Kyeongha+Kwon
-
 Is 24-hour health monitoring possible with ambient light energy?
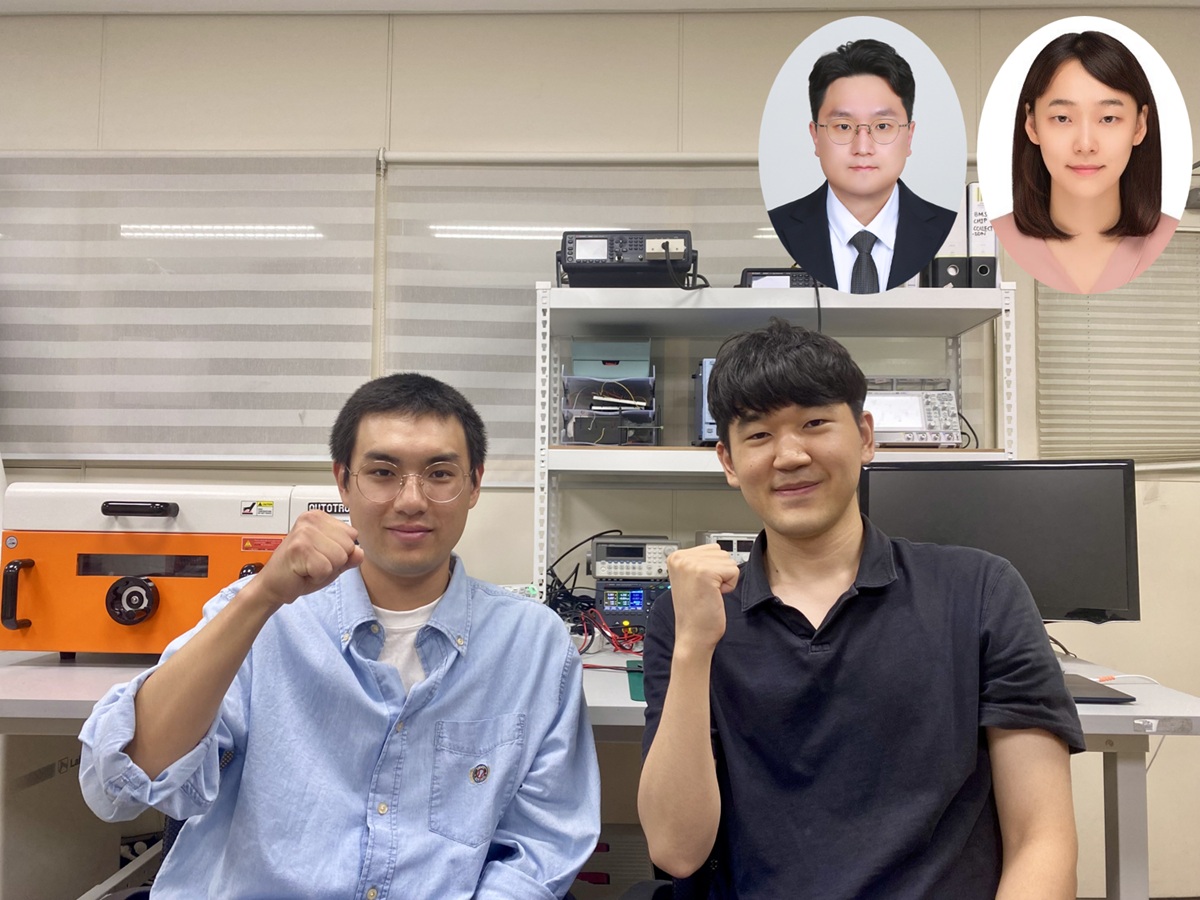
<(From left) Ph.D candidate Youngmin Sim, Ph.D candidate Do Yun Park, Dr. Chanho Park, Professor Kyeongha Kwon>
Miniaturization and weight reduction of medical wearable devices for continuous health monitoring such as heart rate, blood oxygen saturation, and sweat component analysis remain major challenges. In particular, optical sensors consume a significant amount of power for LED operation and wireless transmission, requiring heavy and bulky batteries. To overcome these limitations, KAIST researchers have developed a next-generation wearable platform that enables 24-hour continuous measurement by using ambient light as an energy source and optimizing power management according to the power environment.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that Professor Kyeongha Kwon's team from the School of Electrical Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Chanho Park’s team at Northwestern University in the U.S., has developed an adaptive wireless wearable platform that reduces battery load by utilizing ambient light.
To address the battery issue of medical wearable devices, Professor Kyeongha Kwon’s research team developed an innovative platform that utilizes ambient natural light as an energy source. This platform integrates three complementary light energy technologies.
<Figure1.The wireless wearable platform minimizes the energy required for light sources through i) Photometric system that directly utilizes ambient light passing through windows for measurements, ii) Photovoltaic system that receives power from high-efficiency photovoltaic cells and wireless power receiver coils, and iii) Photoluminescent system that stores light using photoluminescent materials and emits light in dark conditions to support the two aforementioned systems. In-sensor computing minimizes power consumption by wirelessly transmitting only essential data. The adaptive power management system efficiently manages power by automatically selecting the optimal mode among 11 different power modes through a power selector based on the power supply level from the photovoltaic system and battery charge status.>
The first core technology, the Photometric Method, is a technique that adaptively adjusts LED brightness depending on the intensity of the ambient light source. By combining ambient natural light with LED light to maintain a constant total illumination level, it automatically dims the LED when natural light is strong and brightens it when natural light is weak.
Whereas conventional sensors had to keep the LED on at a fixed brightness regardless of the environment, this technology optimizes LED power in real time according to the surrounding environment. Experimental results showed that it reduced power consumption by as much as 86.22% under sufficient lighting conditions.
The second is the Photovoltaic Method using high-efficiency multijunction solar cells. This goes beyond simple solar power generation to convert light in both indoor and outdoor environments into electricity. In particular, the adaptive power management system automatically switches among 11 different power configurations based on ambient conditions and battery status to achieve optimal energy efficiency.
The third innovative technology is the Photoluminescent Method. By mixing strontium aluminate microparticles* into the sensor’s silicone encapsulation structure, light from the surroundings is absorbed and stored during the day and slowly released in the dark. As a result, after being exposed to 500W/m² of sunlight for 10 minutes, continuous measurement is possible for 2.5 minutes even in complete darkness.
*Strontium aluminate microparticles: A photoluminescent material used in glow-in-the-dark paint or safety signs, which absorbs light and emits it in the dark for an extended time.
These three technologies work complementarily—during bright conditions, the first and second methods are active, and in dark conditions, the third method provides additional support—enabling 24-hour continuous operation.
The research team applied this platform to various medical sensors to verify its practicality. The photoplethysmography sensor monitors heart rate and blood oxygen saturation in real time, allowing early detection of cardiovascular diseases. The blue light dosimeter accurately measures blue light, which causes skin aging and damage, and provides personalized skin protection guidance. The sweat analysis sensor uses microfluidic technology to simultaneously analyze salt, glucose, and pH in sweat, enabling real-time detection of dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Additionally, introducing in-sensor data computing significantly reduced wireless communication power consumption. Previously, all raw data had to be transmitted externally, but now only the necessary results are calculated and transmitted within the sensor, reducing data transmission requirements from 400B/s to 4B/s—a 100-fold decrease.
To validate performance, the research tested the device on healthy adult subjects in four different environments: bright indoor lighting, dim lighting, infrared lighting, and complete darkness. The results showed measurement accuracy equivalent to that of commercial medical devices in all conditions A mouse model experiment confirmed accurate blood oxygen saturation measurement in hypoxic conditions.
<Frigure2.The multimodal device applying the energy harvesting and power management platform consists of i) photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor, ii) blue light dosimeter, iii) photoluminescent microfluidic channel for sweat analysis and biomarker sensors (chloride ion, glucose, and pH), and iv) temperature sensor. This device was implemented with flexible printed circuit board (fPCB) to enable attachment to the skin. A silicon substrate with a window that allows ambient light and measurement light to pass through, along with photoluminescent encapsulation layer, encapsulates the PPG, blue light dosimeter, and temperature sensors, while the photoluminescent microfluidic channel is attached below the photoluminescent encapsulation layer to collect sweat>
Professor Kyeongha Kwon of KAIST, who led the research, stated, “This technology will enable 24-hour continuous health monitoring, shifting the medical paradigm from treatment-centered to prevention-centered shifting the medical paradigm from treatment-centered to prevention-centered,” further stating that “cost savings through early diagnosis as well as strengthened technological competitiveness in the next-generation wearable healthcare market are anticipated.”
This research was published on July 1 in the international journal Nature Communications, with Do Yun Park, a doctoral student in the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program, as co–first author.
※ Paper title: Adaptive Electronics for Photovoltaic, Photoluminescent and Photometric Methods in Power Harvesting for Wireless and Wearable Sensors ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60911-1 ※ URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-60911-1
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Outstanding Young Researcher Program and Regional Innovation Leading Research Center Project), the Ministry of Science and ICT and Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) AI Semiconductor Graduate Program, and the BK FOUR Program (Connected AI Education & Research Program for Industry and Society Innovation, KAIST EE).
2025.07.30 View 442
Is 24-hour health monitoring possible with ambient light energy?
<(From left) Ph.D candidate Youngmin Sim, Ph.D candidate Do Yun Park, Dr. Chanho Park, Professor Kyeongha Kwon>
Miniaturization and weight reduction of medical wearable devices for continuous health monitoring such as heart rate, blood oxygen saturation, and sweat component analysis remain major challenges. In particular, optical sensors consume a significant amount of power for LED operation and wireless transmission, requiring heavy and bulky batteries. To overcome these limitations, KAIST researchers have developed a next-generation wearable platform that enables 24-hour continuous measurement by using ambient light as an energy source and optimizing power management according to the power environment.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 30th that Professor Kyeongha Kwon's team from the School of Electrical Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Chanho Park’s team at Northwestern University in the U.S., has developed an adaptive wireless wearable platform that reduces battery load by utilizing ambient light.
To address the battery issue of medical wearable devices, Professor Kyeongha Kwon’s research team developed an innovative platform that utilizes ambient natural light as an energy source. This platform integrates three complementary light energy technologies.
<Figure1.The wireless wearable platform minimizes the energy required for light sources through i) Photometric system that directly utilizes ambient light passing through windows for measurements, ii) Photovoltaic system that receives power from high-efficiency photovoltaic cells and wireless power receiver coils, and iii) Photoluminescent system that stores light using photoluminescent materials and emits light in dark conditions to support the two aforementioned systems. In-sensor computing minimizes power consumption by wirelessly transmitting only essential data. The adaptive power management system efficiently manages power by automatically selecting the optimal mode among 11 different power modes through a power selector based on the power supply level from the photovoltaic system and battery charge status.>
The first core technology, the Photometric Method, is a technique that adaptively adjusts LED brightness depending on the intensity of the ambient light source. By combining ambient natural light with LED light to maintain a constant total illumination level, it automatically dims the LED when natural light is strong and brightens it when natural light is weak.
Whereas conventional sensors had to keep the LED on at a fixed brightness regardless of the environment, this technology optimizes LED power in real time according to the surrounding environment. Experimental results showed that it reduced power consumption by as much as 86.22% under sufficient lighting conditions.
The second is the Photovoltaic Method using high-efficiency multijunction solar cells. This goes beyond simple solar power generation to convert light in both indoor and outdoor environments into electricity. In particular, the adaptive power management system automatically switches among 11 different power configurations based on ambient conditions and battery status to achieve optimal energy efficiency.
The third innovative technology is the Photoluminescent Method. By mixing strontium aluminate microparticles* into the sensor’s silicone encapsulation structure, light from the surroundings is absorbed and stored during the day and slowly released in the dark. As a result, after being exposed to 500W/m² of sunlight for 10 minutes, continuous measurement is possible for 2.5 minutes even in complete darkness.
*Strontium aluminate microparticles: A photoluminescent material used in glow-in-the-dark paint or safety signs, which absorbs light and emits it in the dark for an extended time.
These three technologies work complementarily—during bright conditions, the first and second methods are active, and in dark conditions, the third method provides additional support—enabling 24-hour continuous operation.
The research team applied this platform to various medical sensors to verify its practicality. The photoplethysmography sensor monitors heart rate and blood oxygen saturation in real time, allowing early detection of cardiovascular diseases. The blue light dosimeter accurately measures blue light, which causes skin aging and damage, and provides personalized skin protection guidance. The sweat analysis sensor uses microfluidic technology to simultaneously analyze salt, glucose, and pH in sweat, enabling real-time detection of dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Additionally, introducing in-sensor data computing significantly reduced wireless communication power consumption. Previously, all raw data had to be transmitted externally, but now only the necessary results are calculated and transmitted within the sensor, reducing data transmission requirements from 400B/s to 4B/s—a 100-fold decrease.
To validate performance, the research tested the device on healthy adult subjects in four different environments: bright indoor lighting, dim lighting, infrared lighting, and complete darkness. The results showed measurement accuracy equivalent to that of commercial medical devices in all conditions A mouse model experiment confirmed accurate blood oxygen saturation measurement in hypoxic conditions.
<Frigure2.The multimodal device applying the energy harvesting and power management platform consists of i) photoplethysmography (PPG) sensor, ii) blue light dosimeter, iii) photoluminescent microfluidic channel for sweat analysis and biomarker sensors (chloride ion, glucose, and pH), and iv) temperature sensor. This device was implemented with flexible printed circuit board (fPCB) to enable attachment to the skin. A silicon substrate with a window that allows ambient light and measurement light to pass through, along with photoluminescent encapsulation layer, encapsulates the PPG, blue light dosimeter, and temperature sensors, while the photoluminescent microfluidic channel is attached below the photoluminescent encapsulation layer to collect sweat>
Professor Kyeongha Kwon of KAIST, who led the research, stated, “This technology will enable 24-hour continuous health monitoring, shifting the medical paradigm from treatment-centered to prevention-centered shifting the medical paradigm from treatment-centered to prevention-centered,” further stating that “cost savings through early diagnosis as well as strengthened technological competitiveness in the next-generation wearable healthcare market are anticipated.”
This research was published on July 1 in the international journal Nature Communications, with Do Yun Park, a doctoral student in the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program, as co–first author.
※ Paper title: Adaptive Electronics for Photovoltaic, Photoluminescent and Photometric Methods in Power Harvesting for Wireless and Wearable Sensors ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-60911-1 ※ URL: https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-025-60911-1
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Outstanding Young Researcher Program and Regional Innovation Leading Research Center Project), the Ministry of Science and ICT and Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) AI Semiconductor Graduate Program, and the BK FOUR Program (Connected AI Education & Research Program for Industry and Society Innovation, KAIST EE).
2025.07.30 View 442 -
 KAIST Succeeds in Real-Time Carbon Dioxide Monitoring Without Batteries or External Power
< (From left) Master's Student Gyurim Jang, Professor Kyeongha Kwon >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on June 9th that a research team led by Professor Kyeongha Kwon from the School of Electrical Engineering, in a joint study with Professor Hanjun Ryu's team at Chung-Ang University, has developed a self-powered wireless carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring system. This innovative system harvests fine vibrational energy from its surroundings to periodically measure CO2 concentrations.
This breakthrough addresses a critical need in environmental monitoring: accurately understanding "how much" CO2 is being emitted to combat climate change and global warming. While CO2 monitoring technology is key to this, existing systems largely rely on batteries or wired power system, imposing limitations on installation and maintenance. The KAIST team tackled this by creating a self-powered wireless system that operates without external power.
The core of this new system is an "Inertia-driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator (TENG)" that converts vibrations (with amplitudes ranging from 20-4000 ㎛ and frequencies from 0-300 Hz) generated by industrial equipment or pipelines into electricity. This enables periodic CO2 concentration measurements and wireless transmission without the need for batteries.
< Figure 1. Concept and configuration of self-powered wireless CO2 monitoring system using fine vibration harvesting (a) System block diagram (b) Photo of fabricated system prototype >
The research team successfully amplified fine vibrations and induced resonance by combining spring-attached 4-stack TENGs. They achieved stable power production of 0.5 mW under conditions of 13 Hz and 0.56 g acceleration. The generated power was then used to operate a CO2 sensor and a Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) system-on-a-chip (SoC).
Professor Kyeongha Kwon emphasized, "For efficient environmental monitoring, a system that can operate continuously without power limitations is essential." She explained, "In this research, we implemented a self-powered system that can periodically measure and wirelessly transmit CO2 concentrations based on the energy generated from an inertia-driven TENG." She added, "This technology can serve as a foundational technology for future self-powered environmental monitoring platforms integrating various sensors."
< Figure 2. TENG energy harvesting-based wireless CO2 sensing system operation results (c) Experimental setup (d) Measured CO2 concentration results powered by TENG and conventional DC power source >
This research was published on June 1st in the internationally renowned academic journal `Nano Energy (IF 16.8)`. Gyurim Jang, a master's student at KAIST, and Daniel Manaye Tiruneh, a master's student at Chung-Ang University, are the co-first authors of the paper.*Paper Title: Highly compact inertia-driven triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered wireless CO2 monitoring via fine-vibration harvesting*DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2025.110872
This research was supported by the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
2025.06.09 View 49385
KAIST Succeeds in Real-Time Carbon Dioxide Monitoring Without Batteries or External Power
< (From left) Master's Student Gyurim Jang, Professor Kyeongha Kwon >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on June 9th that a research team led by Professor Kyeongha Kwon from the School of Electrical Engineering, in a joint study with Professor Hanjun Ryu's team at Chung-Ang University, has developed a self-powered wireless carbon dioxide (CO2) monitoring system. This innovative system harvests fine vibrational energy from its surroundings to periodically measure CO2 concentrations.
This breakthrough addresses a critical need in environmental monitoring: accurately understanding "how much" CO2 is being emitted to combat climate change and global warming. While CO2 monitoring technology is key to this, existing systems largely rely on batteries or wired power system, imposing limitations on installation and maintenance. The KAIST team tackled this by creating a self-powered wireless system that operates without external power.
The core of this new system is an "Inertia-driven Triboelectric Nanogenerator (TENG)" that converts vibrations (with amplitudes ranging from 20-4000 ㎛ and frequencies from 0-300 Hz) generated by industrial equipment or pipelines into electricity. This enables periodic CO2 concentration measurements and wireless transmission without the need for batteries.
< Figure 1. Concept and configuration of self-powered wireless CO2 monitoring system using fine vibration harvesting (a) System block diagram (b) Photo of fabricated system prototype >
The research team successfully amplified fine vibrations and induced resonance by combining spring-attached 4-stack TENGs. They achieved stable power production of 0.5 mW under conditions of 13 Hz and 0.56 g acceleration. The generated power was then used to operate a CO2 sensor and a Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) system-on-a-chip (SoC).
Professor Kyeongha Kwon emphasized, "For efficient environmental monitoring, a system that can operate continuously without power limitations is essential." She explained, "In this research, we implemented a self-powered system that can periodically measure and wirelessly transmit CO2 concentrations based on the energy generated from an inertia-driven TENG." She added, "This technology can serve as a foundational technology for future self-powered environmental monitoring platforms integrating various sensors."
< Figure 2. TENG energy harvesting-based wireless CO2 sensing system operation results (c) Experimental setup (d) Measured CO2 concentration results powered by TENG and conventional DC power source >
This research was published on June 1st in the internationally renowned academic journal `Nano Energy (IF 16.8)`. Gyurim Jang, a master's student at KAIST, and Daniel Manaye Tiruneh, a master's student at Chung-Ang University, are the co-first authors of the paper.*Paper Title: Highly compact inertia-driven triboelectric nanogenerator for self-powered wireless CO2 monitoring via fine-vibration harvesting*DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2025.110872
This research was supported by the Saudi Aramco-KAIST CO2 Management Center.
2025.06.09 View 49385 -
 KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 8058
KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 8058 -
 KAIST Develops Healthcare Device Tracking Chronic Diabetic Wounds
A KAIST research team has developed an effective wireless system that monitors the wound healing process by tracking the spatiotemporal temperature changes and heat transfer characteristics of damaged areas such as diabetic wounds.
On the 5th of March, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the research team led by Professor Kyeongha Kwon from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, in association with Chung-Ang University professor Hanjun Ryu, developed digital healthcare technology that tracks the wound healing process in real time, which allows appropriate treatments to be administered.
< Figure 1. Schematic illustrations and diagrams of real-time wound monitoring systems. >
The skin serves as a barrier protecting the body from harmful substances, therefore damage to the skin may cause severe health risks to patients in need of intensive care. Especially in the case of diabetic patients, chronic wounds are easily formed due to complications in normal blood circulation and the wound healing process. In the United States alone, hundreds of billions of dollars of medical costs stem from regenerating the skin from such wounds. While various methods exist to promote wound healing, personalized management is essential depending on the condition of each patient's wounds.
Accordingly, the research team tracked the heating response within the wound by utilizing the differences in temperature between the damaged area and the surrounding healthy skin. They then measured heat transfer characteristics to observe moisture changes near the skin surface, ultimately establishing a basis for understanding the formation process of scar tissue. The team conducted experiments using diabetic mice models regarding the delay in wound healing under pathological conditions, and it was demonstrated that the collected data accurately tracks the wound healing process and the formation of scar tissue.
To minimize the tissue damage that may occur in the process of removing the tracking device after healing, the system integrates biodegradable sensor modules capable of natural decomposition within the body. These biodegradable modules disintegrate within the body after use, thus reducing the risk of additional discomfort or tissue damage upon device removal. Furthermore, the device could one day be used for monitoring inside the wound area as there is no need for removal.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon, who led the research, anticipates that continuous monitoring of wound temperature and heat transfer characteristics will enable medical professionals to more accurately assess the status of diabetic patients' wounds and provide appropriate treatment. He further predicted that the implementation of biodegradable sensors allows for the safe decomposition of the device after wound healing without the need for removal, making live monitoring possible not only in hospitals but also at home.
The research team plans to integrate antimicrobial materials into this device, aiming to expand its technological capabilities to enable the observation and prevention of inflammatory responses, bacterial infections, and other complications. The goal is to provide a multi-purpose wound monitoring platform capable of real-time antimicrobial monitoring in hospitals or homes by detecting changes in temperature and heat transfer characteristics indicative of infection levels.
< Image 1. Image of the bioresorbable temperature sensor >
The results of this study were published on February 19th in the international journal Advanced Healthcare Materials and selected as the inside back cover article, titled "Materials and Device Designs for Wireless Monitoring of Temperature and Thermal Transport Properties of Wound Beds during Healing."
This research was conducted with support from the Basic Research Program, the Regional Innovation Center Program, and the BK21 Program.
2024.03.11 View 9467
KAIST Develops Healthcare Device Tracking Chronic Diabetic Wounds
A KAIST research team has developed an effective wireless system that monitors the wound healing process by tracking the spatiotemporal temperature changes and heat transfer characteristics of damaged areas such as diabetic wounds.
On the 5th of March, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the research team led by Professor Kyeongha Kwon from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering, in association with Chung-Ang University professor Hanjun Ryu, developed digital healthcare technology that tracks the wound healing process in real time, which allows appropriate treatments to be administered.
< Figure 1. Schematic illustrations and diagrams of real-time wound monitoring systems. >
The skin serves as a barrier protecting the body from harmful substances, therefore damage to the skin may cause severe health risks to patients in need of intensive care. Especially in the case of diabetic patients, chronic wounds are easily formed due to complications in normal blood circulation and the wound healing process. In the United States alone, hundreds of billions of dollars of medical costs stem from regenerating the skin from such wounds. While various methods exist to promote wound healing, personalized management is essential depending on the condition of each patient's wounds.
Accordingly, the research team tracked the heating response within the wound by utilizing the differences in temperature between the damaged area and the surrounding healthy skin. They then measured heat transfer characteristics to observe moisture changes near the skin surface, ultimately establishing a basis for understanding the formation process of scar tissue. The team conducted experiments using diabetic mice models regarding the delay in wound healing under pathological conditions, and it was demonstrated that the collected data accurately tracks the wound healing process and the formation of scar tissue.
To minimize the tissue damage that may occur in the process of removing the tracking device after healing, the system integrates biodegradable sensor modules capable of natural decomposition within the body. These biodegradable modules disintegrate within the body after use, thus reducing the risk of additional discomfort or tissue damage upon device removal. Furthermore, the device could one day be used for monitoring inside the wound area as there is no need for removal.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon, who led the research, anticipates that continuous monitoring of wound temperature and heat transfer characteristics will enable medical professionals to more accurately assess the status of diabetic patients' wounds and provide appropriate treatment. He further predicted that the implementation of biodegradable sensors allows for the safe decomposition of the device after wound healing without the need for removal, making live monitoring possible not only in hospitals but also at home.
The research team plans to integrate antimicrobial materials into this device, aiming to expand its technological capabilities to enable the observation and prevention of inflammatory responses, bacterial infections, and other complications. The goal is to provide a multi-purpose wound monitoring platform capable of real-time antimicrobial monitoring in hospitals or homes by detecting changes in temperature and heat transfer characteristics indicative of infection levels.
< Image 1. Image of the bioresorbable temperature sensor >
The results of this study were published on February 19th in the international journal Advanced Healthcare Materials and selected as the inside back cover article, titled "Materials and Device Designs for Wireless Monitoring of Temperature and Thermal Transport Properties of Wound Beds during Healing."
This research was conducted with support from the Basic Research Program, the Regional Innovation Center Program, and the BK21 Program.
2024.03.11 View 9467 -
 Wearable Device to Monitor Sweat in Real Time
An on-skin platform for the wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss, and temperature of sweat in real time
An electronic patch can monitor your sweating and check your health status. Even more, the soft microfluidic device that adheres to the surface of the skin, captures, stores, and performs biomarker analysis of sweat as it is released through the eccrine glands.
This wearable and wireless electronic device developed by Professor Kyeongha Kwon and her collaborators is a digital and wireless platform that could help track the so-called ‘filling process’ of sweat without having to visually examine the device. The platform was integrated with microfluidic systems to analyze the sweat’s components.
To monitor the sweat release rate in real time, the researchers created a ‘thermal flow sensing module.’ They designed a sophisticated microfluidic channel to allow the collected sweat to flow through a narrow passage and a heat source was placed on the outer surface of the channel to induce a heat exchange between the sweat and the heated channel.
As a result, the researchers could develop a wireless electronic patch that can measure the temperature difference in a specific location upstream and downstream of the heat source with an electronic circuit and convert it into a digital signal to measure the sweat release rate in real time. The patch accurately measured the perspiration rate in the range of 0-5 microliters/minute (μl/min), which was considered physiologically significant. The sensor can measure the flow of sweat directly and then use the information it collected to quantify total sweat loss. Moreover, the device features advanced microfluidic systems and colorimetric chemical reagents to gather pH measurements and determine the concentration of chloride, creatinine, and glucose in a user's sweat.
Professor Kwon said that these indicators could be used to diagnose various diseases related with sweating such as cystic fibrosis, diabetes, kidney dysfunction, and metabolic alkalosis. “As the sweat flowing in the microfluidic channel is completely separated from the electronic circuit, the new patch overcame the shortcomings of existing flow rate measuring devices, which were vulnerable to corrosion and aging,” she explained.
The patch can be easily attached to the skin with flexible circuit board printing technology and silicone sealing technology. It has an additional sensor that detects changes in skin temperature. Using a smartphone app, a user can check the data measured by the wearable patch in real time.
Professor Kwon added, “This patch can be widely used for personal hydration strategies, the detection of dehydration symptoms, and other health management purposes. It can also be used in a systematic drug delivery system, such as for measuring the blood flow rate in blood vessels near the skin’s surface or measuring a drug’s release rate in real time to calculate the exact dosage.”
-PublicationKyeongha Kwon, Jong Uk Kim, John A. Rogers, et al. “An on-skin platform for wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss and temperature of sweat in real time.” Nature Electronics (doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00556-2)
-ProfileProfessor Kyeongha KwonSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.25 View 13348
Wearable Device to Monitor Sweat in Real Time
An on-skin platform for the wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss, and temperature of sweat in real time
An electronic patch can monitor your sweating and check your health status. Even more, the soft microfluidic device that adheres to the surface of the skin, captures, stores, and performs biomarker analysis of sweat as it is released through the eccrine glands.
This wearable and wireless electronic device developed by Professor Kyeongha Kwon and her collaborators is a digital and wireless platform that could help track the so-called ‘filling process’ of sweat without having to visually examine the device. The platform was integrated with microfluidic systems to analyze the sweat’s components.
To monitor the sweat release rate in real time, the researchers created a ‘thermal flow sensing module.’ They designed a sophisticated microfluidic channel to allow the collected sweat to flow through a narrow passage and a heat source was placed on the outer surface of the channel to induce a heat exchange between the sweat and the heated channel.
As a result, the researchers could develop a wireless electronic patch that can measure the temperature difference in a specific location upstream and downstream of the heat source with an electronic circuit and convert it into a digital signal to measure the sweat release rate in real time. The patch accurately measured the perspiration rate in the range of 0-5 microliters/minute (μl/min), which was considered physiologically significant. The sensor can measure the flow of sweat directly and then use the information it collected to quantify total sweat loss. Moreover, the device features advanced microfluidic systems and colorimetric chemical reagents to gather pH measurements and determine the concentration of chloride, creatinine, and glucose in a user's sweat.
Professor Kwon said that these indicators could be used to diagnose various diseases related with sweating such as cystic fibrosis, diabetes, kidney dysfunction, and metabolic alkalosis. “As the sweat flowing in the microfluidic channel is completely separated from the electronic circuit, the new patch overcame the shortcomings of existing flow rate measuring devices, which were vulnerable to corrosion and aging,” she explained.
The patch can be easily attached to the skin with flexible circuit board printing technology and silicone sealing technology. It has an additional sensor that detects changes in skin temperature. Using a smartphone app, a user can check the data measured by the wearable patch in real time.
Professor Kwon added, “This patch can be widely used for personal hydration strategies, the detection of dehydration symptoms, and other health management purposes. It can also be used in a systematic drug delivery system, such as for measuring the blood flow rate in blood vessels near the skin’s surface or measuring a drug’s release rate in real time to calculate the exact dosage.”
-PublicationKyeongha Kwon, Jong Uk Kim, John A. Rogers, et al. “An on-skin platform for wireless monitoring of flow rate, cumulative loss and temperature of sweat in real time.” Nature Electronics (doi.org/10.1038/s41928-021-00556-2)
-ProfileProfessor Kyeongha KwonSchool of Electrical EngineeringKAIST
2021.06.25 View 13348