical properties of the proposed material, and device-scale electromagnetic simulations were conducted to suggest that the material could indeed serve as a promising photovoltaic substance at the device level.
From this point onward, the research team plans to extend the study in two directions: an empirical study to apply the perovskite material in real-world photovoltaic cells and a theoretical analysis to find the optimal and highly stable material for photovoltaic cells. The team said, “Perovskite materials are highly efficient, but in order to completely replace the conventional solar cells, their stability and toxicity issues must first be resolved.” They added that this research is expected to accelerate related studies in pursuit of high-efficiency, environment-friendly perovskite materials.
This research, led by post-doc researcher Lamjed Debbichi and master’s candidate Songju Lee, was selected as the front cover article of Advanced Materials on March 22.
Figure 1. Cover of Advanced Materials
Figure 2. Schematic of full solar cell device structure
2018.06.08 View 10579 -
 Platinum Catalyst Has Price Lowed and Durability Doubled
(Professor Cho in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering)
Professor EunAe Cho in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering reported a fuel cell catalyst that shows 12 times higher performance and twice the durability than previously used platinum catalyst.
Fuel cells, eco-friendly power generators, are said to be running air purifiers. A hydrogen vehicle powered by fuel cells can allegedly purify more than 98 percent of the particulate matter and ultrafine particles from the amount of air that 70 adults breathe.
Despite this peculiarity, the high price of platinum, which is used as an electrode catalyst, remains a big challenge to accelerating commercialization. In addition, recently developed ‘nano-structured platinum catalysts’ have not yet commercialized due to its meager oxygen reduction reaction and durability in fuel cell.
Addressing all those challenges, Professor Cho’s team reported a platinum catalyst costing 30 percent less but boasting 12 times higher performance.
The research team, to this end, combined the platinum with nickel, then applied various metallic elements for making the most efficient performance. Among others, they found that the addition of gallium can modulate the oxygen intermediate binding energy, leading to enhanced catalytic activity of the oxygen reduction reaction.
They made octahedron nanoparticle platinum-nickel alloy and could efficiently achieve 12-times high performance with the platinum catalyst by adding gallium to the surface of octahedron.
Existing fuel cell catalysts have issues in practical fuel cell applications. However, Professor Cho’s team experimentally proved the high performance of the catalyst even in the fuel cell, and is expected to be practically applied to the existing procedure.
First author JeongHoon Lim said their work demonstrates the gallium-added octahedral nanoparticles can be utilized as a highly active and durable oxygen reduction reaction catalyst in practical fuel cell applications. It will make it feasible for the mass production of the catalysts.
Professor Cho also said, “Our study realized the two main goals: an affordable price and increased performance of fuel cells. We hope this will make a contribution to the market competitiveness of fuel cell electric vehicles.”
This research was described in Nano Letters in April and was supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP), the National Research Foundation (NRF), and the Agency for Defense Development (ADD).
(Figure: HAADF STEM images with EDX analyses and line scanning profiles of (a) Ga-PtNi/C and (b) PtNi/C during the voltage-cycling tests. The composition changes of Ni, Pt, and Ga atoms in the nanoparticles were determined by EDX (inset in the EDX mapping results)).
2018.05.15 View 8453
Platinum Catalyst Has Price Lowed and Durability Doubled
(Professor Cho in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering)
Professor EunAe Cho in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering reported a fuel cell catalyst that shows 12 times higher performance and twice the durability than previously used platinum catalyst.
Fuel cells, eco-friendly power generators, are said to be running air purifiers. A hydrogen vehicle powered by fuel cells can allegedly purify more than 98 percent of the particulate matter and ultrafine particles from the amount of air that 70 adults breathe.
Despite this peculiarity, the high price of platinum, which is used as an electrode catalyst, remains a big challenge to accelerating commercialization. In addition, recently developed ‘nano-structured platinum catalysts’ have not yet commercialized due to its meager oxygen reduction reaction and durability in fuel cell.
Addressing all those challenges, Professor Cho’s team reported a platinum catalyst costing 30 percent less but boasting 12 times higher performance.
The research team, to this end, combined the platinum with nickel, then applied various metallic elements for making the most efficient performance. Among others, they found that the addition of gallium can modulate the oxygen intermediate binding energy, leading to enhanced catalytic activity of the oxygen reduction reaction.
They made octahedron nanoparticle platinum-nickel alloy and could efficiently achieve 12-times high performance with the platinum catalyst by adding gallium to the surface of octahedron.
Existing fuel cell catalysts have issues in practical fuel cell applications. However, Professor Cho’s team experimentally proved the high performance of the catalyst even in the fuel cell, and is expected to be practically applied to the existing procedure.
First author JeongHoon Lim said their work demonstrates the gallium-added octahedral nanoparticles can be utilized as a highly active and durable oxygen reduction reaction catalyst in practical fuel cell applications. It will make it feasible for the mass production of the catalysts.
Professor Cho also said, “Our study realized the two main goals: an affordable price and increased performance of fuel cells. We hope this will make a contribution to the market competitiveness of fuel cell electric vehicles.”
This research was described in Nano Letters in April and was supported by the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning (KETEP), the National Research Foundation (NRF), and the Agency for Defense Development (ADD).
(Figure: HAADF STEM images with EDX analyses and line scanning profiles of (a) Ga-PtNi/C and (b) PtNi/C during the voltage-cycling tests. The composition changes of Ni, Pt, and Ga atoms in the nanoparticles were determined by EDX (inset in the EDX mapping results)).
2018.05.15 View 8453 -
 KAIST-KU Sign MOU on 4th Industrial Technology Development
(President Shin(second from left) poses with Khalifa University President Tod Laursen after signing an MOU in the UAE on March 25. Far left is Chairman of the NST Kwangyun Wohn and far right is the UAE Minister of Educatiion Hussain Al Hammadi.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and Khalifa University Interim President Tod Laursen signed an MOU on the Fourth Industrial Technology Development on March 25 in the UAE.
They signed the MOU during the UAE-ROK Nuclear Friendship and KAIST Alumni Night at Khalifa University co-hosted by KAIST and the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI). The MOU will bring new opportunities to further expand bilateral cooperation in education and training in the relevant technologies called for the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
More than 100 dignitaries including Chairman of National Research Council of Science and Technology (NST) in Korea Dr. Kwangyun Wohn, President of KAERI Jaejoo Ha, the UAE Minister of Education His Excellency Hussain Al Hammadi, Minister of State for Advanced Sciences Her Excellency Sarah bint Yousef Al Amiri, and His Excellency Federal Authority for Nuclear Regulation (FANR) Director General Christopher Viktorsson attended the event. In particular, a significant number of Emirati graduates of the KUSTAR-KAIST education program and many others who completed various KAIST training programs joined the event.
The Nuclear Friendship Night was celebrating the completion of the first nuclear power plant in Barakah exported by Korea. This is the first nuclear reactor in the Middle East, which is to start operation later this year. The event also coincided with Korean President Moon Jae-In’s state visit to the UAE.
KAIST and KAERI gathered distinguished leaders from the higher education and nuclear industries at the event in response to the UAE government’s top national agenda of fostering future talents and promoting the nuclear industry in order to ensure energy security.
KAIST and Khalifa University signed an initial agreement in education and research in 2009 when the governments of Korea and the UAE signed a contract to build four nuclear power plants in Barakah. Since then, the two universities have worked together closely in the areas of nuclear engineering, bio-medical engineering, robotics, mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, and materials science. With this signing on the new MOU, the partnership between the two institutions will mark the second phase of educating high-caliber human resources in science and technology of the two countries.
The KAIST Alumni Night also brought more opportunities to appreciate the achievements that the two countries have made through collaboration in education and research, mostly represented in the field of nuclear technology between KAIST and Khalifa University. During the event, KAIST graduates also shared their experiences from the education at KAIST, followed by the welcoming speeches from the UAE Minister of Education and the UAE Minister of State for Advanced Sciences.
KAIST President Shin, in his welcoming speech at the event, said, “I look forward to more students in the UAE having the opportunity to experience the world’s top-level education and global environment that KAIST offers. The collaboration with Khalifa University and the UAE is very important for building both countries’ future growth.”
KU President Laursen said, “This MOU on research cooperation focusing on technologies for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, nuclear engineering, and other technical areas will further consolidate our partnership with KAIST and support us in developing human capital suitable to take on future challenges in the science and technology sectors. We firmly believe the talent pool of experts created by this initiative will contribute to the overall economic growth of the UAE.”
2018.03.26 View 12408
KAIST-KU Sign MOU on 4th Industrial Technology Development
(President Shin(second from left) poses with Khalifa University President Tod Laursen after signing an MOU in the UAE on March 25. Far left is Chairman of the NST Kwangyun Wohn and far right is the UAE Minister of Educatiion Hussain Al Hammadi.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin and Khalifa University Interim President Tod Laursen signed an MOU on the Fourth Industrial Technology Development on March 25 in the UAE.
They signed the MOU during the UAE-ROK Nuclear Friendship and KAIST Alumni Night at Khalifa University co-hosted by KAIST and the Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute (KAERI). The MOU will bring new opportunities to further expand bilateral cooperation in education and training in the relevant technologies called for the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
More than 100 dignitaries including Chairman of National Research Council of Science and Technology (NST) in Korea Dr. Kwangyun Wohn, President of KAERI Jaejoo Ha, the UAE Minister of Education His Excellency Hussain Al Hammadi, Minister of State for Advanced Sciences Her Excellency Sarah bint Yousef Al Amiri, and His Excellency Federal Authority for Nuclear Regulation (FANR) Director General Christopher Viktorsson attended the event. In particular, a significant number of Emirati graduates of the KUSTAR-KAIST education program and many others who completed various KAIST training programs joined the event.
The Nuclear Friendship Night was celebrating the completion of the first nuclear power plant in Barakah exported by Korea. This is the first nuclear reactor in the Middle East, which is to start operation later this year. The event also coincided with Korean President Moon Jae-In’s state visit to the UAE.
KAIST and KAERI gathered distinguished leaders from the higher education and nuclear industries at the event in response to the UAE government’s top national agenda of fostering future talents and promoting the nuclear industry in order to ensure energy security.
KAIST and Khalifa University signed an initial agreement in education and research in 2009 when the governments of Korea and the UAE signed a contract to build four nuclear power plants in Barakah. Since then, the two universities have worked together closely in the areas of nuclear engineering, bio-medical engineering, robotics, mechanical engineering, chemical engineering, and materials science. With this signing on the new MOU, the partnership between the two institutions will mark the second phase of educating high-caliber human resources in science and technology of the two countries.
The KAIST Alumni Night also brought more opportunities to appreciate the achievements that the two countries have made through collaboration in education and research, mostly represented in the field of nuclear technology between KAIST and Khalifa University. During the event, KAIST graduates also shared their experiences from the education at KAIST, followed by the welcoming speeches from the UAE Minister of Education and the UAE Minister of State for Advanced Sciences.
KAIST President Shin, in his welcoming speech at the event, said, “I look forward to more students in the UAE having the opportunity to experience the world’s top-level education and global environment that KAIST offers. The collaboration with Khalifa University and the UAE is very important for building both countries’ future growth.”
KU President Laursen said, “This MOU on research cooperation focusing on technologies for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, nuclear engineering, and other technical areas will further consolidate our partnership with KAIST and support us in developing human capital suitable to take on future challenges in the science and technology sectors. We firmly believe the talent pool of experts created by this initiative will contribute to the overall economic growth of the UAE.”
2018.03.26 View 12408 -
 Aqueous Storage Device Needs Only 20 Seconds to Go
(from left: PhD candidate Il Woo Ock and Professor Jeung Ku Kang)
A KAIST research team developed a new hybrid energy storage device that can be charged in less than half a minute. It employs aqueous electrolytes instead of flammable organic solvents, so it is both environmentally friendly and safe. It also facilitates a boosting charge with high energy density, which makes it suitable for portable electronic devices.
Professor Jeung Ku Kang and his team from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability developed this hybrid energy storage with high energy and power densities along over a long cycle life by assembling fibre-like polymer chain anodes and sub-nanoscale metal oxide cathodes on graphene.
Conventional aqueous electrolyte-based energy storage devices have a limitation for boosting charges and high energy density due to low driving voltage and a shortage of anode materials.
Energy storage device capacity is determined by the two electrodes, and the balance between cathode and anode leads to high stability. In general, two electrodes show differences in electrical properties and differ in ion storage mechanism processes, resulting in poor storage and stability from the imbalance.
The research team came up with new structures and materials to facilitate rapid speed in energy exchange on the surfaces of the electrodes and minimize the energy loss between the two electrodes.
The team made anodes with graphene-based polymer chain materials. The web-like structure of graphene leads to a high surface area, thereby allowing higher capacitance.
For cathode materials, the team used metal oxide in sub-nanoscale structures to elevate atom-by-ion redox reactions. This method realized higher energy density and faster energy exchange while minimizing energy loss.
The developed device can be charged within 20 to 30 seconds using a low-power charging system, such as a USB switching charger or a flexible photovoltaic cell. The developed aqueous hybrid energy device shows more than 100-fold higher power density compared to conventional aqueous batteries and can be rapidly recharged. Further, the device showed high stability with its capacity maintained at 100% at a high charge/discharge current.
Professor Kang said, “This eco-friendly technology can be easily manufactured and is highly applicable. In particular, its high capacity and high stability, compared to existing technologies, could contribute to the commercialization of aqueous capacitors. The device can be rapidly charged using a low-power charging system, and thus can be applied to portable electronic device.”
This research, led by a PhD candidate Il Woo Ock, was published in Advanced Energy Materials on January 15.
Figure 1. Switching wearable LED kit with two AHCs in series charged by a flexible photovoltaic cell
Figure 2. Schematic diagram for aqueous hybrid capacitors
Figure 3. TEM images of anode and cathode
2018.02.28 View 13524
Aqueous Storage Device Needs Only 20 Seconds to Go
(from left: PhD candidate Il Woo Ock and Professor Jeung Ku Kang)
A KAIST research team developed a new hybrid energy storage device that can be charged in less than half a minute. It employs aqueous electrolytes instead of flammable organic solvents, so it is both environmentally friendly and safe. It also facilitates a boosting charge with high energy density, which makes it suitable for portable electronic devices.
Professor Jeung Ku Kang and his team from the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability developed this hybrid energy storage with high energy and power densities along over a long cycle life by assembling fibre-like polymer chain anodes and sub-nanoscale metal oxide cathodes on graphene.
Conventional aqueous electrolyte-based energy storage devices have a limitation for boosting charges and high energy density due to low driving voltage and a shortage of anode materials.
Energy storage device capacity is determined by the two electrodes, and the balance between cathode and anode leads to high stability. In general, two electrodes show differences in electrical properties and differ in ion storage mechanism processes, resulting in poor storage and stability from the imbalance.
The research team came up with new structures and materials to facilitate rapid speed in energy exchange on the surfaces of the electrodes and minimize the energy loss between the two electrodes.
The team made anodes with graphene-based polymer chain materials. The web-like structure of graphene leads to a high surface area, thereby allowing higher capacitance.
For cathode materials, the team used metal oxide in sub-nanoscale structures to elevate atom-by-ion redox reactions. This method realized higher energy density and faster energy exchange while minimizing energy loss.
The developed device can be charged within 20 to 30 seconds using a low-power charging system, such as a USB switching charger or a flexible photovoltaic cell. The developed aqueous hybrid energy device shows more than 100-fold higher power density compared to conventional aqueous batteries and can be rapidly recharged. Further, the device showed high stability with its capacity maintained at 100% at a high charge/discharge current.
Professor Kang said, “This eco-friendly technology can be easily manufactured and is highly applicable. In particular, its high capacity and high stability, compared to existing technologies, could contribute to the commercialization of aqueous capacitors. The device can be rapidly charged using a low-power charging system, and thus can be applied to portable electronic device.”
This research, led by a PhD candidate Il Woo Ock, was published in Advanced Energy Materials on January 15.
Figure 1. Switching wearable LED kit with two AHCs in series charged by a flexible photovoltaic cell
Figure 2. Schematic diagram for aqueous hybrid capacitors
Figure 3. TEM images of anode and cathode
2018.02.28 View 13524 -
 Lifespan of Fuel Cells Maximized Using Small Amount of Metals
(Professor Jung (far right) and his team)
Fuel cells are key future energy technology that is emerging as eco-friendly and renewable energy sources. In particular, solid oxide fuel cells composed of ceramic materials gain increasing attention for their ability to directly convert various forms of fuel such as biomass, LNG, and LPG to electric energy.
KAIST researchers described a new technique to improve chemical stability of electrode materials which can extend the lifespan by employing a very little amount of metals.
The core factor that determines the performance of solid oxide fuel cells is the cathode at which the reduction reaction of oxygen occurs. Conventionally, oxides with perovskite structure (ABO3) are used in cathodes. However, despite the high performance of perovskite oxides at initial operation, the performance decreases with time, limiting their long-term use. In particular, the condition of high temperature oxidation state required for cathode operation leads to surface segregation phenomenon, in which second phases such as strontium oxide (SrOx) accumulate on the surface of oxides, resulting in decrease in electrode performance. The detailed mechanism of this phenomenon and a way to effectively inhibit it has not been suggested.
Using computational chemistry and experimental data, Professor WooChul Jung’s team at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering observed that local compressive states around the Sr atoms in a perovskite electrode lattice weakened the Sr-O bond strength, which in turn promote strontium segregation. The team identified local changes in strain distribution in perovskite oxide as the main cause of segregation on strontium surface. Based on these findings, the team doped different sizes of metals in oxides to control the extent of lattice strain in cathode material and effectively inhibited strontium segregation.
Professor Jung said, “This technology can be implemented by adding a small amount of metal atoms during material synthesis, without any additional process.” He continued, “I hope this technology will be useful in developing high-durable perovskite oxide electrode in the future.”
The study co-led by Professor Jung and Professor Jeong Woo Han at Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Seoul was featured as the cover of Energy and Environmental Science in the first issue of 2018.
(Figure1.Correlation between the extent of lattice strain in electrode, strontium segregation, and electrode reaction.)
(Figure 2. Cathode surface of solid oxide fuel cell stabilized using the developed technology)
2018.01.18 View 9238
Lifespan of Fuel Cells Maximized Using Small Amount of Metals
(Professor Jung (far right) and his team)
Fuel cells are key future energy technology that is emerging as eco-friendly and renewable energy sources. In particular, solid oxide fuel cells composed of ceramic materials gain increasing attention for their ability to directly convert various forms of fuel such as biomass, LNG, and LPG to electric energy.
KAIST researchers described a new technique to improve chemical stability of electrode materials which can extend the lifespan by employing a very little amount of metals.
The core factor that determines the performance of solid oxide fuel cells is the cathode at which the reduction reaction of oxygen occurs. Conventionally, oxides with perovskite structure (ABO3) are used in cathodes. However, despite the high performance of perovskite oxides at initial operation, the performance decreases with time, limiting their long-term use. In particular, the condition of high temperature oxidation state required for cathode operation leads to surface segregation phenomenon, in which second phases such as strontium oxide (SrOx) accumulate on the surface of oxides, resulting in decrease in electrode performance. The detailed mechanism of this phenomenon and a way to effectively inhibit it has not been suggested.
Using computational chemistry and experimental data, Professor WooChul Jung’s team at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering observed that local compressive states around the Sr atoms in a perovskite electrode lattice weakened the Sr-O bond strength, which in turn promote strontium segregation. The team identified local changes in strain distribution in perovskite oxide as the main cause of segregation on strontium surface. Based on these findings, the team doped different sizes of metals in oxides to control the extent of lattice strain in cathode material and effectively inhibited strontium segregation.
Professor Jung said, “This technology can be implemented by adding a small amount of metal atoms during material synthesis, without any additional process.” He continued, “I hope this technology will be useful in developing high-durable perovskite oxide electrode in the future.”
The study co-led by Professor Jung and Professor Jeong Woo Han at Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Seoul was featured as the cover of Energy and Environmental Science in the first issue of 2018.
(Figure1.Correlation between the extent of lattice strain in electrode, strontium segregation, and electrode reaction.)
(Figure 2. Cathode surface of solid oxide fuel cell stabilized using the developed technology)
2018.01.18 View 9238