ICA
-
 The Future Mobility of the Year 2019
KAIST announced the Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) 2019. The winners are Volvo 360C, Toyota e-Palette, and Toyota Concept-i WALK.
FMOTY are the first awards that recognizes concept cars that exhibit innovative services and practical transportation technology in three categories: private mobility, public and commercial mobility, and personal mobility.
Figure 1. The winner in the private mobility division, the Volvo 360C
In the private mobility division, the award went to the Volvo 360C. With targeted routes of roughly 186 miles, this vehicle has an ambitious service goal to replace airplanes by traveling these routes with great comfort. Goro Okazaki, a journalist with Car and Driver Japan, said, “The Volvo 360C clearly shows how highly personalized autonomous driving can change the future.”
Figure 2. The winner in the public mobility division, the Toyota e-Palette
The Toyota e-Palette was the winning car in commercial mobility division. This vehicle provides the best solution as a mobile service platform by transforming itself into mobile hospitals, hotels, stores and food trucks. Carlo Calderón, a journalist for Autopista Spain, said, “It has a great strength in remodeling its indoor and outdoor spaces according to various commercial uses.”
Figure 3. The winner in the personal mobility division, the Toyota Concept-i WALK
In the personal mobility division, the award went to the Toyota Concept-i WALK. It was recognized for having an exquisite user environment and artificial intelligent agent, along with an excellent completion. Jun Miao, a journalist with MJ CarShow China, said, “It is aesthetically pleasing. Beyond the upright control of conventional personal mobility, it allows agile control with a joystick.”
FMOTY conducted a screening process for 45 concept cars over three months and 16 renowned automotive experts from 11 countries participated as judges for this award, including Editor in Chief of BBC Top Gear Magazine Charlie Turner and European Bureau Chief of Automobile Magazine Georg Kacher. The judges said that FMOTY was born to propose a new aspect of future mobility, and in terms of evaluating technical and social values of concept cars, FMOTY carries great significance.
Kyung-soo Kim, Dean of the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation said, “Globally renowned experts in the automotive field participated as judges to elevate the prestige and fairness of the awards. KAIST members were excluded from the entire judging process. I believe that the FMOTY Awards will expand public attention from the present to the future.”
Details can be found on the official website of FMOTY ( www.fmoty.org ).
2019.03.11 View 8862
The Future Mobility of the Year 2019
KAIST announced the Future Mobility of the Year (FMOTY) 2019. The winners are Volvo 360C, Toyota e-Palette, and Toyota Concept-i WALK.
FMOTY are the first awards that recognizes concept cars that exhibit innovative services and practical transportation technology in three categories: private mobility, public and commercial mobility, and personal mobility.
Figure 1. The winner in the private mobility division, the Volvo 360C
In the private mobility division, the award went to the Volvo 360C. With targeted routes of roughly 186 miles, this vehicle has an ambitious service goal to replace airplanes by traveling these routes with great comfort. Goro Okazaki, a journalist with Car and Driver Japan, said, “The Volvo 360C clearly shows how highly personalized autonomous driving can change the future.”
Figure 2. The winner in the public mobility division, the Toyota e-Palette
The Toyota e-Palette was the winning car in commercial mobility division. This vehicle provides the best solution as a mobile service platform by transforming itself into mobile hospitals, hotels, stores and food trucks. Carlo Calderón, a journalist for Autopista Spain, said, “It has a great strength in remodeling its indoor and outdoor spaces according to various commercial uses.”
Figure 3. The winner in the personal mobility division, the Toyota Concept-i WALK
In the personal mobility division, the award went to the Toyota Concept-i WALK. It was recognized for having an exquisite user environment and artificial intelligent agent, along with an excellent completion. Jun Miao, a journalist with MJ CarShow China, said, “It is aesthetically pleasing. Beyond the upright control of conventional personal mobility, it allows agile control with a joystick.”
FMOTY conducted a screening process for 45 concept cars over three months and 16 renowned automotive experts from 11 countries participated as judges for this award, including Editor in Chief of BBC Top Gear Magazine Charlie Turner and European Bureau Chief of Automobile Magazine Georg Kacher. The judges said that FMOTY was born to propose a new aspect of future mobility, and in terms of evaluating technical and social values of concept cars, FMOTY carries great significance.
Kyung-soo Kim, Dean of the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation said, “Globally renowned experts in the automotive field participated as judges to elevate the prestige and fairness of the awards. KAIST members were excluded from the entire judging process. I believe that the FMOTY Awards will expand public attention from the present to the future.”
Details can be found on the official website of FMOTY ( www.fmoty.org ).
2019.03.11 View 8862 -
 KAIST Develops Analog Memristive Synapses for Neuromorphic Chips
(Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering)
A KAIST research team developed a technology that makes a transition of the operation mode of flexible memristors to synaptic analog switching by reducing the size of the formed filament. Through this technology, memristors can extend their role to memristive synapses for neuromorphic chips, which will lead to developing soft neuromorphic intelligent systems.
Brain-inspired neuromorphic chips have been gaining a great deal of attention for reducing the power consumption and integrating data processing, compared to conventional semiconductor chips. Similarly, memristors are known to be the most suitable candidate for making a crossbar array which is the most efficient architecture for realizing hardware-based artificial neural network (ANN) inside a neuromorphic chip.
A hardware-based ANN consists of a neuron circuit and synapse elements, the connecting pieces. In the neuromorphic system, the synaptic weight, which represents the connection strength between neurons, should be stored and updated as the type of analog data at each synapse.
However, most memristors have digital characteristics suitable for nonvolatile memory. These characteristics put a limitation on the analog operation of the memristors, which makes it difficult to apply them to synaptic devices.
Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team fabricated a flexible polymer memristor on a plastic substrate, and found that changing the size of the conductive metal filaments formed inside the device on the scale of metal atoms can make a transition of the memristor behavior from digital to analog.
Using this phenomenon, the team developed flexible memristor-based electronic synapses, which can continuously and linearly update synaptic weight, and operate under mechanical deformations such as bending.
The team confirmed that the ANN based on these memristor synapses can effectively classify person’s facial images even when they were damaged. This research demonstrated the possibility of a neuromorphic chip that can efficiently recognize faces, numbers, and objects.
Professor Choi said, “We found the principles underlying the transition from digital to analog operation of the memristors. I believe that this research paves the way for applying various memristors to either digital memory or electronic synapses, and will accelerate the development of a high-performing neuromorphic chip.”
In a joint research project with Professor Sung Gap Im (KAIST) and Professor V. P. Dravid (Northwestern University), this study was led by Dr. Byung Chul Jang (Samsung Electronics), Dr. Sungkyu Kim (Northwestern University) and Dr. Sang Yoon Yang (KAIST), and was published online in Nano Letters (10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04023) on January 4, 2019.
Figure 1. a) Schematic illustration of a flexible pV3D3 memristor-based electronic synapse array. b) Cross-sectional TEM image of the flexible pV3D3 memristor
2019.02.28 View 11403
KAIST Develops Analog Memristive Synapses for Neuromorphic Chips
(Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering)
A KAIST research team developed a technology that makes a transition of the operation mode of flexible memristors to synaptic analog switching by reducing the size of the formed filament. Through this technology, memristors can extend their role to memristive synapses for neuromorphic chips, which will lead to developing soft neuromorphic intelligent systems.
Brain-inspired neuromorphic chips have been gaining a great deal of attention for reducing the power consumption and integrating data processing, compared to conventional semiconductor chips. Similarly, memristors are known to be the most suitable candidate for making a crossbar array which is the most efficient architecture for realizing hardware-based artificial neural network (ANN) inside a neuromorphic chip.
A hardware-based ANN consists of a neuron circuit and synapse elements, the connecting pieces. In the neuromorphic system, the synaptic weight, which represents the connection strength between neurons, should be stored and updated as the type of analog data at each synapse.
However, most memristors have digital characteristics suitable for nonvolatile memory. These characteristics put a limitation on the analog operation of the memristors, which makes it difficult to apply them to synaptic devices.
Professor Sung-Yool Choi from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team fabricated a flexible polymer memristor on a plastic substrate, and found that changing the size of the conductive metal filaments formed inside the device on the scale of metal atoms can make a transition of the memristor behavior from digital to analog.
Using this phenomenon, the team developed flexible memristor-based electronic synapses, which can continuously and linearly update synaptic weight, and operate under mechanical deformations such as bending.
The team confirmed that the ANN based on these memristor synapses can effectively classify person’s facial images even when they were damaged. This research demonstrated the possibility of a neuromorphic chip that can efficiently recognize faces, numbers, and objects.
Professor Choi said, “We found the principles underlying the transition from digital to analog operation of the memristors. I believe that this research paves the way for applying various memristors to either digital memory or electronic synapses, and will accelerate the development of a high-performing neuromorphic chip.”
In a joint research project with Professor Sung Gap Im (KAIST) and Professor V. P. Dravid (Northwestern University), this study was led by Dr. Byung Chul Jang (Samsung Electronics), Dr. Sungkyu Kim (Northwestern University) and Dr. Sang Yoon Yang (KAIST), and was published online in Nano Letters (10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04023) on January 4, 2019.
Figure 1. a) Schematic illustration of a flexible pV3D3 memristor-based electronic synapse array. b) Cross-sectional TEM image of the flexible pV3D3 memristor
2019.02.28 View 11403 -
 Kimchi Toolkit by Costa Rican Summa Cum Laude Helps Make the Best Flavor
(Maria Jose Reyes Castro with her kimchi toolkit application)
Every graduate feels a special attachment to their school, but for Maria Jose Reyes Castro who graduated summa cum laude in the Department of Industrial Design this year, KAIST will be remembered for more than just academics. She appreciates KAIST for not only giving her great professional opportunities, but also helping her find the love of her life.
During her master’s course, she completed an electronic kimchi toolkit, which optimizes kimchi’s flavor. Her kit uses a mobile application and smart sensor to find the fermentation level of kimchi by measuring its pH level, which is closely related to its fermentation. A user can set a desired fermentation level or salinity on the mobile application, and it provides the best date to serve it.
Under the guidance of Professor Daniel Saakes, she conducted research on developing a kimchi toolkit for beginners (Qualified Kimchi: Improving the experience of inexperienced kimchi makers by developing a monitoring toolkit for kimchi).
“I’ve seen many foreigners saying it’s quite difficult to make kimchi. So I chose to study kimchi to help people, especially those who are first-experienced making kimchi more easily,” she said. She got recipes from YouTube and studied fermentation through academic journals. She also asked kimchi experts to have a more profound understanding of it.
Extending her studies, she now works for a startup specializing in smart farms after starting last month. She conducts research on biology and applies it to designs that can be used practically in daily life.
Her tie with KAIST goes back to 2011 when she attended an international science camp in Germany. She met Sunghan Ro (’19 PhD in Nanoscience and Technology), a student from KAIST and now her husband. He recommended for her to enroll at KAIST because the school offers an outstanding education and research infrastructure along with support for foreign students.
At that time, Castro had just begun her first semester in electrical engineering at the University of Costa Rica, but she decided to apply to KAIST and seek a better opportunity in a new environment. One year later, she began her fresh start at KAIST in the fall semester of 2012.
Instead of choosing her original major, electrical engineering, she decided to pursue her studies in the Department of Industrial Design, because it is an interdisciplinary field where students get to study design while learning business models and making prototypes.
She said, “I felt encouraged by my professors and colleagues in my department to be creative and follow my passion. I never regret entering this major.”
When Castro was pursuing her master’s program in the same department, she became interested in interaction designs with food and biological designs by Professor Saakes, who is her advisor specializing in these areas.
After years of following her passion in design, she now graduates with academic honors in her department.
It is a bittersweet moment to close her journey at KAIST, but “I want to thank KAIST for the opportunity to change my life for the better. I also thank my parents for being supportive and encouraging me. I really appreciate the professors from the Department of Industrial Design who guided and shaped who I am,” she said.
Figure 1. The concept of the kimchi toolkit
Figure 2. The scenario of the kimchi toolkit
2019.02.19 View 6943
Kimchi Toolkit by Costa Rican Summa Cum Laude Helps Make the Best Flavor
(Maria Jose Reyes Castro with her kimchi toolkit application)
Every graduate feels a special attachment to their school, but for Maria Jose Reyes Castro who graduated summa cum laude in the Department of Industrial Design this year, KAIST will be remembered for more than just academics. She appreciates KAIST for not only giving her great professional opportunities, but also helping her find the love of her life.
During her master’s course, she completed an electronic kimchi toolkit, which optimizes kimchi’s flavor. Her kit uses a mobile application and smart sensor to find the fermentation level of kimchi by measuring its pH level, which is closely related to its fermentation. A user can set a desired fermentation level or salinity on the mobile application, and it provides the best date to serve it.
Under the guidance of Professor Daniel Saakes, she conducted research on developing a kimchi toolkit for beginners (Qualified Kimchi: Improving the experience of inexperienced kimchi makers by developing a monitoring toolkit for kimchi).
“I’ve seen many foreigners saying it’s quite difficult to make kimchi. So I chose to study kimchi to help people, especially those who are first-experienced making kimchi more easily,” she said. She got recipes from YouTube and studied fermentation through academic journals. She also asked kimchi experts to have a more profound understanding of it.
Extending her studies, she now works for a startup specializing in smart farms after starting last month. She conducts research on biology and applies it to designs that can be used practically in daily life.
Her tie with KAIST goes back to 2011 when she attended an international science camp in Germany. She met Sunghan Ro (’19 PhD in Nanoscience and Technology), a student from KAIST and now her husband. He recommended for her to enroll at KAIST because the school offers an outstanding education and research infrastructure along with support for foreign students.
At that time, Castro had just begun her first semester in electrical engineering at the University of Costa Rica, but she decided to apply to KAIST and seek a better opportunity in a new environment. One year later, she began her fresh start at KAIST in the fall semester of 2012.
Instead of choosing her original major, electrical engineering, she decided to pursue her studies in the Department of Industrial Design, because it is an interdisciplinary field where students get to study design while learning business models and making prototypes.
She said, “I felt encouraged by my professors and colleagues in my department to be creative and follow my passion. I never regret entering this major.”
When Castro was pursuing her master’s program in the same department, she became interested in interaction designs with food and biological designs by Professor Saakes, who is her advisor specializing in these areas.
After years of following her passion in design, she now graduates with academic honors in her department.
It is a bittersweet moment to close her journey at KAIST, but “I want to thank KAIST for the opportunity to change my life for the better. I also thank my parents for being supportive and encouraging me. I really appreciate the professors from the Department of Industrial Design who guided and shaped who I am,” she said.
Figure 1. The concept of the kimchi toolkit
Figure 2. The scenario of the kimchi toolkit
2019.02.19 View 6943 -
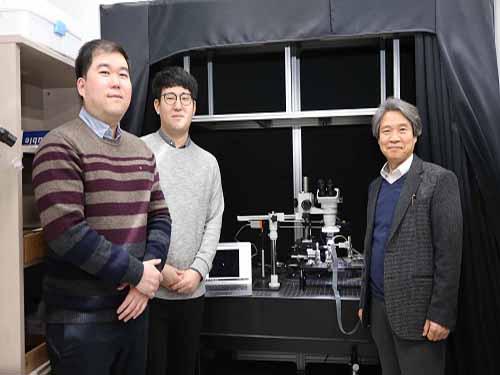 KAIST Develops Core Technology for Ultra-small 3D Image Sensor
(from left: Dr. Jong-Bum Yo, PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kimand Professor Hyo-Hoon Park)
A KAIST research team developed a silicon optical phased array (OPA) chip, which can be a core component for three-dimensional image sensors. This research was co-led by PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kim and Dr. Jong-Bum You from the National Nanofab Center (NNFC).
A 3D image sensor adds distance information to a two-dimensional image, such as a photo, to recognize it as a 3D image. It plays a vital role in various electronics including autonomous vehicles, drones, robots, and facial recognition systems, which require accurate measurement of the distance from objects.
Many automobile and drone companies are focusing on developing 3D image sensor systems, based on mechanical light detection and ranging (LiDAR) systems. However, it can only get as small as the size of a fist and has a high possibility of malfunctioning because it employs a mechanical method for laser beam-steering.
OPAs have gained a great attention as a key component to implement solid-state LiDAR because it can control the light direction electronically without moving parts. Silicon-based OPAs are small, durable, and can be mass-produced through conventional Si-CMOS processes.
However, in the development of OPAs, a big issue has been raised about how to achieve wide beam-steering in transversal and longitudinal directions. In the transversal direction, a wide beam-steering has been implemented, relatively easily, through a thermo-optic or electro-optic control of the phase shifters integrated with a 1D array. But the longitudinal beam-steering has been remaining as a technical challenge since only a narrow steering was possible with the same 1D array by changing the wavelengths of light, which is hard to implement in semiconductor processes.
If a light wavelength is changed, characteristics of element devices consisting the OPA can vary, which makes it difficult to control the light direction with reliability as well as to integrate a wavelength-tunable laser on a silicon-based chip. Therefore, it is essential to devise a new structure that can easily adjust the radiated light in both transversal and longitudinal directions.
By integrating tunable radiator, instead of tunable laser in a conventional OPA, Professor Hyo-Hoon Park from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team developed an ultra-small, low-power OPA chip that facilitates a wide 2D beam-steering with a monochromatic light source.
This OPA structure allows the minimizing of the 3D image sensors, as small as a dragonfly’s eye.
According to the team, the OPA can function as a 3D image sensor and also as a wireless transmitter sending the image data to a desired direction, enabling high-quality image data to be freely communicated between electronic devices.
Kim said, “It’s not an easy task to integrate a tunable light source in the OPA structures of previous works. We hope our research proposing a tunable radiator makes a big step towards commercializing OPAs.”
Dr. You added, “We will be able to support application researches of 3D image sensors, especially for facial recognition with smartphones and augmented reality services. We will try to prepare a processing platform in NNFC that provides core technologies of the 3D image sensor fabrication.”
This research was published in Optics Letters on January 15.
Figure 1.The manufactured OPA chip
Figure 2. Schematic feature showing an application of the OPA to a 3D image sensor
2019.02.08 View 8201
KAIST Develops Core Technology for Ultra-small 3D Image Sensor
(from left: Dr. Jong-Bum Yo, PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kimand Professor Hyo-Hoon Park)
A KAIST research team developed a silicon optical phased array (OPA) chip, which can be a core component for three-dimensional image sensors. This research was co-led by PhD candidate Seong-Hwan Kim and Dr. Jong-Bum You from the National Nanofab Center (NNFC).
A 3D image sensor adds distance information to a two-dimensional image, such as a photo, to recognize it as a 3D image. It plays a vital role in various electronics including autonomous vehicles, drones, robots, and facial recognition systems, which require accurate measurement of the distance from objects.
Many automobile and drone companies are focusing on developing 3D image sensor systems, based on mechanical light detection and ranging (LiDAR) systems. However, it can only get as small as the size of a fist and has a high possibility of malfunctioning because it employs a mechanical method for laser beam-steering.
OPAs have gained a great attention as a key component to implement solid-state LiDAR because it can control the light direction electronically without moving parts. Silicon-based OPAs are small, durable, and can be mass-produced through conventional Si-CMOS processes.
However, in the development of OPAs, a big issue has been raised about how to achieve wide beam-steering in transversal and longitudinal directions. In the transversal direction, a wide beam-steering has been implemented, relatively easily, through a thermo-optic or electro-optic control of the phase shifters integrated with a 1D array. But the longitudinal beam-steering has been remaining as a technical challenge since only a narrow steering was possible with the same 1D array by changing the wavelengths of light, which is hard to implement in semiconductor processes.
If a light wavelength is changed, characteristics of element devices consisting the OPA can vary, which makes it difficult to control the light direction with reliability as well as to integrate a wavelength-tunable laser on a silicon-based chip. Therefore, it is essential to devise a new structure that can easily adjust the radiated light in both transversal and longitudinal directions.
By integrating tunable radiator, instead of tunable laser in a conventional OPA, Professor Hyo-Hoon Park from the School of Electrical Engineering and his team developed an ultra-small, low-power OPA chip that facilitates a wide 2D beam-steering with a monochromatic light source.
This OPA structure allows the minimizing of the 3D image sensors, as small as a dragonfly’s eye.
According to the team, the OPA can function as a 3D image sensor and also as a wireless transmitter sending the image data to a desired direction, enabling high-quality image data to be freely communicated between electronic devices.
Kim said, “It’s not an easy task to integrate a tunable light source in the OPA structures of previous works. We hope our research proposing a tunable radiator makes a big step towards commercializing OPAs.”
Dr. You added, “We will be able to support application researches of 3D image sensors, especially for facial recognition with smartphones and augmented reality services. We will try to prepare a processing platform in NNFC that provides core technologies of the 3D image sensor fabrication.”
This research was published in Optics Letters on January 15.
Figure 1.The manufactured OPA chip
Figure 2. Schematic feature showing an application of the OPA to a 3D image sensor
2019.02.08 View 8201 -
 Stretchable Multi-functional Fiber for Energy Harvesting and Strain Sensing
(from left: Professor Steve Park, Jeongjae Ryu and Professor Seungbum Hong)
Fiber-based electronics are expected to play a vital role in next-generation wearable electronics. Woven into textiles, they can provide higher durability, comfort, and integrated multi-functionality. A KAIST team has developed a stretchable multi-functional fiber (SMF) that can harvest energy and detect strain, which can be applied to future wearable electronics.
With wearable electronics, health and physical conditions can be assessed by analyzing biological signals from the human body, such as pulse and muscle movements. Fibers are highly suitable for future wearable electronics because they can be easily integrated into textiles, which are designed to be conformable to curvilinear surfaces and comfortable to wear. Moreover, their weave structures offer support that makes them resistant to fatigue. Many research groups have developed fiber-based strain sensors to sense external biological signals. However, their sensitivities were relatively low.
The applicability of wearable devices is currently limited by their power source, as the size, weight, and lifetime of the battery lessens their versatility. Harvesting mechanical energy from the human body is a promising solution to overcome such limitations by utilizing various types of motions like bending, stretching, and pressing. However, previously reported, fiber-based energy harvesters were not stretchable and could not fully harvest the available mechanical energy.
Professor Seungbum Hong and Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and their team fabricated a stretchable fiber by using a ferroelectric layer composed of P(VDF-TrFE)/PDMS sandwiched between stretchable electrodes composed of a composite of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene polystyrenesulfonate (PEDOT:PSS).
Cracks formed in MWCNT/PEDOT:PSS layer help the fiber show high sensitivity compared to the previously reported fiber strain sensors. Furthermore, the new fiber can harvest mechanical energy under various mechanical stimuli such as stretching, tapping, and injecting water into the fiber using the piezoelectric effect of the P(VDF-TrFE)/PDMS layer.
Professor Hong said, “This new fiber has various functionalities and makes the device simple and compact. It is a core technology for developing wearable devices with energy harvesting and strain sensing capabilities.”
This article, led by PhD candidate Jeongjae Ryu, was published in the January 2019 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1.Schematic illustration of an SMF fiber and its piezoelectric voltage output and response to strain.
Figure 2. Photographs of a stretchable multi-functional fiber being stretched by 100%, bent, and twisted.
2019.01.31 View 10361
Stretchable Multi-functional Fiber for Energy Harvesting and Strain Sensing
(from left: Professor Steve Park, Jeongjae Ryu and Professor Seungbum Hong)
Fiber-based electronics are expected to play a vital role in next-generation wearable electronics. Woven into textiles, they can provide higher durability, comfort, and integrated multi-functionality. A KAIST team has developed a stretchable multi-functional fiber (SMF) that can harvest energy and detect strain, which can be applied to future wearable electronics.
With wearable electronics, health and physical conditions can be assessed by analyzing biological signals from the human body, such as pulse and muscle movements. Fibers are highly suitable for future wearable electronics because they can be easily integrated into textiles, which are designed to be conformable to curvilinear surfaces and comfortable to wear. Moreover, their weave structures offer support that makes them resistant to fatigue. Many research groups have developed fiber-based strain sensors to sense external biological signals. However, their sensitivities were relatively low.
The applicability of wearable devices is currently limited by their power source, as the size, weight, and lifetime of the battery lessens their versatility. Harvesting mechanical energy from the human body is a promising solution to overcome such limitations by utilizing various types of motions like bending, stretching, and pressing. However, previously reported, fiber-based energy harvesters were not stretchable and could not fully harvest the available mechanical energy.
Professor Seungbum Hong and Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and their team fabricated a stretchable fiber by using a ferroelectric layer composed of P(VDF-TrFE)/PDMS sandwiched between stretchable electrodes composed of a composite of multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) and poly 3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene polystyrenesulfonate (PEDOT:PSS).
Cracks formed in MWCNT/PEDOT:PSS layer help the fiber show high sensitivity compared to the previously reported fiber strain sensors. Furthermore, the new fiber can harvest mechanical energy under various mechanical stimuli such as stretching, tapping, and injecting water into the fiber using the piezoelectric effect of the P(VDF-TrFE)/PDMS layer.
Professor Hong said, “This new fiber has various functionalities and makes the device simple and compact. It is a core technology for developing wearable devices with energy harvesting and strain sensing capabilities.”
This article, led by PhD candidate Jeongjae Ryu, was published in the January 2019 issue of Nano Energy.
Figure 1.Schematic illustration of an SMF fiber and its piezoelectric voltage output and response to strain.
Figure 2. Photographs of a stretchable multi-functional fiber being stretched by 100%, bent, and twisted.
2019.01.31 View 10361 -
 President Shin Speaks on Closing the Skills Gap at the WEF
(President Shin poses (far right) with the National University of Singapore President Tan Eng Chye (center) along with Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in Davos last week.)
President Sung-Chul Shin shared his ideas on how reskilling is a critical element of growth, dynamism, and competitiveness for countries during a session titled “Closing the Skills Gap: Creating a Reskilling Revolution” at the World Economic Forum on January 24 in Davos.
While discussing a reskilling imperative alongside French Labor Minister Muriel Penicaud, he presented how the Korean government and KAIST are responding to the socio-economic transformation of workforces in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. After their presentation, Minister of Economy and Enterprise of Spain Nadia Calvirno Santamaria, Minister of Commerce and Industry of Oman Ali bin Masoud bin Ali Al Sunaidy, and Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Skill Development, and Entrepreneurship of India Dharmendra Pradhan shared their views on the course of decision making regarding the proactive practices and policies they have applied for closing the gaps from their countries’ perspectives.
President Shin presented how to upskill and reskill SMEs and startups, the real players who will jumpstart the economy in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He explained that the government is striving to change the existing structure of the economy, which is dominated by a few giant conglomerates. He added that the Korean government is trying to support SMEs and startups in terms of both funding and technology reskilling in order to rejuvenate the economy.
To better align itself with the government’s efforts, KAIST has introduced SME 4.0. SME 4.0 proposes to innovate the production process through the creation of a partnered platform between KAIST and SMEs across the country. With this platform, KAIST assists local SMEs for standardizing and systemizing all their processes of production, delivery, and management with enterprise resources planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES). In addition, SME 4.0 offers retraining and re-tooling programs by linking the data generated through this platform in real time to better facilitate SMEs’ smart business.
(President Shin shakes hands with H.E.Mohammed Al-Tuwairi, Minister of Economy and Planning of Saudi Arabia before holding a bilaterla meeting in Davos.)
President Shin also explained about upskilling the leading corporations’ technological competitiveness, partnering with major leading corporations for upskilling their advanced technologies.
He also held a series of bilateral meetings with dignitaries attending the WEF annual meeting to discuss partnerships and collaborations. He also attended the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), a community composed of 28 presidents from the world’s top universities on January 23. President Shin, who is on the advisory board of the Center for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR), also participated in the board meeting and discussed the upcoming launching of the Korea C4IR, which will open at KAIST in March.
2019.01.28 View 8397
President Shin Speaks on Closing the Skills Gap at the WEF
(President Shin poses (far right) with the National University of Singapore President Tan Eng Chye (center) along with Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee in Davos last week.)
President Sung-Chul Shin shared his ideas on how reskilling is a critical element of growth, dynamism, and competitiveness for countries during a session titled “Closing the Skills Gap: Creating a Reskilling Revolution” at the World Economic Forum on January 24 in Davos.
While discussing a reskilling imperative alongside French Labor Minister Muriel Penicaud, he presented how the Korean government and KAIST are responding to the socio-economic transformation of workforces in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. After their presentation, Minister of Economy and Enterprise of Spain Nadia Calvirno Santamaria, Minister of Commerce and Industry of Oman Ali bin Masoud bin Ali Al Sunaidy, and Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas, Skill Development, and Entrepreneurship of India Dharmendra Pradhan shared their views on the course of decision making regarding the proactive practices and policies they have applied for closing the gaps from their countries’ perspectives.
President Shin presented how to upskill and reskill SMEs and startups, the real players who will jumpstart the economy in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He explained that the government is striving to change the existing structure of the economy, which is dominated by a few giant conglomerates. He added that the Korean government is trying to support SMEs and startups in terms of both funding and technology reskilling in order to rejuvenate the economy.
To better align itself with the government’s efforts, KAIST has introduced SME 4.0. SME 4.0 proposes to innovate the production process through the creation of a partnered platform between KAIST and SMEs across the country. With this platform, KAIST assists local SMEs for standardizing and systemizing all their processes of production, delivery, and management with enterprise resources planning (ERP) and manufacturing execution systems (MES). In addition, SME 4.0 offers retraining and re-tooling programs by linking the data generated through this platform in real time to better facilitate SMEs’ smart business.
(President Shin shakes hands with H.E.Mohammed Al-Tuwairi, Minister of Economy and Planning of Saudi Arabia before holding a bilaterla meeting in Davos.)
President Shin also explained about upskilling the leading corporations’ technological competitiveness, partnering with major leading corporations for upskilling their advanced technologies.
He also held a series of bilateral meetings with dignitaries attending the WEF annual meeting to discuss partnerships and collaborations. He also attended the Global University Leaders Forum (GULF), a community composed of 28 presidents from the world’s top universities on January 23. President Shin, who is on the advisory board of the Center for Fourth Industrial Revolution (C4IR), also participated in the board meeting and discussed the upcoming launching of the Korea C4IR, which will open at KAIST in March.
2019.01.28 View 8397 -
 A Novel Material for Transparent and Flexible Displays
(Research team led by Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry)
The next generation of flexible and transparent displays will require a high-performing and flexible polymeric material that has the optical and thermal properties of glass. The material must be transparent to visible light and have a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). Unfortunately, such a polymeric material has not been available. A KAIST research team has succeeded in making a new polymeric material with an exceptionally low CTE value while retaining high transparency and excellent thermal and mechanical properties. The method developed for amorphous polymers with a controlled CTE can be applied to control the thermal expansion of organic materials as well.
Most of objects expands upon heating and shrinks by cooling, and organic polymers have a relatively large CTE compared to that of ceramics or metals. Thin, light-weight planar substrates for semiconductor devices should have a similar CTE of ceramics. Otherwise, the device can be cracked due to the stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction. Therefore, matching the CTE of the semiconductor device and the substrate is crucial for successful manufacturing of display devices. Forming a network structure by connecting polymer chains is a well-known method of reducing the CTE of amorphous polymers. However, polymers with a network structure eventually lose their flexibility and becomes brittle.
As an alternative method, Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry and his team chose to adjust the distance and interaction between polymer chains. Thermal expansion and contraction of polymer films can be minimized by introducing interaction forces between the polymer chains and by arranging the direction of the force perpendicularly. The team successfully implemented this approach by appropriately designing the chemical structure of a transparent polymeric material. It is called poly (amide-imide) film, which is a transparent, flexible, and high-performing polymeric material. It is thermally stable enough to be used in the AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) fabrication process (stable at >400℃) with a low CTE (4ppm/℃).
The team made IGZO TFT (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Thin Film Transistor) devices on the newly synthesized transparent poly(amide-imide) film, and confirmed that the device could indeed operate normally even when it is folded down to a radius of 1mm.
Professor Kim said, “Our results suggest a way of controlling the thermal expansion of amorphous polymers similar to a level of glass without chemical cross-linking, which has long been regarded as a challenging problem. At the same time, we succeeded in making the polymer transparent and flexible. We expect that it can be applied to controlling the thermal expansion of various organic materials.”
This research, led by researchers Sun Dal Kim and Byungyoung Lee, was published in Science Advances on October 26. (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau1956v)
2019.01.24 View 7745
A Novel Material for Transparent and Flexible Displays
(Research team led by Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry)
The next generation of flexible and transparent displays will require a high-performing and flexible polymeric material that has the optical and thermal properties of glass. The material must be transparent to visible light and have a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE). Unfortunately, such a polymeric material has not been available. A KAIST research team has succeeded in making a new polymeric material with an exceptionally low CTE value while retaining high transparency and excellent thermal and mechanical properties. The method developed for amorphous polymers with a controlled CTE can be applied to control the thermal expansion of organic materials as well.
Most of objects expands upon heating and shrinks by cooling, and organic polymers have a relatively large CTE compared to that of ceramics or metals. Thin, light-weight planar substrates for semiconductor devices should have a similar CTE of ceramics. Otherwise, the device can be cracked due to the stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction. Therefore, matching the CTE of the semiconductor device and the substrate is crucial for successful manufacturing of display devices. Forming a network structure by connecting polymer chains is a well-known method of reducing the CTE of amorphous polymers. However, polymers with a network structure eventually lose their flexibility and becomes brittle.
As an alternative method, Professor Sang Youl Kim from the Department of Chemistry and his team chose to adjust the distance and interaction between polymer chains. Thermal expansion and contraction of polymer films can be minimized by introducing interaction forces between the polymer chains and by arranging the direction of the force perpendicularly. The team successfully implemented this approach by appropriately designing the chemical structure of a transparent polymeric material. It is called poly (amide-imide) film, which is a transparent, flexible, and high-performing polymeric material. It is thermally stable enough to be used in the AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) fabrication process (stable at >400℃) with a low CTE (4ppm/℃).
The team made IGZO TFT (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide Thin Film Transistor) devices on the newly synthesized transparent poly(amide-imide) film, and confirmed that the device could indeed operate normally even when it is folded down to a radius of 1mm.
Professor Kim said, “Our results suggest a way of controlling the thermal expansion of amorphous polymers similar to a level of glass without chemical cross-linking, which has long been regarded as a challenging problem. At the same time, we succeeded in making the polymer transparent and flexible. We expect that it can be applied to controlling the thermal expansion of various organic materials.”
This research, led by researchers Sun Dal Kim and Byungyoung Lee, was published in Science Advances on October 26. (DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aau1956v)
2019.01.24 View 7745 -
 A Comprehensive Metabolic Map for Bio-Based Chemicals Production
A KAIST research team completed a metabolic map that charts all available strategies and pathways of chemical reactions that lead to the production of various industrial bio-based chemicals.
The team was led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, who has produced high-quality metabolic engineering and systems engineering research for decades, and made the hallmark chemicals map after seven years of studies.
The team presented a very detailed analysis on metabolic engineering for the production of a wide range of industrial chemicals, fuels, and materials. Surveying the current trends in the bio-based production of chemicals in industrial biotechnology, the team thoroughly examined the current status of industrial chemicals produced using biological and/or chemical reactions.
This comprehensive map is expected to serve as a blueprint for the visual and intuitive inspection of biological and/or chemical reactions for the production of interest from renewable resources. The team also compiled an accompanying poster to visually present the synthetic pathways of chemicals in the context of their microbial metabolism.
As metabolic engineering has become increasing powerful in addressing limited fossil resources, climate change, and other environmental issues, the number of microbially produced chemicals using biomass as a carbon source has increased substantially. The sustainable production of industrial chemicals and materials has been explored with micro-organisms as cell factories and renewable nonfood biomass as raw materials for alternative petroleum. The engineering of these micro-organism has increasingly become more efficient and effective with the help of metabolic engineering – a practice of engineering using the metabolism of living organisms to produce a desired metabolite.
With the establishment of systems metabolic engineering – the integration of metabolic engineering with tools and strategies from systems biology, synthetic biology and evolutionary engineering – the speed at which micro-organisms are being engineered has reached an unparalleled pace.
In order to evaluate the current state at which metabolically engineered micro-organisms can produce a large portfolio of industrial chemicals, the team conducted an extensive review of the literature and mapped them out on a poster. This resulting poster, termed the bio-based chemicals map, presents synthetic pathways for industrial chemicals, which consist of biological and/or chemical reactions.
Industrial chemicals and their production routes are presented in the context of central carbon metabolic pathways as these key metabolites serve as precursors for the chemicals to be produced. The resulting biochemical map allows the detection and analysis of optimal synthetic pathways for a given industrial chemical. In addition to the poster, the authors have compiled a list of chemicals that have successfully been produced using micro-organisms and a list of the corresponding companies producing them commercially. This thorough review of the literature and the accompanying analytical summary will be an important resource for researchers interested in the production of chemicals from renewable biomass sources.
Metabolically engineered micro-organisms have already made a huge contribution toward the sustainable production of chemicals using renewable resources. Professor Lee said he wanted a detailed survey of the current state and capacity of bio-based chemicals production.
“We are so excited that this review and poster will expand further discussion on the production of important chemicals through engineered micro-organisms and also combined biological and chemical means in a more sustainable manner,” he explained.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biofineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
For further information, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST ( leesy@kaist.ac.kr , Tel: +82-42-350-3930)
Figure: Bio-based chemicals production through biological and chemical routes. This metabolic map describes representative chemicals that can be produced either by biological and/or chemical means. Red arrows represent chemical routes and blue arrows represent biological routes. Intermediate metabolites in the metabolism of a living organism can serve as a platform toward the production of industrially relevant chemicals. A more comprehensive map presented by the team can be found as a poster in the review.
2019.01.15 View 8393
A Comprehensive Metabolic Map for Bio-Based Chemicals Production
A KAIST research team completed a metabolic map that charts all available strategies and pathways of chemical reactions that lead to the production of various industrial bio-based chemicals.
The team was led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee, who has produced high-quality metabolic engineering and systems engineering research for decades, and made the hallmark chemicals map after seven years of studies.
The team presented a very detailed analysis on metabolic engineering for the production of a wide range of industrial chemicals, fuels, and materials. Surveying the current trends in the bio-based production of chemicals in industrial biotechnology, the team thoroughly examined the current status of industrial chemicals produced using biological and/or chemical reactions.
This comprehensive map is expected to serve as a blueprint for the visual and intuitive inspection of biological and/or chemical reactions for the production of interest from renewable resources. The team also compiled an accompanying poster to visually present the synthetic pathways of chemicals in the context of their microbial metabolism.
As metabolic engineering has become increasing powerful in addressing limited fossil resources, climate change, and other environmental issues, the number of microbially produced chemicals using biomass as a carbon source has increased substantially. The sustainable production of industrial chemicals and materials has been explored with micro-organisms as cell factories and renewable nonfood biomass as raw materials for alternative petroleum. The engineering of these micro-organism has increasingly become more efficient and effective with the help of metabolic engineering – a practice of engineering using the metabolism of living organisms to produce a desired metabolite.
With the establishment of systems metabolic engineering – the integration of metabolic engineering with tools and strategies from systems biology, synthetic biology and evolutionary engineering – the speed at which micro-organisms are being engineered has reached an unparalleled pace.
In order to evaluate the current state at which metabolically engineered micro-organisms can produce a large portfolio of industrial chemicals, the team conducted an extensive review of the literature and mapped them out on a poster. This resulting poster, termed the bio-based chemicals map, presents synthetic pathways for industrial chemicals, which consist of biological and/or chemical reactions.
Industrial chemicals and their production routes are presented in the context of central carbon metabolic pathways as these key metabolites serve as precursors for the chemicals to be produced. The resulting biochemical map allows the detection and analysis of optimal synthetic pathways for a given industrial chemical. In addition to the poster, the authors have compiled a list of chemicals that have successfully been produced using micro-organisms and a list of the corresponding companies producing them commercially. This thorough review of the literature and the accompanying analytical summary will be an important resource for researchers interested in the production of chemicals from renewable biomass sources.
Metabolically engineered micro-organisms have already made a huge contribution toward the sustainable production of chemicals using renewable resources. Professor Lee said he wanted a detailed survey of the current state and capacity of bio-based chemicals production.
“We are so excited that this review and poster will expand further discussion on the production of important chemicals through engineered micro-organisms and also combined biological and chemical means in a more sustainable manner,” he explained.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes on Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biofineries from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
For further information, Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST ( leesy@kaist.ac.kr , Tel: +82-42-350-3930)
Figure: Bio-based chemicals production through biological and chemical routes. This metabolic map describes representative chemicals that can be produced either by biological and/or chemical means. Red arrows represent chemical routes and blue arrows represent biological routes. Intermediate metabolites in the metabolism of a living organism can serve as a platform toward the production of industrially relevant chemicals. A more comprehensive map presented by the team can be found as a poster in the review.
2019.01.15 View 8393 -
 Fabrication of Shape-conformable Batteries with 3D-Printing
(from left: Dr. Bok Yeop Ahn, Dr. Chanhoon Kim, Professor Il-Doo Kim and Professor Jennifer A. Lewis)
Flexible, wireless electronic devices are rapidly emerging and have reached the level of commercialization; nevertheless, most of battery shapes are limited to either spherical and/or rectangular structures, which results in inefficient space use. Professor Il-Doo Kim’s team from the Department of Materials Science at KAIST has successfully developed technology to significantly enhance the variability of battery design through collaboration research with Professor Jennifer A. Lewis and her team from the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences at Harvard University.
Most of the battery shapes today are optimized for coin cell and/or pouch cells. Since the battery as an energy storage device occupies most of the space in microelectronic devices with different designs, new technology to freely change the shape of the battery is required.
The KAIST-Harvard research collaboration team has successfully manufactured various kinds of battery shapes, such as ring-type, H, and U shape, using 3D printing technology. And through the research collaboration with Dr. Youngmin Choi at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT), 3D-printed batteries were applied to small-scale wearable electronic devices (wearable light sensor rings).
The research group has adopted environmentally friendly aqueous Zn-ion batteries to make customized battery packs. This system, which uses Zn2+ instead of Li+ as charge carriers, is much safer compared with the conventional lithium rechargeable batteries that use highly inflammable organic electrolytes. Moreover, the processing conditions of lithium-ion batteries are very complicated because organic solvents can ignite upon exposure to moisture and oxygen.
As the aqueous Zn-ion batteries adopted by the research team are stable upon contact with atmospheric moisture and oxygen, they can be fabricated in the ambient air condition, and have advantages in packaging since packaged plastic does not dissolve in water even when plastic packaging is applied using a 3D printer.
To fabricate a stable cathode that can be modulated in various forms and allows high charge-discharge, the research team fabricated a carbon fiber current collector using electrospinning process and uniformly coated electrochemically active polyaniline conductive polymer on the surface of carbon fiber for a current collector-active layer integrated cathode. The cathode, based on conductive polyaniline consisting of a 3D structure, exhibits very fast charging speeds (50% of the charge in two minutes) and can be fabricated without the detachment of active cathode materials, so various battery forms with high mechanical stability can be manufactured.
Prof. Kim said, “Zn-ion batteries employing aqueous electrolytes have the advantage of fabrication under ambient conditions, so it is easy to fabricate the customized battery packs using 3D printing.”
“3D-printed batteries can be easily applied for niche applications such as wearable, personalized, miniaturized micro-robots, and implantable medical devices or microelectronic storage devices with unique designs,” added Professor Lewis.
With Dr. Chanhoon Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST and Dr. Bok Yeop Ahn School of Engineering and Applied Sciences at Harvard University participating as equally contributing first authors, this work was published in the December issue of ACS Nano.
This work was financially supported by the Global Research Laboratory (NRF-2015K1A1A2029679) and Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center (2016R1A5A1009926).
Figure 1.Fabrication of shape-conformable batteries based on 3D-printing technology and the application of polyaniline carbon nanofiber cathodes and wearable electronic devices
Figure 2.Fabricated shape-conformable batteries based on a 3D-printing method
Meanwhile, Professor Il-Doo Kim was recently appointed as an Associate Editor of ACS Nano, a highly renowned journal in the field of nanoscience.
Professor Kim said, “It is my great honor to be an Associate Editor of the highly renowned journal ACS Nano, which has an impact factor reaching 13.709 with 134,596 citations as of 2017. Through the editorial activities in the fields of energy, I will dedicate myself to improving the prominence of KAIST and expanding the scope of Korea’s science and technology. I will also contribute to carrying out more international collaborations with world-leading research groups.”
(Associate Editor of ACS Nano Professor Il-Doo Kim)
2018.12.20 View 12313
Fabrication of Shape-conformable Batteries with 3D-Printing
(from left: Dr. Bok Yeop Ahn, Dr. Chanhoon Kim, Professor Il-Doo Kim and Professor Jennifer A. Lewis)
Flexible, wireless electronic devices are rapidly emerging and have reached the level of commercialization; nevertheless, most of battery shapes are limited to either spherical and/or rectangular structures, which results in inefficient space use. Professor Il-Doo Kim’s team from the Department of Materials Science at KAIST has successfully developed technology to significantly enhance the variability of battery design through collaboration research with Professor Jennifer A. Lewis and her team from the School of Engineering and Applied Sciences at Harvard University.
Most of the battery shapes today are optimized for coin cell and/or pouch cells. Since the battery as an energy storage device occupies most of the space in microelectronic devices with different designs, new technology to freely change the shape of the battery is required.
The KAIST-Harvard research collaboration team has successfully manufactured various kinds of battery shapes, such as ring-type, H, and U shape, using 3D printing technology. And through the research collaboration with Dr. Youngmin Choi at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT), 3D-printed batteries were applied to small-scale wearable electronic devices (wearable light sensor rings).
The research group has adopted environmentally friendly aqueous Zn-ion batteries to make customized battery packs. This system, which uses Zn2+ instead of Li+ as charge carriers, is much safer compared with the conventional lithium rechargeable batteries that use highly inflammable organic electrolytes. Moreover, the processing conditions of lithium-ion batteries are very complicated because organic solvents can ignite upon exposure to moisture and oxygen.
As the aqueous Zn-ion batteries adopted by the research team are stable upon contact with atmospheric moisture and oxygen, they can be fabricated in the ambient air condition, and have advantages in packaging since packaged plastic does not dissolve in water even when plastic packaging is applied using a 3D printer.
To fabricate a stable cathode that can be modulated in various forms and allows high charge-discharge, the research team fabricated a carbon fiber current collector using electrospinning process and uniformly coated electrochemically active polyaniline conductive polymer on the surface of carbon fiber for a current collector-active layer integrated cathode. The cathode, based on conductive polyaniline consisting of a 3D structure, exhibits very fast charging speeds (50% of the charge in two minutes) and can be fabricated without the detachment of active cathode materials, so various battery forms with high mechanical stability can be manufactured.
Prof. Kim said, “Zn-ion batteries employing aqueous electrolytes have the advantage of fabrication under ambient conditions, so it is easy to fabricate the customized battery packs using 3D printing.”
“3D-printed batteries can be easily applied for niche applications such as wearable, personalized, miniaturized micro-robots, and implantable medical devices or microelectronic storage devices with unique designs,” added Professor Lewis.
With Dr. Chanhoon Kim in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST and Dr. Bok Yeop Ahn School of Engineering and Applied Sciences at Harvard University participating as equally contributing first authors, this work was published in the December issue of ACS Nano.
This work was financially supported by the Global Research Laboratory (NRF-2015K1A1A2029679) and Wearable Platform Materials Technology Center (2016R1A5A1009926).
Figure 1.Fabrication of shape-conformable batteries based on 3D-printing technology and the application of polyaniline carbon nanofiber cathodes and wearable electronic devices
Figure 2.Fabricated shape-conformable batteries based on a 3D-printing method
Meanwhile, Professor Il-Doo Kim was recently appointed as an Associate Editor of ACS Nano, a highly renowned journal in the field of nanoscience.
Professor Kim said, “It is my great honor to be an Associate Editor of the highly renowned journal ACS Nano, which has an impact factor reaching 13.709 with 134,596 citations as of 2017. Through the editorial activities in the fields of energy, I will dedicate myself to improving the prominence of KAIST and expanding the scope of Korea’s science and technology. I will also contribute to carrying out more international collaborations with world-leading research groups.”
(Associate Editor of ACS Nano Professor Il-Doo Kim)
2018.12.20 View 12313 -
 Optimal Immuno-Therapeutic Strategies for Liver Cancer
KAIST medical scientists have presented a heterogeneity of immune cell exhaustion in the cancer environment, providing evidence and rationale for designing optimal strategies for immune checkpoint inhibitors in liver cancer patients.
They succeeded in distinguishing the hepatocellular carcinoma group from the exhausted tumor infiltrating immune cell composition of liver cancer patients. The study, conducted in collaboration with Asan Medical Center, confirmed the applicability for liver cancer patients, providing a new path for personalized precision medicine as well as a new model for translational research.
Our immune system is able to destroy cancerous cells in our body, however sometimes cancer cells can adapt and mutate, effectively hiding from our immune system. One of the mechanisms that has evolved to prevent eradication by the immune system is to functionally silence effector T cells, termed T-cell exhaustion, that is mainly mediated by immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-1, TIM-3, and LAG-3.
Recent breakthroughs and encouraging clinical results with various immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and anti-CTLA-4 mAbs, have demonstrated tremendous potential to cure cancers through the immune activation of exhausted T cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors showed significant clinical benefits for several types of cancers, leading to their wide application in clinical practice.
Anti-PD1 blocking antibodies are one of the most representative agents in this class of drug. However, it has been challenging to precisely understand the biological and clinical significance of T-cell exhaustion in cancer. A KAIST research team led by Professor Su-Hyung Park reported the heterogeneity of T-cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its potential clinical implications in Gastroenterology on December 4.
The team revealed that heterogeneous T-cell exhaustion status is determined by the differential PD-1 expression levels in CD8+ T cells in liver cancer patients. The authors found that tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells with high PD-1 expression from liver cancer patients are functionally impaired and co-express other immune checkpoint receptors such as TIM-3 and/or LAG3, compared to those with low PD-1 expression.
Moreover, based on these results, the authors suggested that liver cancer patients can be classified into two distinct subgroups. Patients having high PD-1 expression levels in the tumor microenvironment showed more aggressive tumor features and biomarkers predicting a favorable response to anti-PD1 therapy. The research team also demonstrated that only liver cancer patients having high PD-1 expression are susceptible to combined immune checkpoint blockade-based therapies.
Prof. Park said, “The new classification of liver cancer patients identified by this study can be utilized as a biomarker to predict the response of current cancer immunotherapy targeting the PD-1 pathway.” He also said they will continue to conduct research on T-cell exhaustion and activation in various types of cancer, which could lead to a better understanding of T-cell response against cancer, thereby providing evidence for future cancer immunotherapy to achieve the ultimate goal to prolong the survival of cancer patients.
2018.12.18 View 6064
Optimal Immuno-Therapeutic Strategies for Liver Cancer
KAIST medical scientists have presented a heterogeneity of immune cell exhaustion in the cancer environment, providing evidence and rationale for designing optimal strategies for immune checkpoint inhibitors in liver cancer patients.
They succeeded in distinguishing the hepatocellular carcinoma group from the exhausted tumor infiltrating immune cell composition of liver cancer patients. The study, conducted in collaboration with Asan Medical Center, confirmed the applicability for liver cancer patients, providing a new path for personalized precision medicine as well as a new model for translational research.
Our immune system is able to destroy cancerous cells in our body, however sometimes cancer cells can adapt and mutate, effectively hiding from our immune system. One of the mechanisms that has evolved to prevent eradication by the immune system is to functionally silence effector T cells, termed T-cell exhaustion, that is mainly mediated by immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-1, TIM-3, and LAG-3.
Recent breakthroughs and encouraging clinical results with various immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and anti-CTLA-4 mAbs, have demonstrated tremendous potential to cure cancers through the immune activation of exhausted T cells. Immune checkpoint inhibitors showed significant clinical benefits for several types of cancers, leading to their wide application in clinical practice.
Anti-PD1 blocking antibodies are one of the most representative agents in this class of drug. However, it has been challenging to precisely understand the biological and clinical significance of T-cell exhaustion in cancer. A KAIST research team led by Professor Su-Hyung Park reported the heterogeneity of T-cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its potential clinical implications in Gastroenterology on December 4.
The team revealed that heterogeneous T-cell exhaustion status is determined by the differential PD-1 expression levels in CD8+ T cells in liver cancer patients. The authors found that tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells with high PD-1 expression from liver cancer patients are functionally impaired and co-express other immune checkpoint receptors such as TIM-3 and/or LAG3, compared to those with low PD-1 expression.
Moreover, based on these results, the authors suggested that liver cancer patients can be classified into two distinct subgroups. Patients having high PD-1 expression levels in the tumor microenvironment showed more aggressive tumor features and biomarkers predicting a favorable response to anti-PD1 therapy. The research team also demonstrated that only liver cancer patients having high PD-1 expression are susceptible to combined immune checkpoint blockade-based therapies.
Prof. Park said, “The new classification of liver cancer patients identified by this study can be utilized as a biomarker to predict the response of current cancer immunotherapy targeting the PD-1 pathway.” He also said they will continue to conduct research on T-cell exhaustion and activation in various types of cancer, which could lead to a better understanding of T-cell response against cancer, thereby providing evidence for future cancer immunotherapy to achieve the ultimate goal to prolong the survival of cancer patients.
2018.12.18 View 6064 -
 Professor Baik Awarded Sangsan Young Mathematician Prize
(Professor Hyungryul Baik)
Professor Hyungryul Baik from the Department of Mathematical Sciences was honored as the recipient of the 2018 Sangsan Prize for Young Mathematicians by the Korean Mathematical Society (KMS).
The Sangsan Prize recognizes young mathematicians who finished their degree within the previous five years and have begun an outstanding research career. Professor Baik was recognized for his studies in the fields of low-dimensional topology, geophysical mathematics, and geometric theory. In particular, his Ph.D. dissertation presented a new criterion that completely identifies the hyperbolic surface group, making an inference about the nature of the hyperbolic manifold group.
Recently, Professor Baik co-published a paper entitled Spaces of Invariant Circular Orders of Groups with Professor Eric Samperton at the University of California Santa Barbara in the renowned academic journal Groups, Geometry, and Dynamics in 2018.
Professor Baik earned his BS at KAIST and finished his MS and Ph.D. in mathematics in 2014 at Cornell University. He joined KAIST as a faculty member last year.
2018.10.30 View 8462
Professor Baik Awarded Sangsan Young Mathematician Prize
(Professor Hyungryul Baik)
Professor Hyungryul Baik from the Department of Mathematical Sciences was honored as the recipient of the 2018 Sangsan Prize for Young Mathematicians by the Korean Mathematical Society (KMS).
The Sangsan Prize recognizes young mathematicians who finished their degree within the previous five years and have begun an outstanding research career. Professor Baik was recognized for his studies in the fields of low-dimensional topology, geophysical mathematics, and geometric theory. In particular, his Ph.D. dissertation presented a new criterion that completely identifies the hyperbolic surface group, making an inference about the nature of the hyperbolic manifold group.
Recently, Professor Baik co-published a paper entitled Spaces of Invariant Circular Orders of Groups with Professor Eric Samperton at the University of California Santa Barbara in the renowned academic journal Groups, Geometry, and Dynamics in 2018.
Professor Baik earned his BS at KAIST and finished his MS and Ph.D. in mathematics in 2014 at Cornell University. He joined KAIST as a faculty member last year.
2018.10.30 View 8462 -
 Spray Coated Tactile Sensor on a 3-D Surface for Robotic Skin
Robots will be able to conduct a wide variety of tasks as well as humans if they can be given tactile sensing capabilities.
A KAIST research team has reported a stretchable pressure insensitive strain sensor by using an all solution-based process. The solution-based process is easily scalable to accommodate for large areas and can be coated as a thin-film on 3-dimensional irregularly shaped objects via spray coating. These conditions make their processing technique unique and highly suitable for robotic electronic skin or wearable electronic applications.
The making of electronic skin to mimic the tactile sensing properties of human skin is an active area of research for various applications such as wearable electronics, robotics, and prosthetics. One of the major challenges in electronic skin research is differentiating various external stimuli, particularly between strain and pressure. Another issue is uniformly depositing electrical skin on 3-dimensional irregularly shaped objects.
To overcome these issues, the research team led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Jung Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed electronic skin that can be uniformly coated on 3-dimensional surfaces and distinguish mechanical stimuli. The new electronic skin can also distinguish mechanical stimuli analogous to human skin. The structure of the electronic skin was designed to respond differently under applied pressure and strain. Under applied strain, conducting pathways undergo significant conformational changes, considerably changing the resistance. On the other hand, under applied pressure, negligible conformational change in the conducting pathway occurs; e-skin is therefore non-responsive to pressure. The research team is currently working on strain insensitive pressure sensors to use with the developed strain sensors.
The research team also spatially mapped the local strain without the use of patterned electrode arrays utilizing electrical impedance tomography (EIT). By using EIT, it is possible to minimize the number of electrodes, increase durability, and enable facile fabrication onto 3-dimensional surfaces.
Professor Park said, “Our electronic skin can be mass produced at a low cost and can easily be coated onto complex 3-dimensional surfaces. It is a key technology that can bring us closer to the commercialization of electronic skin for various applications in the near future.”
The result of this work entitled “Pressure Insensitive Strain Sensor with Facile Solution-based Process for Tactile Sensing Applications” was published in the August issue of ACS Nano as a cover article.
(Figure: Detecting mechanical stimuli using electrical impedance tomography.)
2018.09.21 View 9462
Spray Coated Tactile Sensor on a 3-D Surface for Robotic Skin
Robots will be able to conduct a wide variety of tasks as well as humans if they can be given tactile sensing capabilities.
A KAIST research team has reported a stretchable pressure insensitive strain sensor by using an all solution-based process. The solution-based process is easily scalable to accommodate for large areas and can be coated as a thin-film on 3-dimensional irregularly shaped objects via spray coating. These conditions make their processing technique unique and highly suitable for robotic electronic skin or wearable electronic applications.
The making of electronic skin to mimic the tactile sensing properties of human skin is an active area of research for various applications such as wearable electronics, robotics, and prosthetics. One of the major challenges in electronic skin research is differentiating various external stimuli, particularly between strain and pressure. Another issue is uniformly depositing electrical skin on 3-dimensional irregularly shaped objects.
To overcome these issues, the research team led by Professor Steve Park from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Jung Kim from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed electronic skin that can be uniformly coated on 3-dimensional surfaces and distinguish mechanical stimuli. The new electronic skin can also distinguish mechanical stimuli analogous to human skin. The structure of the electronic skin was designed to respond differently under applied pressure and strain. Under applied strain, conducting pathways undergo significant conformational changes, considerably changing the resistance. On the other hand, under applied pressure, negligible conformational change in the conducting pathway occurs; e-skin is therefore non-responsive to pressure. The research team is currently working on strain insensitive pressure sensors to use with the developed strain sensors.
The research team also spatially mapped the local strain without the use of patterned electrode arrays utilizing electrical impedance tomography (EIT). By using EIT, it is possible to minimize the number of electrodes, increase durability, and enable facile fabrication onto 3-dimensional surfaces.
Professor Park said, “Our electronic skin can be mass produced at a low cost and can easily be coated onto complex 3-dimensional surfaces. It is a key technology that can bring us closer to the commercialization of electronic skin for various applications in the near future.”
The result of this work entitled “Pressure Insensitive Strain Sensor with Facile Solution-based Process for Tactile Sensing Applications” was published in the August issue of ACS Nano as a cover article.
(Figure: Detecting mechanical stimuli using electrical impedance tomography.)
2018.09.21 View 9462