Atom
-
 KAIST Nanosatellite LINK Launched to the ISS
Courtesy: United Launch Alliance
The KAIST nanosatellite LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was successfully launched on an Atlas V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18 at Space Launch Complex 41, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The KAIST nanosatellite was developed by the research team led by Professor Hyochoong Bang of the Department of Aerospace Engineering.
Aboard the flight to the ISS (International Space Station) were 28 satellites including LINK. They are part of the QB50 Project, an international educational initiative which aims to deploy an array of CubeSat-mounted sensors into Earth’s thermosphere. The project is funded by the European Commission and managed by the von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics in Belgium.
The small satellites are hitching a lift into orbit aboard the unmanned resupply spacecraft Cygnus, with a total mass of 83 kilograms. Built to CubeSat specifications, Cygnus will deploy four of the spacecraft following its departure from the space station. LINK will conduct its scientific mission for three months at the station.
The majority of QB50 satellites carry one of three standard instrument packages, consisting of a primary instrument and an array of thermistors, thermocouples, and resistant temperature detectors. LINK is a two-unit CubeSat and weighs two kilograms. It carries an ion-neutral mass spectrometer (INMS), which measures the mass of ions and neutral atoms, as the primary payload of the QB50 project. The secondary payload is two Langmuir probes, which are in-house sensors (m-NLP) developed by Professor Kyong Wook Min’s team of the Department of Physics at KAIST. These are all geared toward collecting long-term continuous in-situ measurements of conditions in Earth’s lower thermosphere.
Professor Bang said, “The QB50 Project is being used for educational purposes. However, the LINK launch will bring a new breakthrough toward collecting information on Earth’s lower thermosphere. Building on these experiences of designing and launching the CubeSat will serve as an opportunity to verify the research results made in our lab firsthand in space.”
(Caption: LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was launched on an Atlast V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18.)
2017.04.25 View 9958
KAIST Nanosatellite LINK Launched to the ISS
Courtesy: United Launch Alliance
The KAIST nanosatellite LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was successfully launched on an Atlas V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18 at Space Launch Complex 41, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The KAIST nanosatellite was developed by the research team led by Professor Hyochoong Bang of the Department of Aerospace Engineering.
Aboard the flight to the ISS (International Space Station) were 28 satellites including LINK. They are part of the QB50 Project, an international educational initiative which aims to deploy an array of CubeSat-mounted sensors into Earth’s thermosphere. The project is funded by the European Commission and managed by the von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics in Belgium.
The small satellites are hitching a lift into orbit aboard the unmanned resupply spacecraft Cygnus, with a total mass of 83 kilograms. Built to CubeSat specifications, Cygnus will deploy four of the spacecraft following its departure from the space station. LINK will conduct its scientific mission for three months at the station.
The majority of QB50 satellites carry one of three standard instrument packages, consisting of a primary instrument and an array of thermistors, thermocouples, and resistant temperature detectors. LINK is a two-unit CubeSat and weighs two kilograms. It carries an ion-neutral mass spectrometer (INMS), which measures the mass of ions and neutral atoms, as the primary payload of the QB50 project. The secondary payload is two Langmuir probes, which are in-house sensors (m-NLP) developed by Professor Kyong Wook Min’s team of the Department of Physics at KAIST. These are all geared toward collecting long-term continuous in-situ measurements of conditions in Earth’s lower thermosphere.
Professor Bang said, “The QB50 Project is being used for educational purposes. However, the LINK launch will bring a new breakthrough toward collecting information on Earth’s lower thermosphere. Building on these experiences of designing and launching the CubeSat will serve as an opportunity to verify the research results made in our lab firsthand in space.”
(Caption: LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was launched on an Atlast V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18.)
2017.04.25 View 9958 -
 The 2016 Research Highlights
KAIST has selected the ten most outstanding projects of 2016 conducted by its faculty and researchers. This selection embodies the KAIST research portfolios that translate their discoveries into meaningful and measurable impact toward a better world. All of them demonstrate exceptional creativity, which open new research paths for each field in its novelty, innovation, and impact.
The following list has been reviewed by a committee of faculty peers headed by Associate Vice President for Research. Following are the 2016 KAIST research highlights:
□ Commercialization of 3D Holographic Microscopy
By YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics
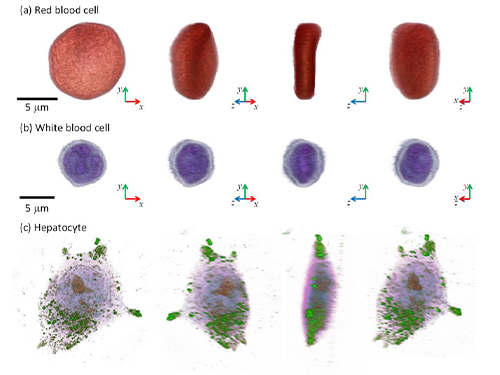
Professor YongKeun Park and his colleagues develop a powerful technique to measure 3D images of live cells without labeling agents. This technique, called 3D holographic microscopy or holotomography, will open a new avenue for the study of cell biology and its applications in medical diagnosis. This research also led to the founding of a start-up company Tomocube Inc. and the successful commercialization of the technique.
Professor Park and his research team developed a solution based on digital holography technology used to visualize 3D refractive index tomograms of live cells without staining. This allowed the real-time observation of biological cells in 2D, 3D, and 4D without the use of labeling agents. Conventional techniques for 3D cell imaging requires the use of labeling agents such as fluorescence dyes and proteins, which prevent from investigating the physiology of intact untreated cells. In particular, label-free imaging capability becomes more important in several emerging fields such as stem cell research and immunotherapy.
The team employs the concept of 3D digital holography to achieve the optical measurements of 3D refractive index tomograms of live cells and tissues. Also, a digital micromirror device (DMD), which has been used for DLPTM projectors, was utilized to steer a laser beam for 3D measurements.
Tomocube, founded from seed money funded by the EndRun Project of the Institute for Startup KAIST, succeeded in the commercialization of the 3D holographic microscopy and established an international distribution network in more than ten countries. It now has started exporting the product to several countries. The microscopes are being used in several leading research institutes including MIT, German Cancer Center, Pittsburg Medical Center, and Seoul National University Hospital Selected as one of the top ten mechanical technologies of 2016 by the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers, the team raised four billion KRW investment from industry leaders including Soft Bank Venture Korea, Hanmi Pharmaceutical, and InterVest investment.
(Figure: Images of cells measured by 3D microscopy)
□ Designer Proteins with Chemical Modifications
By Hee-Sung Park and Hee Yoon Lee of the Department of Chemistry
Professor Hee-Sung Park developed a new strategy for installing authentic post-translational modifications (PTM) into recombinant proteins. Most essential biological processes are controlled by PTM, which plays a critical role in metabolic changes. However, abnormal protein modification aroused by environmental or genetic factors induce diverse diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and many other chronic diseases.
Professor Park has conceived a novel chemical biology route to achieve authentic and selective chemical modifications in proteins.He first used the established O-phosphoserine (Sep) orthogonal translational system to create a Sep-containing protein. The Sep residue is then dephosphorylated to dehydroalanine (Dha). Finally, Zn-Cu is conjugated to Dha of alkyl iodides, which enables it to form chemo-selective carbon-carbon bonds.
This approach offers a powerful tool to engineer designer proteins with diverse chemical modifications, providing a novel platform for investigating numerous diseases and drug development including for cancer and Alzheimer's. Furthermore, this research will allow mass production of abnormally modified proteins that could induce diseases, opening up new prospects in disease treatment research. It will help to enable investigation and discovery of new drug inhibitors that directly target abnormally modified proteins.
(Figure: Application of Customized Protein Modification Technology)
□ Lanthanum-Catalyzed Synthesis of Microporous 3D Graphene-Like Carbons in a Zeolite Template
By Ryong Ryoo, of the Department of Chemistry
Professor Ryong Ryoo’s team presented a scaled-up carbon synthesis viable for practical applications such as Li-ion batteries and catalyst supports.
Zeolite-templated carbon has an extremely large surface area and a regular microporous structure. As a result, it was expected to show excellent performance in various applications, such as for electrode materials or catalyst supports. However, until recently difficulties in synthesis have hindered research on application and properties of zeolited-templated carbon compared to other porous carbon materials.
Professor Ryoo’s team demonstrated that lanthanum ions embedded in zeolite pores lowered the temperature for carbonization of ethylene or acetylene. In this contribution, a graphene-like carbon structure was selectively formed inside zeolite template without the non-selective carbon deposition. Single crystal X-ray diffraction data revealed that carbon formed along the micropore surface. After removal of zeolite template, the carbon framework showed high electrical conductivity.
His synthesis method not only allowed selectivity in ethylene carbonization inside zeolite pore but permitted the diffusion of carbon material even when a large amount of zeolites was synthesized at once, allowing mass production of carbon. Thus, this method is expected to accelerate research on the application and properties of zeolite-templated carbon.
(Figure: Electron density distribution of zeolite that underwent selective pore carbonization. The structure of carbon determined by electron density distributions of carbon atoms, shown in yellow and red, within the framework of zeolite, shown in blue, can be observed.)
□ Complete Prevention of Blood Loss by Self-Sealing Hemostatic Needles
By Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry
Professor Haeshin Lee’s team invented a hemostatic hypodermic needle, which prevented bleeding of punctured tissue during and after injections.
Bleeding unavoidably accompanies injections when a conventional needle penetrates tissue. Though the scale of bleeding from controlled injections does not cause harm to healthy individuals, uncontrolled bleeding may bring serious complications for those who suffer from hemophilia, coagulopathy, or who have been exposed to infectious diseases.
Professor Lee’s hemostatic hypodermic needle is coated with partially cross-linked catechol-functionalized chitosan that undergoes a solid-to-gel phase transition in situ to seal-seal punctured tissues. The team reported a complete prevention of blood loss following intravenous and intramuscular injections in animal models. They observed a 100% survival rate in hemophiliac mice following a syringe injection into a jugular vein.
The self-sealing hemostatic needles may help to prevent complications associated with bleeding in clinical settings such as for diabetic patients who experience delayed hemostasis and in the procedure of biopsy thereby preventing profuse bleeding.
□ An Immunological Mechanism for the Contribution of Commensal Microbiota Against Herpes Simplex Virus Infection in Genital Mucosa
By Heung Kyu Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
Professor Heung Kyu Lee identified an immunological mechanism of commensal microbiota against herpes virus infections. The protective mechanisms of commensal bacteria against viral infections was limited to how immune inductive signals are provided by commensal bacteria for enhancing innate and adaptive immunity. Until Professor Lee’s research discovery, whether, or how, commensal bacteria might influence the effector arm of immune responses such as effector T cells to eliminate infected virus remained unknown.
Professor Lee’s team demonstrated that dysbiosis within the vaginal microbiota resulted in severe impairment of antiviral protection against HSV-2 infection. IL-33 released into the vaginal tract after antibiotic treatment blocked the ability of effector T cells to migrate into vaginal tissues and secrete the antiviral cytokine, IFN-γ. Thus, the findings suggested a previously unstudied role of commensal bacteria in the effector phase of the antiviral immune response against genital herpes. These findings provided insight into the mechanisms by which the secretion of proteases from opportunistic pathogens in susceptibility to various sexually transmitted pathogens might induce type 2 immunity within the female genital tract.
Promoting awareness of overuse of antibiotics, the research is expected to contribute to the development of viral vaccines with enhanced defense capacity by regulating commensal bacteria to promote health.
□ Development of a Pulse-Echo Laser Ultrasonic Propagation Imaging System
By Jung-Ryul Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering
Professor Jung-Ryul Lee’s team for the first time developed a mobile laser ultrasonic propagation imaging system that is capable of 2500-point inspection per second and visualization of pulse-echo ultrasonic wave through the thickness of a solid medium. This novel ultrasonic propagation visualization system has been successfully prototyped for the application of in-situ and in-process nondestructive evaluation of aerospace structures.
The real world proof-of-concept was achieved by testing the new system in the inspection of a space launcher fuselage (KSLV-II), control surfaces of military transport (CN-235), and the brake disk of F-16, guided weapon fuselage. In addition, the system has passed F-16 standard specimen test done by Korea Air Force and got a US patent. The prototype which was developed over a period of two years has been successfully delivered to Korea Air Force last December.
Furthermore, Boeing has expressed interest in prototype development project and KAIST OESL has been selected as the Boeing-KAIST technical contact lab and received a two-year grant from Boeing. The second prototype is under construction for Boeing and the third prototype will be delivered to an optional research institute and used as a standard inspection instrument.
□ Birefractive Stereo Imaging for Single-Shot Depth Acquisition
By Min H. Kim of the School of Computing
Professor Min H. Kim’s team proposed a novel 3D imaging method that allows the capture of not only color pictures but also corresponding depth images while traditional cameras capture just color pictures.
Depending on the polarization state of light, the incident light on a birefringent material such as calcite can be refracted into two different angles. This physical phenomenon is called double refraction. Whereas traditional stereo imaging requires at least two stereo cameras, 3D imaging method can capture depth from a single picture of double refraction. This proposed 3D imaging technique can be applied to many graphics and computer vision applications such as AR/VR applications that require color and depth information simultaneously.
This technology, which could measure depth images, is currently needed for various industrial applications. The suggested method in this research to measure depth information from one photo using double refraction media accurately can be used in areas where system size and cost are important, such as mobile cameras, VR/ARs, driverless cars, and 3D microscopes.
(Figure: Measuring high-resolution depth of single image via bi-refringent medium)
□Development of Environment Friendly Geotechnical Construction Material Using Biopolymer
By Gye-Chun Cho of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Professor Gye-Chun Cho has succeeded in making a 100% bio-based KABS (KAIST Bio-Soil) binder using biopolymer, an eco-friendly geotechnical construction material. A biopolymer is an organic polymer produced in the course of microbial activities and thus is an eco-friendly material manufactured without generating carbon dioxide. Biopolymers have been used in food, agriculture, cosmetics, and medicine as hardener and gelling agents, but have never been applied in construction. His team verified the microscopic interaction, feasibility, and strengthening mechanism of microbial biopolymers for soils for the first time in the world, suggesting that biopolymers be an eco-friendly soil binder.
In addition to soil binders, biopolymers can also be applied to various fields of ground construction (e.g., ground improvement, grouting, erosion control, vegetation, anti-desertification, etc.). The team expects more biopolymer applications in construction since increasing demands for replacing cement-based or chemical ground materials have surged.
With KABS binder, the team has performed several field tests along with industrial technology transfer underway. In collaboration with the Korea Expressway Corporation and LH Corporation, Professor Cho’s team is working on additional commercial applications.
(Figure: Strength enhancement effect of soil grain processed by biopolymer )
□ Protein Delivery Via Engineered Exosomes
By Chulhee Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Professor Chulhee Choi’s team unveiled a new tool for intracellular delivery of target proteins, named “exosomes for protein loading via optically reversible protein-protein interactions” or “EXPLORs”.
Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of functional macromolecules is a promising method for treating a variety of human diseases. Among nanoparticles, cell-derived exosomes have recently gained attention as a new therapeutic strategy for the in vivo delivery of nucleotides and chemical drugs.
By integrating a reversible protein-protein interaction module controlled by blue light with the endogenous process of exosome biogenesis, the team successfully loaded cargo proteins into newly generated exosomes. Treatment with protein-loaded EXPLORs is shown to significantly increase intracellular levels of cargo proteins and their function in recipient cells in vitro and in vivo.
These results clearly indicate the potential of EXPLORs as a mechanism for the efficient intracellular transfer of protein-based therapeutics into recipient cells and tissues. This technology has been transferred to KAIST bio-venture Cellex Life Science, Incorporated for commercialization.
□ Hot Electron Detection under Catalytic Reactions
By Jeong Young Park of the Graduate School of EEWS
Professor Jeong Young Park’s team developed a novel catalytic nanodiode consisting of a thin metal catalyst deposited onto a semiconductor support. The team succeeded in observing in real-time hot electrons created in the course of catalytic reaction occurring at atmospheric pressure or at liquid-solid interfaces.
Use of a noble catalytic nanodiode is a new measurement system that detects hot electrons produced on catalyst surface through atmospheric pressure and liquid chemical reaction in real time that allows direct identification of the catalytic activity of catalytic reactions. In particular, the system allows macro-observation of hot-electron movements that change with the type of nano-catalyst without high-priced equipment in atmospheric pressure and liquidation, and thus is not limited to experimental conditions such as in ultrahigh vacuums.
Therefore, it could be applied in the future to analyze complex chemical reaction mechanisms of catalysts used in high temperature and various pressure conditions, and to develop high efficiency next-generation catalyst materials. This finding may lead not only to the fundamental understanding in the mechanism of the catalytic reactions but also to the development of next-generation catalysts with enhanced catalytic performance.
(Figure: Schematic diagrams of nano-catalyst hot electron element and graphene hot electron detector)
2017.02.20 View 14331
The 2016 Research Highlights
KAIST has selected the ten most outstanding projects of 2016 conducted by its faculty and researchers. This selection embodies the KAIST research portfolios that translate their discoveries into meaningful and measurable impact toward a better world. All of them demonstrate exceptional creativity, which open new research paths for each field in its novelty, innovation, and impact.
The following list has been reviewed by a committee of faculty peers headed by Associate Vice President for Research. Following are the 2016 KAIST research highlights:
□ Commercialization of 3D Holographic Microscopy
By YongKeun Park of the Department of Physics
Professor YongKeun Park and his colleagues develop a powerful technique to measure 3D images of live cells without labeling agents. This technique, called 3D holographic microscopy or holotomography, will open a new avenue for the study of cell biology and its applications in medical diagnosis. This research also led to the founding of a start-up company Tomocube Inc. and the successful commercialization of the technique.
Professor Park and his research team developed a solution based on digital holography technology used to visualize 3D refractive index tomograms of live cells without staining. This allowed the real-time observation of biological cells in 2D, 3D, and 4D without the use of labeling agents. Conventional techniques for 3D cell imaging requires the use of labeling agents such as fluorescence dyes and proteins, which prevent from investigating the physiology of intact untreated cells. In particular, label-free imaging capability becomes more important in several emerging fields such as stem cell research and immunotherapy.
The team employs the concept of 3D digital holography to achieve the optical measurements of 3D refractive index tomograms of live cells and tissues. Also, a digital micromirror device (DMD), which has been used for DLPTM projectors, was utilized to steer a laser beam for 3D measurements.
Tomocube, founded from seed money funded by the EndRun Project of the Institute for Startup KAIST, succeeded in the commercialization of the 3D holographic microscopy and established an international distribution network in more than ten countries. It now has started exporting the product to several countries. The microscopes are being used in several leading research institutes including MIT, German Cancer Center, Pittsburg Medical Center, and Seoul National University Hospital Selected as one of the top ten mechanical technologies of 2016 by the Korean Society of Mechanical Engineers, the team raised four billion KRW investment from industry leaders including Soft Bank Venture Korea, Hanmi Pharmaceutical, and InterVest investment.
(Figure: Images of cells measured by 3D microscopy)
□ Designer Proteins with Chemical Modifications
By Hee-Sung Park and Hee Yoon Lee of the Department of Chemistry
Professor Hee-Sung Park developed a new strategy for installing authentic post-translational modifications (PTM) into recombinant proteins. Most essential biological processes are controlled by PTM, which plays a critical role in metabolic changes. However, abnormal protein modification aroused by environmental or genetic factors induce diverse diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases, cancer, and many other chronic diseases.
Professor Park has conceived a novel chemical biology route to achieve authentic and selective chemical modifications in proteins.He first used the established O-phosphoserine (Sep) orthogonal translational system to create a Sep-containing protein. The Sep residue is then dephosphorylated to dehydroalanine (Dha). Finally, Zn-Cu is conjugated to Dha of alkyl iodides, which enables it to form chemo-selective carbon-carbon bonds.
This approach offers a powerful tool to engineer designer proteins with diverse chemical modifications, providing a novel platform for investigating numerous diseases and drug development including for cancer and Alzheimer's. Furthermore, this research will allow mass production of abnormally modified proteins that could induce diseases, opening up new prospects in disease treatment research. It will help to enable investigation and discovery of new drug inhibitors that directly target abnormally modified proteins.
(Figure: Application of Customized Protein Modification Technology)
□ Lanthanum-Catalyzed Synthesis of Microporous 3D Graphene-Like Carbons in a Zeolite Template
By Ryong Ryoo, of the Department of Chemistry
Professor Ryong Ryoo’s team presented a scaled-up carbon synthesis viable for practical applications such as Li-ion batteries and catalyst supports.
Zeolite-templated carbon has an extremely large surface area and a regular microporous structure. As a result, it was expected to show excellent performance in various applications, such as for electrode materials or catalyst supports. However, until recently difficulties in synthesis have hindered research on application and properties of zeolited-templated carbon compared to other porous carbon materials.
Professor Ryoo’s team demonstrated that lanthanum ions embedded in zeolite pores lowered the temperature for carbonization of ethylene or acetylene. In this contribution, a graphene-like carbon structure was selectively formed inside zeolite template without the non-selective carbon deposition. Single crystal X-ray diffraction data revealed that carbon formed along the micropore surface. After removal of zeolite template, the carbon framework showed high electrical conductivity.
His synthesis method not only allowed selectivity in ethylene carbonization inside zeolite pore but permitted the diffusion of carbon material even when a large amount of zeolites was synthesized at once, allowing mass production of carbon. Thus, this method is expected to accelerate research on the application and properties of zeolite-templated carbon.
(Figure: Electron density distribution of zeolite that underwent selective pore carbonization. The structure of carbon determined by electron density distributions of carbon atoms, shown in yellow and red, within the framework of zeolite, shown in blue, can be observed.)
□ Complete Prevention of Blood Loss by Self-Sealing Hemostatic Needles
By Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry
Professor Haeshin Lee’s team invented a hemostatic hypodermic needle, which prevented bleeding of punctured tissue during and after injections.
Bleeding unavoidably accompanies injections when a conventional needle penetrates tissue. Though the scale of bleeding from controlled injections does not cause harm to healthy individuals, uncontrolled bleeding may bring serious complications for those who suffer from hemophilia, coagulopathy, or who have been exposed to infectious diseases.
Professor Lee’s hemostatic hypodermic needle is coated with partially cross-linked catechol-functionalized chitosan that undergoes a solid-to-gel phase transition in situ to seal-seal punctured tissues. The team reported a complete prevention of blood loss following intravenous and intramuscular injections in animal models. They observed a 100% survival rate in hemophiliac mice following a syringe injection into a jugular vein.
The self-sealing hemostatic needles may help to prevent complications associated with bleeding in clinical settings such as for diabetic patients who experience delayed hemostasis and in the procedure of biopsy thereby preventing profuse bleeding.
□ An Immunological Mechanism for the Contribution of Commensal Microbiota Against Herpes Simplex Virus Infection in Genital Mucosa
By Heung Kyu Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering
Professor Heung Kyu Lee identified an immunological mechanism of commensal microbiota against herpes virus infections. The protective mechanisms of commensal bacteria against viral infections was limited to how immune inductive signals are provided by commensal bacteria for enhancing innate and adaptive immunity. Until Professor Lee’s research discovery, whether, or how, commensal bacteria might influence the effector arm of immune responses such as effector T cells to eliminate infected virus remained unknown.
Professor Lee’s team demonstrated that dysbiosis within the vaginal microbiota resulted in severe impairment of antiviral protection against HSV-2 infection. IL-33 released into the vaginal tract after antibiotic treatment blocked the ability of effector T cells to migrate into vaginal tissues and secrete the antiviral cytokine, IFN-γ. Thus, the findings suggested a previously unstudied role of commensal bacteria in the effector phase of the antiviral immune response against genital herpes. These findings provided insight into the mechanisms by which the secretion of proteases from opportunistic pathogens in susceptibility to various sexually transmitted pathogens might induce type 2 immunity within the female genital tract.
Promoting awareness of overuse of antibiotics, the research is expected to contribute to the development of viral vaccines with enhanced defense capacity by regulating commensal bacteria to promote health.
□ Development of a Pulse-Echo Laser Ultrasonic Propagation Imaging System
By Jung-Ryul Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering
Professor Jung-Ryul Lee’s team for the first time developed a mobile laser ultrasonic propagation imaging system that is capable of 2500-point inspection per second and visualization of pulse-echo ultrasonic wave through the thickness of a solid medium. This novel ultrasonic propagation visualization system has been successfully prototyped for the application of in-situ and in-process nondestructive evaluation of aerospace structures.
The real world proof-of-concept was achieved by testing the new system in the inspection of a space launcher fuselage (KSLV-II), control surfaces of military transport (CN-235), and the brake disk of F-16, guided weapon fuselage. In addition, the system has passed F-16 standard specimen test done by Korea Air Force and got a US patent. The prototype which was developed over a period of two years has been successfully delivered to Korea Air Force last December.
Furthermore, Boeing has expressed interest in prototype development project and KAIST OESL has been selected as the Boeing-KAIST technical contact lab and received a two-year grant from Boeing. The second prototype is under construction for Boeing and the third prototype will be delivered to an optional research institute and used as a standard inspection instrument.
□ Birefractive Stereo Imaging for Single-Shot Depth Acquisition
By Min H. Kim of the School of Computing
Professor Min H. Kim’s team proposed a novel 3D imaging method that allows the capture of not only color pictures but also corresponding depth images while traditional cameras capture just color pictures.
Depending on the polarization state of light, the incident light on a birefringent material such as calcite can be refracted into two different angles. This physical phenomenon is called double refraction. Whereas traditional stereo imaging requires at least two stereo cameras, 3D imaging method can capture depth from a single picture of double refraction. This proposed 3D imaging technique can be applied to many graphics and computer vision applications such as AR/VR applications that require color and depth information simultaneously.
This technology, which could measure depth images, is currently needed for various industrial applications. The suggested method in this research to measure depth information from one photo using double refraction media accurately can be used in areas where system size and cost are important, such as mobile cameras, VR/ARs, driverless cars, and 3D microscopes.
(Figure: Measuring high-resolution depth of single image via bi-refringent medium)
□Development of Environment Friendly Geotechnical Construction Material Using Biopolymer
By Gye-Chun Cho of the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering
Professor Gye-Chun Cho has succeeded in making a 100% bio-based KABS (KAIST Bio-Soil) binder using biopolymer, an eco-friendly geotechnical construction material. A biopolymer is an organic polymer produced in the course of microbial activities and thus is an eco-friendly material manufactured without generating carbon dioxide. Biopolymers have been used in food, agriculture, cosmetics, and medicine as hardener and gelling agents, but have never been applied in construction. His team verified the microscopic interaction, feasibility, and strengthening mechanism of microbial biopolymers for soils for the first time in the world, suggesting that biopolymers be an eco-friendly soil binder.
In addition to soil binders, biopolymers can also be applied to various fields of ground construction (e.g., ground improvement, grouting, erosion control, vegetation, anti-desertification, etc.). The team expects more biopolymer applications in construction since increasing demands for replacing cement-based or chemical ground materials have surged.
With KABS binder, the team has performed several field tests along with industrial technology transfer underway. In collaboration with the Korea Expressway Corporation and LH Corporation, Professor Cho’s team is working on additional commercial applications.
(Figure: Strength enhancement effect of soil grain processed by biopolymer )
□ Protein Delivery Via Engineered Exosomes
By Chulhee Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Professor Chulhee Choi’s team unveiled a new tool for intracellular delivery of target proteins, named “exosomes for protein loading via optically reversible protein-protein interactions” or “EXPLORs”.
Nanoparticle-mediated delivery of functional macromolecules is a promising method for treating a variety of human diseases. Among nanoparticles, cell-derived exosomes have recently gained attention as a new therapeutic strategy for the in vivo delivery of nucleotides and chemical drugs.
By integrating a reversible protein-protein interaction module controlled by blue light with the endogenous process of exosome biogenesis, the team successfully loaded cargo proteins into newly generated exosomes. Treatment with protein-loaded EXPLORs is shown to significantly increase intracellular levels of cargo proteins and their function in recipient cells in vitro and in vivo.
These results clearly indicate the potential of EXPLORs as a mechanism for the efficient intracellular transfer of protein-based therapeutics into recipient cells and tissues. This technology has been transferred to KAIST bio-venture Cellex Life Science, Incorporated for commercialization.
□ Hot Electron Detection under Catalytic Reactions
By Jeong Young Park of the Graduate School of EEWS
Professor Jeong Young Park’s team developed a novel catalytic nanodiode consisting of a thin metal catalyst deposited onto a semiconductor support. The team succeeded in observing in real-time hot electrons created in the course of catalytic reaction occurring at atmospheric pressure or at liquid-solid interfaces.
Use of a noble catalytic nanodiode is a new measurement system that detects hot electrons produced on catalyst surface through atmospheric pressure and liquid chemical reaction in real time that allows direct identification of the catalytic activity of catalytic reactions. In particular, the system allows macro-observation of hot-electron movements that change with the type of nano-catalyst without high-priced equipment in atmospheric pressure and liquidation, and thus is not limited to experimental conditions such as in ultrahigh vacuums.
Therefore, it could be applied in the future to analyze complex chemical reaction mechanisms of catalysts used in high temperature and various pressure conditions, and to develop high efficiency next-generation catalyst materials. This finding may lead not only to the fundamental understanding in the mechanism of the catalytic reactions but also to the development of next-generation catalysts with enhanced catalytic performance.
(Figure: Schematic diagrams of nano-catalyst hot electron element and graphene hot electron detector)
2017.02.20 View 14331 -
 Adsorbent That Can Selectively Remove Water Contaminants
Professor Cafer T. Yavuz and his team at the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) have developed an adsorbent that can selectively capture soluble organic contaminants in water.
This water treatment adsorbent is a fluorine-based nanoporous polymer that can selectively remove water-soluble micromolecules. It has the added advantage of being cheap and easily synthesized, while also being renewable.
The results of this research have been published online in Nature Communication on November 10, 2016. The research paper is titled “Charge-specific Size-dependent Separation of Water-soluble Organic Molecules by Fluorinated Nanoporous Networks.” (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13377)
Water pollution is accelerating as a result of global industrial development and warming. As new materials are produced and applied in the agricultural and industrial sectors, the types of contaminants expelled as sewage and waste water are also becoming diverse.
Chemicals such as dyes and pesticides can be especially harmful because they are made up of small and highly soluble organic particles that cannot be completely removed during the water treatment process, ultimately ending up in our drinking water.
The current conventional water treatment systems utilize processes such as activated carbon, ozonolysis, and reverse osmosis membrane. These processes, however, are designed to remove larger organic molecules with lower solubility, thus removal of very small molecules with high solubility is difficult. In addition, these micromolecules tend to be charged, therefore are less easily separated in aqueous form.
The research team aimed to remove these small molecules using a new adsorbent technology.
In order to remove aqueous organic molecular contaminants, the team needed an adsorbent that can adsorb micro-sized molecules. It also needed to introduce a chemical function that would allow it to selectively adsorb molecules, and lastly, the adsorbent needed to be structurally stable as it would be used underwater.
The team subsequently developed an adsorbent of fluorine-based porous organic polymer that met all the conditions listed above. By controlling the size of the pores, this adsorbent is able to selectively adsorb aqueous micromolecules of less than 1-2 nm in size.
In addition, in order to separate specific contaminants, there should be a chemical functionality, such as the ability to strongly interact with the target material. Fluorine, the most electronegative atom, interacts strongly with charged soluble organic molecules.
The research team incorporated fluorine into an adsorbent, enabling it to separate charged organic molecules up to 8 times faster than neutral molecules.
The adsorbent developed by Professor Yavuz’s team has wide industrial applications. It can be used in batch-adsorption tests, as well as in column separation for size- and charge-specific adsorption.
Professor Yavuz stated that “the charge-selective properties displayed by fluorine has the potential to be applied in desalination or water treatment processes using membranes."
This paper was first-authored by Dr. Jeehye Byun, and the research was funded by KAIST’s High Risk High Return Program and the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program, as well as its Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change.
Figure 1. Diagram conceptualizing the process of charge- and size-specific separation by the fluorine-based porous polymer adsorbent
Figure 2. Difference in absorbance before and after using a porous fluorine polymer column to separate organic molecules
Figure 3. Adsorption properties of a fluorine polymer according to the charge and size of organic molecules
2017.01.17 View 11605
Adsorbent That Can Selectively Remove Water Contaminants
Professor Cafer T. Yavuz and his team at the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water, and Sustainability (EEWS) have developed an adsorbent that can selectively capture soluble organic contaminants in water.
This water treatment adsorbent is a fluorine-based nanoporous polymer that can selectively remove water-soluble micromolecules. It has the added advantage of being cheap and easily synthesized, while also being renewable.
The results of this research have been published online in Nature Communication on November 10, 2016. The research paper is titled “Charge-specific Size-dependent Separation of Water-soluble Organic Molecules by Fluorinated Nanoporous Networks.” (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms13377)
Water pollution is accelerating as a result of global industrial development and warming. As new materials are produced and applied in the agricultural and industrial sectors, the types of contaminants expelled as sewage and waste water are also becoming diverse.
Chemicals such as dyes and pesticides can be especially harmful because they are made up of small and highly soluble organic particles that cannot be completely removed during the water treatment process, ultimately ending up in our drinking water.
The current conventional water treatment systems utilize processes such as activated carbon, ozonolysis, and reverse osmosis membrane. These processes, however, are designed to remove larger organic molecules with lower solubility, thus removal of very small molecules with high solubility is difficult. In addition, these micromolecules tend to be charged, therefore are less easily separated in aqueous form.
The research team aimed to remove these small molecules using a new adsorbent technology.
In order to remove aqueous organic molecular contaminants, the team needed an adsorbent that can adsorb micro-sized molecules. It also needed to introduce a chemical function that would allow it to selectively adsorb molecules, and lastly, the adsorbent needed to be structurally stable as it would be used underwater.
The team subsequently developed an adsorbent of fluorine-based porous organic polymer that met all the conditions listed above. By controlling the size of the pores, this adsorbent is able to selectively adsorb aqueous micromolecules of less than 1-2 nm in size.
In addition, in order to separate specific contaminants, there should be a chemical functionality, such as the ability to strongly interact with the target material. Fluorine, the most electronegative atom, interacts strongly with charged soluble organic molecules.
The research team incorporated fluorine into an adsorbent, enabling it to separate charged organic molecules up to 8 times faster than neutral molecules.
The adsorbent developed by Professor Yavuz’s team has wide industrial applications. It can be used in batch-adsorption tests, as well as in column separation for size- and charge-specific adsorption.
Professor Yavuz stated that “the charge-selective properties displayed by fluorine has the potential to be applied in desalination or water treatment processes using membranes."
This paper was first-authored by Dr. Jeehye Byun, and the research was funded by KAIST’s High Risk High Return Program and the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program, as well as its Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Change.
Figure 1. Diagram conceptualizing the process of charge- and size-specific separation by the fluorine-based porous polymer adsorbent
Figure 2. Difference in absorbance before and after using a porous fluorine polymer column to separate organic molecules
Figure 3. Adsorption properties of a fluorine polymer according to the charge and size of organic molecules
2017.01.17 View 11605 -
 KAIST Alumni of the Year
(From left Chul-Hwan Kim, president and CEO of Orange Power, Hooshik Kim, president & CEO of Vieworks, Chilhee Chung, presient of Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology, KAIST President Sung-Mo Kang, KAIST Alumni Association President Jung-Sik Ko, Won-Pil Baek, senior vice president for R&D program at Korea Atomic Energy Research Insitute, Hyonho Jung, CEO of Medytox, Jaehwa Kim on behalf of Han-Oh Park, president & CEO of Bioneer Corporation)
The KAIST Alumni Association presented the Alumni of the Year award to six of its most accomplished alumni at the New Year dinner held at the Lotte Hotel in Seoul on January 14.
KAIST alumni community, which numbers over 500,000, has made a significant impact around the globe in science and technology, industry, education, and the public sector. Each year, the KAIST Alumni Association honors individuals who have made a significant contribution with outstanding leadership through the Alumni of the Year awards.
KAIST Alumni Association President Jung-Sik Ko awarded the recipients at the dinner. About 200 alumni, faculty, and students, including KAIST President Sung-Mo Kang, joined the celebration.
The 2016 awardees are Dr. Chilhee Chung, president of Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology(SAIT); Dr.Won-Pil Baek, senior vice president for R&D program at Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute(KAERI); Dr.Han-Oh Park, president & CEO of Bioneer Corporation; Dr.Hyonho Jung, CEO of Medytox; Hooshik Kim, president & CEO of Vieworks; and Dr.Chul-Hwan Kim, president & CEO of Orange Power.
Dr. Chung of SAIT (MS in physics ’79) played a leading role in developing top-notch system semiconductors and memory device technology while serving as president of the Samsung Electronic Semiconductor R&D Center. He has focused on the development of cutting-edge future technology, the Quantum Dot, by incorporating eco-friendly materials with the highest efficiency and color purity which is cadmium-free.
Working at KAERI since 2001, Dr. Baek (Ph.D. in nuclear and quantum engineering ’87) has made contributions to help Korea emerge as a nuclear technology powerhouse. He played a critical role in developing and facilitating a global nuclear safety verification facility dubbed ‘ATLAS.’ Such nuclear technological prowess led the Korean government to advance into the foreign markets, such as exporting nuclear power plants to United Arab Emirates.
The CEO of Bioneer, Dr. Park (Ph.D. in chemistry ’87) started a bio-venture in Korea. His company has developed hundreds of reagents, diagnostic kits, and advanced equipment for gene research over two decades. Bioneer has paved the way for establishing a world-class level of infrastructure in genomic technology. By developing the innovative technology "SAMiRNA ™ (Self-Assembled-Micelle-inhibitory-RNA)" that overcomes the problems in drug development, Bioneer presented a new solution for the treatment of incurable diseases. In collaboration with global pharmaceutical companies and research groups, Dr. Park has successfully led joint development in the licensing of new therapeutic medicine candidates for various incurable diseases.
Dr. Jung (Ph.D. in biological sciences ’88) founded the bio-pharmaceutical company Medytox in 2000. Medytox is the first company in Korea that commercialized botulinum toxin formulation. Medytox developed the non-animal liquid botulinum toxin formulation for the first time in the world. It successfully localized botulinum preparation that can treat various neurological diseases. Medytox’s new toxin formulation resulted in improving public health care as well as relieving the heavy dependence on importing bio-pharmaceutical products.
As the CEO of Vieworks, Kim (MS in physics ’95) succeeded in commercializing of digital X-ray. Especially, it is leading the design of optical and image systems that affect the quality of digital X-ray image. Kim’s company established related technology base, contributing to human health promotion and national industrial development.
President Kim of Orange Power (Ph.D. in chemical and biomolecular engineering ’93) is also the founder of the KITE Entrepreneurship Foundation. He launched Biogenix Co., Ltd. and Image and Materials Co. in 2005. In order to nurture an entrepreneurship and start-ups eco-system, he invested 10 billion KRW from the proceeds of the sale of one of his start-ups. In addition, he started Orange Power Co., Ltd. in 2012 to solve the secondary battery heat problem and established a global partnership with Hydro Quebec in Canada, Nexion in UK, Volkswagen of Germany, and Tesla of the US.
2017.01.16 View 14107
KAIST Alumni of the Year
(From left Chul-Hwan Kim, president and CEO of Orange Power, Hooshik Kim, president & CEO of Vieworks, Chilhee Chung, presient of Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology, KAIST President Sung-Mo Kang, KAIST Alumni Association President Jung-Sik Ko, Won-Pil Baek, senior vice president for R&D program at Korea Atomic Energy Research Insitute, Hyonho Jung, CEO of Medytox, Jaehwa Kim on behalf of Han-Oh Park, president & CEO of Bioneer Corporation)
The KAIST Alumni Association presented the Alumni of the Year award to six of its most accomplished alumni at the New Year dinner held at the Lotte Hotel in Seoul on January 14.
KAIST alumni community, which numbers over 500,000, has made a significant impact around the globe in science and technology, industry, education, and the public sector. Each year, the KAIST Alumni Association honors individuals who have made a significant contribution with outstanding leadership through the Alumni of the Year awards.
KAIST Alumni Association President Jung-Sik Ko awarded the recipients at the dinner. About 200 alumni, faculty, and students, including KAIST President Sung-Mo Kang, joined the celebration.
The 2016 awardees are Dr. Chilhee Chung, president of Samsung Advanced Institute of Technology(SAIT); Dr.Won-Pil Baek, senior vice president for R&D program at Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute(KAERI); Dr.Han-Oh Park, president & CEO of Bioneer Corporation; Dr.Hyonho Jung, CEO of Medytox; Hooshik Kim, president & CEO of Vieworks; and Dr.Chul-Hwan Kim, president & CEO of Orange Power.
Dr. Chung of SAIT (MS in physics ’79) played a leading role in developing top-notch system semiconductors and memory device technology while serving as president of the Samsung Electronic Semiconductor R&D Center. He has focused on the development of cutting-edge future technology, the Quantum Dot, by incorporating eco-friendly materials with the highest efficiency and color purity which is cadmium-free.
Working at KAERI since 2001, Dr. Baek (Ph.D. in nuclear and quantum engineering ’87) has made contributions to help Korea emerge as a nuclear technology powerhouse. He played a critical role in developing and facilitating a global nuclear safety verification facility dubbed ‘ATLAS.’ Such nuclear technological prowess led the Korean government to advance into the foreign markets, such as exporting nuclear power plants to United Arab Emirates.
The CEO of Bioneer, Dr. Park (Ph.D. in chemistry ’87) started a bio-venture in Korea. His company has developed hundreds of reagents, diagnostic kits, and advanced equipment for gene research over two decades. Bioneer has paved the way for establishing a world-class level of infrastructure in genomic technology. By developing the innovative technology "SAMiRNA ™ (Self-Assembled-Micelle-inhibitory-RNA)" that overcomes the problems in drug development, Bioneer presented a new solution for the treatment of incurable diseases. In collaboration with global pharmaceutical companies and research groups, Dr. Park has successfully led joint development in the licensing of new therapeutic medicine candidates for various incurable diseases.
Dr. Jung (Ph.D. in biological sciences ’88) founded the bio-pharmaceutical company Medytox in 2000. Medytox is the first company in Korea that commercialized botulinum toxin formulation. Medytox developed the non-animal liquid botulinum toxin formulation for the first time in the world. It successfully localized botulinum preparation that can treat various neurological diseases. Medytox’s new toxin formulation resulted in improving public health care as well as relieving the heavy dependence on importing bio-pharmaceutical products.
As the CEO of Vieworks, Kim (MS in physics ’95) succeeded in commercializing of digital X-ray. Especially, it is leading the design of optical and image systems that affect the quality of digital X-ray image. Kim’s company established related technology base, contributing to human health promotion and national industrial development.
President Kim of Orange Power (Ph.D. in chemical and biomolecular engineering ’93) is also the founder of the KITE Entrepreneurship Foundation. He launched Biogenix Co., Ltd. and Image and Materials Co. in 2005. In order to nurture an entrepreneurship and start-ups eco-system, he invested 10 billion KRW from the proceeds of the sale of one of his start-ups. In addition, he started Orange Power Co., Ltd. in 2012 to solve the secondary battery heat problem and established a global partnership with Hydro Quebec in Canada, Nexion in UK, Volkswagen of Germany, and Tesla of the US.
2017.01.16 View 14107 -
 2016 KAIST EEWS Workshop
The Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS) Graduate School of KAIST hosted a workshop entitled “Progress and Perspectives of Energy Science and Technology” on October 20, 2016. The workshop took place at the Fusion Hall of the KAIST Institute on campus.
About 400 experts in energy science and engineering participated in the event. Eight globally recognized scientists introduced the latest research trends in nanomaterials, energy theory, catalysts, and photocatalysts and led discussions on the current status and prospects of EEWS.
Professors Yi Cui of Stanford University, an expert in nanomaterials, and William A. Goddard of California Institute of Technology presented their research experiments on materials design and recent results on the direction of theory under the topics of energy and environment.
Dr. Miquel Salmeron, a former head of the Material Science Division of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and Professor Yuichi Ikuhara of Tokyo University introduced their analysis of catalysts and energy matters at an atomic scale.
Professor Sukbok Chang of the Chemistry Department at KAIST, a deputy editor of ACS Catalysis and the head of the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute of Basic Science, and Professor Yang-Kook Sun of Energy Engineering at Hanyang University, who is also a deputy editor of ACS Energy Letters, presented their latest research results on new catalytic reaction development and energy storage.
The workshop consisted of three sections which addressed the design of energy and environment materials; analysis of energy and catalytic materials; and energy conversion and catalysts.
The EEWS Graduate School was established in 2008 with the sponsorship of the Korean government’s World Class University (WCU) project to support science education in Korea. Professor J. Fraser Stoddart, the winner of the 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, was previously worked at the KAIST EEWS Graduate School as a WCU visiting professor for two years, from 2011 to 2013. Professor Ali Coskun, who was a postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Professor Stoddart, now teaches and conducts research as a full-time professor at the graduate school.
Dean Yousung Jung of the EEWS Graduate School said:
“This workshop has provided us with a meaningful opportunity to engage in discussions on energy science and technology with world-class scholars from all around the world. It is also a good venue for our graduate school to share with them what we have been doing in research and education.”
2016.10.20 View 15364
2016 KAIST EEWS Workshop
The Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS) Graduate School of KAIST hosted a workshop entitled “Progress and Perspectives of Energy Science and Technology” on October 20, 2016. The workshop took place at the Fusion Hall of the KAIST Institute on campus.
About 400 experts in energy science and engineering participated in the event. Eight globally recognized scientists introduced the latest research trends in nanomaterials, energy theory, catalysts, and photocatalysts and led discussions on the current status and prospects of EEWS.
Professors Yi Cui of Stanford University, an expert in nanomaterials, and William A. Goddard of California Institute of Technology presented their research experiments on materials design and recent results on the direction of theory under the topics of energy and environment.
Dr. Miquel Salmeron, a former head of the Material Science Division of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and Professor Yuichi Ikuhara of Tokyo University introduced their analysis of catalysts and energy matters at an atomic scale.
Professor Sukbok Chang of the Chemistry Department at KAIST, a deputy editor of ACS Catalysis and the head of the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute of Basic Science, and Professor Yang-Kook Sun of Energy Engineering at Hanyang University, who is also a deputy editor of ACS Energy Letters, presented their latest research results on new catalytic reaction development and energy storage.
The workshop consisted of three sections which addressed the design of energy and environment materials; analysis of energy and catalytic materials; and energy conversion and catalysts.
The EEWS Graduate School was established in 2008 with the sponsorship of the Korean government’s World Class University (WCU) project to support science education in Korea. Professor J. Fraser Stoddart, the winner of the 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, was previously worked at the KAIST EEWS Graduate School as a WCU visiting professor for two years, from 2011 to 2013. Professor Ali Coskun, who was a postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Professor Stoddart, now teaches and conducts research as a full-time professor at the graduate school.
Dean Yousung Jung of the EEWS Graduate School said:
“This workshop has provided us with a meaningful opportunity to engage in discussions on energy science and technology with world-class scholars from all around the world. It is also a good venue for our graduate school to share with them what we have been doing in research and education.”
2016.10.20 View 15364 -
 'The 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea'
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea recently released a list of the 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea. The list included the work of KAIST Professors Dong-Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering, Jeung Ku Kang of the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS), and Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department.
Experts from academia, universities, and industries selected the 100 research projects, among 620 projects recommended by various government offices, in consideration of their contribution to the growth of science and technology in the nation.
Professor Cho conducts research on the development of 5G mobile communication systems based on the pattern polarization beam-division multiple access method.
Professor Kang works on the production of highly efficient energy materials and equipment by controlling them at the electron and atomic level.
Professor Lee focuses on the creation of strategies to produce important chemicals through a biological approach, i.e., microorganisms, which will help develop the means to mitigate climate change.
The MISP will publish a book that describes in detail each research project and will distribute copies of it to the National Assembly of Korea, libraries, and other public organizations.
For more information on the list, please go to www.ntis.go.kr.
Pictured from left to right are Professors Dong-Ho Cho, Jeung Ku Kang, and Sang Yup Lee.
2016.07.21 View 5881
'The 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea'
The Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP) of Korea recently released a list of the 2016 Top 100 Research Projects in Korea. The list included the work of KAIST Professors Dong-Ho Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering, Jeung Ku Kang of the Graduate School of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS), and Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department.
Experts from academia, universities, and industries selected the 100 research projects, among 620 projects recommended by various government offices, in consideration of their contribution to the growth of science and technology in the nation.
Professor Cho conducts research on the development of 5G mobile communication systems based on the pattern polarization beam-division multiple access method.
Professor Kang works on the production of highly efficient energy materials and equipment by controlling them at the electron and atomic level.
Professor Lee focuses on the creation of strategies to produce important chemicals through a biological approach, i.e., microorganisms, which will help develop the means to mitigate climate change.
The MISP will publish a book that describes in detail each research project and will distribute copies of it to the National Assembly of Korea, libraries, and other public organizations.
For more information on the list, please go to www.ntis.go.kr.
Pictured from left to right are Professors Dong-Ho Cho, Jeung Ku Kang, and Sang Yup Lee.
2016.07.21 View 5881 -
 Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
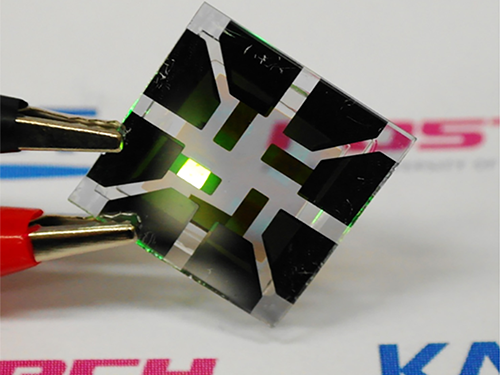
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).
2016.06.07 View 16067
Graphene-Based Transparent Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible OLEDs
A Korean research team developed an ideal electrode structure composed of graphene and layers of titanium dioxide and conducting polymers, resulting in highly flexible and efficient OLEDs.
The arrival of a thin and lightweight computer that even rolls up like a piece of paper will not be in the far distant future. Flexible organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs), built upon a plastic substrate, have received greater attention lately for their use in next-generation displays that can be bent or rolled while still operating.
A Korean research team led by Professor Seunghyup Yoo from the School of Electrical Engineering, KAIST and Professor Tae-Woo Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH) has developed highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE) which is placed in between titanium dioxide (TiO2) and conducting polymer layers. The research results were published online on June 2, 2016 in Nature Communications.
OLEDs are stacked in several ultra-thin layers on glass, foil, or plastic substrates, in which multi-layers of organic compounds are sandwiched between two electrodes (cathode and anode). When voltage is applied across the electrodes, electrons from the cathode and holes (positive charges) from the anode draw toward each other and meet in the emissive layer. OLEDs emit light as an electron recombines with a positive hole, releasing energy in the form of a photon. One of the electrodes in OLEDs is usually transparent, and depending on which electrode is transparent, OLEDs can either emit from the top or bottom.
In conventional bottom-emission OLEDs, an anode is transparent in order for the emitted photons to exit the device through its substrate. Indium-tin-oxide (ITO) is commonly used as a transparent anode because of its high transparency, low sheet resistance, and well-established manufacturing process. However, ITO can potentially be expensive, and moreover, is brittle, being susceptible to bending-induced formation of cracks.
Graphene, a two-dimensional thin layer of carbon atoms tightly bonded together in a hexagonal honeycomb lattice, has recently emerged as an alternative to ITO. With outstanding electrical, physical, and chemical properties, its atomic thinness leading to a high degree of flexibility and transparency makes it an ideal candidate for TEs. Nonetheless, the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs reported to date has been, at best, about the same level of ITO-based OLEDs.
As a solution, the Korean research team, which further includes Professors Sung-Yool Choi (Electrical Engineering) and Taek-Soo Kim (Mechanical Engineering) of KAIST and their students, proposed a new device architecture that can maximize the efficiency of graphene-based OLEDs. They fabricated a transparent anode in a composite structure in which a TiO2 layer with a high refractive index (high-n) and a hole-injection layer (HIL) of conducting polymers with a low refractive index (low-n) sandwich graphene electrodes. This is an optical design that induces a synergistic collaboration between the high-n and low-n layers to increase the effective reflectance of TEs. As a result, the enhancement of the optical cavity resonance is maximized. The optical cavity resonance is related to the improvement of efficiency and color gamut in OLEDs. At the same time, the loss from surface plasmon polariton (SPP), a major cause for weak photon emissions in OLEDs, is also reduced due to the presence of the low-n conducting polymers.
Under this approach, graphene-based OLEDs exhibit 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency, which is unprecedented in those using graphene as a TE. Furthermore, these devices remain intact and operate well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm. This is a remarkable result for OLEDs containing oxide layers such as TiO2 because oxides are typically brittle and prone to bending-induced fractures even at a relatively low strain. The research team discovered that TiO2 has a crack-deflection toughening mechanism that tends to prevent bending-induced cracks from being formed easily.
Professor Yoo said, “What’s unique and advanced about this technology, compared with previous graphene-based OLEDs, is the synergistic collaboration of high- and low-index layers that enables optical management of both resonance effect and SPP loss, leading to significant enhancement in efficiency, all with little compromise in flexibility.” He added, “Our work was the achievement of collaborative research, transcending the boundaries of different fields, through which we have often found meaningful breakthroughs.”
Professor Lee said, “We expect that our technology will pave the way to develop an OLED light source for highly flexible and wearable displays, or flexible sensors that can be attached to the human body for health monitoring, for instance.”
The research paper is entitled “Synergistic Electrode Architecture for Efficient Graphene-based Flexible Organic Light-emitting Diodes” (DOI. 10.1038/NCOMMS11791). The lead authors are Jae-Ho Lee, a Ph.D. candidate at KAIST; Tae-Hee Han, a Ph.D. researcher at POSTECH; and Min-Ho Park, a Ph.D. candidate at POSTECH.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) through the Center for Advanced Flexible Display (CAFDC) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning (MSIP); by the Center for Advanced Soft-Electronics funded by the MSIP as a Global Frontier Project; by the Graphene Research Center Program of KAIST; and by grants from the IT R&D Program of the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea (MOTIE).
Figure 1: Application of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows an OLED with the composite structure of TiO2/graphene/conducting polymer electrode in operation. The OLED exhibits 40.8% of ultrahigh external quantum efficiency (EQE) and 160.3 lm/W of power efficiency. The device prepared on a plastic substrate shown in the right remains intact and operates well even after 1,000 bending cycles at a radius of curvature as small as 2.3 mm.
Figure 2: Schematic Device Structure of Graphene-based OLEDs
This picture shows the new architecture to develop highly flexible OLEDs with excellent efficiency by using graphene as a transparent electrode (TE).
2016.06.07 View 16067 -
 KAIST Team Develops Technology to Enable Unzipping of the Graphene Plane
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
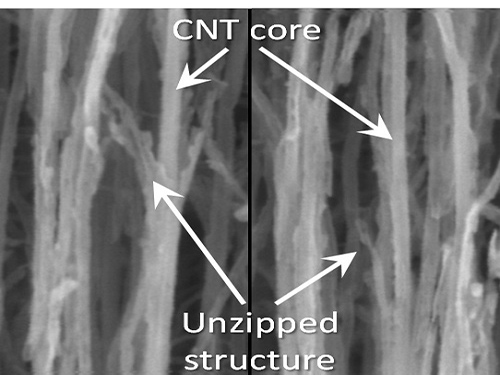
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
2016.03.22 View 10057
KAIST Team Develops Technology to Enable Unzipping of the Graphene Plane
Professor Sang-Wook Kim’s research team of the Material Science and Engineering Department has developed a technique, which enables unzipping of the graphene plane without uncontrollable damage. The research findings were published online on the January 22 issue of Nature Communications.
Graphene is a form of carbon in which its atoms form a honey-comb structure through chemical bonding. If this structure can be cut to a desired form, other carbon materials with nanostructure can be created. Many researchers have tried to obtain the accurate unzipping of graphene structures, but faced challenges doing so.
To break a very strong bond between carbon atoms, an equivalently strong chemical reaction must be induced. But the chemical reaction not only cuts out the desirable borders, but also damages the surrounding ones. Conventional techniques, which cut out graphene at once, damaged the chemical properties of the graphene structure after unzipping. This is similar to wearing out paper while manipulating it.
To solve this problem, the research team adopted “heteroatom doping.” The idea is similar to a sheet of paper being split following a groove drawn on the sheet. After making some regions of the structure unstable by doping other atoms such as nitrogen on a carbon plane, the regions are electrochemically stimulated to split the parts. Nitrogen or other atoms act as the groove on the grapheme plane.
The researchers finely controlled the amount of unzipping graphene by adjusting the amount of heteroatom dopants, from which they were able to create a quality nano graphene without any damage in its 2-dimensional crystalline structure. Using this technique, the researchers were able to obtain a capacitor with state-of-the-art energy transfer speed. The nano graphene can be combined with polymer, metal, and semiconductor nano molecules to form carbon composites.
Professor Kim said, “In order to commercialize this technique, heteroatom doping should be researched further. We plan to develop fabric-like carbon materials with excellent mechanical and electrical properties using this technique.”
Picture 1: Unzipped Carbon Nano Tube
Picture 2: Development of Nano Graphene from Carbon Nano Tube Using Heteroatom Dopants
Korean descriptions translated into English:
Unzipping Process of Graphene
Carbon Nano Tube → Nano Graphen
Heteroatom
This process is similar to a paper being split in two from a tiny hole punched therein.
2016.03.22 View 10057 -
 Two Undergraduate KAIST Students Publish a Book on Health Management
Joonho Suh of the Aerospace Engineering Department and Jiho Suh of the Mechanical Engineering Department are both brothers and undergraduates at KAIST.
The Suh brothers, who are three years apart, have recently published a self-help book in English on staying healthy entitled “A Scientific Approach to Building Muscle: Mass Effect.”
The book introduces techniques to build muscles, adapting them from an engineering concept called "Active Torque Control (ACT)," the management of turning forces imposed on a vehicle. Just as ACT influences the performance of a vehicle, good exercise involves the right degree of body angles and the right direction of body movements to keep the best posture necessary for burning calories and strengthening muscles.
In the book, they also suggest healthy diet plans based on scientific knowledge and data that the writers borrowed from such fields as anatomy, physiology, and motor mechanics to maintain a healthy weight.
Joonho Suh said,
“If we understand the mechanism of how our body works, the chances are high we will have good muscle tone and a balanced diet. We used a great deal of scientific knowledge and turned it into a health management program that can be customized per individual needs.”
The younger brother, Jiho, added,
“In fact, we applied our methods in the book to beginners who took weight training and fitness for one hour a day for one month, we learned that their muscle mass increased by 1-1.5 kg while losing body fat by 2-3 kg.”
The brothers said they planned to publish a Korean language version of the book next year.
The authors of "Mass Effect": Joonho Suh (left) and Jiho Suh (right)
2015.10.26 View 8940
Two Undergraduate KAIST Students Publish a Book on Health Management
Joonho Suh of the Aerospace Engineering Department and Jiho Suh of the Mechanical Engineering Department are both brothers and undergraduates at KAIST.
The Suh brothers, who are three years apart, have recently published a self-help book in English on staying healthy entitled “A Scientific Approach to Building Muscle: Mass Effect.”
The book introduces techniques to build muscles, adapting them from an engineering concept called "Active Torque Control (ACT)," the management of turning forces imposed on a vehicle. Just as ACT influences the performance of a vehicle, good exercise involves the right degree of body angles and the right direction of body movements to keep the best posture necessary for burning calories and strengthening muscles.
In the book, they also suggest healthy diet plans based on scientific knowledge and data that the writers borrowed from such fields as anatomy, physiology, and motor mechanics to maintain a healthy weight.
Joonho Suh said,
“If we understand the mechanism of how our body works, the chances are high we will have good muscle tone and a balanced diet. We used a great deal of scientific knowledge and turned it into a health management program that can be customized per individual needs.”
The younger brother, Jiho, added,
“In fact, we applied our methods in the book to beginners who took weight training and fitness for one hour a day for one month, we learned that their muscle mass increased by 1-1.5 kg while losing body fat by 2-3 kg.”
The brothers said they planned to publish a Korean language version of the book next year.
The authors of "Mass Effect": Joonho Suh (left) and Jiho Suh (right)
2015.10.26 View 8940 -
 Mapping the Folding Process of a Single Membrane Protein
KAIST and UCLA scientists were able to observe an individual membrane protein fold and unfold by pulling and releasing magnetically trapped protein molecules.
Proteins are huge molecules containing hundreds to thousands of atoms that adopt a unique three dimensional structure, placing chemical groups in just the right place to catalyze reactions or build cellular structures. How all those atoms manage to find the right location - the so-called folding problem - has fascinated molecular biologists since the first structures were seen in the 1950s. Moreover, folding has important medical implications because most genetic defects cause protein misfolding.
About a third of all proteins float around in the cell membrane where they ensure the right chemicals get in the cell in the right amounts. Membrane proteins also provide key information links between the cell and its environment. Indeed, most drugs target membrane proteins. Nevertheless, the folding of membrane proteins has been particularly difficult to study and has rarely been studied in natural environments, leaving the folding process for a large fraction of the protein universe still largely cloaked in mystery.
In a recent issue of Nature Chemical Biology, published on October 19, 2015, a research team led by Tae-Young Yoon of the Department of Physics at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and James U. Bowie of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), report a new method for manipulating the folding of membrane proteins in a membrane environment using a tool called a magnetic tweezer.
Researchers first attach long DNA handles to the ends of the protein. One handle is attached to a glass surface and the other to a magnetic bead. Using a magnet, they can essentially grab the protein and pull on it, inducing it to unfold. By playing with the bead attached to the protein, they can force the protein to unfold or allow it to refold, and watch all this happening by 3D-tracking of the magnetic bead. With this novel strategy, they were able to quantitatively map the folding energy landscape, the folding kinetic rate, and folding intermediates of a membrane protein in a membrane environment for the first time.
“I have been dreaming about this experiment for a decade. To see it work so well is really gratifying,” said Dr. Bowie.
One of the major surprises in the study was that essentially all the atoms of the protein jump into the correct structure together. The researchers expected that the protein structure would come together in a more piecemeal fashion, with different parts of the structure forming separately, but that was not the case. It is possible that nature evolved such a smooth, highly cooperative folding process to prevent partially folded forms that could get into trouble in the crowded cell membrane. On the other hand, the cooperative folding seen here might not apply to other membrane proteins.
“We need to look at more proteins. The technique developed here may allow us to do just that,” said Dr. Yoon.
The single molecule mechanical manipulation technique could enable detailed folding studies of many other membrane proteins. A major barrier to the study of membrane proteins previously is that the proteins tend to stick together and get tangled up, as computer cords lying at your feet tend to do. With the tweezer technique used in this work, the protein cords are held apart from other cords so they can’t get knotted up. It is hoped that the new approach will open up an important part of the protein universe to scrutiny, including many proteins that become misfolded in disease states.
The title of the research paper is “Mapping the energy landscape for second-stage folding of a single membrane protein” (DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1939).
Picture: Single-molecule magnetic tweezers that induce mechanical unfolding and refolding of a single membrane protein. Since the force applied is parallel to the biological lipid membrane, the unfolding and refolding processes occur within the membrane.
2015.10.20 View 11002
Mapping the Folding Process of a Single Membrane Protein
KAIST and UCLA scientists were able to observe an individual membrane protein fold and unfold by pulling and releasing magnetically trapped protein molecules.
Proteins are huge molecules containing hundreds to thousands of atoms that adopt a unique three dimensional structure, placing chemical groups in just the right place to catalyze reactions or build cellular structures. How all those atoms manage to find the right location - the so-called folding problem - has fascinated molecular biologists since the first structures were seen in the 1950s. Moreover, folding has important medical implications because most genetic defects cause protein misfolding.
About a third of all proteins float around in the cell membrane where they ensure the right chemicals get in the cell in the right amounts. Membrane proteins also provide key information links between the cell and its environment. Indeed, most drugs target membrane proteins. Nevertheless, the folding of membrane proteins has been particularly difficult to study and has rarely been studied in natural environments, leaving the folding process for a large fraction of the protein universe still largely cloaked in mystery.
In a recent issue of Nature Chemical Biology, published on October 19, 2015, a research team led by Tae-Young Yoon of the Department of Physics at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and James U. Bowie of the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), report a new method for manipulating the folding of membrane proteins in a membrane environment using a tool called a magnetic tweezer.
Researchers first attach long DNA handles to the ends of the protein. One handle is attached to a glass surface and the other to a magnetic bead. Using a magnet, they can essentially grab the protein and pull on it, inducing it to unfold. By playing with the bead attached to the protein, they can force the protein to unfold or allow it to refold, and watch all this happening by 3D-tracking of the magnetic bead. With this novel strategy, they were able to quantitatively map the folding energy landscape, the folding kinetic rate, and folding intermediates of a membrane protein in a membrane environment for the first time.
“I have been dreaming about this experiment for a decade. To see it work so well is really gratifying,” said Dr. Bowie.
One of the major surprises in the study was that essentially all the atoms of the protein jump into the correct structure together. The researchers expected that the protein structure would come together in a more piecemeal fashion, with different parts of the structure forming separately, but that was not the case. It is possible that nature evolved such a smooth, highly cooperative folding process to prevent partially folded forms that could get into trouble in the crowded cell membrane. On the other hand, the cooperative folding seen here might not apply to other membrane proteins.
“We need to look at more proteins. The technique developed here may allow us to do just that,” said Dr. Yoon.
The single molecule mechanical manipulation technique could enable detailed folding studies of many other membrane proteins. A major barrier to the study of membrane proteins previously is that the proteins tend to stick together and get tangled up, as computer cords lying at your feet tend to do. With the tweezer technique used in this work, the protein cords are held apart from other cords so they can’t get knotted up. It is hoped that the new approach will open up an important part of the protein universe to scrutiny, including many proteins that become misfolded in disease states.
The title of the research paper is “Mapping the energy landscape for second-stage folding of a single membrane protein” (DOI: 10.1038/nchembio.1939).
Picture: Single-molecule magnetic tweezers that induce mechanical unfolding and refolding of a single membrane protein. Since the force applied is parallel to the biological lipid membrane, the unfolding and refolding processes occur within the membrane.
2015.10.20 View 11002 -
 Professor Rim Presents at IAEA Workshop in Vienna
Professor Chun-Taek Rim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST recently attended the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’s workshop on the Application of Wireless Technologies in Nuclear Power Plant Instrumentation and Control System. It took place on March 30-April 2, 2015, in Vienna, Austria.
Representing Korea, Professor Rim gave a talk entitled “Highly Reliable Wireless Power and Communications under Severe Accident of Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs).” About 20 industry experts from 12 countries such as AREVA (France), Westinghouse (US), Oak Ridge National Laboratory (US), Hitachi (Japan), and ENEA (Italy) joined the meeting.
The IAEA hosted the workshop to explore the application of wireless technology for the operation and management of NPPs. It formed a committee consisting of eminent professionals worldwide in NPP instrumentation and control systems, communications, and nuclear power to examine this issue in-depth and to conduct various research projects for the next three years.
In particular, the committee will concentrate its research on improving the reliability and safety of using wireless technology, not only in the normal operation of nuclear plants but also in extreme conditions such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. The complementation, economic feasibility, and standardization of NPPs when applying wireless technology will be also discussed.
Professor Rim currently leads the Nuclear Power Electronics
and Robotics Lab at KAIST (http://tesla.kaist.ac.kr/index_eng.php?lag=eng).
Picture 1: Professors Rim presents his topic at the IAEA Workshop in Vienna.
Picture 2: The IAEA Workshop Participants
2015.04.07 View 15068
Professor Rim Presents at IAEA Workshop in Vienna
Professor Chun-Taek Rim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST recently attended the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA)’s workshop on the Application of Wireless Technologies in Nuclear Power Plant Instrumentation and Control System. It took place on March 30-April 2, 2015, in Vienna, Austria.
Representing Korea, Professor Rim gave a talk entitled “Highly Reliable Wireless Power and Communications under Severe Accident of Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs).” About 20 industry experts from 12 countries such as AREVA (France), Westinghouse (US), Oak Ridge National Laboratory (US), Hitachi (Japan), and ENEA (Italy) joined the meeting.
The IAEA hosted the workshop to explore the application of wireless technology for the operation and management of NPPs. It formed a committee consisting of eminent professionals worldwide in NPP instrumentation and control systems, communications, and nuclear power to examine this issue in-depth and to conduct various research projects for the next three years.
In particular, the committee will concentrate its research on improving the reliability and safety of using wireless technology, not only in the normal operation of nuclear plants but also in extreme conditions such as the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear accident. The complementation, economic feasibility, and standardization of NPPs when applying wireless technology will be also discussed.
Professor Rim currently leads the Nuclear Power Electronics
and Robotics Lab at KAIST (http://tesla.kaist.ac.kr/index_eng.php?lag=eng).
Picture 1: Professors Rim presents his topic at the IAEA Workshop in Vienna.
Picture 2: The IAEA Workshop Participants
2015.04.07 View 15068 -
 The Real Time Observation of the Birth of a Molecule
From right to left: Dr. Kyung-Hwan Kim, Professor Hyotcherl Lhee, and Jong-Gu Kim, a Ph.D. candidate
Professor Hyotcherl Lhee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST and Japanese research teams jointly published their research results showing that they have succeeded in the direct observation of how atoms form a molecule in the online issue of Nature on February 19, 2015.
The researchers used water in which gold atoms ([Au(CN) 2- ]) are dissolved and fired X-ray pulses over the specimen in femtosecond timescales to study chemical reactions taking place among the gold atoms. They were able to examine in real time the instant process of how gold atoms bond together to become a molecule, to a trimer or tetramer state.
This direct viewing of the formation of a gold trimer complex ([Au(CN) 2- ] 3 ) will provide an opportunity to understand complex chemical and biological systems.
For details, please see the following press release that was distributed by the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, KEK, in Japan:
Direct Observation of Bond Formations
February 18, 2015
A collaboration between researchers from KEK, the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) used the SACLA X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) facility for a real time visualization of the birth of a molecular that occurs via photoinduced formation of a chemical bonds. This achievement was published in the online version of the scientific journal “Nature” (published on 19 February 2015).
Direct “observation” of the bond making, through a chemical reaction, has been longstanding dream for chemists. However, the distance between atoms is very small, at about 100 picometer, and the bonding is completed very quickly, taking less than one picosecond (ps). Hence, previously, one could only imagine the bond formation between atoms while looking at the chemical reaction progressing in the test-tube.
In this study, the research group focused on the process of photoinduced bond formation between gold (Au) ions dissolved in water. In the ground state (S 0 state in Fig. 1) Au ions that are weakly bound to each other by an electron affinity and aligned in a bent geometry. Upon a photoexcitation, the S 0 state rapidly converts into an excited (S 1 state in Fig. 1) state where Au-Au covalent bonds are formed among Au ions aligned in a linear geometry. Subsequently, the S 1 state transforms to a triplet state (T 1 state in Fig. 1) in 1.6 ps while accompanying further contraction of Au-Au bonds by 0.1 Å. Later, the T 1 state of the trimer converts to a tetramer (tetramer state in Fig. 1) on nanosecond time scale. Finally, the Au ions returned to their original loosely interacting bent structure.
In this research, the direct observation of a very fast chemical reaction, induced by the photo-excitation, was succeeded (Fig. 2, 3). Therefore, this method is expected to be a fundamental technology for understanding the light energy conversion reaction. The research group is actively working to apply this method to the development of viable renewable energy resources, such as a photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis using sunlight.
This research was supported by the X-ray Free Electron Laser Priority Strategy Program of the MEXT, PRESTO of the JST, and the the Innovative Areas "Artificial Photosynthesis (AnApple)" grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Publication: Nature , 518 (19 February 2015)
Title: Direct observation of bond formation in solution with femtosecond X-ray scattering
Authors: K. H. Kim 1 , J. G. Kim 1 , S. Nozawa 1 , T. Sato 1 , K. Y. Oang, T. W. Kim, H. Ki, J. Jo, S. Park, C. Song, T. Sato, K. Ogawa, T. Togashi, K. Tono, M. Yabashi, T. Ishikawa, J. Kim, R. Ryoo, J. Kim, H. Ihee, S. Adachi. ※ 1: These authors contributed equally to the work.
DOI: 10.1038/nature14163
Figure 1. Structure of a gold cyano trimer complex (Au(CN) 2 - ) 3 .
Figure 2. Observed changes in the molecular structure of the gold complex
Figure 3. Schematic view of the research of photo-chemical reactions by the molecular movie
2015.02.27 View 14562
The Real Time Observation of the Birth of a Molecule
From right to left: Dr. Kyung-Hwan Kim, Professor Hyotcherl Lhee, and Jong-Gu Kim, a Ph.D. candidate
Professor Hyotcherl Lhee of the Department of Chemistry at KAIST and Japanese research teams jointly published their research results showing that they have succeeded in the direct observation of how atoms form a molecule in the online issue of Nature on February 19, 2015.
The researchers used water in which gold atoms ([Au(CN) 2- ]) are dissolved and fired X-ray pulses over the specimen in femtosecond timescales to study chemical reactions taking place among the gold atoms. They were able to examine in real time the instant process of how gold atoms bond together to become a molecule, to a trimer or tetramer state.
This direct viewing of the formation of a gold trimer complex ([Au(CN) 2- ] 3 ) will provide an opportunity to understand complex chemical and biological systems.
For details, please see the following press release that was distributed by the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization, KEK, in Japan:
Direct Observation of Bond Formations
February 18, 2015
A collaboration between researchers from KEK, the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), RIKEN, and the Japan Synchrotron Radiation Research Institute (JASRI) used the SACLA X-ray free electron laser (XFEL) facility for a real time visualization of the birth of a molecular that occurs via photoinduced formation of a chemical bonds. This achievement was published in the online version of the scientific journal “Nature” (published on 19 February 2015).
Direct “observation” of the bond making, through a chemical reaction, has been longstanding dream for chemists. However, the distance between atoms is very small, at about 100 picometer, and the bonding is completed very quickly, taking less than one picosecond (ps). Hence, previously, one could only imagine the bond formation between atoms while looking at the chemical reaction progressing in the test-tube.
In this study, the research group focused on the process of photoinduced bond formation between gold (Au) ions dissolved in water. In the ground state (S 0 state in Fig. 1) Au ions that are weakly bound to each other by an electron affinity and aligned in a bent geometry. Upon a photoexcitation, the S 0 state rapidly converts into an excited (S 1 state in Fig. 1) state where Au-Au covalent bonds are formed among Au ions aligned in a linear geometry. Subsequently, the S 1 state transforms to a triplet state (T 1 state in Fig. 1) in 1.6 ps while accompanying further contraction of Au-Au bonds by 0.1 Å. Later, the T 1 state of the trimer converts to a tetramer (tetramer state in Fig. 1) on nanosecond time scale. Finally, the Au ions returned to their original loosely interacting bent structure.
In this research, the direct observation of a very fast chemical reaction, induced by the photo-excitation, was succeeded (Fig. 2, 3). Therefore, this method is expected to be a fundamental technology for understanding the light energy conversion reaction. The research group is actively working to apply this method to the development of viable renewable energy resources, such as a photocatalysts for artificial photosynthesis using sunlight.
This research was supported by the X-ray Free Electron Laser Priority Strategy Program of the MEXT, PRESTO of the JST, and the the Innovative Areas "Artificial Photosynthesis (AnApple)" grant from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (JSPS).
Publication: Nature , 518 (19 February 2015)
Title: Direct observation of bond formation in solution with femtosecond X-ray scattering
Authors: K. H. Kim 1 , J. G. Kim 1 , S. Nozawa 1 , T. Sato 1 , K. Y. Oang, T. W. Kim, H. Ki, J. Jo, S. Park, C. Song, T. Sato, K. Ogawa, T. Togashi, K. Tono, M. Yabashi, T. Ishikawa, J. Kim, R. Ryoo, J. Kim, H. Ihee, S. Adachi. ※ 1: These authors contributed equally to the work.
DOI: 10.1038/nature14163
Figure 1. Structure of a gold cyano trimer complex (Au(CN) 2 - ) 3 .
Figure 2. Observed changes in the molecular structure of the gold complex
Figure 3. Schematic view of the research of photo-chemical reactions by the molecular movie
2015.02.27 View 14562