CO
-
 UN biological weapons expert gives lecture at KAIST
KAIST’s student organization, the ICISTS Organizing Committee, invited United Nations Security Council expert Terence Taylor to deliver a speech under the topic of ‘Terrorists and Scientists: Biological Weapons and its impact on Global Society’. The lecture took place on November 19 on the Daejeon campus.
Taylor shared his experiences as a biochemical weapons expert at Iraq and discussed the fast-approaching future of the world with biochemical weapons.
Terence Taylor is a former British military officer, who served various governmental and non-governmental organizations around the world, including UK and U.S. agencies, as well as the UN. His current work involves the non-proliferation and disarmament of nuclear or biological weapons, toxic substances and other weapons of mass destruction.
ICISTS Organizing Committee is a student organization run by of KAIST students. Since 2005, it has actively held one of the largest student conferences in Asia, ICISTS-KAIST, at KAIST every year. "ICISTS" stands for “International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society”, which conveys its vision in achieving a harmony between science and society.
UN Security Council expert Terence Taylor
2013.11.28 View 9365
UN biological weapons expert gives lecture at KAIST
KAIST’s student organization, the ICISTS Organizing Committee, invited United Nations Security Council expert Terence Taylor to deliver a speech under the topic of ‘Terrorists and Scientists: Biological Weapons and its impact on Global Society’. The lecture took place on November 19 on the Daejeon campus.
Taylor shared his experiences as a biochemical weapons expert at Iraq and discussed the fast-approaching future of the world with biochemical weapons.
Terence Taylor is a former British military officer, who served various governmental and non-governmental organizations around the world, including UK and U.S. agencies, as well as the UN. His current work involves the non-proliferation and disarmament of nuclear or biological weapons, toxic substances and other weapons of mass destruction.
ICISTS Organizing Committee is a student organization run by of KAIST students. Since 2005, it has actively held one of the largest student conferences in Asia, ICISTS-KAIST, at KAIST every year. "ICISTS" stands for “International Conference for the Integration of Science, Technology, and Society”, which conveys its vision in achieving a harmony between science and society.
UN Security Council expert Terence Taylor
2013.11.28 View 9365 -
 Cambridge University Press and HISTAC to Publish Science and Civilization in Korea
The KAIST Research Institute for the History of Science, Technology and Civilization of Korea (HISTAC) and Cambridge University Press have agreed to publish a 10-volume collection entitled “Science and Civilization in Korea” in collaboration with the Needham Research Institute.
HISTAC was found in December 2012 with the support of the Academy of Korean Studies and the Korean Studies Promotion Service with the aim of publishing a collection composed of 30 Korean books and 7 English books on Korean science and civilization.
By November 2013, the HISTAC research team submitted a research paper composed of 11 Korean and 1 English book. It has now exceeded its initial goal of publishing 7 English books by signing the recent agreement with the Cambridge University Press.
“Science and Civilization in Korea” is the second collection of non-western science to be published by the Cambridge University Press since 1954 following “Science and Civilization in China” by Joseph Needham who is well-known for his momentous achievements in history of science in East Asia. This collection will highlight the achievements of Korea in science and civilization of Korea, much of which has been under-valued compared to those of China and Japan.[ It now has the significance similar to the Western science and civilization].
HISTAC appointed Professor Hong-Gi Yoon from the University of Auckland as the translator and invited Professor Christopher Cullen from Cambridge University and Professor Morris Low from the University of Queensland as co-editors. Professor Cullen was an editor of “Science and Civilization in China” and is now the director of the Needham Research Institute and Professor Low is an expert in modern science of East Asia.
The series includes:
- History of Science and Technology in Korea
- Technology, Everyday Life, and Korean Civilization
- History and Cultural Studies of Geomancy in Korea
- Patients, Doctors and the State: History of Korean Medical and Pharmaceutical Culture
- History of Astronomy in Korea
- Mathematics and the History of Korean Civilization
- The West and Korea in the History of Science and Technology, 1600-1950
- Imperialism, Colonialism, Post-colonialism and Technological Science in Korea
- Development of Science and Technology Under the Korean Authoritarian Regime
- Dynamics of Technological Development in Korean Industrialization
The HISTAC team believes that the publication will illuminate the nation’s triumphs in science and technology and expects that the publication will serve as valuable research resources for the study of the history of East Asian scientific civilization which has mainly focused on China and Japan. Further, by adopting various case studies of scientific achievements of South Korea and developing countries, they hope to propose a new model for studying history of science and civilization.
2013.11.28 View 9338
Cambridge University Press and HISTAC to Publish Science and Civilization in Korea
The KAIST Research Institute for the History of Science, Technology and Civilization of Korea (HISTAC) and Cambridge University Press have agreed to publish a 10-volume collection entitled “Science and Civilization in Korea” in collaboration with the Needham Research Institute.
HISTAC was found in December 2012 with the support of the Academy of Korean Studies and the Korean Studies Promotion Service with the aim of publishing a collection composed of 30 Korean books and 7 English books on Korean science and civilization.
By November 2013, the HISTAC research team submitted a research paper composed of 11 Korean and 1 English book. It has now exceeded its initial goal of publishing 7 English books by signing the recent agreement with the Cambridge University Press.
“Science and Civilization in Korea” is the second collection of non-western science to be published by the Cambridge University Press since 1954 following “Science and Civilization in China” by Joseph Needham who is well-known for his momentous achievements in history of science in East Asia. This collection will highlight the achievements of Korea in science and civilization of Korea, much of which has been under-valued compared to those of China and Japan.[ It now has the significance similar to the Western science and civilization].
HISTAC appointed Professor Hong-Gi Yoon from the University of Auckland as the translator and invited Professor Christopher Cullen from Cambridge University and Professor Morris Low from the University of Queensland as co-editors. Professor Cullen was an editor of “Science and Civilization in China” and is now the director of the Needham Research Institute and Professor Low is an expert in modern science of East Asia.
The series includes:
- History of Science and Technology in Korea
- Technology, Everyday Life, and Korean Civilization
- History and Cultural Studies of Geomancy in Korea
- Patients, Doctors and the State: History of Korean Medical and Pharmaceutical Culture
- History of Astronomy in Korea
- Mathematics and the History of Korean Civilization
- The West and Korea in the History of Science and Technology, 1600-1950
- Imperialism, Colonialism, Post-colonialism and Technological Science in Korea
- Development of Science and Technology Under the Korean Authoritarian Regime
- Dynamics of Technological Development in Korean Industrialization
The HISTAC team believes that the publication will illuminate the nation’s triumphs in science and technology and expects that the publication will serve as valuable research resources for the study of the history of East Asian scientific civilization which has mainly focused on China and Japan. Further, by adopting various case studies of scientific achievements of South Korea and developing countries, they hope to propose a new model for studying history of science and civilization.
2013.11.28 View 9338 -
 Green Technology for Data Centers: Ultra-low Power 100 Gbps Ethernet Integrated Circuit Developed
A new integrated circuit (IC), consuming only 0.75W of electricity, will reduce the power usage of data chips installed at data centers by one-third.
Each day, billions of people surf the Internet for information, entertainment, and educational content. The Internet contains an immeasurable amount of information and knowledge generated every minute all around the world that is readily available to everyone with a click of a computer mouse. The real magic of the Internet, however, lies in data centers, where hundreds of billions of data are stored and distributed to designated users around the clock.
Today, almost every business or organization either has its own data centers or outsources data center services to a third party. These centers house highly specialized equipment responsible for the support of computers, networks, data storage, and business security. Accordingly, the operational cost of data centers is tremendous because they consume a large amount of electricity.
Data centers can consume up to 100 times more energy than a standard office building. Data center energy consumption doubled from 2000 to 2006, reaching more than 60 billion kilowatt hours per year. If the current usage and technology trends continue, the energy consumption of data centers in the US will reach 8% of the country’s total electric power consumption by 2020.
A research team at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Terasquare, Inc. (
http://www.terasquare.co.kr
), a spin-off company of the university,
developed an extremely low-powered integrated circuit for Ethernet that consumes less than 0.75W of electricity but is able to send and receive data at the high speed of 100 gigabits per second (Gbps). The research team, headed by Hyeon-Min Bae, assistant professor of electrical engineering at KAIST, claims that the new microchip uses only one-third of the electricity consumed by the currently installed chips at data centers, thereby helping the centers to save energy.
Integrated circuits are embedded on communication modules that are inserted into a line card. Data centers have numerous line cards to build a network including routers and switches. Currently, 8W ICs are the most common in the market, and they consume a lot of energy and require the largest modules (112 cm
2
of CFP), decreasing the port density of line cards and, thus, limiting the amount of data transmission.
The ultra-low-power-circuit, 100-gigabit, full-transceiver CDR, is the world’s first solution that can be loaded to the smallest communication modules (20 cm
2
of CFP4 or 16 cm
2
of
QSFP28), the next-generation chips for data centers. Compared with other chip producers, the 100 Gbps CDR is a greener version of the technology that improves the energy efficiency of data centers while maintaining the high speed of data transmission.
Professor Hyeon-Min Bae said, “When we demonstrate our chip in September of this year at one of the leading companies that manufacture optical communication components and systems, they said that our product is two years ahead of those of our competitors. We plan to produce the chip from 2014 and expect that it will lead the 100 Gbps Ethernet IC market, which is expected to grow to USD 1 billion by 2017.”
The commercial model of the IC was first introduced at the 39
th
European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication (ECOC), the largest optical communication forum for new results and developments in Europe, held from September 22-26 at ExCeL London, an international exhibition and convention center.
Professor Bae added, “We received positive responses to our ultra-low-power 100-Gbps Ethernet IC at the ECOC. The chip will be used not only for a particular industry but also for many of next-generation, super-high-speed information communications technologies, such as high-speed USB, high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI), and TV interface.”
Before joining KAIST, Hyeon-Min Bae worked for many years at Finisar as a researcher who designed and developed the world’s first super-high-speed circuit, the 100 Gbps Ethernet IC.
2013.11.25 View 9769
Green Technology for Data Centers: Ultra-low Power 100 Gbps Ethernet Integrated Circuit Developed
A new integrated circuit (IC), consuming only 0.75W of electricity, will reduce the power usage of data chips installed at data centers by one-third.
Each day, billions of people surf the Internet for information, entertainment, and educational content. The Internet contains an immeasurable amount of information and knowledge generated every minute all around the world that is readily available to everyone with a click of a computer mouse. The real magic of the Internet, however, lies in data centers, where hundreds of billions of data are stored and distributed to designated users around the clock.
Today, almost every business or organization either has its own data centers or outsources data center services to a third party. These centers house highly specialized equipment responsible for the support of computers, networks, data storage, and business security. Accordingly, the operational cost of data centers is tremendous because they consume a large amount of electricity.
Data centers can consume up to 100 times more energy than a standard office building. Data center energy consumption doubled from 2000 to 2006, reaching more than 60 billion kilowatt hours per year. If the current usage and technology trends continue, the energy consumption of data centers in the US will reach 8% of the country’s total electric power consumption by 2020.
A research team at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and Terasquare, Inc. (
http://www.terasquare.co.kr
), a spin-off company of the university,
developed an extremely low-powered integrated circuit for Ethernet that consumes less than 0.75W of electricity but is able to send and receive data at the high speed of 100 gigabits per second (Gbps). The research team, headed by Hyeon-Min Bae, assistant professor of electrical engineering at KAIST, claims that the new microchip uses only one-third of the electricity consumed by the currently installed chips at data centers, thereby helping the centers to save energy.
Integrated circuits are embedded on communication modules that are inserted into a line card. Data centers have numerous line cards to build a network including routers and switches. Currently, 8W ICs are the most common in the market, and they consume a lot of energy and require the largest modules (112 cm
2
of CFP), decreasing the port density of line cards and, thus, limiting the amount of data transmission.
The ultra-low-power-circuit, 100-gigabit, full-transceiver CDR, is the world’s first solution that can be loaded to the smallest communication modules (20 cm
2
of CFP4 or 16 cm
2
of
QSFP28), the next-generation chips for data centers. Compared with other chip producers, the 100 Gbps CDR is a greener version of the technology that improves the energy efficiency of data centers while maintaining the high speed of data transmission.
Professor Hyeon-Min Bae said, “When we demonstrate our chip in September of this year at one of the leading companies that manufacture optical communication components and systems, they said that our product is two years ahead of those of our competitors. We plan to produce the chip from 2014 and expect that it will lead the 100 Gbps Ethernet IC market, which is expected to grow to USD 1 billion by 2017.”
The commercial model of the IC was first introduced at the 39
th
European Conference and Exhibition on Optical Communication (ECOC), the largest optical communication forum for new results and developments in Europe, held from September 22-26 at ExCeL London, an international exhibition and convention center.
Professor Bae added, “We received positive responses to our ultra-low-power 100-Gbps Ethernet IC at the ECOC. The chip will be used not only for a particular industry but also for many of next-generation, super-high-speed information communications technologies, such as high-speed USB, high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI), and TV interface.”
Before joining KAIST, Hyeon-Min Bae worked for many years at Finisar as a researcher who designed and developed the world’s first super-high-speed circuit, the 100 Gbps Ethernet IC.
2013.11.25 View 9769 -
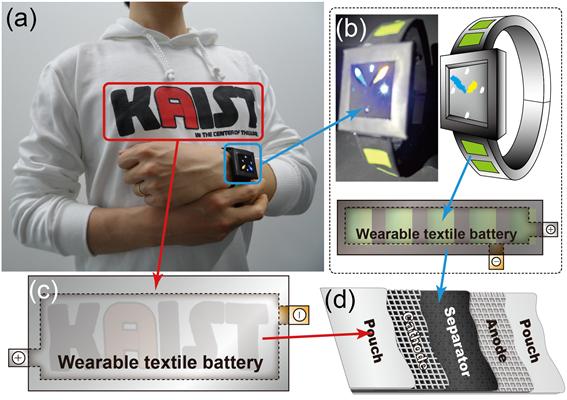 Technology Developed for Flexible, Foldable & Rechargeable Battery
Flexible, Foldable & Rechargeable Battery
The research group of professors Jang-Wook Choi & Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of EEWS and Taek-Soo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST has developed technology for flexible and foldable batteries which are rechargeable using solar energy. The research result was published in the online issue of Nano Letters on November 5.
Trial versions of flexible and wearable electronics are being developed and introduced in the market such as Galaxy Gear, Apple’s i-Watch, and Google Glass. Research is being conducted to make the batteries softer and more wearable and to compete in the fast-growing market for flexible electronics.
This new technology is expected to be applied to the development of wearable computers as well as winter outdoor clothing since it is flexible and light. The research group expects that the new technology can be applied to current battery production lines without additional investment.
Professor Choi said, “It can be used as a core-source technology in the rechargeable battery industry in the future. Various wearable mobile electronic products can be developed through cooperation and collaboration within the industry.”
2013.11.21 View 12120
Technology Developed for Flexible, Foldable & Rechargeable Battery
Flexible, Foldable & Rechargeable Battery
The research group of professors Jang-Wook Choi & Jung-Yong Lee from the Graduate School of EEWS and Taek-Soo Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST has developed technology for flexible and foldable batteries which are rechargeable using solar energy. The research result was published in the online issue of Nano Letters on November 5.
Trial versions of flexible and wearable electronics are being developed and introduced in the market such as Galaxy Gear, Apple’s i-Watch, and Google Glass. Research is being conducted to make the batteries softer and more wearable and to compete in the fast-growing market for flexible electronics.
This new technology is expected to be applied to the development of wearable computers as well as winter outdoor clothing since it is flexible and light. The research group expects that the new technology can be applied to current battery production lines without additional investment.
Professor Choi said, “It can be used as a core-source technology in the rechargeable battery industry in the future. Various wearable mobile electronic products can be developed through cooperation and collaboration within the industry.”
2013.11.21 View 12120 -
 One Day Idea Hackathon, GoGeeks 2013
GoGeeks Creation Group, founded by KAIST alumni, is hosting the GoGeeks One Day Idea Hackathon 2013 on November 23 at the Microsoft (MS) Building in Seoul. The contest was organized to support creative ideas proposed by college students and help them to be applied in real life.
The first GoGeeks contest was held last year by a group of KAIST undergraduate students, which was influenced by Duke University’s Elevator Pitch Competition, an entrepreneurial competition started in 1999.
Applications for the contest should be submitted on www.gogeeks.co.kr by November 20, and the first 30 groups registered will get to compete in the contest.
Each group will make one-minute presentations after six hours of planning on the theme of “Color Your Society.” Then five-minute presentations will follow by the top ten groups selected from the first stage. The top five groups will be each awarded the prize of 2 million Korean won.
The five selected teams will work on their proposed projects during the winter vacation with support from MS Korea and the Center for Science-based Entrepreneurship at KAIST.
Fundraising for the event is going on at http://tumblbug.com/gogeeks2013.
2013.11.21 View 7608
One Day Idea Hackathon, GoGeeks 2013
GoGeeks Creation Group, founded by KAIST alumni, is hosting the GoGeeks One Day Idea Hackathon 2013 on November 23 at the Microsoft (MS) Building in Seoul. The contest was organized to support creative ideas proposed by college students and help them to be applied in real life.
The first GoGeeks contest was held last year by a group of KAIST undergraduate students, which was influenced by Duke University’s Elevator Pitch Competition, an entrepreneurial competition started in 1999.
Applications for the contest should be submitted on www.gogeeks.co.kr by November 20, and the first 30 groups registered will get to compete in the contest.
Each group will make one-minute presentations after six hours of planning on the theme of “Color Your Society.” Then five-minute presentations will follow by the top ten groups selected from the first stage. The top five groups will be each awarded the prize of 2 million Korean won.
The five selected teams will work on their proposed projects during the winter vacation with support from MS Korea and the Center for Science-based Entrepreneurship at KAIST.
Fundraising for the event is going on at http://tumblbug.com/gogeeks2013.
2013.11.21 View 7608 -
 Professor Ji-Yun Lee, Received FAA Recognition Award
Professor Ji-Yun Lee, from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, received the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Recognition Award for her Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) and her contribution to the development of satellite navigation technology.
GBAS contributes to the safety of aircraft navigation by providing flawless information with real-time location accuracy within one meter.
Professor Lee developed the monitoring software to improve the safety of GBAS users in her paper published in the International Journal of Radio Science in July of 2012.
The software will be distributed and used by many organizations including Eurocontrol following verification from the FAA technical center. It is expected to be standardized after discussions among international organizations.Professor Lee said, “As satellite navigation is applied to the infrastructure of air, marine, and ground transportation, as well as information & communications and finance, ensuring the performance and safety of the system is the most important factor. GBAS will be further developed and applied as a part of a global service system through international collaboration.”
2013.11.15 View 11696
Professor Ji-Yun Lee, Received FAA Recognition Award
Professor Ji-Yun Lee, from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, received the US Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) Recognition Award for her Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) and her contribution to the development of satellite navigation technology.
GBAS contributes to the safety of aircraft navigation by providing flawless information with real-time location accuracy within one meter.
Professor Lee developed the monitoring software to improve the safety of GBAS users in her paper published in the International Journal of Radio Science in July of 2012.
The software will be distributed and used by many organizations including Eurocontrol following verification from the FAA technical center. It is expected to be standardized after discussions among international organizations.Professor Lee said, “As satellite navigation is applied to the infrastructure of air, marine, and ground transportation, as well as information & communications and finance, ensuring the performance and safety of the system is the most important factor. GBAS will be further developed and applied as a part of a global service system through international collaboration.”
2013.11.15 View 11696 -
 KAIST's Partnership Agreement with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, UK
KAIST signed an agreement on academic and research cooperation with the Imperial College of Science, Technology (Imperial College London) and Medicine in the United Kingdom (UK) on November 6th, 2013 in London.
The two universities have been implementing collaboration programs at the department level in the areas of plastic electronics since September 2012 and systems engineering and molecular simulation since February 2013, but have never had a formal partnership agreement.
President Steve Kang from KAIST and Provost James Stirling from Imperial College London signed the comprehensive cooperation agreement which will not only strengthen the existing collaborations between the two institutions but also explore areas of mutual interest in the interdisciplinary study of big data, as well as in the fields of mechanical engineering, synthetic biology, and quantum physics.
Workshops, seminars, lectures, and conferences will be jointly organized and held to facilitate the exchange of research staff and faculty and to promote collaborations in research assignments. The universities will also look into the possibility of exchange programs for undergraduate and graduate students.
The partnership agreement will be effective for five years.
Minister Moon-Gi Choi from the Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Science, Information and Communications Technology (ICT) & Future Planning attended the signing ceremony as well and congratulated the establishment of the partnership, saying:
“We are living in the age of highly advanced science and technology that requires us to have a new economic development paradigm for sustainable growth. Through convergence research based on the application of ICT and technology innovation, we will have new opportunities for development. I hope KAIST and the Imperial College London will be at the forefront of such endeavors in coming years.”With its history spanning over 100 years, the Imperial College London is a public research university located in London, UK, specializing in science, engineering, medicine, and business. The university is regarded as being one of the most prestigious universities in the world, having eminent alumni such as Thomas Henry Huxley (biologist), H.G. Wells (author), and Sir Alexander Fleming (pharmacologist).
From left to right: Provost James Stirling, Minister Moon-Gi Choi, and President Steve Kang
2013.11.12 View 9667
KAIST's Partnership Agreement with the Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, UK
KAIST signed an agreement on academic and research cooperation with the Imperial College of Science, Technology (Imperial College London) and Medicine in the United Kingdom (UK) on November 6th, 2013 in London.
The two universities have been implementing collaboration programs at the department level in the areas of plastic electronics since September 2012 and systems engineering and molecular simulation since February 2013, but have never had a formal partnership agreement.
President Steve Kang from KAIST and Provost James Stirling from Imperial College London signed the comprehensive cooperation agreement which will not only strengthen the existing collaborations between the two institutions but also explore areas of mutual interest in the interdisciplinary study of big data, as well as in the fields of mechanical engineering, synthetic biology, and quantum physics.
Workshops, seminars, lectures, and conferences will be jointly organized and held to facilitate the exchange of research staff and faculty and to promote collaborations in research assignments. The universities will also look into the possibility of exchange programs for undergraduate and graduate students.
The partnership agreement will be effective for five years.
Minister Moon-Gi Choi from the Republic of Korea’s Ministry of Science, Information and Communications Technology (ICT) & Future Planning attended the signing ceremony as well and congratulated the establishment of the partnership, saying:
“We are living in the age of highly advanced science and technology that requires us to have a new economic development paradigm for sustainable growth. Through convergence research based on the application of ICT and technology innovation, we will have new opportunities for development. I hope KAIST and the Imperial College London will be at the forefront of such endeavors in coming years.”With its history spanning over 100 years, the Imperial College London is a public research university located in London, UK, specializing in science, engineering, medicine, and business. The university is regarded as being one of the most prestigious universities in the world, having eminent alumni such as Thomas Henry Huxley (biologist), H.G. Wells (author), and Sir Alexander Fleming (pharmacologist).
From left to right: Provost James Stirling, Minister Moon-Gi Choi, and President Steve Kang
2013.11.12 View 9667 -
 KAIST student wins Aerospace Student Papers Grand Prize
Dong-Il Yoo, a doctoral candidate under Professor Hyun-Chul Shim, at the Department of Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, has been awarded the Second Prize Award at the 11th Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) Paper Contest. The award ceremony was held on October 30th at the media conference room at the KINTEX ADEX 2013 Exhibition in Seoul.
Yoo"s paper, titled "A Study on Virtual Pursuit Point-based Autonomous Air Combat Guidance Law for UCAV," is highly regarded for originality and creativity. The Field Robotics Center at the KAIST Institute, where Yoo conducted his research, also received the first prize at the 7th KAI Paper Contest.
The KAI Paper Contest was first organized in 2003 to promote academic interest and advance research and development in aerospace engineering among university students.
The KAI Paper Contest is one of the most prestigious contests in Korea. It is sponsored by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, the Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, the Korea Aerospace Industries Association, and the Korea Civil Aviation Development Association.
Dong-Il Yoo (left) and Professor Hyun-Chul Shim (right)
2013.11.11 View 13080
KAIST student wins Aerospace Student Papers Grand Prize
Dong-Il Yoo, a doctoral candidate under Professor Hyun-Chul Shim, at the Department of Aerospace Engineering, KAIST, has been awarded the Second Prize Award at the 11th Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI) Paper Contest. The award ceremony was held on October 30th at the media conference room at the KINTEX ADEX 2013 Exhibition in Seoul.
Yoo"s paper, titled "A Study on Virtual Pursuit Point-based Autonomous Air Combat Guidance Law for UCAV," is highly regarded for originality and creativity. The Field Robotics Center at the KAIST Institute, where Yoo conducted his research, also received the first prize at the 7th KAI Paper Contest.
The KAI Paper Contest was first organized in 2003 to promote academic interest and advance research and development in aerospace engineering among university students.
The KAI Paper Contest is one of the most prestigious contests in Korea. It is sponsored by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport, the Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, the Korea Aerospace Industries Association, and the Korea Civil Aviation Development Association.
Dong-Il Yoo (left) and Professor Hyun-Chul Shim (right)
2013.11.11 View 13080 -
 The World Economic Forum Invites KAIST to 2014 Davos Forum
President Steve Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee have been invited by the World Economic Forum (WEF) to attend its annual meeting slated for January 22-25, 2014 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland.
The president will also join the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) to be held during the annual meeting. The GULF consists of leading research universities throughout the world, at which President Kang will address agenda related to higher education and research.
From September 11th to 13th, KAIST was invited to the WEF’s 2013 Summer Davos Forum held in Dalian, China. The Summer Davos Forum is recognized as a barometer of the world economy, and KAIST hosted three sessions there.
In a session titled “Smart Regulations,” Professor Sang Yup Lee hosted presentations and discussions under the topic of “How regulation models can strengthen technical innovation and expansion.” President Steve Kang, Peter Sands, CEO of Standard Chartered Bank Group, Mark Weinberger, CEO of Ernest & Young, and Peter Terium, CEO of RWE, participated in the discussions.
The KAIST delegates also presented and participated in a session titled “From Trade Center to Innovative Hub” to discuss how to lead innovations in Asia, as well as “Marine Resources: Finding New Frontier” to address issues of how to develop and manage oceanic resources for potential growth.
President Kang said, “The World Economic Forum allows us to introduce the results of our innovative and creative research to global leaders and to demonstrate that our global position continues to grow.”
The WEF has been hosting Summer Davos Forum in China since 2007. About 1,500 participants from over 90 countries joined in this year’s summer forum under the theme of “Innovation: Inevitable Mainstream.” New strategies for innovations and solutions for global threats were suggested through presentations and discussions in 125 sessions.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an independent, international, and non-profit organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. It is committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and government leaders to shape global, regional and industry agenda.
Among the meetings and forums organized by the WEF, its annual meeting held each January in Davos, a.k.a. the Davos Forum, has been the best known gathering. The Davos Forum brings together some 2,500 top business leaders, international political leaders, selected intellectuals and journalists to discuss the most pressing issues facing the world including health and environment.
2013.11.07 View 11549
The World Economic Forum Invites KAIST to 2014 Davos Forum
President Steve Kang and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee have been invited by the World Economic Forum (WEF) to attend its annual meeting slated for January 22-25, 2014 in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland.
The president will also join the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF) to be held during the annual meeting. The GULF consists of leading research universities throughout the world, at which President Kang will address agenda related to higher education and research.
From September 11th to 13th, KAIST was invited to the WEF’s 2013 Summer Davos Forum held in Dalian, China. The Summer Davos Forum is recognized as a barometer of the world economy, and KAIST hosted three sessions there.
In a session titled “Smart Regulations,” Professor Sang Yup Lee hosted presentations and discussions under the topic of “How regulation models can strengthen technical innovation and expansion.” President Steve Kang, Peter Sands, CEO of Standard Chartered Bank Group, Mark Weinberger, CEO of Ernest & Young, and Peter Terium, CEO of RWE, participated in the discussions.
The KAIST delegates also presented and participated in a session titled “From Trade Center to Innovative Hub” to discuss how to lead innovations in Asia, as well as “Marine Resources: Finding New Frontier” to address issues of how to develop and manage oceanic resources for potential growth.
President Kang said, “The World Economic Forum allows us to introduce the results of our innovative and creative research to global leaders and to demonstrate that our global position continues to grow.”
The WEF has been hosting Summer Davos Forum in China since 2007. About 1,500 participants from over 90 countries joined in this year’s summer forum under the theme of “Innovation: Inevitable Mainstream.” New strategies for innovations and solutions for global threats were suggested through presentations and discussions in 125 sessions.
The World Economic Forum (WEF) is an independent, international, and non-profit organization based in Geneva, Switzerland. It is committed to improving the state of the world by engaging business, political, academic, and government leaders to shape global, regional and industry agenda.
Among the meetings and forums organized by the WEF, its annual meeting held each January in Davos, a.k.a. the Davos Forum, has been the best known gathering. The Davos Forum brings together some 2,500 top business leaders, international political leaders, selected intellectuals and journalists to discuss the most pressing issues facing the world including health and environment.
2013.11.07 View 11549 -
 Professor Jae-Hyung Lee appointed as AIChE fellow
Professor Jae-Hyung Lee from the Department of Chemical and Bimolecular Engineering at KAIST was appointed as a fellow in the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE).
Established in 1908, AIChE is the largest association of chemical engineers worldwide, which now boasts more than 40,000 members from 90 countries.
Following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the same department at KAIST, Professor Jae-Hyung Lee is the second Korean appointed as a fellow by the organization.
He has been acknowledged for his innovative research on the improvement of model predictive control of industrial processes.
Professor Lee is the director of the Saudi Armaco-KAIST CO2 Management Center at KAIST, a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC), and a member of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
He received the Young Investigator Award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) in 1994 and the Computing in Chemical Engineering Award from AIChE in 2013.
2013.11.05 View 10087
Professor Jae-Hyung Lee appointed as AIChE fellow
Professor Jae-Hyung Lee from the Department of Chemical and Bimolecular Engineering at KAIST was appointed as a fellow in the American Institute of Chemical Engineers (AIChE).
Established in 1908, AIChE is the largest association of chemical engineers worldwide, which now boasts more than 40,000 members from 90 countries.
Following Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the same department at KAIST, Professor Jae-Hyung Lee is the second Korean appointed as a fellow by the organization.
He has been acknowledged for his innovative research on the improvement of model predictive control of industrial processes.
Professor Lee is the director of the Saudi Armaco-KAIST CO2 Management Center at KAIST, a fellow of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) and the International Federation of Automatic Control (IFAC), and a member of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology.
He received the Young Investigator Award from the National Science Foundation (NSF) in 1994 and the Computing in Chemical Engineering Award from AIChE in 2013.
2013.11.05 View 10087 -
 KAIST announced a novel technology to produce gasoline by a metabolically engineered microorganism
A major scientific breakthrough in the development of renewable energy sources and other important chemicals; The research team succeeded in producing 580 mg of gasoline per liter of cultured broth by converting in vivo generated fatty acids
For many decades, we have been relying on fossil resources to produce liquid fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and many industrial and consumer chemicals for daily use. However, increasing strains on natural resources as well as environmental issues including global warming have triggered a strong interest in developing sustainable ways to obtain fuels and chemicals.
Gasoline, the petroleum-derived product that is most widely used as a fuel for transportation, is a mixture of hydrocarbons, additives, and blending agents. The hydrocarbons, called alkanes, consist only of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Gasoline has a combination of straight-chain and branched-chain alkanes (hydrocarbons) consisted of 4-12 carbon atoms linked by direct carbon-carbon bonds.
Previously, through metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli (E. coli), there have been a few research results on the production of long-chain alkanes, which consist of 13-17 carbon atoms, suitable for replacing diesel. However, there has been no report on the microbial production of short-chain alkanes, a possible substitute for gasoline.
In the paper (entitled "Microbial Production of Short-chain Alkanes") published online in Nature on September 29, a Korean research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) reported, for the first time, the development of a novel strategy for microbial gasoline production through metabolic engineering of E. coli.
The research team engineered the fatty acid metabolism to provide the fatty acid derivatives that are shorter than normal intracellular fatty acid metabolites, and introduced a novel synthetic pathway for the biosynthesis of short-chain alkanes. This allowed the development of platform E. coli strain capable of producing gasoline for the first time. Furthermore, this platform strain, if desired, can be modified to produce other products such as short-chain fatty esters and short-chain fatty alcohols.
In this paper, the Korean researchers described detailed strategies for 1) screening of enzymes associated with the production of fatty acids, 2) engineering of enzymes and fatty acid biosynthetic pathways to concentrate carbon flux towards the short-chain fatty acid production, and 3) converting short-chain fatty acids to their corresponding alkanes (gasoline) by introducing a novel synthetic pathway and optimization of culture conditions. Furthermore, the research team showed the possibility of producing fatty esters and alcohols by introducing responsible enzymes into the same platform strain.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "It is only the beginning of the work towards sustainable production of gasoline. The titer is rather low due to the low metabolic flux towards the formation of short-chain fatty acids and their derivatives. We are currently working on increasing the titer, yield and productivity of bio-gasoline. Nonetheless, we are pleased to report, for the first time, the production of gasoline through the metabolic engineering of E. coli, which we hope will serve as a basis for the metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce fuels and chemicals from renewable resources."
This research was supported by the Advanced Biomass Research and Development Center of Korea (ABC-2010-0029799) through the Global Frontier Research Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation (NRF), Republic of Korea. Systems metabolic engineering work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012-C1AAA001-2012M1A2A2026556) by MSIP through NRF.
Short-Chain Alkanes Generated from Renewable Biomass
This diagram shows the metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of short-chain alkanes (gasoline) from renewable biomass.
Nature Cover Page (September 29th, 2013)
2013.11.04 View 12584
KAIST announced a novel technology to produce gasoline by a metabolically engineered microorganism
A major scientific breakthrough in the development of renewable energy sources and other important chemicals; The research team succeeded in producing 580 mg of gasoline per liter of cultured broth by converting in vivo generated fatty acids
For many decades, we have been relying on fossil resources to produce liquid fuels such as gasoline, diesel, and many industrial and consumer chemicals for daily use. However, increasing strains on natural resources as well as environmental issues including global warming have triggered a strong interest in developing sustainable ways to obtain fuels and chemicals.
Gasoline, the petroleum-derived product that is most widely used as a fuel for transportation, is a mixture of hydrocarbons, additives, and blending agents. The hydrocarbons, called alkanes, consist only of carbon and hydrogen atoms. Gasoline has a combination of straight-chain and branched-chain alkanes (hydrocarbons) consisted of 4-12 carbon atoms linked by direct carbon-carbon bonds.
Previously, through metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli (E. coli), there have been a few research results on the production of long-chain alkanes, which consist of 13-17 carbon atoms, suitable for replacing diesel. However, there has been no report on the microbial production of short-chain alkanes, a possible substitute for gasoline.
In the paper (entitled "Microbial Production of Short-chain Alkanes") published online in Nature on September 29, a Korean research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) reported, for the first time, the development of a novel strategy for microbial gasoline production through metabolic engineering of E. coli.
The research team engineered the fatty acid metabolism to provide the fatty acid derivatives that are shorter than normal intracellular fatty acid metabolites, and introduced a novel synthetic pathway for the biosynthesis of short-chain alkanes. This allowed the development of platform E. coli strain capable of producing gasoline for the first time. Furthermore, this platform strain, if desired, can be modified to produce other products such as short-chain fatty esters and short-chain fatty alcohols.
In this paper, the Korean researchers described detailed strategies for 1) screening of enzymes associated with the production of fatty acids, 2) engineering of enzymes and fatty acid biosynthetic pathways to concentrate carbon flux towards the short-chain fatty acid production, and 3) converting short-chain fatty acids to their corresponding alkanes (gasoline) by introducing a novel synthetic pathway and optimization of culture conditions. Furthermore, the research team showed the possibility of producing fatty esters and alcohols by introducing responsible enzymes into the same platform strain.
Professor Sang Yup Lee said, "It is only the beginning of the work towards sustainable production of gasoline. The titer is rather low due to the low metabolic flux towards the formation of short-chain fatty acids and their derivatives. We are currently working on increasing the titer, yield and productivity of bio-gasoline. Nonetheless, we are pleased to report, for the first time, the production of gasoline through the metabolic engineering of E. coli, which we hope will serve as a basis for the metabolic engineering of microorganisms to produce fuels and chemicals from renewable resources."
This research was supported by the Advanced Biomass Research and Development Center of Korea (ABC-2010-0029799) through the Global Frontier Research Program of the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) through the National Research Foundation (NRF), Republic of Korea. Systems metabolic engineering work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries (NRF-2012-C1AAA001-2012M1A2A2026556) by MSIP through NRF.
Short-Chain Alkanes Generated from Renewable Biomass
This diagram shows the metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli for the production of short-chain alkanes (gasoline) from renewable biomass.
Nature Cover Page (September 29th, 2013)
2013.11.04 View 12584 -
 Collaboration with Korea Institute of Energy Research
KAIST and the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) agreed on September 4th to further collaboration on energy research such as the development of nano-based hybrid solar cells, bio-fuels, artificial photosynthesis, and carbon dioxide reduction.
The two institutions will select 11 research projects to focus on their cooperation. President Steve Kang (in the right) stood with Jooho Whang, the president of KIER (in the left), holding the signed memorandum of understanding.
2013.11.04 View 8372
Collaboration with Korea Institute of Energy Research
KAIST and the Korea Institute of Energy Research (KIER) agreed on September 4th to further collaboration on energy research such as the development of nano-based hybrid solar cells, bio-fuels, artificial photosynthesis, and carbon dioxide reduction.
The two institutions will select 11 research projects to focus on their cooperation. President Steve Kang (in the right) stood with Jooho Whang, the president of KIER (in the left), holding the signed memorandum of understanding.
2013.11.04 View 8372