merging
-
 Professor YongKeun Park Wins the 2018 Fumio Okano Award
(Professor Park)
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics won the 2018 Fumio Okano Award in recognition of his contributions to 3D display technology development during the annual conference of the International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE) held last month in Orlando, Florida in the US.
The Fumio Okano Best 3D Paper Prize is presented annually in memory of Dr. Fumio Okano, a pioneer and innovator of 3D displays who passed away in 2013, for his contributions to the field of 3D TVs and displays. The award is sponsored by NHK-ES.
Professor Park and his team are developing novel technology for measuring and visualizing 3D images by applying random light scattering. He has published numerous papers on 3D holographic camera technology and 3000x enhanced performance of 3D holographic displays in renowned international journals such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, and Science Advances. His technology has drawn international attention from renowned media outlets including Newsweek and Forbes.
He has established two startups to commercialize his technology. Tomocube specializes in 3D imaging microscopes using holotomographic technology and the company exports their products to several countries including the US and Japan. The.Wave.Talk is exploring technology for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
Professor Park’s innovations have already been recognized in and out of KAIST. In February, he was selected as the KAISTian of the Year for his outstanding research, commercialization, and startups. He was also decorated with the National Science Award in April by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Hong Jin-Ki Innovation Award later in May by the Yumin Cultural Foundation.
Professor Park said, “3D holography is emerging as a significant technology with growing potential and positive impacts on our daily lives. However, the current technology lags far behind the levels displayed in SF movies. We will do our utmost to reach this level with more commercialization."
2018.05.31 View 13921
Professor YongKeun Park Wins the 2018 Fumio Okano Award
(Professor Park)
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics won the 2018 Fumio Okano Award in recognition of his contributions to 3D display technology development during the annual conference of the International Society for Optics and Photonics (SPIE) held last month in Orlando, Florida in the US.
The Fumio Okano Best 3D Paper Prize is presented annually in memory of Dr. Fumio Okano, a pioneer and innovator of 3D displays who passed away in 2013, for his contributions to the field of 3D TVs and displays. The award is sponsored by NHK-ES.
Professor Park and his team are developing novel technology for measuring and visualizing 3D images by applying random light scattering. He has published numerous papers on 3D holographic camera technology and 3000x enhanced performance of 3D holographic displays in renowned international journals such as Nature Photonics, Nature Communications, and Science Advances. His technology has drawn international attention from renowned media outlets including Newsweek and Forbes.
He has established two startups to commercialize his technology. Tomocube specializes in 3D imaging microscopes using holotomographic technology and the company exports their products to several countries including the US and Japan. The.Wave.Talk is exploring technology for examining pre-existing bacteria anywhere and anytime.
Professor Park’s innovations have already been recognized in and out of KAIST. In February, he was selected as the KAISTian of the Year for his outstanding research, commercialization, and startups. He was also decorated with the National Science Award in April by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the Hong Jin-Ki Innovation Award later in May by the Yumin Cultural Foundation.
Professor Park said, “3D holography is emerging as a significant technology with growing potential and positive impacts on our daily lives. However, the current technology lags far behind the levels displayed in SF movies. We will do our utmost to reach this level with more commercialization."
2018.05.31 View 13921 -
 New Material for Generating Energy-Efficient Spin Currents
(Professor Byong-Guk Park (left) and Professor Kab-Jin Kim)
Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is emerging as next-generation memory. It allows information to be kept even without an external power supply and its unique blend of high density and high speed operation is driving global semiconductor manufacturers to develop new versions continuously.
A KAIST team, led by Professor Byong-Guk Park in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Kab-Jin Kim in the Department of Physics, recently has developed a new material which enables the efficient generation of a spin current, the core part of operating MRAM. This new material consisting of ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current unlike the existing ones.
They also described a mechanism for spin-current generation at the interface between the bottom ferromagnetic layer and the non-magnetic spacer layer, which gives torques on the top magnetic layer that are consistent with the measured magnetization dependence.
When applying this to spin-orbit torque magnetic memory, it shows the increased efficiency of spin torque and generation of the spin current without an external magnetic field. High-speed operation, the distinct feature of spin-orbit torque-based MRAM that carries its non-volatility, can significantly reduce the standby power better than SRAM.
This new material will expect to speed up the commercialization of MRAM. The research team said that this magnetic memory will further be applied to mobile, wearable, and IoT devices.
This study, conducted in collaboration with Professor Kyung-Jin Lee from Korea University and Dr. Mark Stiles from the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the US, was featured in Nature Materials in March. The research was funded by the Creative Materials Discovery Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers which can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current)
2018.05.11 View 11934
New Material for Generating Energy-Efficient Spin Currents
(Professor Byong-Guk Park (left) and Professor Kab-Jin Kim)
Magnetic random access memory (MRAM) is emerging as next-generation memory. It allows information to be kept even without an external power supply and its unique blend of high density and high speed operation is driving global semiconductor manufacturers to develop new versions continuously.
A KAIST team, led by Professor Byong-Guk Park in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Kab-Jin Kim in the Department of Physics, recently has developed a new material which enables the efficient generation of a spin current, the core part of operating MRAM. This new material consisting of ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current unlike the existing ones.
They also described a mechanism for spin-current generation at the interface between the bottom ferromagnetic layer and the non-magnetic spacer layer, which gives torques on the top magnetic layer that are consistent with the measured magnetization dependence.
When applying this to spin-orbit torque magnetic memory, it shows the increased efficiency of spin torque and generation of the spin current without an external magnetic field. High-speed operation, the distinct feature of spin-orbit torque-based MRAM that carries its non-volatility, can significantly reduce the standby power better than SRAM.
This new material will expect to speed up the commercialization of MRAM. The research team said that this magnetic memory will further be applied to mobile, wearable, and IoT devices.
This study, conducted in collaboration with Professor Kyung-Jin Lee from Korea University and Dr. Mark Stiles from the National Institute of Standards and Technology in the US, was featured in Nature Materials in March. The research was funded by the Creative Materials Discovery Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure: Ferromagnet-transition metal bilayers which can randomly control the direction of the generated spin current)
2018.05.11 View 11934 -
 KAIST to Host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit in 2019
KAIST and Times Higher Education (THE) agreed to co-host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST from April 1 to 3, 2019.
Global leaders from higher education, government, and industry will gather at KAIST to discuss how universities can better innovate for creating a greater impact.
(from left: THE Managing Director Trevor Barratt and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Trevor Barratt, managing director at the THE, signed an agreement to host the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST next April. The agreement was signed on February 6 during the THE Asia Universities Summit held at SUSTech in Shenzhen in China. Phil Baty, editorial director at the THE was also present during the agreement.
By hosting the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit, KAIST has a chance to introduce its innovative research and performance and its educational environment and startup ecosystem to the world. Having educational and industrial leaders meet at KAIST will add more power to the global status and capacity of KAIST.
The THE Innovation & Impact Summit, first held in 2017, is one in the seven presidential summit series held by THE. During the second summit at KAIST, THE will launch their world university innovation rankings for the first time.
As innovation at universities and its impact have been a crucial indicator in building an institutional brand and reputation, leading universities are gearing up to encourage startups and entrepreneurship education. Even more, innovation at universities is emerging as one of the growth engines of economies.
The innovation indicators of KAIST have been highly recognized by many global ranking institutions in terms of the volume of patents and the patents-to-article citation impact. Thomson Reuters has recognized KAIST for two consecutive years as the most innovative university in Asia, and sixth in the world.
President Shin has high expectations for the hosting of the Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST. He explained, “Innovation makes up the DNA of KAIST and it has been our institutional mission from the start in 1971. KAIST was commissioned to make innovation for industrialization and economic development through education and research. I do not see any university more suitable than KAIST to host this innovation summit. I hope the summit at KAIST will serve as a global platform to provide very creative ideas for making innovation and collaboration among the leading universities for all the participants.”
Meanwhile, at the THE Asia Universities Summit in Shenzhen, how to respond to the implications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution was the key agenda piercing the two-day sessions.
As a panelist, President Shin shared his experiences on innovative strategies viable for spearheading university reform for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, along with Vice-Chancellor of the University of Sheffield Sir Keith Burnett, President of Monash University Margaret Gardner, and President of Hong Kong Polytechnic University President Timothy W. Tong. He said that universities should foster young talents by equipping them with creativity, collaboration, and convergent minds. To swiftly respond to the new industrial environment, President Shin said that universities should remove the high barriers between departments and establish cross- and inter-disciplinary education systems, convergence research and technology commercialization.
2018.02.06 View 11220
KAIST to Host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit in 2019
KAIST and Times Higher Education (THE) agreed to co-host the THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST from April 1 to 3, 2019.
Global leaders from higher education, government, and industry will gather at KAIST to discuss how universities can better innovate for creating a greater impact.
(from left: THE Managing Director Trevor Barratt and KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Trevor Barratt, managing director at the THE, signed an agreement to host the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST next April. The agreement was signed on February 6 during the THE Asia Universities Summit held at SUSTech in Shenzhen in China. Phil Baty, editorial director at the THE was also present during the agreement.
By hosting the 2019 THE Innovation & Impact Summit, KAIST has a chance to introduce its innovative research and performance and its educational environment and startup ecosystem to the world. Having educational and industrial leaders meet at KAIST will add more power to the global status and capacity of KAIST.
The THE Innovation & Impact Summit, first held in 2017, is one in the seven presidential summit series held by THE. During the second summit at KAIST, THE will launch their world university innovation rankings for the first time.
As innovation at universities and its impact have been a crucial indicator in building an institutional brand and reputation, leading universities are gearing up to encourage startups and entrepreneurship education. Even more, innovation at universities is emerging as one of the growth engines of economies.
The innovation indicators of KAIST have been highly recognized by many global ranking institutions in terms of the volume of patents and the patents-to-article citation impact. Thomson Reuters has recognized KAIST for two consecutive years as the most innovative university in Asia, and sixth in the world.
President Shin has high expectations for the hosting of the Innovation & Impact Summit at KAIST. He explained, “Innovation makes up the DNA of KAIST and it has been our institutional mission from the start in 1971. KAIST was commissioned to make innovation for industrialization and economic development through education and research. I do not see any university more suitable than KAIST to host this innovation summit. I hope the summit at KAIST will serve as a global platform to provide very creative ideas for making innovation and collaboration among the leading universities for all the participants.”
Meanwhile, at the THE Asia Universities Summit in Shenzhen, how to respond to the implications of the Fourth Industrial Revolution was the key agenda piercing the two-day sessions.
As a panelist, President Shin shared his experiences on innovative strategies viable for spearheading university reform for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, along with Vice-Chancellor of the University of Sheffield Sir Keith Burnett, President of Monash University Margaret Gardner, and President of Hong Kong Polytechnic University President Timothy W. Tong. He said that universities should foster young talents by equipping them with creativity, collaboration, and convergent minds. To swiftly respond to the new industrial environment, President Shin said that universities should remove the high barriers between departments and establish cross- and inter-disciplinary education systems, convergence research and technology commercialization.
2018.02.06 View 11220 -
 Lifespan of Fuel Cells Maximized Using Small Amount of Metals
(Professor Jung (far right) and his team)
Fuel cells are key future energy technology that is emerging as eco-friendly and renewable energy sources. In particular, solid oxide fuel cells composed of ceramic materials gain increasing attention for their ability to directly convert various forms of fuel such as biomass, LNG, and LPG to electric energy.
KAIST researchers described a new technique to improve chemical stability of electrode materials which can extend the lifespan by employing a very little amount of metals.
The core factor that determines the performance of solid oxide fuel cells is the cathode at which the reduction reaction of oxygen occurs. Conventionally, oxides with perovskite structure (ABO3) are used in cathodes. However, despite the high performance of perovskite oxides at initial operation, the performance decreases with time, limiting their long-term use. In particular, the condition of high temperature oxidation state required for cathode operation leads to surface segregation phenomenon, in which second phases such as strontium oxide (SrOx) accumulate on the surface of oxides, resulting in decrease in electrode performance. The detailed mechanism of this phenomenon and a way to effectively inhibit it has not been suggested.
Using computational chemistry and experimental data, Professor WooChul Jung’s team at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering observed that local compressive states around the Sr atoms in a perovskite electrode lattice weakened the Sr-O bond strength, which in turn promote strontium segregation. The team identified local changes in strain distribution in perovskite oxide as the main cause of segregation on strontium surface. Based on these findings, the team doped different sizes of metals in oxides to control the extent of lattice strain in cathode material and effectively inhibited strontium segregation.
Professor Jung said, “This technology can be implemented by adding a small amount of metal atoms during material synthesis, without any additional process.” He continued, “I hope this technology will be useful in developing high-durable perovskite oxide electrode in the future.”
The study co-led by Professor Jung and Professor Jeong Woo Han at Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Seoul was featured as the cover of Energy and Environmental Science in the first issue of 2018.
(Figure1.Correlation between the extent of lattice strain in electrode, strontium segregation, and electrode reaction.)
(Figure 2. Cathode surface of solid oxide fuel cell stabilized using the developed technology)
2018.01.18 View 9238
Lifespan of Fuel Cells Maximized Using Small Amount of Metals
(Professor Jung (far right) and his team)
Fuel cells are key future energy technology that is emerging as eco-friendly and renewable energy sources. In particular, solid oxide fuel cells composed of ceramic materials gain increasing attention for their ability to directly convert various forms of fuel such as biomass, LNG, and LPG to electric energy.
KAIST researchers described a new technique to improve chemical stability of electrode materials which can extend the lifespan by employing a very little amount of metals.
The core factor that determines the performance of solid oxide fuel cells is the cathode at which the reduction reaction of oxygen occurs. Conventionally, oxides with perovskite structure (ABO3) are used in cathodes. However, despite the high performance of perovskite oxides at initial operation, the performance decreases with time, limiting their long-term use. In particular, the condition of high temperature oxidation state required for cathode operation leads to surface segregation phenomenon, in which second phases such as strontium oxide (SrOx) accumulate on the surface of oxides, resulting in decrease in electrode performance. The detailed mechanism of this phenomenon and a way to effectively inhibit it has not been suggested.
Using computational chemistry and experimental data, Professor WooChul Jung’s team at the Department of Materials Science and Engineering observed that local compressive states around the Sr atoms in a perovskite electrode lattice weakened the Sr-O bond strength, which in turn promote strontium segregation. The team identified local changes in strain distribution in perovskite oxide as the main cause of segregation on strontium surface. Based on these findings, the team doped different sizes of metals in oxides to control the extent of lattice strain in cathode material and effectively inhibited strontium segregation.
Professor Jung said, “This technology can be implemented by adding a small amount of metal atoms during material synthesis, without any additional process.” He continued, “I hope this technology will be useful in developing high-durable perovskite oxide electrode in the future.”
The study co-led by Professor Jung and Professor Jeong Woo Han at Department of Chemical Engineering, University of Seoul was featured as the cover of Energy and Environmental Science in the first issue of 2018.
(Figure1.Correlation between the extent of lattice strain in electrode, strontium segregation, and electrode reaction.)
(Figure 2. Cathode surface of solid oxide fuel cell stabilized using the developed technology)
2018.01.18 View 9238 -
 WEF-KAIST to Host a Forum Next April in Korea
(President Shin poses with Chairman Schwab at the meeting in Dubai)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab of the World Economic Forum agreed to co-host the Fourth Industrial Revolution Forum next April in Seoul during a meeting at the WEF Global Future Councils 2017 held in Dubai November 11-12.
Next April’s forum will be a follow-up event of the roundtable discussion KAIST and the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution co-hosted in October in Seoul. The two hosted the roundtable discussion titled “Mastering the Fourth Industrial Revolution: The Future of Jobs and Inclusive Growth in Korea.”
During the annual meeting in Dubai, Chairman Schwab expressed his deep appreciation to President Shin for hosting the roundtable discussion and proposed a full-fledged forum in partnership with KAIST once again, which Chairman Schwab will be scheduled to attend.
Chairman Schwab emphasized once again that Korea, who has the world’s top high-end technologies such as 5G telecommunications and semiconductor memory, will be the best fit to realize the Fourth Industrial Revolution most rapidly. He also expressed his great interest in the city of Daejeon in which is being considered to become the Special City for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The Global Future Council of the WEF is the interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking on the future. The annual council convenes in Dubai the most relevant and knowledgeable thought leaders from academia, government, business, and civil society to challenge conventional thinking and develop new insights and perspectives on key global systems, as well as the impact and governance of key emerging technologies. This year, more than 850 world-leading experts from 74 countries participated.
Under the theme of ‘Vision 2030,’ participants explored systematic changes in key areas such as energy, mobility, and infrastructure while reflecting on the impact of technological breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and other areas related to the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
2017.11.13 View 11284
WEF-KAIST to Host a Forum Next April in Korea
(President Shin poses with Chairman Schwab at the meeting in Dubai)
President Sung-Chul Shin and Executive Chairman Klaus Schwab of the World Economic Forum agreed to co-host the Fourth Industrial Revolution Forum next April in Seoul during a meeting at the WEF Global Future Councils 2017 held in Dubai November 11-12.
Next April’s forum will be a follow-up event of the roundtable discussion KAIST and the WEF Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution co-hosted in October in Seoul. The two hosted the roundtable discussion titled “Mastering the Fourth Industrial Revolution: The Future of Jobs and Inclusive Growth in Korea.”
During the annual meeting in Dubai, Chairman Schwab expressed his deep appreciation to President Shin for hosting the roundtable discussion and proposed a full-fledged forum in partnership with KAIST once again, which Chairman Schwab will be scheduled to attend.
Chairman Schwab emphasized once again that Korea, who has the world’s top high-end technologies such as 5G telecommunications and semiconductor memory, will be the best fit to realize the Fourth Industrial Revolution most rapidly. He also expressed his great interest in the city of Daejeon in which is being considered to become the Special City for the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
The Global Future Council of the WEF is the interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking on the future. The annual council convenes in Dubai the most relevant and knowledgeable thought leaders from academia, government, business, and civil society to challenge conventional thinking and develop new insights and perspectives on key global systems, as well as the impact and governance of key emerging technologies. This year, more than 850 world-leading experts from 74 countries participated.
Under the theme of ‘Vision 2030,’ participants explored systematic changes in key areas such as energy, mobility, and infrastructure while reflecting on the impact of technological breakthroughs in artificial intelligence, biotechnology, and other areas related to the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
2017.11.13 View 11284 -
 Scientist of November, Professor Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Hyung Jin Sung from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST received a ‘Science and Technology Award of the Month’ given by the Ministry of ICT and Science and the National Research Foundation of Korea for November 2017. He developed technology that can exquisitely control a micrometer-scaled liquid drop on a dime-sized lab-on-a-chip. With his work, he was recognized for reinforcing research capability on microfluidics.
Lab-on-a-chip is an emerging experiment and diagnostic technology in the form of a bio-microchip that facilitates complex and various experiments with only a minimal sample size required. This technology draws a lot of attention not only from medical and pharmaceutical areas, but also the health and environmental field. The biggest problem was that technology for the temperature control of a fluid sample, which is one of the core technologies in microfluidics, has low accuracy. This limit had to be overcome in order to use the lab-on-a-chip more widely.
Professor Sung developed an acoustic and thermal method which controls the temperature of a droplet quickly and meticulously by using sound and energy. This is a thermal method that uses heat generated during the absorption of an acoustic wave into viscoelastic substances. It facilitates a rapid heating rate and spatial-temporal temperature control, allowing heating in desired areas. In addition, Professor Sung applied his technology to polymerase chain reactions, which are used to amplify DNA.
Through this experiment, he successfully shortened the reaction time from 1-2 hours to only three minutes, making this a groundbreaking achievement.
Professor Sung said, “My research is significant for enhancing the applicability of microfluidics. I expect that it will lead to technological innovations in healthcare fields including biochemistry, medical checkups, and new medicine development.”
2017.11.03 View 12581
Scientist of November, Professor Hyung Jin Sung
Professor Hyung Jin Sung from the Department of Mechanical Engineering at KAIST received a ‘Science and Technology Award of the Month’ given by the Ministry of ICT and Science and the National Research Foundation of Korea for November 2017. He developed technology that can exquisitely control a micrometer-scaled liquid drop on a dime-sized lab-on-a-chip. With his work, he was recognized for reinforcing research capability on microfluidics.
Lab-on-a-chip is an emerging experiment and diagnostic technology in the form of a bio-microchip that facilitates complex and various experiments with only a minimal sample size required. This technology draws a lot of attention not only from medical and pharmaceutical areas, but also the health and environmental field. The biggest problem was that technology for the temperature control of a fluid sample, which is one of the core technologies in microfluidics, has low accuracy. This limit had to be overcome in order to use the lab-on-a-chip more widely.
Professor Sung developed an acoustic and thermal method which controls the temperature of a droplet quickly and meticulously by using sound and energy. This is a thermal method that uses heat generated during the absorption of an acoustic wave into viscoelastic substances. It facilitates a rapid heating rate and spatial-temporal temperature control, allowing heating in desired areas. In addition, Professor Sung applied his technology to polymerase chain reactions, which are used to amplify DNA.
Through this experiment, he successfully shortened the reaction time from 1-2 hours to only three minutes, making this a groundbreaking achievement.
Professor Sung said, “My research is significant for enhancing the applicability of microfluidics. I expect that it will lead to technological innovations in healthcare fields including biochemistry, medical checkups, and new medicine development.”
2017.11.03 View 12581 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Named International Fellow of the CAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was awarded the title of distinguished professor and international fellow from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and honorary professor from its affiliated organization the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology (TIB).
The CAS recognized Distinguished Professor Lee for his significant contributions to biotechnology. He has made significant pioneering academic achievements in the area of systems metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals from microorganisms. Not only did he develop the first and best source technology in that field, but also came out with processes for the production of biofuel and environmentally-friendly chemicals.”
As a global leader in systems metabolic engineering, Distinguished Professor Lee has also been appointed as an honorary professor at Jiangnan University in Wuxi, China.
Distinguished Professor Lee was listed in the ‘Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014’ selected by the renowned international journal Nature Biotechnology. Moreover, he was the first Asian recipient of the James E. Bailey Award in 2016 and Marvin J. Johnson Award in 2012, which are given to scholars in the field of biotechnology.
He is also one of 13 global scientists who are foreign members of the renowned academic societies the National Academy of Engineering and the National Academy of Sciences in the US. Furthermore, he received the ‘2017 Korea Best Scientist Award’ from the president of Korea in July. Finally, his founding field, systems metabolic engineering, was chosen as one of the ‘Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016’ by the World Economic Forum.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences, established in November 1949, is an academic organization that carries out research on basic sciences and natural sciences in China. It defined its science and technology system to include the fields of basic sciences, natural sciences, and high technology. While having a base in Beijing, its branch academies are located in 12 main cities along with 117 affiliates and 100 national key labs.
2017.10.26 View 14489
Distinguished Professor Lee Named International Fellow of the CAS
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was awarded the title of distinguished professor and international fellow from the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), and honorary professor from its affiliated organization the Tianjin Institute of Industrial Biotechnology (TIB).
The CAS recognized Distinguished Professor Lee for his significant contributions to biotechnology. He has made significant pioneering academic achievements in the area of systems metabolic engineering, which produces useful chemicals from microorganisms. Not only did he develop the first and best source technology in that field, but also came out with processes for the production of biofuel and environmentally-friendly chemicals.”
As a global leader in systems metabolic engineering, Distinguished Professor Lee has also been appointed as an honorary professor at Jiangnan University in Wuxi, China.
Distinguished Professor Lee was listed in the ‘Top 20 Translational Researchers of 2014’ selected by the renowned international journal Nature Biotechnology. Moreover, he was the first Asian recipient of the James E. Bailey Award in 2016 and Marvin J. Johnson Award in 2012, which are given to scholars in the field of biotechnology.
He is also one of 13 global scientists who are foreign members of the renowned academic societies the National Academy of Engineering and the National Academy of Sciences in the US. Furthermore, he received the ‘2017 Korea Best Scientist Award’ from the president of Korea in July. Finally, his founding field, systems metabolic engineering, was chosen as one of the ‘Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016’ by the World Economic Forum.
The Chinese Academy of Sciences, established in November 1949, is an academic organization that carries out research on basic sciences and natural sciences in China. It defined its science and technology system to include the fields of basic sciences, natural sciences, and high technology. While having a base in Beijing, its branch academies are located in 12 main cities along with 117 affiliates and 100 national key labs.
2017.10.26 View 14489 -
 Discovery of an Optimal Drug Combination: Overcoming Resistance to Targeted Drugs for Liver Cancer
A KAIST research team presented a novel method for improving medication treatment for liver cancer using Systems Biology, combining research from information technology and the life sciences. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST conducted the research in collaboration with Professor Jung-Hwan Yoon in the Department of Internal Medicine at Seoul National University Hospital. This research was published in Hepatology in September 2017 (available online from August 24, 2017).
Liver cancer is the fifth and seventh most common cancer found in men and women throughout the world, which places it second in the cause of cancer deaths. In particular, Korea has 28.4 deaths from liver cancer per 100,000 persons, the highest death rate among OECD countries and twice that of Japan.
Each year in Korea, 16,000 people get liver cancer on average, yet the five-year survival rate stands below 12%. According to the National Cancer Information Center, lung cancer (17,399) took the highest portion of cancer-related deaths, followed by liver cancer (11,311) based on last year data.
Liver cancer is known to carry the highest social cost in comparison to other cancers and it causes the highest fatality in earlier age groups (40s-50s). In that sense, it is necessary to develop a new treatment that mitigates side effects yet elevates the survival rate.
There are ways in which liver cancer can be cured, such as surgery, embolization, and medication treatments; however, the options become limited for curing progressive cancer, a stage in which surgical methods cannot be executed.
Among anticancer medications, Sorafenib, a drug known for enhancing the survival rate of cancer patients, is a unique drug allowed for use as a targeted anticancer medication for progressive liver cancer patients. Its sales reached more than ten billion KRW annually in Korea, but its efficacy works on only about 20% of the treated patients. Also, acquired resistance to Sorafenib is emerging. Additionally, the action mechanism and resistance mechanism of Sorafenib is only vaguely identified.Although Sorafenib only extends the survival rate of terminal cancer patients less than three months on average, it is widely being used because drugs developed by global pharmaceutical companies failed to outperform its effectiveness.
Professor Cho’s research team analyzed the expression changes of genes in cell lines in response to Sorafenib in order to identify the effect and the resistance mechanism of Sorafenib.
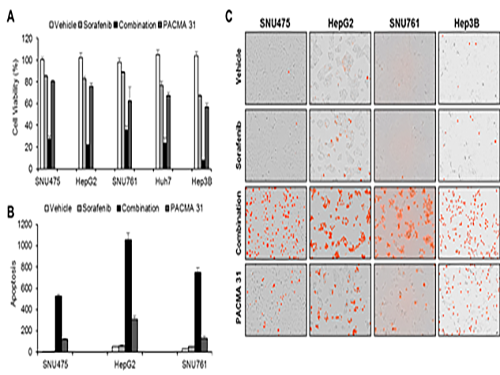
As a result, the team discovered the resistance mechanism of Sorafenib using Systems Biology analysis. By combining computer simulations and biological experiments, it was revealed that protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) plays a crucial role in the resistance mechanism of Sorafenib and that its efficacy can be improved significantly by blocking PDI.
The research team used mice in the experiment and discovered the synergic effect of PDI inhibition with Sorafenib for reducing liver cancer cells, known as hepatocellular carcinoma. Also, more PDIs are shown in tissue from patients who possess a resistance to Sorafenib. From these findings, the team could identify the possibility of its clinical applications. The team also confirmed these findings from clinical data through a retrospective cohort study.
“Molecules that play an important role in cell lines are mostly put under complex regulation. For this reason, the existing biological research has a fundamental limitations for discovering its underlying principles,” Professor Cho said. “This research is a representative case of overcoming this limitation of traditional life science research by using a Systems Biology approach, combining IT and life science. It suggests the possibility of developing a new method that overcomes drug resistance with a network analysis of the targeted drug action mechanism of cancer.”
The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure 1. Simulation results from cellular experiments using hepatocellular carcinoma)
(Figure 2. Network analysis and computer simulation by using the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress network)
(Figure 3. ER stress network model)
2017.08.30 View 13820
Discovery of an Optimal Drug Combination: Overcoming Resistance to Targeted Drugs for Liver Cancer
A KAIST research team presented a novel method for improving medication treatment for liver cancer using Systems Biology, combining research from information technology and the life sciences. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST conducted the research in collaboration with Professor Jung-Hwan Yoon in the Department of Internal Medicine at Seoul National University Hospital. This research was published in Hepatology in September 2017 (available online from August 24, 2017).
Liver cancer is the fifth and seventh most common cancer found in men and women throughout the world, which places it second in the cause of cancer deaths. In particular, Korea has 28.4 deaths from liver cancer per 100,000 persons, the highest death rate among OECD countries and twice that of Japan.
Each year in Korea, 16,000 people get liver cancer on average, yet the five-year survival rate stands below 12%. According to the National Cancer Information Center, lung cancer (17,399) took the highest portion of cancer-related deaths, followed by liver cancer (11,311) based on last year data.
Liver cancer is known to carry the highest social cost in comparison to other cancers and it causes the highest fatality in earlier age groups (40s-50s). In that sense, it is necessary to develop a new treatment that mitigates side effects yet elevates the survival rate.
There are ways in which liver cancer can be cured, such as surgery, embolization, and medication treatments; however, the options become limited for curing progressive cancer, a stage in which surgical methods cannot be executed.
Among anticancer medications, Sorafenib, a drug known for enhancing the survival rate of cancer patients, is a unique drug allowed for use as a targeted anticancer medication for progressive liver cancer patients. Its sales reached more than ten billion KRW annually in Korea, but its efficacy works on only about 20% of the treated patients. Also, acquired resistance to Sorafenib is emerging. Additionally, the action mechanism and resistance mechanism of Sorafenib is only vaguely identified.Although Sorafenib only extends the survival rate of terminal cancer patients less than three months on average, it is widely being used because drugs developed by global pharmaceutical companies failed to outperform its effectiveness.
Professor Cho’s research team analyzed the expression changes of genes in cell lines in response to Sorafenib in order to identify the effect and the resistance mechanism of Sorafenib.
As a result, the team discovered the resistance mechanism of Sorafenib using Systems Biology analysis. By combining computer simulations and biological experiments, it was revealed that protein disulfide isomerase (PDI) plays a crucial role in the resistance mechanism of Sorafenib and that its efficacy can be improved significantly by blocking PDI.
The research team used mice in the experiment and discovered the synergic effect of PDI inhibition with Sorafenib for reducing liver cancer cells, known as hepatocellular carcinoma. Also, more PDIs are shown in tissue from patients who possess a resistance to Sorafenib. From these findings, the team could identify the possibility of its clinical applications. The team also confirmed these findings from clinical data through a retrospective cohort study.
“Molecules that play an important role in cell lines are mostly put under complex regulation. For this reason, the existing biological research has a fundamental limitations for discovering its underlying principles,” Professor Cho said. “This research is a representative case of overcoming this limitation of traditional life science research by using a Systems Biology approach, combining IT and life science. It suggests the possibility of developing a new method that overcomes drug resistance with a network analysis of the targeted drug action mechanism of cancer.”
The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) and funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
(Figure 1. Simulation results from cellular experiments using hepatocellular carcinoma)
(Figure 2. Network analysis and computer simulation by using the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress network)
(Figure 3. ER stress network model)
2017.08.30 View 13820 -
 Global ITTP Graduates 12 Public Officials from 11 Countries
The 18th Global Information and Telecommunication Technology Program (ITTP) graduated 12 public officials from 11 countries in a commencement ceremony held on August 23.
Distinguished guests, faculty, and family of graduates including President Sung-Chul Shin, the Chair of the School of Business and Technology Youngsun Kown, and the Director of Global ITTP Jaejung Rho attended the commencement. Ghana Ambassador Joseph Agoe, Mrs. Lyudmila Fen, the spouse of Uzbekistan Ambassador Vitali Fen, and other dignitaries came to congratulate the 12 master’s students on their successful graduation.
The Global ITTP was launched in 2006 and offers customized master’s and doctoral degree programs to elite public officials from diverse countries on information and communication technology. This program plays a vital role for transferring Korea’s advanced ICT to countries whose industries are in the budding stages. Since 2006, the program has produced 181 alumni (48 PhDs and 133 masters) from 60 countries.
In his congratulatory message during the ceremony, President Shin congratulated the graduates on the long journey they had been through while completing their courses and welcomed the newest addition of KAIST 12 alumni.
“Back in the 1960s, Korea was one of the poorest countries in the world. Korea’s GDP stood at less than 100 US dollars. Through it all, Korean companies are now taking the lead in the global high-tech market, emerging as movers and shakers. I believe that ‘VIP’ changed it all; in other words, visionary leaders, innovative ideas, and passionate people all combined to make the difference in Korea,” said President Shin.
He also shared a new formula for success in the wake of the new industrial environment of the Fourth Industrial Revolution with the graduates who will soon begin a new ambitious professional journey in their countries. “I think Innovation, Collaboration, and Speed will be the key words to make a difference in every sector of each and every country in this dynamic new era. When making a national development strategies, please keep in mind ‘ICS’ for the development of your country as well as the world’s sustainable development.”
Finally, he said, “As a KAIST alumnus, always be sincere wherever you work and whatever you do during your service. I advise you to become a leader who is doing one’s best at all times.”
☞ Link to the 18th commencement address
2017.08.24 View 8534
Global ITTP Graduates 12 Public Officials from 11 Countries
The 18th Global Information and Telecommunication Technology Program (ITTP) graduated 12 public officials from 11 countries in a commencement ceremony held on August 23.
Distinguished guests, faculty, and family of graduates including President Sung-Chul Shin, the Chair of the School of Business and Technology Youngsun Kown, and the Director of Global ITTP Jaejung Rho attended the commencement. Ghana Ambassador Joseph Agoe, Mrs. Lyudmila Fen, the spouse of Uzbekistan Ambassador Vitali Fen, and other dignitaries came to congratulate the 12 master’s students on their successful graduation.
The Global ITTP was launched in 2006 and offers customized master’s and doctoral degree programs to elite public officials from diverse countries on information and communication technology. This program plays a vital role for transferring Korea’s advanced ICT to countries whose industries are in the budding stages. Since 2006, the program has produced 181 alumni (48 PhDs and 133 masters) from 60 countries.
In his congratulatory message during the ceremony, President Shin congratulated the graduates on the long journey they had been through while completing their courses and welcomed the newest addition of KAIST 12 alumni.
“Back in the 1960s, Korea was one of the poorest countries in the world. Korea’s GDP stood at less than 100 US dollars. Through it all, Korean companies are now taking the lead in the global high-tech market, emerging as movers and shakers. I believe that ‘VIP’ changed it all; in other words, visionary leaders, innovative ideas, and passionate people all combined to make the difference in Korea,” said President Shin.
He also shared a new formula for success in the wake of the new industrial environment of the Fourth Industrial Revolution with the graduates who will soon begin a new ambitious professional journey in their countries. “I think Innovation, Collaboration, and Speed will be the key words to make a difference in every sector of each and every country in this dynamic new era. When making a national development strategies, please keep in mind ‘ICS’ for the development of your country as well as the world’s sustainable development.”
Finally, he said, “As a KAIST alumnus, always be sincere wherever you work and whatever you do during your service. I advise you to become a leader who is doing one’s best at all times.”
☞ Link to the 18th commencement address
2017.08.24 View 8534 -
 KAIST to Host the 2017 AI World Cup in November
KAIST, the birthplace of the Robot World Cup in 1996, now presents a new technology matchup, the AI World Cup this November, which will be held at KAIST. The event is being organized by the Machine Intelligence and Robotics Multi-Sponsored Research and Education Platform (MIR-MSREP) of KAIST. The online, simulated AI soccer game, based on rolling updates, will be a draw for avid online gamers and tech-savvy university students from around the nation.
The tournament is comprised of three events: ▲A 5 on 5 AI soccer match to be played after self-learning using AI technology in an online simulation environment ▲Commentary in which online soccer videos are analyzed and commented on, and ▲Game reporters who will write articles on online soccer event results.
The participants will undergo a month-long online practice period in October and compete in preliminary matches from November 1 through 24. The top teams that scored the highest accumulated points will compete in the finals on December 1. In the finals, each team’s AI technology implementation method will be evaluated to select the final winning team. To ensure a successful event, KAIST will host a briefing session for participants on July 28.
Technological prowess and early exposure to AI accumulated at KAIST led to the launching of this tournament. Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the chair of the Organizing Committee of the AI World Cup, hosted the first ever Robot World Cup back in 1996. His concept has now evolved into the emerging technology of AI and the members of the Organizing Committee encompass the professors from the various departments of electrical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, aerospace engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and the graduate schools of Green Transportation, Cultural Technology, and Science and Technology Policy.
In particular, ongoing convergence research initiatives incorporating AI into a wide arrays of disciplines such as bio, nano, and IT, played a crucial role for making this AI World Cup happen. Professor Kim said, “The winner of this year’s competition will be awarded a certificate and a small gift. In 2018, we aim to expand the event to an international scale by allowing international teams.”
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can apply to participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017’. KAIST will host a public trial event during the ‘Open KAIST’ event period to be held November 2-3 to help participating students understand the event better. ‘Open KAIST’ allows the general public to personally visit and experience what goes on in engineering departments and laboratories on the KAIST main campus. It is hosted by the College of Engineering every two years and is the largest event hosted by KAIST.
To participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017,’ teams consisting of Korean undergraduates or graduate students can fill out application forms and submit them by September 30 on http://mir.kaist.ac.kr .
2017.07.14 View 14100
KAIST to Host the 2017 AI World Cup in November
KAIST, the birthplace of the Robot World Cup in 1996, now presents a new technology matchup, the AI World Cup this November, which will be held at KAIST. The event is being organized by the Machine Intelligence and Robotics Multi-Sponsored Research and Education Platform (MIR-MSREP) of KAIST. The online, simulated AI soccer game, based on rolling updates, will be a draw for avid online gamers and tech-savvy university students from around the nation.
The tournament is comprised of three events: ▲A 5 on 5 AI soccer match to be played after self-learning using AI technology in an online simulation environment ▲Commentary in which online soccer videos are analyzed and commented on, and ▲Game reporters who will write articles on online soccer event results.
The participants will undergo a month-long online practice period in October and compete in preliminary matches from November 1 through 24. The top teams that scored the highest accumulated points will compete in the finals on December 1. In the finals, each team’s AI technology implementation method will be evaluated to select the final winning team. To ensure a successful event, KAIST will host a briefing session for participants on July 28.
Technological prowess and early exposure to AI accumulated at KAIST led to the launching of this tournament. Professor Jong-Hwan Kim, the chair of the Organizing Committee of the AI World Cup, hosted the first ever Robot World Cup back in 1996. His concept has now evolved into the emerging technology of AI and the members of the Organizing Committee encompass the professors from the various departments of electrical engineering, computing, industrial and systems engineering, aerospace engineering, civil and environmental engineering, and the graduate schools of Green Transportation, Cultural Technology, and Science and Technology Policy.
In particular, ongoing convergence research initiatives incorporating AI into a wide arrays of disciplines such as bio, nano, and IT, played a crucial role for making this AI World Cup happen. Professor Kim said, “The winner of this year’s competition will be awarded a certificate and a small gift. In 2018, we aim to expand the event to an international scale by allowing international teams.”
Any undergraduate or graduate student in Korea can apply to participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017’. KAIST will host a public trial event during the ‘Open KAIST’ event period to be held November 2-3 to help participating students understand the event better. ‘Open KAIST’ allows the general public to personally visit and experience what goes on in engineering departments and laboratories on the KAIST main campus. It is hosted by the College of Engineering every two years and is the largest event hosted by KAIST.
To participate in the ‘AI World Cup 2017,’ teams consisting of Korean undergraduates or graduate students can fill out application forms and submit them by September 30 on http://mir.kaist.ac.kr .
2017.07.14 View 14100 -
 Reform of Universities Key in the Wake of the 4th Industrial Revolution
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that innovations in education, research, and technology commercialization of universities are critical for responding to the transformations that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about.
In his keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4, he cited connectivity, superintelligence, and convergence in science and technology as three components the Fourth Industrial Revolution will pierce, saying the speed and breadth of the transformation will be beyond our imagination. He also presented megatrends in science and technology in the years to come and how KAIST is addressing the challenges and opportunities.
“It is imperative to foster creative young talents fluent in convergence, collaboration, and communication skills in the new era. To this end, we need to focus on whole brain education by enhancing basic education in science and engineering plus humanities and social studies,” he stressed. He also presented a Non-Departmental Education Track, which KAIST plans to implement from next semester. The track, designed to prepare students for the new industrial era, will focus on whole brain education including entrepreneurship and leadership education during the undergraduate period.
He also emphasized an effective new teaching methodology. “We need to develop various new teaching methods. The paradigm should shift from lecturer-centered to student-centered. KAIST is revising our curriculum to facilitate team-based, project-based learning and flipped learning,” he explained.
President Shin also pointed out that the educational goals for the next generation should be to sustain the value of people’s own thoughtfulness, wisdom, emotion, and caring against the advent of a new tribe of AI, dubbed Robo Sapiens. “Those traits add undeniable educational value that we should continue to pursue even in the era of Robo Sapiens,” he added.
As for research innovation, he emphasized inter- and multi-disciplinary collaborative research. “Especially, in addressing pressing global issues and big science, international collaboration will be very effective and crucial,” he said.
At the summit, convergence research projects currently underway at KAIST using emerging technologies such as the smart mobile healthcare project, Dr, M; the humanoid robot, HUBO; and AI drone swarms drew lots of attention from the participants, even receiving proposals to join the projects as collaborators.
In the new era, according to Shin, technology commercialization at universities will emerge as a hub of R&DB. Citing that KAIST has long been a draw for startups, he noted that KAIST has also set a high value on entrepreneurship education including social entrepreneurship and startups.
He continued, “The Korean government is making every effort to harness the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by creating a new economic growth engine. For the success of the government initiative, universities should also respond to make innovations commensurate with the changing needs and challenges. KAIST will take the lead in this new initiative for making a new future.”
2017.07.06 View 9164
Reform of Universities Key in the Wake of the 4th Industrial Revolution
(President Shin makes a keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4.)
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin stressed that innovations in education, research, and technology commercialization of universities are critical for responding to the transformations that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about.
In his keynote speech at the Times Higher Education Research Excellence Summit held in Taiwan on July 4, he cited connectivity, superintelligence, and convergence in science and technology as three components the Fourth Industrial Revolution will pierce, saying the speed and breadth of the transformation will be beyond our imagination. He also presented megatrends in science and technology in the years to come and how KAIST is addressing the challenges and opportunities.
“It is imperative to foster creative young talents fluent in convergence, collaboration, and communication skills in the new era. To this end, we need to focus on whole brain education by enhancing basic education in science and engineering plus humanities and social studies,” he stressed. He also presented a Non-Departmental Education Track, which KAIST plans to implement from next semester. The track, designed to prepare students for the new industrial era, will focus on whole brain education including entrepreneurship and leadership education during the undergraduate period.
He also emphasized an effective new teaching methodology. “We need to develop various new teaching methods. The paradigm should shift from lecturer-centered to student-centered. KAIST is revising our curriculum to facilitate team-based, project-based learning and flipped learning,” he explained.
President Shin also pointed out that the educational goals for the next generation should be to sustain the value of people’s own thoughtfulness, wisdom, emotion, and caring against the advent of a new tribe of AI, dubbed Robo Sapiens. “Those traits add undeniable educational value that we should continue to pursue even in the era of Robo Sapiens,” he added.
As for research innovation, he emphasized inter- and multi-disciplinary collaborative research. “Especially, in addressing pressing global issues and big science, international collaboration will be very effective and crucial,” he said.
At the summit, convergence research projects currently underway at KAIST using emerging technologies such as the smart mobile healthcare project, Dr, M; the humanoid robot, HUBO; and AI drone swarms drew lots of attention from the participants, even receiving proposals to join the projects as collaborators.
In the new era, according to Shin, technology commercialization at universities will emerge as a hub of R&DB. Citing that KAIST has long been a draw for startups, he noted that KAIST has also set a high value on entrepreneurship education including social entrepreneurship and startups.
He continued, “The Korean government is making every effort to harness the challenges and opportunities of the Fourth Industrial Revolution by creating a new economic growth engine. For the success of the government initiative, universities should also respond to make innovations commensurate with the changing needs and challenges. KAIST will take the lead in this new initiative for making a new future.”
2017.07.06 View 9164 -
 Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2017
The World Economic Forum’s Expert Network and Global Future Councils in collaboration with Scientific American and its Board of Advisors announced the top 10 emerging technologies of 2017 on June 26 in Dalian, China where the 2017 Summer Davos Forum is being held. Each technology was chosen for its potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet.
The KAIST delegation, headed by President Sung-Chul Shin, is participating in the forum’s diverse activities including IdeasLab and GULF (Global University Leaders Forum). KAIST is the only Korean representative participating in the IdeasLab. KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, director of KAIST Institute, has served as a committee member of the Global Agenda Council on Emerging Technologies since 2012 and Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He also chairs the Global Future Council on Biotechnologies.
Professor Lee said, “Very diverse technological breakthroughs were proposed for the final list of candidates. We made the final selections through very in-depth discussion with experts in each field.
We focused on the technologies which have a level of maturity that will enable them to be adopted widely within three to five years."
The top 10 emerging technologies are
(courtesy from https://
www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/06/these-are-the-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2017):
2017 10대 기술.
1. Liquid biopsies
Liquid biopsies mark a step forward in the fight against cancer. First, they are an alternative where traditional tissue-based biopsies are not possible. Second, they provide a full spectrum of information compared to tissue samples, which only reflect the information available in the sample. Lastly, by homing in on circulating-tumor DNA (ctDNA), genetic material that routinely finds its way from cancer cells into the bloodstream, disease progression or resistance to treatment can be spotted much faster than otherwise relying on symptoms or imaging.
2. Harvesting clean water from air
The ability to extract clean water from air is not new, however existing techniques require high moisture levels and a lot of electricity. This is changing. A team from MIT and University of California, Berkeley has successfully tested a process using porous crystals that convert the water using no energy at all.
3. Deep learning for visual tasks
Computers are beginning to recognize images better than humans. Thanks to deep learning, an emerging field of artificial intelligence, computer-vision technologies are increasingly being used in applications as diverse as driving autonomous vehicles, medical diagnostics, damage assessment for insurance claims, and monitoring water levels and crop yield.
4. Liquid fuels from sunshine
Can we mimic the humble leaf to create artificial photosynthesis to generate and store energy? The prospects are looking increasingly positive. The answer lies in using sunlight-activated catalysts to split water molecules into water and hydrogen, and then using the same hydrogen to convert CO2 into hydrocarbons.
5. The Human Cell Atlas
An international collaboration aimed at deciphering the human body, called the Human Cell Atlas, was launched in October 2016. The project aims to identify every cell type in every tissue; learn exactly which genes, proteins, and other molecules are active in each type, and the processes which control that activity.
6. Precision farming
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is providing farmers with a new set of tools to boost crop yield and quality while reducing water and chemical use. Sensors, robots, GPS, mapping tools, and data-analytics software are all being used to customize the care that plants need.
7. Affordable catalysts for green vehicles
Progress is being made on a promising zero-emission technology, the hydrogen-fed fuel cell. Progress to date has been stymied by the high price of catalysts which contain platinum. However, much progress has been made in reducing reliance on this rare and expensive metal, and the latest developments involve catalysts that include no platinum, or in some cases no metal at all.
8. Genomic vaccines
Vaccines based on genes are superior to more conventional ones in a number of ways. They are faster to manufacture, which is crucial during violent outbreaks. Compared to manufacturing proteins in cell cultures or eggs, producing genetic material should also be simpler and less expensive.
9. Sustainable design of communities
Applying green construction to multiple buildings at once has the potential to revolutionize the amount of energy and water we consume. Sending locally-generated solar power to a smart microgrid could reduce electricity consumption by half and reduce carbon emissions to zero if a project currently under development at the University of California at Berkeley goes according to plan.
10. Quantum computing
Quantum computers’ almost limitless potential has only ever been matched by the difficulty and cost of their construction. This explains why today the small ones that have been built have not yet managed to exceed the power of supercomputers. But progress is being made and in 2016 the technology firm IBM provided public access to the first quantum computer in the cloud.
2017.06.28 View 14731
Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2017
The World Economic Forum’s Expert Network and Global Future Councils in collaboration with Scientific American and its Board of Advisors announced the top 10 emerging technologies of 2017 on June 26 in Dalian, China where the 2017 Summer Davos Forum is being held. Each technology was chosen for its potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet.
The KAIST delegation, headed by President Sung-Chul Shin, is participating in the forum’s diverse activities including IdeasLab and GULF (Global University Leaders Forum). KAIST is the only Korean representative participating in the IdeasLab. KAIST Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering, director of KAIST Institute, has served as a committee member of the Global Agenda Council on Emerging Technologies since 2012 and Global Future Council on the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He also chairs the Global Future Council on Biotechnologies.
Professor Lee said, “Very diverse technological breakthroughs were proposed for the final list of candidates. We made the final selections through very in-depth discussion with experts in each field.
We focused on the technologies which have a level of maturity that will enable them to be adopted widely within three to five years."
The top 10 emerging technologies are
(courtesy from https://
www.weforum.org/agenda/2017/06/these-are-the-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2017):
2017 10대 기술.
1. Liquid biopsies
Liquid biopsies mark a step forward in the fight against cancer. First, they are an alternative where traditional tissue-based biopsies are not possible. Second, they provide a full spectrum of information compared to tissue samples, which only reflect the information available in the sample. Lastly, by homing in on circulating-tumor DNA (ctDNA), genetic material that routinely finds its way from cancer cells into the bloodstream, disease progression or resistance to treatment can be spotted much faster than otherwise relying on symptoms or imaging.
2. Harvesting clean water from air
The ability to extract clean water from air is not new, however existing techniques require high moisture levels and a lot of electricity. This is changing. A team from MIT and University of California, Berkeley has successfully tested a process using porous crystals that convert the water using no energy at all.
3. Deep learning for visual tasks
Computers are beginning to recognize images better than humans. Thanks to deep learning, an emerging field of artificial intelligence, computer-vision technologies are increasingly being used in applications as diverse as driving autonomous vehicles, medical diagnostics, damage assessment for insurance claims, and monitoring water levels and crop yield.
4. Liquid fuels from sunshine
Can we mimic the humble leaf to create artificial photosynthesis to generate and store energy? The prospects are looking increasingly positive. The answer lies in using sunlight-activated catalysts to split water molecules into water and hydrogen, and then using the same hydrogen to convert CO2 into hydrocarbons.
5. The Human Cell Atlas
An international collaboration aimed at deciphering the human body, called the Human Cell Atlas, was launched in October 2016. The project aims to identify every cell type in every tissue; learn exactly which genes, proteins, and other molecules are active in each type, and the processes which control that activity.
6. Precision farming
The Fourth Industrial Revolution is providing farmers with a new set of tools to boost crop yield and quality while reducing water and chemical use. Sensors, robots, GPS, mapping tools, and data-analytics software are all being used to customize the care that plants need.
7. Affordable catalysts for green vehicles
Progress is being made on a promising zero-emission technology, the hydrogen-fed fuel cell. Progress to date has been stymied by the high price of catalysts which contain platinum. However, much progress has been made in reducing reliance on this rare and expensive metal, and the latest developments involve catalysts that include no platinum, or in some cases no metal at all.
8. Genomic vaccines
Vaccines based on genes are superior to more conventional ones in a number of ways. They are faster to manufacture, which is crucial during violent outbreaks. Compared to manufacturing proteins in cell cultures or eggs, producing genetic material should also be simpler and less expensive.
9. Sustainable design of communities
Applying green construction to multiple buildings at once has the potential to revolutionize the amount of energy and water we consume. Sending locally-generated solar power to a smart microgrid could reduce electricity consumption by half and reduce carbon emissions to zero if a project currently under development at the University of California at Berkeley goes according to plan.
10. Quantum computing
Quantum computers’ almost limitless potential has only ever been matched by the difficulty and cost of their construction. This explains why today the small ones that have been built have not yet managed to exceed the power of supercomputers. But progress is being made and in 2016 the technology firm IBM provided public access to the first quantum computer in the cloud.
2017.06.28 View 14731