School+of+Computing
-
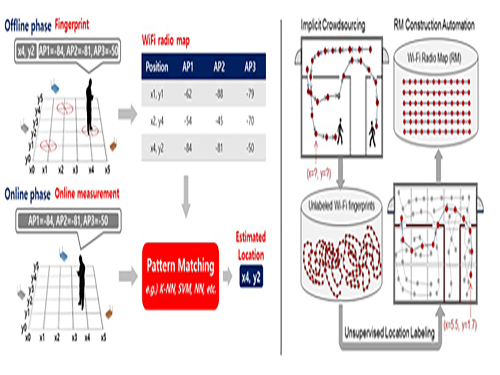 Crowdsourcing-Based Global Indoor Positioning System
Research team of Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing Intelligent Service Lab at KAIST developed a system for providing global indoor localization using Wi-Fi signals. The technology uses numerous smartphones to collect fingerprints of location data and label them automatically, significantly reducing the cost of constructing an indoor localization system while maintaining high accuracy.
The method can be used in any building in the world, provided the floor plan is available and there are Wi-Fi fingerprints to collect. To accurately collect and label the location information of the Wi-Fi fingerprints, the research team analyzed indoor space utilization. This led to technology that classified indoor spaces into places used for stationary tasks (resting spaces) and spaces used to reach said places (transient spaces), and utilized separate algorithms to optimally and automatically collect location labelling data.
Years ago, the team implemented a way to automatically label resting space locations from signals collected in various contexts such as homes, shops, and offices via the users’ home or office address information. The latest method allows for the automatic labelling of transient space locations such as hallways, lobbies, and stairs using unsupervised learning, without any additional location information. Testing in KAIST’s N5 building and the 7th floor of N1 building manifested the technology is capable of accuracy up to three or four meters given enough training data. The accuracy level is comparable to technology using manually-labeled location information.
Google, Microsoft, and other multinational corporations collected tens of thousands of floor plans for their indoor localization projects. Indoor radio map construction was also attempted by the firms but proved more difficult. As a result, existing indoor localization services were often plagued by inaccuracies. In Korea, COEX, Lotte World Tower, and other landmarks provide comparatively accurate indoor localization, but most buildings suffer from the lack of radio maps, preventing indoor localization services.
Professor Han said, “This technology allows the easy deployment of highly accurate indoor localization systems in any building in the world. In the near future, most indoor spaces will be able to provide localization services, just like outdoor spaces.” He further added that smartphone-collected Wi-Fi fingerprints have been unutilized and often discarded, but now they should be treated as invaluable resources, which create a new big data field of Wi-Fi fingerprints. This new indoor navigation technology is likely to be valuable to Google, Apple, or other global firms providing indoor positioning services globally. The technology will also be valuable for helping domestic firms provide positioning services.
Professor Han added that “the new global indoor localization system deployment technology will be added to KAILOS, KAIST’s indoor localization system.” KAILOS was released in 2014 as KAIST’s open platform for indoor localization service, allowing anyone in the world to add floor plans to KAILOS, and collect the building’s Wi-Fi fingerprints for a universal indoor localization service. As localization accuracy improves in indoor environments, despite the absence of GPS signals, applications such as location-based SNS, location-based IoT, and location-based O2O are expected to take off, leading to various improvements in convenience and safety. Integrated indoor-outdoor navigation services are also visible on the horizon, fusing vehicular navigation technology with indoor navigation.
Professor Han’s research was published in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) in November in 2016.
For more, please visit http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=7349230http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7805133/
2017.04.06 View 11120
Crowdsourcing-Based Global Indoor Positioning System
Research team of Professor Dong-Soo Han of the School of Computing Intelligent Service Lab at KAIST developed a system for providing global indoor localization using Wi-Fi signals. The technology uses numerous smartphones to collect fingerprints of location data and label them automatically, significantly reducing the cost of constructing an indoor localization system while maintaining high accuracy.
The method can be used in any building in the world, provided the floor plan is available and there are Wi-Fi fingerprints to collect. To accurately collect and label the location information of the Wi-Fi fingerprints, the research team analyzed indoor space utilization. This led to technology that classified indoor spaces into places used for stationary tasks (resting spaces) and spaces used to reach said places (transient spaces), and utilized separate algorithms to optimally and automatically collect location labelling data.
Years ago, the team implemented a way to automatically label resting space locations from signals collected in various contexts such as homes, shops, and offices via the users’ home or office address information. The latest method allows for the automatic labelling of transient space locations such as hallways, lobbies, and stairs using unsupervised learning, without any additional location information. Testing in KAIST’s N5 building and the 7th floor of N1 building manifested the technology is capable of accuracy up to three or four meters given enough training data. The accuracy level is comparable to technology using manually-labeled location information.
Google, Microsoft, and other multinational corporations collected tens of thousands of floor plans for their indoor localization projects. Indoor radio map construction was also attempted by the firms but proved more difficult. As a result, existing indoor localization services were often plagued by inaccuracies. In Korea, COEX, Lotte World Tower, and other landmarks provide comparatively accurate indoor localization, but most buildings suffer from the lack of radio maps, preventing indoor localization services.
Professor Han said, “This technology allows the easy deployment of highly accurate indoor localization systems in any building in the world. In the near future, most indoor spaces will be able to provide localization services, just like outdoor spaces.” He further added that smartphone-collected Wi-Fi fingerprints have been unutilized and often discarded, but now they should be treated as invaluable resources, which create a new big data field of Wi-Fi fingerprints. This new indoor navigation technology is likely to be valuable to Google, Apple, or other global firms providing indoor positioning services globally. The technology will also be valuable for helping domestic firms provide positioning services.
Professor Han added that “the new global indoor localization system deployment technology will be added to KAILOS, KAIST’s indoor localization system.” KAILOS was released in 2014 as KAIST’s open platform for indoor localization service, allowing anyone in the world to add floor plans to KAILOS, and collect the building’s Wi-Fi fingerprints for a universal indoor localization service. As localization accuracy improves in indoor environments, despite the absence of GPS signals, applications such as location-based SNS, location-based IoT, and location-based O2O are expected to take off, leading to various improvements in convenience and safety. Integrated indoor-outdoor navigation services are also visible on the horizon, fusing vehicular navigation technology with indoor navigation.
Professor Han’s research was published in IEEE Transactions on Mobile Computing (TMC) in November in 2016.
For more, please visit http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/stamp/stamp.jsp?arnumber=7349230http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/7805133/
2017.04.06 View 11120 -
 KAIST and Oberthur Technologies Agree for Research and Development in Mobile Security
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the School of Computing at KAIST has signed a research and development (R&D) agreement with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (OT), a French security solutions firm, on September 18, 2015 in Paris.
Under the agreement, KAIST and OT will conduct joint research on mobile security as well as implement an internship program for KAIST graduate students to work either at OT’s R&D center in Korea or in France.
OT has established a research center in Korea in July 2014, which was the fourth of its research centers in Asia.
Professor Kim said, “Our goal at KAIST is to cultivate top-level security experts in security technologies. By partnering with such a leader in security technologies as OT, we know that we will both help shape tomorrow’s security solution for the IoT (Internet of Things) space.”
In the picture, Professor Kwangjo Kim (left) shakes hands with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (right), after the signing of a memorandum of understanding.
2015.09.24 View 9185
KAIST and Oberthur Technologies Agree for Research and Development in Mobile Security
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the School of Computing at KAIST has signed a research and development (R&D) agreement with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (OT), a French security solutions firm, on September 18, 2015 in Paris.
Under the agreement, KAIST and OT will conduct joint research on mobile security as well as implement an internship program for KAIST graduate students to work either at OT’s R&D center in Korea or in France.
OT has established a research center in Korea in July 2014, which was the fourth of its research centers in Asia.
Professor Kim said, “Our goal at KAIST is to cultivate top-level security experts in security technologies. By partnering with such a leader in security technologies as OT, we know that we will both help shape tomorrow’s security solution for the IoT (Internet of Things) space.”
In the picture, Professor Kwangjo Kim (left) shakes hands with Marc Bertin, the Chief Technology Officer of Oberthur Technologies (right), after the signing of a memorandum of understanding.
2015.09.24 View 9185 -
 KAIST and the Naver Corporation Agree to Cooperate in Computer Science
KAIST and Naver, a Korean Internet corporation, concluded a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on April 17, 2015, to cooperate in advancing research and education in computer science.
Doo-Hwan Bae (pictured on the right below), the Dean of School of Computing at KAIST and Jong-Mok Park (pictured on left), the Director of Technical Cooperation at Naver, signed the MOU.
Under this agreement, the two organizations will foster computer scientists and engineers, conduct joint research projects, and develop training programs for entrepreneurs.
KAIST and Naver will organize a steering committee to lay out further details on the agreement.
2015.04.17 View 10015
KAIST and the Naver Corporation Agree to Cooperate in Computer Science
KAIST and Naver, a Korean Internet corporation, concluded a memorandum of understanding (MOU) on April 17, 2015, to cooperate in advancing research and education in computer science.
Doo-Hwan Bae (pictured on the right below), the Dean of School of Computing at KAIST and Jong-Mok Park (pictured on left), the Director of Technical Cooperation at Naver, signed the MOU.
Under this agreement, the two organizations will foster computer scientists and engineers, conduct joint research projects, and develop training programs for entrepreneurs.
KAIST and Naver will organize a steering committee to lay out further details on the agreement.
2015.04.17 View 10015 -
 Household Scale Indoor Position Tracking Technology Developed
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situation or aid in the finding of a lost smartphone.
Professor Han Dong Soo (Department of Computer Sciences) and his research team has developed the technology that enables tracking a smartphone’s location indoors using wireless LAN signals accurate to 10 meters.
Because the technology utilizes wireless LAN signals and the address of smartphone users, the technology can be implemented for a low cost all over the world.
Conventionally the location of a lost smartphone can be found through a telecommunications company. However the location found using the base station is only accurate to 500m~700m and therefore reclaiming lost smartphones is nearly impossible.
In addition, there have been unfortunate events where the kidnapped victim called the police but was murdered due to the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
The newly developed technology by Professor Han’s team remedies the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
Professor Han’s team collected wireless LAN data recorded in the smartphones for a week to analyze the patterns to distinguish patterns between signals recorded in the workplace and in the household.
The stability and accuracy of the technology was verified over a period of five months in various locations across Korea with varying population densities.
The result was when the total amount of data collected passes 50% of the number of households, the technology show accuracy to 10 meters. The result showed that the new technology can track the location of the smartphone to 10 meters on a household scale. In addition it was possible to distinguish which floor the smartphone was located.
The technology is anticipated to improve smartphone positioning. However caution needs to be practiced as the technology requires the address of the user’s workplace and home.
2012.12.21 View 9402
Household Scale Indoor Position Tracking Technology Developed
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situation or aid in the finding of a lost smartphone.
Professor Han Dong Soo (Department of Computer Sciences) and his research team has developed the technology that enables tracking a smartphone’s location indoors using wireless LAN signals accurate to 10 meters.
Because the technology utilizes wireless LAN signals and the address of smartphone users, the technology can be implemented for a low cost all over the world.
Conventionally the location of a lost smartphone can be found through a telecommunications company. However the location found using the base station is only accurate to 500m~700m and therefore reclaiming lost smartphones is nearly impossible.
In addition, there have been unfortunate events where the kidnapped victim called the police but was murdered due to the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
The newly developed technology by Professor Han’s team remedies the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
Professor Han’s team collected wireless LAN data recorded in the smartphones for a week to analyze the patterns to distinguish patterns between signals recorded in the workplace and in the household.
The stability and accuracy of the technology was verified over a period of five months in various locations across Korea with varying population densities.
The result was when the total amount of data collected passes 50% of the number of households, the technology show accuracy to 10 meters. The result showed that the new technology can track the location of the smartphone to 10 meters on a household scale. In addition it was possible to distinguish which floor the smartphone was located.
The technology is anticipated to improve smartphone positioning. However caution needs to be practiced as the technology requires the address of the user’s workplace and home.
2012.12.21 View 9402 -
 Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situ
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situation or aid in the finding of a lost smartphone.
Professor Han Dong Soo (Department of Computer Sciences) and his research team has developed the technology that enables tracking a smartphone’s location indoors using wireless LAN signals accurate to 10 meters.
Because the technology utilizes wireless LAN signals and the address of smartphone users, the technology can be implemented for a low cost all over the world.
Conventionally the location of a lost smartphone can be found through a telecommunications company. However the location found using the base station is only accurate to 500m~700m and therefore reclaiming lost smartphones is nearly impossible.
In addition, there have been unfortunate events where the kidnapped victim called the police but was murdered due to the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
The newly developed technology by Professor Han’s team remedies the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
Professor Han’s team collected wireless LAN data recorded in the smartphones for a week to analyze the patterns to distinguish patterns between signals recorded in the workplace and in the household.
The stability and accuracy of the technology was verified over a period of five months in various locations across Korea with varying population densities.
The result was when the total amount of data collected passes 50% of the number of households, the technology show accuracy to 10 meters. The result showed that the new technology can track the location of the smartphone to 10 meters on a household scale. In addition it was possible to distinguish which floor the smartphone was located.
The technology is anticipated to improve smartphone positioning. However caution needs to be practiced as the technology requires the address of the user’s workplace and home.
2012.12.21 View 10201
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situ
Technology that will allow household scale position tracking of smartphones indoors, where GPS signals do not reach, has been developed. It is anticipated that the newly developed technology will enable the tracking of persons indoors in an emergency situation or aid in the finding of a lost smartphone.
Professor Han Dong Soo (Department of Computer Sciences) and his research team has developed the technology that enables tracking a smartphone’s location indoors using wireless LAN signals accurate to 10 meters.
Because the technology utilizes wireless LAN signals and the address of smartphone users, the technology can be implemented for a low cost all over the world.
Conventionally the location of a lost smartphone can be found through a telecommunications company. However the location found using the base station is only accurate to 500m~700m and therefore reclaiming lost smartphones is nearly impossible.
In addition, there have been unfortunate events where the kidnapped victim called the police but was murdered due to the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
The newly developed technology by Professor Han’s team remedies the inaccuracy of smartphone location tracking.
Professor Han’s team collected wireless LAN data recorded in the smartphones for a week to analyze the patterns to distinguish patterns between signals recorded in the workplace and in the household.
The stability and accuracy of the technology was verified over a period of five months in various locations across Korea with varying population densities.
The result was when the total amount of data collected passes 50% of the number of households, the technology show accuracy to 10 meters. The result showed that the new technology can track the location of the smartphone to 10 meters on a household scale. In addition it was possible to distinguish which floor the smartphone was located.
The technology is anticipated to improve smartphone positioning. However caution needs to be practiced as the technology requires the address of the user’s workplace and home.
2012.12.21 View 10201