research
-
 Closer to the Dream: Graphene
A technique that allows easy and larger observation area of graphene’s crystal face was developed by Korean Research Team.
The research team, led by Professor Jeong Hui Tae (KAIST), consists of Doctorate candidate Kim Dae Woo, Dr. Kim Yoon Ho (primary author), Doctorate candidate Jeong Hyun Soo. The research is supported by WCU (World Class Research University) Development Plan, Mid-Aged Researcher Support Business and was published in the online edition of Nature Nanotechnology.
(Dissertation: Direct visualization of large0area graphene domains and boundaries by optical birefringency)
Professor Jeong’s team used the optical property of the liquid display used in LCD to visualize the size and shape of the single crystals along a flat surface. The visualization of the single crystal allowed the measurement of a near theoretical value of electrical conductivity of graphene.
Graphene has great electrical conductivity, transparent, mechanically stable, flexible, and is therefore regarded as the next generation electrical material. However the polycrystalinity of graphene meant that the actual electrical, mechanical properties were lower than the theoretical values. The reason was thought to be because of the size of the crystal faces and boundary structures.
Therefore, in order to create graphene that has good properties, observing the domain and boundary of graphene crystal faces is essential.
The new technique developed by the research team is another step towards commercializing transparent electrodes, flexible display, and electric materials like solar cells.
2012.01.31 View 12005
Closer to the Dream: Graphene
A technique that allows easy and larger observation area of graphene’s crystal face was developed by Korean Research Team.
The research team, led by Professor Jeong Hui Tae (KAIST), consists of Doctorate candidate Kim Dae Woo, Dr. Kim Yoon Ho (primary author), Doctorate candidate Jeong Hyun Soo. The research is supported by WCU (World Class Research University) Development Plan, Mid-Aged Researcher Support Business and was published in the online edition of Nature Nanotechnology.
(Dissertation: Direct visualization of large0area graphene domains and boundaries by optical birefringency)
Professor Jeong’s team used the optical property of the liquid display used in LCD to visualize the size and shape of the single crystals along a flat surface. The visualization of the single crystal allowed the measurement of a near theoretical value of electrical conductivity of graphene.
Graphene has great electrical conductivity, transparent, mechanically stable, flexible, and is therefore regarded as the next generation electrical material. However the polycrystalinity of graphene meant that the actual electrical, mechanical properties were lower than the theoretical values. The reason was thought to be because of the size of the crystal faces and boundary structures.
Therefore, in order to create graphene that has good properties, observing the domain and boundary of graphene crystal faces is essential.
The new technique developed by the research team is another step towards commercializing transparent electrodes, flexible display, and electric materials like solar cells.
2012.01.31 View 12005 -
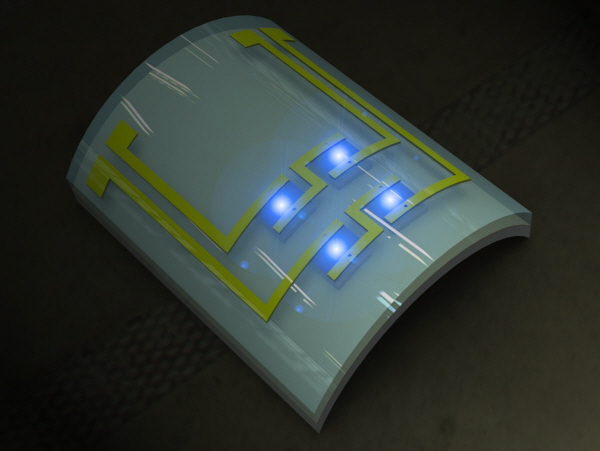 Cancer detection from an implantable, flexible LED
Professor Keon Jae Lee
A KAIST research team has developed a new type of biocompatible and bendable GaN LED biosensor.
Daejeon, the Republic of Korea, August 8, 2011—Can a flexible LED conformably placed on the human heart, situated on the corrugated surface of the human brain, or rolled upon the blood vessels, diagnose or even treat various diseases? These things might be a reality in the near future.
The team of Professor Keon Jae Lee (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST) has developed a new concept: a biocompatible, flexible Gallium Nitride (GaN) LED that can detect prostate cancer.
GaN LED, a highly efficient light emitting device, has been commercialized in LED TVs and in the lighting industry. Until now, it has been difficult to use this semiconductor material to fabricate flexible electronic systems due to its brittleness. The research team, however, has succeeded in developing a highly efficient, flexible GaN LED and in detecting cancer using a flexible LED biosensor.
Prof. Lee was involved in the first co-invention of "High Performance Flexible Single Crystal GaN" during his PhD course at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC). This flexible GaN LED biosensor utilized a similar protocol to transfer thin GaN LED films onto flexible substrates, followed by a biocompatible packaging process; the system’s overall potential for use in implantable biomedical applications was demonstrated.
Professor John Roger (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, UIUC) said,
“Bio-integrated LEDs represent an exciting, new technology with strong potential to address important challenges in human health. This present work represents a very nice contribution to this emerging field.”
This paper was published in the online issue of Nano Energy Elsevier Journal (Editor, Prof. Zhong Lin Wang) dated September 16, 2011.
Flexible GaN LED produces blue light.
2011.09.20 View 13166
Cancer detection from an implantable, flexible LED
Professor Keon Jae Lee
A KAIST research team has developed a new type of biocompatible and bendable GaN LED biosensor.
Daejeon, the Republic of Korea, August 8, 2011—Can a flexible LED conformably placed on the human heart, situated on the corrugated surface of the human brain, or rolled upon the blood vessels, diagnose or even treat various diseases? These things might be a reality in the near future.
The team of Professor Keon Jae Lee (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, KAIST) has developed a new concept: a biocompatible, flexible Gallium Nitride (GaN) LED that can detect prostate cancer.
GaN LED, a highly efficient light emitting device, has been commercialized in LED TVs and in the lighting industry. Until now, it has been difficult to use this semiconductor material to fabricate flexible electronic systems due to its brittleness. The research team, however, has succeeded in developing a highly efficient, flexible GaN LED and in detecting cancer using a flexible LED biosensor.
Prof. Lee was involved in the first co-invention of "High Performance Flexible Single Crystal GaN" during his PhD course at the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign (UIUC). This flexible GaN LED biosensor utilized a similar protocol to transfer thin GaN LED films onto flexible substrates, followed by a biocompatible packaging process; the system’s overall potential for use in implantable biomedical applications was demonstrated.
Professor John Roger (Department of Materials Science and Engineering, UIUC) said,
“Bio-integrated LEDs represent an exciting, new technology with strong potential to address important challenges in human health. This present work represents a very nice contribution to this emerging field.”
This paper was published in the online issue of Nano Energy Elsevier Journal (Editor, Prof. Zhong Lin Wang) dated September 16, 2011.
Flexible GaN LED produces blue light.
2011.09.20 View 13166 -
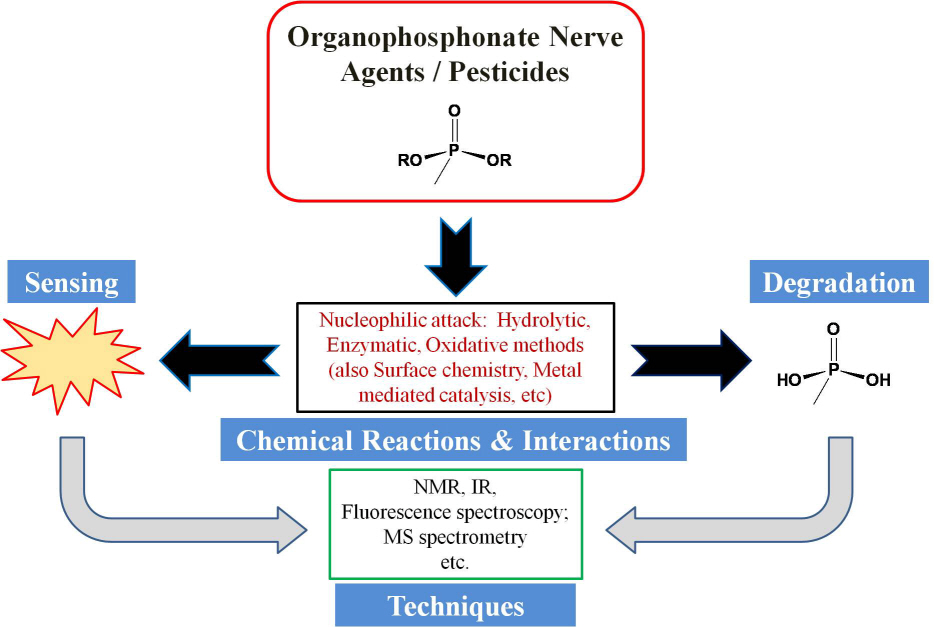 Review of organophosphonate nerve agent remediation and sensing chemistry
Professor David Churchill, Dept. of Chemistry, KAIST
Scientists in Daejeon, South Korea and Lexington, Kentucky (USA) have recently published a review on the subject of nerve agent remediation and probing chemistry (Chemical Reviews, DOI:10.1021/cr100193y). This article endeavored to pursue organophosphonate nerve agent chemistry deeply and comprehensively and to reflect that decontamination / sensing and nerve agents / pesticides are quite inextricable: when one tries to degrade nerve agents one also needs to detect what components are still present “downstream,” etc. Nerve agents and many pesticides also share a common generalized organophosphate / -phosphonate structure.
Also, the use of simulant molecules (mimics) and a consideration of the closely related organophosphonate pesticides were also treated comprehensively in the Review. The authors reached back into the literature when developing some sections to make important connections to the contemporary topics of interest. The review also includes industrial insights.
Kibong Kim, Olga G. Tsay and David G. Churchill of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST and David A. Atwood of the Department of Chemistry of the University of Kentucky endeavored to "make a variety of connections in research strategies and (sub-) fields to present what is still possible, fruitful, practical, and necessary and to facilitate a current comprehensive molecular level understanding of organophosphonate degradation and sensing," Churchill says.
The authors feel that for the time being, researchers in varying research areas “can use this manuscript effectively when considering future research directions.”
2011.09.19 View 9809
Review of organophosphonate nerve agent remediation and sensing chemistry
Professor David Churchill, Dept. of Chemistry, KAIST
Scientists in Daejeon, South Korea and Lexington, Kentucky (USA) have recently published a review on the subject of nerve agent remediation and probing chemistry (Chemical Reviews, DOI:10.1021/cr100193y). This article endeavored to pursue organophosphonate nerve agent chemistry deeply and comprehensively and to reflect that decontamination / sensing and nerve agents / pesticides are quite inextricable: when one tries to degrade nerve agents one also needs to detect what components are still present “downstream,” etc. Nerve agents and many pesticides also share a common generalized organophosphate / -phosphonate structure.
Also, the use of simulant molecules (mimics) and a consideration of the closely related organophosphonate pesticides were also treated comprehensively in the Review. The authors reached back into the literature when developing some sections to make important connections to the contemporary topics of interest. The review also includes industrial insights.
Kibong Kim, Olga G. Tsay and David G. Churchill of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST and David A. Atwood of the Department of Chemistry of the University of Kentucky endeavored to "make a variety of connections in research strategies and (sub-) fields to present what is still possible, fruitful, practical, and necessary and to facilitate a current comprehensive molecular level understanding of organophosphonate degradation and sensing," Churchill says.
The authors feel that for the time being, researchers in varying research areas “can use this manuscript effectively when considering future research directions.”
2011.09.19 View 9809 -
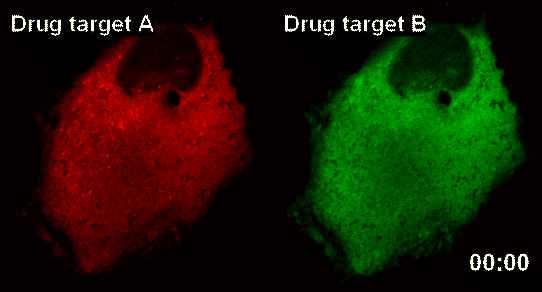 New Technology Developed for Analysis of New Drugs by Using Smart Nano-Sensors
Doctor Sang-Kyu Lee
Doctor Sang-Kyu Lee of the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed the technology that allows biological nano particles to be implanted into human cells for monitoring the effect of new drugs in real time from within the cell. It is expected that this technology will boost the ability to weigh the effects and properties of a new drug more quickly and accurately.
Conventionally, the candidate drug was injected into the human body, and then its cells are extracted to analyze the effects of the drugs. The problem with this method was that the cells were analyzed at a ‘dead’ state which made it incredibly difficult to find candidate substances due to uncontrollable side effects. This made the development of new drugs very difficult despite the large costs and efforts invested into its development.
The research team latched onto the idea that nanoparticles can connect to form a large complex. The complex acts as a nanosensor which allows for real time observation of drug target and the drug itself binding.
The team named the nanosensor technology ‘InCell SMART-i’ and was named ‘Hot Paper’ of the September edition of ‘Angewandte Chemie International Edition’ magazine, a world famous Chemistry Magazine.When a new drug injected into the human body, the drug and drug targets are gradually combined, and the smart nanosensor detects in real time the effect of the new drug as shown in the pictures above (shaded spot).
2011.09.19 View 10439
New Technology Developed for Analysis of New Drugs by Using Smart Nano-Sensors
Doctor Sang-Kyu Lee
Doctor Sang-Kyu Lee of the Department of Biological Sciences, KAIST, has developed the technology that allows biological nano particles to be implanted into human cells for monitoring the effect of new drugs in real time from within the cell. It is expected that this technology will boost the ability to weigh the effects and properties of a new drug more quickly and accurately.
Conventionally, the candidate drug was injected into the human body, and then its cells are extracted to analyze the effects of the drugs. The problem with this method was that the cells were analyzed at a ‘dead’ state which made it incredibly difficult to find candidate substances due to uncontrollable side effects. This made the development of new drugs very difficult despite the large costs and efforts invested into its development.
The research team latched onto the idea that nanoparticles can connect to form a large complex. The complex acts as a nanosensor which allows for real time observation of drug target and the drug itself binding.
The team named the nanosensor technology ‘InCell SMART-i’ and was named ‘Hot Paper’ of the September edition of ‘Angewandte Chemie International Edition’ magazine, a world famous Chemistry Magazine.When a new drug injected into the human body, the drug and drug targets are gradually combined, and the smart nanosensor detects in real time the effect of the new drug as shown in the pictures above (shaded spot).
2011.09.19 View 10439 -
 Future of Petrochemical Industry: The Age of Bio-Refineries
The concept of bio-refinery is based on using biomass from seaweeds and non-edible plant sources to produce various materials.
Bio-refineries has been looked into with increasing interest in modern times due to the advent of global warming (and the subsequent changes in the atmosphere) and the exhaustion of natural resources.
However past 20 years of research in metabolic engineering had a crucial limitation; the need to improve the efficiency of the microorganisms that actually go about converting biomass into biochemical materials.
In order to compensate for the inefficiency, Professor Lee Sang Yeop combined systems biology, composite biology, evolutionary engineering to form ‘systems metabolic engineering’.
This allows combining various data to explain the organism’s state in a multi-dimensional scope and respond accordingly by controlling the metabolism.
The result of the experiment is set as the cover dissertation of ‘Trends in Biotechnology’ magazine’s August edition.
2011.07.28 View 12998
Future of Petrochemical Industry: The Age of Bio-Refineries
The concept of bio-refinery is based on using biomass from seaweeds and non-edible plant sources to produce various materials.
Bio-refineries has been looked into with increasing interest in modern times due to the advent of global warming (and the subsequent changes in the atmosphere) and the exhaustion of natural resources.
However past 20 years of research in metabolic engineering had a crucial limitation; the need to improve the efficiency of the microorganisms that actually go about converting biomass into biochemical materials.
In order to compensate for the inefficiency, Professor Lee Sang Yeop combined systems biology, composite biology, evolutionary engineering to form ‘systems metabolic engineering’.
This allows combining various data to explain the organism’s state in a multi-dimensional scope and respond accordingly by controlling the metabolism.
The result of the experiment is set as the cover dissertation of ‘Trends in Biotechnology’ magazine’s August edition.
2011.07.28 View 12998 -
 Spintronics: A high wire act by Nanowerk News
An article by Nanowerk News on the integration of ferromagnetic nanowire arrays on grapheme substrates was published. Professor Bong-Soo Kim from the Department of Chemistry, KAIST, led the research in conjunction with Hanyang University and Samsung in Korea.
http://www.nanowerk.com/news/newsid=22204.php
Posted: Jul 25th, 2011
Spintronics: A high wire act
(Nanowerk News) Graphene is a promising material for a wide range of applications due to its remarkable mechanical and electronic properties. An application of particular interest is spin-based electronics, or spintronics, in which the spin orientation of an electron is used to perform circuit functions in addition to its charge. Bongsoo Kim and colleagues from KAIST, Hanyang University and Samsung in Korea now report the integration of ferromagnetic nanowire arrays on graphene substrates, opening up a route for the construction of graphene-based spintronic devices using nanowires as spin-injecting contacts ("Epitaxially Integrating Ferromagnetic Fe1.3Ge Nanowire Arrays on Few-Layer Graphene").
The spin of an electron is a property that, like charge, can be used to encode, process and transport information. However, spin information is easily lost in most media, which has made spintronics difficult to realize in practice. In graphene, on the other hand, spin can be preserved for longer due to its peculiar electron transport properties. "Low intrinsic spin–orbit coupling, long spin diffusion lengths and vanishing hyperfine interaction are features of graphene that make it a promising medium for spin transport," explains Kim.
Scanning electron microscopy image of vertical iron germanide nanowires grown on graphene. (© ACS 2011)
A prerequisite for the realization of spintronic devices based on graphene is its integration with ferromagnetic contacts to allow spin injection. Kim and his co-workers found that nanowires of iron germanide (Fe1.3Ge) serve as efficient contacts for this purpose. "Iron germanide nanowires show low resistivity and room-temperature ferromagnetism, and they are compatible with existing complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor technologies," says Kim.
To produce the atomically well-defined interfacial contact between the nanowires and the graphene surface needed for optimum device performance, the researchers deposited the contacts by an epitaxial method based on chemical vapor transport. Through careful adjustment of deposition parameters such as carrier gas flow rate and reaction temperature, the researchers produced vertically aligned nanowires that are closely lattice-matched to the graphene sheets (see image).
Initially preparing the graphene sheets on a substrate of silicon oxide allowed the researchers to isolate the final nanowire–graphene structure by etching and then transfer it to another substrate, greatly expanding the versatility of the approach. It is a delicate process, however. "It is necessary to transfer the graphene films onto the substrate very carefully in order to avoid folding and wrinkling of the graphene," says Kim.
Source: Tokyo Institute of Technology
2011.07.26 View 11713
Spintronics: A high wire act by Nanowerk News
An article by Nanowerk News on the integration of ferromagnetic nanowire arrays on grapheme substrates was published. Professor Bong-Soo Kim from the Department of Chemistry, KAIST, led the research in conjunction with Hanyang University and Samsung in Korea.
http://www.nanowerk.com/news/newsid=22204.php
Posted: Jul 25th, 2011
Spintronics: A high wire act
(Nanowerk News) Graphene is a promising material for a wide range of applications due to its remarkable mechanical and electronic properties. An application of particular interest is spin-based electronics, or spintronics, in which the spin orientation of an electron is used to perform circuit functions in addition to its charge. Bongsoo Kim and colleagues from KAIST, Hanyang University and Samsung in Korea now report the integration of ferromagnetic nanowire arrays on graphene substrates, opening up a route for the construction of graphene-based spintronic devices using nanowires as spin-injecting contacts ("Epitaxially Integrating Ferromagnetic Fe1.3Ge Nanowire Arrays on Few-Layer Graphene").
The spin of an electron is a property that, like charge, can be used to encode, process and transport information. However, spin information is easily lost in most media, which has made spintronics difficult to realize in practice. In graphene, on the other hand, spin can be preserved for longer due to its peculiar electron transport properties. "Low intrinsic spin–orbit coupling, long spin diffusion lengths and vanishing hyperfine interaction are features of graphene that make it a promising medium for spin transport," explains Kim.
Scanning electron microscopy image of vertical iron germanide nanowires grown on graphene. (© ACS 2011)
A prerequisite for the realization of spintronic devices based on graphene is its integration with ferromagnetic contacts to allow spin injection. Kim and his co-workers found that nanowires of iron germanide (Fe1.3Ge) serve as efficient contacts for this purpose. "Iron germanide nanowires show low resistivity and room-temperature ferromagnetism, and they are compatible with existing complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor technologies," says Kim.
To produce the atomically well-defined interfacial contact between the nanowires and the graphene surface needed for optimum device performance, the researchers deposited the contacts by an epitaxial method based on chemical vapor transport. Through careful adjustment of deposition parameters such as carrier gas flow rate and reaction temperature, the researchers produced vertically aligned nanowires that are closely lattice-matched to the graphene sheets (see image).
Initially preparing the graphene sheets on a substrate of silicon oxide allowed the researchers to isolate the final nanowire–graphene structure by etching and then transfer it to another substrate, greatly expanding the versatility of the approach. It is a delicate process, however. "It is necessary to transfer the graphene films onto the substrate very carefully in order to avoid folding and wrinkling of the graphene," says Kim.
Source: Tokyo Institute of Technology
2011.07.26 View 11713 -
 Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
Photo by Hyung-Joon Jun
IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) becomes an icon of green technology, particularly for young students who aspire to transform their nation into the “vanguard of sustainability.”
Seoul, South Korea, July 19, 2011—As young students wrap up their school work before summer vacation in late July, Seoul Grand Park, an amusement park located south of Seoul, is busily preparing to accommodate throngs of summer visitors. Among the park’s routine preparations, however, there is something new to introduce to guests this summer: three wireless electric trams have replaced the old diesel-powered carts used by passengers for transportation within the park.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the city of Seoul held a ceremony this morning, July 19, 2011, to celebrate their joint efforts to adopt a green public transportation system and presented park visitors with the three On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEVs), which will be operated immediately thereafter. Approximately one hundred people, including science high school students across the nation, attended the ceremony and had a chance to ride the trams.
KAIST unveiled the prototype of an electric tram to the public in March 2010, and since then it has developed three commercial trams. The Korean government and the institute have worked on legal issues to embark on the full-scale commercialization of OLEV, and the long awaited approval from the government on such issues as standardization of the OLEV technology and road infrastructure, regulation of electromagnetic fields and electricity safety, and license and permits for vehicle eligibility, finally came through.
The On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) is no ordinary electric car in that it is remotely charged via electromagnetic fields created by electric cables buried beneath the road. Unlike other currently available electric cars, OLEV can travel unlimited distances without having to stop to recharge. OLEV also has a small battery onboard, which enables the vehicle to travel on roads that are not equipped with underground power cables. This battery, however, is only one-fifth of the size of a conventional electric vehicle battery, resulting in considerable savings in the cost, size, and weight of the vehicle.
The OLEV project was initiated in 2009 as a method of resolving the battery problems of electric cars in a creative and disruptive way. KAIST came up with the idea of supplying electricity directly to the cars instead of depending solely on the onboard battery for power. Since then, the university has developed core technologies related to OLEV such as the “Shaped Magnetic Field in Resonance (SMFIR),” which enables an electric car to collect the magnetic fields and convert them into electricity, and the “Segment Technology,” which controls the flow of electromagnetic waves through an automatic power-on/shut-down system, thereby eliminating accidental exposure of the electromagnetic waves to pedestrians or non-OLEV cars.
According to KAIST, three types of OLEV have been developed thus far: electric buses, trams, and sport utility vehicles (SUVs). The technical specifications of the most recently developed OLEV (an electric bus), the OLEV research team at the university said, are as follows:
· Power cables are buried 15cm beneath the road surface.
· On average, over 80% power transmission efficiency is achieved.
· The distance gap between the road surface and the underbody of the vehicle is 20cm.
· The OLEV bus has a maximum electricity pickup capacity of 100kW.
· The OLEV bus complies with international standards for electromagnetic fields (below 24.1 mG).
The eco-friendly electric trams at Seoul Grand Park consume no fossil fuels and do not require any overhead wires or cables. Out of the total circular driving route (2.2km), only 16% of the road, 372.5m, has the embedded power lines, indicating that OLEV does not require extensive reconstruction of the road infrastructure. The city government of Seoul signed a memorandum of understanding with KAIST in 2009 as part of its initiatives to curtail emissions from public transportation and provide cleaner air to its citizens. Both parties plan to expand such collaboration to other transportation systems including buses in the future.
KAIST expects the OLEV technology to be applied in industries ranging from transportation to electronics, aviation, maritime transportation, robotics, and leisure. There are several ongoing international collaborative projects to utilize the OLEV technology for a variety of transportation needs, such as inner city commute systems (bus and trolley) and airport shuttle buses, in nations including Malaysia, US, Germany, and Denmark.
# # #
More information about KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle can be found at http://olev.co.kr/en/index.php. For any inquiries, please contact Lan Yoon at 82-42-350-2295 (cell: 82-10-2539-4303) or by email at hlyoon@kaist.ac.kr.
2011.07.22 View 16631
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
Photo by Hyung-Joon Jun
IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Wireless electric trams at Seoul Amusement Park begin full operations.
KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) becomes an icon of green technology, particularly for young students who aspire to transform their nation into the “vanguard of sustainability.”
Seoul, South Korea, July 19, 2011—As young students wrap up their school work before summer vacation in late July, Seoul Grand Park, an amusement park located south of Seoul, is busily preparing to accommodate throngs of summer visitors. Among the park’s routine preparations, however, there is something new to introduce to guests this summer: three wireless electric trams have replaced the old diesel-powered carts used by passengers for transportation within the park.
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and the city of Seoul held a ceremony this morning, July 19, 2011, to celebrate their joint efforts to adopt a green public transportation system and presented park visitors with the three On-Line Electric Vehicles (OLEVs), which will be operated immediately thereafter. Approximately one hundred people, including science high school students across the nation, attended the ceremony and had a chance to ride the trams.
KAIST unveiled the prototype of an electric tram to the public in March 2010, and since then it has developed three commercial trams. The Korean government and the institute have worked on legal issues to embark on the full-scale commercialization of OLEV, and the long awaited approval from the government on such issues as standardization of the OLEV technology and road infrastructure, regulation of electromagnetic fields and electricity safety, and license and permits for vehicle eligibility, finally came through.
The On-Line Electric Vehicle (OLEV) is no ordinary electric car in that it is remotely charged via electromagnetic fields created by electric cables buried beneath the road. Unlike other currently available electric cars, OLEV can travel unlimited distances without having to stop to recharge. OLEV also has a small battery onboard, which enables the vehicle to travel on roads that are not equipped with underground power cables. This battery, however, is only one-fifth of the size of a conventional electric vehicle battery, resulting in considerable savings in the cost, size, and weight of the vehicle.
The OLEV project was initiated in 2009 as a method of resolving the battery problems of electric cars in a creative and disruptive way. KAIST came up with the idea of supplying electricity directly to the cars instead of depending solely on the onboard battery for power. Since then, the university has developed core technologies related to OLEV such as the “Shaped Magnetic Field in Resonance (SMFIR),” which enables an electric car to collect the magnetic fields and convert them into electricity, and the “Segment Technology,” which controls the flow of electromagnetic waves through an automatic power-on/shut-down system, thereby eliminating accidental exposure of the electromagnetic waves to pedestrians or non-OLEV cars.
According to KAIST, three types of OLEV have been developed thus far: electric buses, trams, and sport utility vehicles (SUVs). The technical specifications of the most recently developed OLEV (an electric bus), the OLEV research team at the university said, are as follows:
· Power cables are buried 15cm beneath the road surface.
· On average, over 80% power transmission efficiency is achieved.
· The distance gap between the road surface and the underbody of the vehicle is 20cm.
· The OLEV bus has a maximum electricity pickup capacity of 100kW.
· The OLEV bus complies with international standards for electromagnetic fields (below 24.1 mG).
The eco-friendly electric trams at Seoul Grand Park consume no fossil fuels and do not require any overhead wires or cables. Out of the total circular driving route (2.2km), only 16% of the road, 372.5m, has the embedded power lines, indicating that OLEV does not require extensive reconstruction of the road infrastructure. The city government of Seoul signed a memorandum of understanding with KAIST in 2009 as part of its initiatives to curtail emissions from public transportation and provide cleaner air to its citizens. Both parties plan to expand such collaboration to other transportation systems including buses in the future.
KAIST expects the OLEV technology to be applied in industries ranging from transportation to electronics, aviation, maritime transportation, robotics, and leisure. There are several ongoing international collaborative projects to utilize the OLEV technology for a variety of transportation needs, such as inner city commute systems (bus and trolley) and airport shuttle buses, in nations including Malaysia, US, Germany, and Denmark.
# # #
More information about KAIST’s On-Line Electric Vehicle can be found at http://olev.co.kr/en/index.php. For any inquiries, please contact Lan Yoon at 82-42-350-2295 (cell: 82-10-2539-4303) or by email at hlyoon@kaist.ac.kr.
2011.07.22 View 16631 -
 Scientists develop highly efficient industrial catalyst
http://english.yonhapnews.co.kr/business/2011/07/14/48/0501000000AEN20110714009600320F.HTML
SEOUL, July 15 (Yonhap) -- South Korean scientists said Friday that they have developed a highly efficient nanoporous industrial catalyst that can have a considerable impact on chemical and oil-refining sectors.
The team of scientists led by Ryoo Ryong, a chemistry professor at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), said the solid zeolite compound developed in the laboratory has a reaction speed five to 10 times faster than that of conventional materials.
Zeolite, which is made from silica and aluminium, is frequently used as an absorbent, water purifier and in nuclear reprocessing, although it is mainly employed in the chemical industry.
The annual size of the zeolite market is estimated at US$2.5 billion with output using the material topping $30 billion. At present, 41 percent of all catalysts used in the chemical sector are nano-scale zeolite materials.
The KAIST team said that because the new zeolite is made up of different sized pores, the material can be used as a catalyst when existing materials are unable to act as a changing agent.
"Existing zeolites only have pores under 1 nanometer in diameter, but the new material has holes that range from 1 nanometer to 3.5 nanometers, which are all arranged in a regular honeycomb arrangement," Ryoo said. A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter.
He said the ability to have both micro- and meso-sized pores is key to the faster reaction speed that is an integral part of raising efficiency. The South Korean researchers used a so-called surfactant process to make the different sizes of pores.
The development is a breakthrough because researchers and companies such as Exxon Mobil Corp. have been trying to build zeolite with different sizes of pores for the past two decades without making serious headway. There are more than 200 different types of zeolites in the world.
Ryoo, who received funding from the government, has requested intellectual property rights for the discovery, which has been published in the latest issue of Science magazine. He also developed another zeolite in the past that can transform methanol to gasoline up to 10 times more efficiently than existing catalysts.
Exxon Mobil has expressed interest in the two zeolites made by Ryoo"s team. Undisclosed South Korean petrochemical companies have also made inquiries that may lead to commercial development in the future.
"There are some technical issues to resolve, mainly related with mass production and stability," the scientist said.
He said full-fledge production will be determined by how much companies are willing to spend on research to speed up development that can bring down overall production costs.
The KAIST team said it took two years to make the new zeolite, which can be custom made to meet specific needs.
(END)
2011.07.15 View 13624
Scientists develop highly efficient industrial catalyst
http://english.yonhapnews.co.kr/business/2011/07/14/48/0501000000AEN20110714009600320F.HTML
SEOUL, July 15 (Yonhap) -- South Korean scientists said Friday that they have developed a highly efficient nanoporous industrial catalyst that can have a considerable impact on chemical and oil-refining sectors.
The team of scientists led by Ryoo Ryong, a chemistry professor at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), said the solid zeolite compound developed in the laboratory has a reaction speed five to 10 times faster than that of conventional materials.
Zeolite, which is made from silica and aluminium, is frequently used as an absorbent, water purifier and in nuclear reprocessing, although it is mainly employed in the chemical industry.
The annual size of the zeolite market is estimated at US$2.5 billion with output using the material topping $30 billion. At present, 41 percent of all catalysts used in the chemical sector are nano-scale zeolite materials.
The KAIST team said that because the new zeolite is made up of different sized pores, the material can be used as a catalyst when existing materials are unable to act as a changing agent.
"Existing zeolites only have pores under 1 nanometer in diameter, but the new material has holes that range from 1 nanometer to 3.5 nanometers, which are all arranged in a regular honeycomb arrangement," Ryoo said. A nanometer is one-billionth of a meter.
He said the ability to have both micro- and meso-sized pores is key to the faster reaction speed that is an integral part of raising efficiency. The South Korean researchers used a so-called surfactant process to make the different sizes of pores.
The development is a breakthrough because researchers and companies such as Exxon Mobil Corp. have been trying to build zeolite with different sizes of pores for the past two decades without making serious headway. There are more than 200 different types of zeolites in the world.
Ryoo, who received funding from the government, has requested intellectual property rights for the discovery, which has been published in the latest issue of Science magazine. He also developed another zeolite in the past that can transform methanol to gasoline up to 10 times more efficiently than existing catalysts.
Exxon Mobil has expressed interest in the two zeolites made by Ryoo"s team. Undisclosed South Korean petrochemical companies have also made inquiries that may lead to commercial development in the future.
"There are some technical issues to resolve, mainly related with mass production and stability," the scientist said.
He said full-fledge production will be determined by how much companies are willing to spend on research to speed up development that can bring down overall production costs.
The KAIST team said it took two years to make the new zeolite, which can be custom made to meet specific needs.
(END)
2011.07.15 View 13624 -
 Using Light to Deliver Drugs to the Brain
The cerebral blood vessels have a unique blood-brain barrier. Using this unique structure, Professor Choi Chul Hee (Department of Bio-Brain Engineering) developed a technique to deliver drugs safely to the brain using lasers to alter the diffusivity of the blood-brain barrier.
The blood-brain barrier allows the entry of only those drugs related to metabolic functions which made the entry of other drugs difficult.
Due to this property it was difficult to administer the drug to a patient and have it affect the patient. Therefore the question was is it possible to maintain the effectiveness of the drug and allow it to pass through the barrier?
The conventional method was to actually alter the structure of the drug or drill of small hole in the head and administering the drug directly, but these methods proved to be high risk and expensive.
Professor Choi’s team used an ultra-short frequency laser beam on the barrier for 1/1000th of a second on the barrier to temporarily inhibit its function thereby allowing the drug to enter the brain safely.
2011.06.20 View 10465
Using Light to Deliver Drugs to the Brain
The cerebral blood vessels have a unique blood-brain barrier. Using this unique structure, Professor Choi Chul Hee (Department of Bio-Brain Engineering) developed a technique to deliver drugs safely to the brain using lasers to alter the diffusivity of the blood-brain barrier.
The blood-brain barrier allows the entry of only those drugs related to metabolic functions which made the entry of other drugs difficult.
Due to this property it was difficult to administer the drug to a patient and have it affect the patient. Therefore the question was is it possible to maintain the effectiveness of the drug and allow it to pass through the barrier?
The conventional method was to actually alter the structure of the drug or drill of small hole in the head and administering the drug directly, but these methods proved to be high risk and expensive.
Professor Choi’s team used an ultra-short frequency laser beam on the barrier for 1/1000th of a second on the barrier to temporarily inhibit its function thereby allowing the drug to enter the brain safely.
2011.06.20 View 10465 -
 Biomimetic Carbon Nanotube Fiber Synthesis Technology Developed
The byssus of the mussel allows it to live in harsh conditions where it is constantly battered by crashing waves by allowing the mussel to latch onto the seaside rocks. This particular characteristic of the mussel is due to the unique structure and high adhesiveness of the mussel’s byssus.
KAIST’s Professor Hong Soon Hyung (Department of Material Science and Engineering) and Professor Lee Hae Shin (Department of Chemistry) and the late Professor Park Tae Kwan (Department of Bio Engineering) were able to reproduce the mussel’s byssus using carbon nanotubes.
The carbon nanotube, since its discovery in 1991, was regarded as the next generation material due to its electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. However due to its short length of several nanometers, its industrial use was limited.
The KAIST research team referred to the structure of the byssus of the mussel to solve this problem.
The byssus is composed of collagen fibers and Mefp-1 protein which are in a cross-linking structure. The Mefp-1 protein has catecholamine that allows it to bind strongly with the collagen fiber.
In the artificial structure, the carbon nanotube took on the role of the collagen fibers and the macromolecular adhesive took on the role of the catecholamine. The result was a fiber that was ultra-light and ultra-strong.
The results of the experiment were published in the Advanced Materials magazine and is patent registered both domestically and internationally.
2011.06.20 View 14411
Biomimetic Carbon Nanotube Fiber Synthesis Technology Developed
The byssus of the mussel allows it to live in harsh conditions where it is constantly battered by crashing waves by allowing the mussel to latch onto the seaside rocks. This particular characteristic of the mussel is due to the unique structure and high adhesiveness of the mussel’s byssus.
KAIST’s Professor Hong Soon Hyung (Department of Material Science and Engineering) and Professor Lee Hae Shin (Department of Chemistry) and the late Professor Park Tae Kwan (Department of Bio Engineering) were able to reproduce the mussel’s byssus using carbon nanotubes.
The carbon nanotube, since its discovery in 1991, was regarded as the next generation material due to its electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. However due to its short length of several nanometers, its industrial use was limited.
The KAIST research team referred to the structure of the byssus of the mussel to solve this problem.
The byssus is composed of collagen fibers and Mefp-1 protein which are in a cross-linking structure. The Mefp-1 protein has catecholamine that allows it to bind strongly with the collagen fiber.
In the artificial structure, the carbon nanotube took on the role of the collagen fibers and the macromolecular adhesive took on the role of the catecholamine. The result was a fiber that was ultra-light and ultra-strong.
The results of the experiment were published in the Advanced Materials magazine and is patent registered both domestically and internationally.
2011.06.20 View 14411 -
 New Scientist: Wind power harnesses the energy of galloping, June 2, 2011
Researchers from the Civil and Environmental Engineering Department, KAIST, released their research results in Smart Materials and Structures on ways to “harness strange properties of turbulent airs.” They built a prototype that produces energy using a specific type of unstable airflow called “wake galloping.” New Scientist wrote an article about the paper, which appeared on June 2, 2011. For the article, please follow the link below.
http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg21028145.700-wind-power-harnesses-the-energy-of-galloping.html?full=true&print=true
2011.06.04 View 10204
New Scientist: Wind power harnesses the energy of galloping, June 2, 2011
Researchers from the Civil and Environmental Engineering Department, KAIST, released their research results in Smart Materials and Structures on ways to “harness strange properties of turbulent airs.” They built a prototype that produces energy using a specific type of unstable airflow called “wake galloping.” New Scientist wrote an article about the paper, which appeared on June 2, 2011. For the article, please follow the link below.
http://www.newscientist.com/article/mg21028145.700-wind-power-harnesses-the-energy-of-galloping.html?full=true&print=true
2011.06.04 View 10204 -
 From Pencil Lead to Batteries: the Unlimited Transformation of Carbon
Those materials, like lead or diamond, made completely up of Carbon are being used in numerous ways as materials or parts. Especially with the discovery of carbon nanotubes, graphemes, and other carbon based materials in nanoscale, the carbon based materials are receiving a lot of interest in both fields of research and industry.
The carbon nanotubes and graphemes are considered as the ‘dream material’ and have a structure of a cross section of a bee hive. Such structure allows the material to have strength higher than that of a diamond and still be able to bend, be transparent and also conduct electricity. However the problem up till now was that these carbon structures appeared in layers and in bunches and were therefore hard to separate to individual layers or tubes.
Professor Kim Sang Wook’s research team developed the technology that can assemble the grapheme and carbon nanotubes in a three dimensional manner.
The team was able to assemble the grapheme ad carbon nanotubes in an entirely new three dimensional structure. In addition, the team was able to efficiently extract single layered grapheme from cheap pencil lead.
Professor Kim is scheduled to give a guest lecture in the “Materials Research Society” in San Francisco and the paper was published in ‘Advanced Functional Materials’ magazine as an ‘Invited Feature Article’.
2011.05.11 View 12753
From Pencil Lead to Batteries: the Unlimited Transformation of Carbon
Those materials, like lead or diamond, made completely up of Carbon are being used in numerous ways as materials or parts. Especially with the discovery of carbon nanotubes, graphemes, and other carbon based materials in nanoscale, the carbon based materials are receiving a lot of interest in both fields of research and industry.
The carbon nanotubes and graphemes are considered as the ‘dream material’ and have a structure of a cross section of a bee hive. Such structure allows the material to have strength higher than that of a diamond and still be able to bend, be transparent and also conduct electricity. However the problem up till now was that these carbon structures appeared in layers and in bunches and were therefore hard to separate to individual layers or tubes.
Professor Kim Sang Wook’s research team developed the technology that can assemble the grapheme and carbon nanotubes in a three dimensional manner.
The team was able to assemble the grapheme ad carbon nanotubes in an entirely new three dimensional structure. In addition, the team was able to efficiently extract single layered grapheme from cheap pencil lead.
Professor Kim is scheduled to give a guest lecture in the “Materials Research Society” in San Francisco and the paper was published in ‘Advanced Functional Materials’ magazine as an ‘Invited Feature Article’.
2011.05.11 View 12753