EC
-
 KAIST perfectly reproduces Joseon-era Irworobongdo without pigments
Typically, chemical pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum are required to produce colors. However, KAIST researchers have successfully reproduced the Joseon-era Irworobongdo [일월오봉도] painting using ultra-precise color graphics without any chemical pigments, allowing for the permanent and eco-friendly preservation of color graphics without fading or discoloration.
< (From left) Chaerim Son, a graduate of the Department of Biochemical Engineering (lead author), Seong Kyeong Nam, a graduate of the PhD program, Jiwoo Lee, a PhD student, and Professor Shin-Hyun Kim >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th of February that a research team led by Professor Shinhyun Kim from the Department of Biological and Chemical Engineering had developed a technology that enables high-resolution color graphics without using any chemical pigments by employing hemisphere-shaped microstructures.
Morpho butterflies that are brilliant blue in color or Panther chameleons that change skin color exhibit coloration without chemical pigments, as ordered nanostructures within a material reflect visible light through optical interference. Since structural colors arise from physical structures rather than chemical substances, a single material can produce a wide range of colors.
However, the artificial implementation of structural coloration is highly challenging due to the complexity of creating ordered nanostructures. Additionally, it is difficult to produce a variety of colors and to pattern them precisely into complex designs.
< Figure 1. Principle of structural color expression using micro-hemispheres (left) and method of forming micro-hemisphere patterns based on photolithography (right) >
Professor Kim’s team overcame these challenges by using smooth-surfaced hemispherical microstructures instead of ordered nanostructures, enabling the high-precision patterning of diverse structural colors.
When light enters the inverted hemispherical microstructures, the portion of light entering from the sides undergoes total internal reflection along the curved surface, creating retroreflection. When the hemisphere diameter is approximately 10 micrometers (about one-tenth the thickness of a human hair), light traveling along different reflection paths interferes within the visible spectrum, producing structural coloration.
< Figure 2. “Irworobongdo”, the Painting of the Sun, Moon, and the Five Peaks, reproduced in fingernail size without pigment using approximately 200,000 micro-hemispheres >
The structural color can be tuned by adjusting the size of the hemispheres. By arranging hemispheres of varying sizes, much like mixing paints on a palette, an infinite range of colors can be generated.
To precisely pattern microscale hemispheres of different sizes, the research team employed photolithography* using positive photoresists** commonly used in semiconductor processing. They first patterned photoresists into micropillar structures, then induced reflow*** by heating the material, forming hemispherical microstructures.
*Photolithography: A technique used in semiconductor fabrication to pattern microscale structures.
**Positive photoresist: A photosensitive polymer that dissolves more easily in a developer solution after exposure to ultraviolet light.
***Reflow: A process in which a polymer material softens and reshapes into a curved structure when heated.
This method enables the formation of hemisphere-shaped microstructures with the desired sizes and colors in a single-step fabrication process. It also allows for the reproduction of arbitrary color graphics using a single material without any pigments.
The ultra-precise color graphics created with this technique can exhibit color variations depending on the angle of incident light or the viewing perspective. The pattern appears colored from one direction while remaining transparent from the opposite side, exhibiting a Janus effect. These structural color graphics achieve resolution comparable to cutting-edge LED displays, allowing complex color images to be captured within a fingernail-sized area and projected onto large screens.
< Figure 3. “Irworobongdo” that displays different shades depending on the angle of light and viewing direction >
Professor Shinhyun Kim, who led the research, stated, “Our newly developed pigment-free color graphics technology can serve as an innovative method for artistic expression, merging art with advanced materials. Additionally, it holds broad application potential in optical devices and sensors, anti-counterfeiting materials, aesthetic photocard printing, and many other fields.”
This research, with KAIST researcher Chaerim Son as the first author, was published in the prestigious materials science journal Advanced Materials on February 5.
(Paper title: “Retroreflective Multichrome Microdome Arrays Created by Single-Step Reflow”, DOI: 10.1002/adma.202413143 )
< Figure 4. Famous paintings reproduced without pigment: “Impression, Sunrise” (left), “Girl with a Pearl Earring” (right) >
The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Pioneer Converging Technology R&D Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program.
2025.02.26 View 1882
KAIST perfectly reproduces Joseon-era Irworobongdo without pigments
Typically, chemical pigments that absorb specific wavelengths of light within the visible spectrum are required to produce colors. However, KAIST researchers have successfully reproduced the Joseon-era Irworobongdo [일월오봉도] painting using ultra-precise color graphics without any chemical pigments, allowing for the permanent and eco-friendly preservation of color graphics without fading or discoloration.
< (From left) Chaerim Son, a graduate of the Department of Biochemical Engineering (lead author), Seong Kyeong Nam, a graduate of the PhD program, Jiwoo Lee, a PhD student, and Professor Shin-Hyun Kim >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 26th of February that a research team led by Professor Shinhyun Kim from the Department of Biological and Chemical Engineering had developed a technology that enables high-resolution color graphics without using any chemical pigments by employing hemisphere-shaped microstructures.
Morpho butterflies that are brilliant blue in color or Panther chameleons that change skin color exhibit coloration without chemical pigments, as ordered nanostructures within a material reflect visible light through optical interference. Since structural colors arise from physical structures rather than chemical substances, a single material can produce a wide range of colors.
However, the artificial implementation of structural coloration is highly challenging due to the complexity of creating ordered nanostructures. Additionally, it is difficult to produce a variety of colors and to pattern them precisely into complex designs.
< Figure 1. Principle of structural color expression using micro-hemispheres (left) and method of forming micro-hemisphere patterns based on photolithography (right) >
Professor Kim’s team overcame these challenges by using smooth-surfaced hemispherical microstructures instead of ordered nanostructures, enabling the high-precision patterning of diverse structural colors.
When light enters the inverted hemispherical microstructures, the portion of light entering from the sides undergoes total internal reflection along the curved surface, creating retroreflection. When the hemisphere diameter is approximately 10 micrometers (about one-tenth the thickness of a human hair), light traveling along different reflection paths interferes within the visible spectrum, producing structural coloration.
< Figure 2. “Irworobongdo”, the Painting of the Sun, Moon, and the Five Peaks, reproduced in fingernail size without pigment using approximately 200,000 micro-hemispheres >
The structural color can be tuned by adjusting the size of the hemispheres. By arranging hemispheres of varying sizes, much like mixing paints on a palette, an infinite range of colors can be generated.
To precisely pattern microscale hemispheres of different sizes, the research team employed photolithography* using positive photoresists** commonly used in semiconductor processing. They first patterned photoresists into micropillar structures, then induced reflow*** by heating the material, forming hemispherical microstructures.
*Photolithography: A technique used in semiconductor fabrication to pattern microscale structures.
**Positive photoresist: A photosensitive polymer that dissolves more easily in a developer solution after exposure to ultraviolet light.
***Reflow: A process in which a polymer material softens and reshapes into a curved structure when heated.
This method enables the formation of hemisphere-shaped microstructures with the desired sizes and colors in a single-step fabrication process. It also allows for the reproduction of arbitrary color graphics using a single material without any pigments.
The ultra-precise color graphics created with this technique can exhibit color variations depending on the angle of incident light or the viewing perspective. The pattern appears colored from one direction while remaining transparent from the opposite side, exhibiting a Janus effect. These structural color graphics achieve resolution comparable to cutting-edge LED displays, allowing complex color images to be captured within a fingernail-sized area and projected onto large screens.
< Figure 3. “Irworobongdo” that displays different shades depending on the angle of light and viewing direction >
Professor Shinhyun Kim, who led the research, stated, “Our newly developed pigment-free color graphics technology can serve as an innovative method for artistic expression, merging art with advanced materials. Additionally, it holds broad application potential in optical devices and sensors, anti-counterfeiting materials, aesthetic photocard printing, and many other fields.”
This research, with KAIST researcher Chaerim Son as the first author, was published in the prestigious materials science journal Advanced Materials on February 5.
(Paper title: “Retroreflective Multichrome Microdome Arrays Created by Single-Step Reflow”, DOI: 10.1002/adma.202413143 )
< Figure 4. Famous paintings reproduced without pigment: “Impression, Sunrise” (left), “Girl with a Pearl Earring” (right) >
The study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Pioneer Converging Technology R&D Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program.
2025.02.26 View 1882 -
 KAIST achieves quantum entanglement essential for quantum error correction
Quantum computing is a technology capable of solving complex problems that classical computers struggle with. To perform accurate computations, quantum computers must correct errors that arise during operations. However, generating the quantum entanglement necessary for quantum error correction has long been considered a major challenge.
< Photo 1. (From left) Students Young-Do Yoon and Chan Roh of the Master's and Doctoral Integrated Program of the Department of Physics poses with Professor Young-Sik Ra and Student Geunhee Gwak of the same program >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of February that a research team led by Professor Young-Sik Ra from the Department of Physics has successfully implemented a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state, a key component for quantum error correction, through experimental demonstration.
Measurement-based quantum computing is an emerging paradigm that implements quantum computations by measuring specially entangled cluster states. The core of this approach lies in the generation of these cluster quantum entangled states, with two-dimensional cluster states commonly used for universal quantum computing.
However, to advance towards fault-tolerant quantum computing, which can correct quantum errors occurring during computations, a more complex three-dimensional cluster state is required. While previous studies have reported the generation of two-dimensional cluster states, experimental implementation of the three-dimensional cluster states necessary for fault-tolerant quantum computing had remained elusive due to the extreme complexity of their entanglement structure.
< Figure 1. (a) Experimental schematic. A pulse laser with a wavelength of 800 nm is converted into a pulse laser with a wavelength of 400 nm through second harmonic generation, and this is incident on a nonlinear crystal (PPKTP) to generate multiple quantum entanglement sources. (b) Generation of a 3D cluster state through optical mode basis change >
The research team overcame this challenge by developing a technique to control femtosecond time-frequency modes, successfully generating a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state for the first time.
The team directed a femtosecond laser into a nonlinear crystal, simultaneously generating quantum light sources across multiple frequency modes. (A femtosecond laser is a device that emits ultrashort, high-intensity light pulses.) Using this approach, they successfully created a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state.
Professor Young-Sik Ra noted, “This study marks the first successful demonstration of a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state, which was previously difficult to achieve with existing technology. This breakthrough is expected to serve as a crucial stepping stone for future research in measurement-based and fault-tolerant quantum computing.”
< Figure 2. Results of 3D cluster state generation. (a) Nullifier measurement of the cluster state. (b) 3D cluster state reconstructed using quantum state tomography. (c) Confirmation of quantum entanglement characteristics of the 3D cluster state >
The study was published online in Nature Photonics on February 24, 2025. The first author is Chan Roh, a Ph.D. candidate in KAIST’s integrated master’s and doctoral program, with Geunhee Gwak and Youngdo Yoon contributing as co-authors. (Paper title: “Generation of Three-Dimensional Cluster Entangled State”, DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01631-2)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Quantum Computing Technology Development Program, Mid-Career Researcher Support Program, and Quantum Simulator for Materials Innovation Program), the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (Quantum Internet Core Technology Program, University ICT Research Center Support Program), and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory.
2025.02.25 View 1172
KAIST achieves quantum entanglement essential for quantum error correction
Quantum computing is a technology capable of solving complex problems that classical computers struggle with. To perform accurate computations, quantum computers must correct errors that arise during operations. However, generating the quantum entanglement necessary for quantum error correction has long been considered a major challenge.
< Photo 1. (From left) Students Young-Do Yoon and Chan Roh of the Master's and Doctoral Integrated Program of the Department of Physics poses with Professor Young-Sik Ra and Student Geunhee Gwak of the same program >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of February that a research team led by Professor Young-Sik Ra from the Department of Physics has successfully implemented a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state, a key component for quantum error correction, through experimental demonstration.
Measurement-based quantum computing is an emerging paradigm that implements quantum computations by measuring specially entangled cluster states. The core of this approach lies in the generation of these cluster quantum entangled states, with two-dimensional cluster states commonly used for universal quantum computing.
However, to advance towards fault-tolerant quantum computing, which can correct quantum errors occurring during computations, a more complex three-dimensional cluster state is required. While previous studies have reported the generation of two-dimensional cluster states, experimental implementation of the three-dimensional cluster states necessary for fault-tolerant quantum computing had remained elusive due to the extreme complexity of their entanglement structure.
< Figure 1. (a) Experimental schematic. A pulse laser with a wavelength of 800 nm is converted into a pulse laser with a wavelength of 400 nm through second harmonic generation, and this is incident on a nonlinear crystal (PPKTP) to generate multiple quantum entanglement sources. (b) Generation of a 3D cluster state through optical mode basis change >
The research team overcame this challenge by developing a technique to control femtosecond time-frequency modes, successfully generating a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state for the first time.
The team directed a femtosecond laser into a nonlinear crystal, simultaneously generating quantum light sources across multiple frequency modes. (A femtosecond laser is a device that emits ultrashort, high-intensity light pulses.) Using this approach, they successfully created a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state.
Professor Young-Sik Ra noted, “This study marks the first successful demonstration of a three-dimensional cluster quantum entangled state, which was previously difficult to achieve with existing technology. This breakthrough is expected to serve as a crucial stepping stone for future research in measurement-based and fault-tolerant quantum computing.”
< Figure 2. Results of 3D cluster state generation. (a) Nullifier measurement of the cluster state. (b) 3D cluster state reconstructed using quantum state tomography. (c) Confirmation of quantum entanglement characteristics of the 3D cluster state >
The study was published online in Nature Photonics on February 24, 2025. The first author is Chan Roh, a Ph.D. candidate in KAIST’s integrated master’s and doctoral program, with Geunhee Gwak and Youngdo Yoon contributing as co-authors. (Paper title: “Generation of Three-Dimensional Cluster Entangled State”, DOI: 10.1038/s41566-025-01631-2)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (Quantum Computing Technology Development Program, Mid-Career Researcher Support Program, and Quantum Simulator for Materials Innovation Program), the Institute for Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (Quantum Internet Core Technology Program, University ICT Research Center Support Program), and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory.
2025.02.25 View 1172 -
 KAIST develops a new, bone-like material that strengthens with use in collaboration with GIT
Materials used in apartment buildings, vehicles, and other structures deteriorate over time under repeated loads, leading to failure and breakage. A joint research team from Korea and the United States has successfully developed a bioinspired material that becomes stronger with use, taking inspiration from the way bones synthesize minerals from bodily fluids under stress, increasing bone density.
< (From left) Professor Sung Hoon Kang of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University Ph.D. candidates Bohan Sun and Grant Kitchen, Professor Yuhang Hu and Ph.D. candidate Dongjung He of Georgia Institute of Technology >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of February that a research team led by Professor Sung Hoon Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Johns Hopkins University and the Georgia Institute of Technology, had developed a new material that strengthens with repeated use, similar to how bones become stronger with exercise.
Professor Kang’s team sought to address the issue of conventional materials degrading with repeated use. Inspired by the biological process where stress triggers cells to form minerals that strengthen bones, the team developed a material that synthesizes minerals under stress without relying on cellular activity. This innovation is expected to enable applications in a variety of fields.
To replace the function of cells, the research team created a porous piezoelectric substrate that converts mechanical force into electricity and actually generates more charge under greater force. They then synthesized a composite material by infusing it with an electrolyte containing mineral components similar to those in blood.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the biomimetic concept based on bone and pitcher plants, the reversible strengthening mechanism, the process of fabricating porous composites, the mechanical property changes with increasing stiffness and energy dissipation after cyclic loading, and the reprogrammable self-folding mechanism and applications >
After subjecting the material to periodic forces and measuring changes in its properties, they observed that its stiffness increased proportionally with the frequency and magnitude of stress and that its energy dissipation capability improved.
The reason for such properties was found to be due to minerals forming inside the porous material under repeated stress, as observed through micro-CT imaging of its internal structure. When subjected to large forces, these minerals fractured and dissipated energy, only to reform under further cyclic stress.
Unlike conventional materials that weaken with repeated use, this new material simultaneously enhances stiffness and impact absorption over time.
< Figure 2. Comparison of the changes in properties of the newly developed new material (LIPPS) with other materials under cyclic loading. (A) Graph showing the relative change rate of energy dissipation after cyclic loading and the relative change rate of elastic modulus upon unloading. LIPPS is in a new area that existing materials have not reached, and shows the characteristics of simultaneous increases in elastic modulus and energy dissipation. (B) Graph comparing the performance of LIPPS with current state-of-the-art mechanically adaptive materials. (Left) The maximum property change rate compared to the baseline after cyclic loading, LIPPS shows much higher changes in elastic modulus, dissipated energy density and ratio, toughness (impact resistance), and stored energy density than the existing adaptive materials. (Right) The absolute value range of the reported properties before and after cyclic loading shows that LIPPS has higher elastic modulus and toughness than the existing adaptive materials. >
Moreover, because its properties improve in proportion to the magnitude and frequency of applied stress, it can self-adjust to achieve mechanical property distributions suitable for different structural applications. It also possesses self-healing capabilities.
Professor Kang stated, "This newly developed material, which strengthens and absorbs impact better with repeated use compared to conventional materials, holds great potential for applications in artificial joints, as well as in aircraft, ships, automobiles, and structural engineering."
This study, with Professor Sung Hoon Kang as the corresponding author, was published in Science Advances (Vol. 11, Issue 6, February).
(Paper title: “A material dynamically enhancing both load-bearing and energy-dissipation capability under cyclic loading”) DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt3979
This research was conducted as a joint effort with Johns Hopkins University's Extreme Materials Institute and the Georgia Institute of Technology, supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Brain Pool Plus program.
2025.02.22 View 1539
KAIST develops a new, bone-like material that strengthens with use in collaboration with GIT
Materials used in apartment buildings, vehicles, and other structures deteriorate over time under repeated loads, leading to failure and breakage. A joint research team from Korea and the United States has successfully developed a bioinspired material that becomes stronger with use, taking inspiration from the way bones synthesize minerals from bodily fluids under stress, increasing bone density.
< (From left) Professor Sung Hoon Kang of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University Ph.D. candidates Bohan Sun and Grant Kitchen, Professor Yuhang Hu and Ph.D. candidate Dongjung He of Georgia Institute of Technology >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of February that a research team led by Professor Sung Hoon Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Johns Hopkins University and the Georgia Institute of Technology, had developed a new material that strengthens with repeated use, similar to how bones become stronger with exercise.
Professor Kang’s team sought to address the issue of conventional materials degrading with repeated use. Inspired by the biological process where stress triggers cells to form minerals that strengthen bones, the team developed a material that synthesizes minerals under stress without relying on cellular activity. This innovation is expected to enable applications in a variety of fields.
To replace the function of cells, the research team created a porous piezoelectric substrate that converts mechanical force into electricity and actually generates more charge under greater force. They then synthesized a composite material by infusing it with an electrolyte containing mineral components similar to those in blood.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the biomimetic concept based on bone and pitcher plants, the reversible strengthening mechanism, the process of fabricating porous composites, the mechanical property changes with increasing stiffness and energy dissipation after cyclic loading, and the reprogrammable self-folding mechanism and applications >
After subjecting the material to periodic forces and measuring changes in its properties, they observed that its stiffness increased proportionally with the frequency and magnitude of stress and that its energy dissipation capability improved.
The reason for such properties was found to be due to minerals forming inside the porous material under repeated stress, as observed through micro-CT imaging of its internal structure. When subjected to large forces, these minerals fractured and dissipated energy, only to reform under further cyclic stress.
Unlike conventional materials that weaken with repeated use, this new material simultaneously enhances stiffness and impact absorption over time.
< Figure 2. Comparison of the changes in properties of the newly developed new material (LIPPS) with other materials under cyclic loading. (A) Graph showing the relative change rate of energy dissipation after cyclic loading and the relative change rate of elastic modulus upon unloading. LIPPS is in a new area that existing materials have not reached, and shows the characteristics of simultaneous increases in elastic modulus and energy dissipation. (B) Graph comparing the performance of LIPPS with current state-of-the-art mechanically adaptive materials. (Left) The maximum property change rate compared to the baseline after cyclic loading, LIPPS shows much higher changes in elastic modulus, dissipated energy density and ratio, toughness (impact resistance), and stored energy density than the existing adaptive materials. (Right) The absolute value range of the reported properties before and after cyclic loading shows that LIPPS has higher elastic modulus and toughness than the existing adaptive materials. >
Moreover, because its properties improve in proportion to the magnitude and frequency of applied stress, it can self-adjust to achieve mechanical property distributions suitable for different structural applications. It also possesses self-healing capabilities.
Professor Kang stated, "This newly developed material, which strengthens and absorbs impact better with repeated use compared to conventional materials, holds great potential for applications in artificial joints, as well as in aircraft, ships, automobiles, and structural engineering."
This study, with Professor Sung Hoon Kang as the corresponding author, was published in Science Advances (Vol. 11, Issue 6, February).
(Paper title: “A material dynamically enhancing both load-bearing and energy-dissipation capability under cyclic loading”) DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt3979
This research was conducted as a joint effort with Johns Hopkins University's Extreme Materials Institute and the Georgia Institute of Technology, supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Brain Pool Plus program.
2025.02.22 View 1539 -
 KAIST Research Team Develops an AI Framework Capable of Overcoming the Strength-Ductility Dilemma in Additive-manufactured Titanium Alloys
<(From Left) Ph.D. Student Jaejung Park and Professor Seungchul Lee of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and , Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, and M.S.–Ph.D. Integrated Program Student Jeong Ah Lee of POSTECH. >
The KAIST research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee from Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyoung Seop Kim’s team at POSTECH, successfully overcame the strength–ductility dilemma of Ti 6Al 4V alloy using artificial intelligence, enabling the production of high strength, high ductility metal products. The AI developed by the team accurately predicts mechanical properties based on various 3D printing process parameters while also providing uncertainty information, and it uses both to recommend process parameters that hold high promise for 3D printing.
Among various 3D printing technologies, laser powder bed fusion is an innovative method for manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy, renowned for its high strength and bio-compatibility. However, this alloy made via 3D printing has traditionally faced challenges in simultaneously achieving high strength and high ductility. Although there have been attempts to address this issue by adjusting both the printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, the vast number of possible combinations made it difficult to explore them all through experiments and simulations alone.
The active learning framework developed by the team quickly explores a wide range of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions to recommend those expected to improve both strength and ductility of the alloy. These recommendations are based on the AI model’s predictions of ultimate tensile strength and total elongation along with associated uncertainty information for each set of process parameters and heat treatment conditions. The recommended conditions are then validated by performing 3D printing and tensile tests to obtain the true mechanical property values. These new data are incorporated into further AI model training, and through iterative exploration, the optimal process parameters and heat treatment conditions for producing high-performance alloys were determined in only five iterations. With these optimized conditions, the 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy achieved an ultimate tensile strength of 1190 MPa and a total elongation of 16.5%, successfully overcoming the strength–ductility dilemma.
Professor Seungchul Lee commented, “In this study, by optimizing the 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, we were able to develop a high-strength, high-ductility Ti-6Al-4V alloy with minimal experimentation trials. Compared to previous studies, we produced an alloy with a similar ultimate tensile strength but higher total elongation, as well as that with a similar elongation but greater ultimate tensile strength.” He added, “Furthermore, if our approach is applied not only to mechanical properties but also to other properties such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, we anticipate that it will enable efficient exploration of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions.”
This study was published in Nature Communications on January 22 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56267-1), and the research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Nano & Material Technology Development Program and the Leading Research Center Program.
2025.02.21 View 2358
KAIST Research Team Develops an AI Framework Capable of Overcoming the Strength-Ductility Dilemma in Additive-manufactured Titanium Alloys
<(From Left) Ph.D. Student Jaejung Park and Professor Seungchul Lee of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and , Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, and M.S.–Ph.D. Integrated Program Student Jeong Ah Lee of POSTECH. >
The KAIST research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee from Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyoung Seop Kim’s team at POSTECH, successfully overcame the strength–ductility dilemma of Ti 6Al 4V alloy using artificial intelligence, enabling the production of high strength, high ductility metal products. The AI developed by the team accurately predicts mechanical properties based on various 3D printing process parameters while also providing uncertainty information, and it uses both to recommend process parameters that hold high promise for 3D printing.
Among various 3D printing technologies, laser powder bed fusion is an innovative method for manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy, renowned for its high strength and bio-compatibility. However, this alloy made via 3D printing has traditionally faced challenges in simultaneously achieving high strength and high ductility. Although there have been attempts to address this issue by adjusting both the printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, the vast number of possible combinations made it difficult to explore them all through experiments and simulations alone.
The active learning framework developed by the team quickly explores a wide range of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions to recommend those expected to improve both strength and ductility of the alloy. These recommendations are based on the AI model’s predictions of ultimate tensile strength and total elongation along with associated uncertainty information for each set of process parameters and heat treatment conditions. The recommended conditions are then validated by performing 3D printing and tensile tests to obtain the true mechanical property values. These new data are incorporated into further AI model training, and through iterative exploration, the optimal process parameters and heat treatment conditions for producing high-performance alloys were determined in only five iterations. With these optimized conditions, the 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy achieved an ultimate tensile strength of 1190 MPa and a total elongation of 16.5%, successfully overcoming the strength–ductility dilemma.
Professor Seungchul Lee commented, “In this study, by optimizing the 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, we were able to develop a high-strength, high-ductility Ti-6Al-4V alloy with minimal experimentation trials. Compared to previous studies, we produced an alloy with a similar ultimate tensile strength but higher total elongation, as well as that with a similar elongation but greater ultimate tensile strength.” He added, “Furthermore, if our approach is applied not only to mechanical properties but also to other properties such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, we anticipate that it will enable efficient exploration of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions.”
This study was published in Nature Communications on January 22 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56267-1), and the research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Nano & Material Technology Development Program and the Leading Research Center Program.
2025.02.21 View 2358 -
 Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
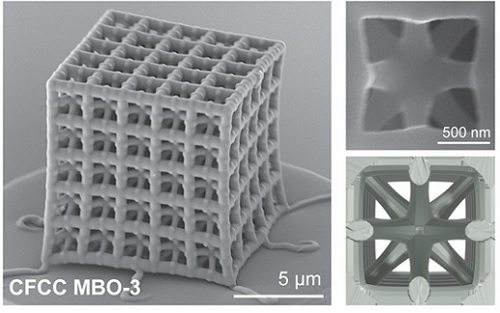
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 2422
Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 2422 -
 KAIST Holds 2025 Commencement Ceremony
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) held its 2025 Commencement Ceremony at the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex on the Daejeon Main Campus at 2 p.m. on the 14th of February.
< A scene from KAIST Commencement 2025 - Guests of Honor and Administrative Professors Entering the Stage headed by the color guards of the ELKA (Encouraging Leaders of KAIST) >
At this ceremony, a total of 3,144 degrees were conferred, including 785 doctorates, 1,643 masters, and 716 bachelors. With this, KAIST has produced a total of 81,156 advanced science and technology personnel, including 17,313 doctorates, 41,566 masters, and 22,277 bachelors since its establishment in 1971.
Changyu Lee from the School of Computing received the Minister of Science and ICT Award, and the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award went to Lance Khizner Dabu Gragasin, an international student from the Philippines of the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering. The President’s Award was given to Seoyeong Yang of the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Alumni Association President’s Award and the Development Foundation Chairman’s Award was given to Gahyeon Bae of the Department of Industrial Design and Buyeon Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, respectively.
Minister of Science and ICT Sang-Im Yoo joined the ceremony to deliver a congratulatory speech and to present the awards to outstanding graduates.
< Minister Sang-Im Yoo of the Ministry of Science, Technology and ICT giving his congratulatory message at KAIST Commencement 2025 >
The valedictorian speeches were given by Minjae Kim of the School of Computing, who has practiced the value of sharing that learning is not competition but cooperation, and Mohammed Haruna Hamza of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, a Nigerian international student. Mr. Hamza is the first foreign student to represent the graduating class as valedictorian since the founding of KAIST.
Hamza lost his home and school in his home country due to a terrorist group’s bombing and moved south, but despite the adversity, he continued his studies while pursuing his dream of becoming an aerospace engineer. As a result of his efforts, Hamza was invited by the Korean government to study at KAIST. He expressed his determination to pursue his dream by saying, “I am grateful for the people and experiences that helped me overcome my adversity. The future is the result of the decisions we make today.”
A Pakistani international student was chosen as one of this year's "Most Talked about Graduates of the Year". It is Ali Syed Sheraz who wore his doctoral cap at this year’s commencement ceremony. Ali, a single father who left his one-year-old son behind in his home country, working as a university lecturer. He joined the Ph.D. program in mechanical engineering in 2019 with a passion for mechanical energy.
Ali’s academic journey was full of challenges and growth. Due to COVID-19, his research was suspended for six months, and he had difficulty continuing his studies undergoing three surgeries after a bicycle accident, including a surgery for a fractured elbow, a nose surgery, and removal of kidney stones.
However, he accepted these failure and hardship as a process of growth and participated in the ‘Failed Project Showcase’ and ‘Failure Essay Contest’ held by the KAIST Failure Society, sharing his experiences and growing into a more solid researcher.
< Most Talked about Graduate Graduate of the Year - Syed Sheraz Ali >
Despite experiencing various hardships, he found lessons to learn from them and changed his perspective, which made him unafraid of taking on new challenges. He showed through his own example that failure is not just stumbling blocks but can be a stepping stone to success by looking at his studies and personal life positively.
Furthermore, after becoming the president of the Muslim Student Association, Ali introduced halal menus to the cafeteria on campus so that more Muslim students could eat comfortably. Thanks to this change, his time at KAIST has become an opportunity to understand and experience various cultures more.
Ali is researching artificial muscles (soft actuators) with the world's highest bending strain using MXene, an artificial muscle nanomaterial that can move smoothly, in Professor Il-kwon Oh's lab.
Ali said, "After completing my Ph.D., I plan to develop soft robots, healthcare electronics, and next-generation tactile technology based on MXene, a next-generation 2D material. It is important for my juniors not to be afraid of failure and to have a challenging attitude."
Another 'Most Talked about Graduate of the Year', Mr. Sung-Hyun Jung, who graduated with a master's degree from the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management, is the CEO of Promedius, a medical AI startup, and has commercialized an osteoporosis diagnosis software based on chest X-rays using AI, and grown it into a leading company in the bone health field.
CEO Jung's challenge shows that KAIST's management education is not just theoretical but practical enough to be applied immediately in the field. CEO Jung, who is also the father of three daughters, experienced business failure in China during the period when the conflict between Korea and China was intensifying.
He moved to Silicon Valley in the United States to revive his business and tried to acquire even small businesses, but the reality was not easy. He worked hard, standing 14 hours a day in a kimchi factory and a restaurant kitchen to make a living. After finishing his life in the United States, CEO Jung returned to Korea and had the opportunity to join Lunit, a global medical AI leader founded by KAIST graduates. CEO Jung experienced the growth of the global medical AI market firsthand with unit Chairman Seungwook Paek.
When he entered the Master's Program at the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management in 2023 to acquire more specialized knowledge, CEO Jung had just transferred to Promedius and was in a crisis situation with only about 6 months left before the company's funds were exhausted.
While considering a change in business direction because he judged that it would be difficult to survive with existing business items, he learned keywords and investment review perspectives that venture capital (VC) pays attention to in Professor Hoonje Cho’s ‘Bio-innovation Business Startup Strategy and Practice’ class. He attracted 11.4 billion won in investment by applying the investment proposal he wrote based on what he learned from the class to actual practice.
< Most Talked about Graduate of the Year - Sung-Hyun Jung >
In addition, he applied the innovation strategy in the medical field he learned in Professor Kihwan Park’s ‘Innovation and Marketing in Bio and Pharmaceutics’ to the field of osteoporosis, and achieved the result of being selected as the first Asian company to be a corporate advisory committee member of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF). Through this, he established the company as a representative global entity in the osteoporosis field in just one year.
CEO Jung, who applied what he learned from KAIST to actual management and achieved results in the global market in a short period of time, said, “I want to prove that KAIST education is not limited to theory, but is very practical.” He said, “I want to let people know that my life, once full of hardship, got on the track toward success after encountering KAIST,” and expressed his ambition, saying, “My long-term goal is to create a world-class company that is recognized globally.”
In addition, an honorary doctorate was awarded to Chairman Joong Keun Lee of Booyoung Group at the commencement ceremony.
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who is an entrepreneur that led Booyoung Group, a leading general construction company, received the honorary doctorate in business administration, for leading the development of domestic housing welfare, education, and culture.
KAIST Provost Gyunmin Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee spared no effort in providing dedicated support for the development of domestic science and technology and the cultivation of future talents. He is awarded the honorary doctorate in recognition of his social responsibility in various fields, including scholarships and support for educational facilities, as well as domestic and international education, culture, veterans affairs, and overseas support.”
Since founding Booyoung Group in 1983, Chairman Lee has boldly entered the rental housing business, a field that large construction companies had avoided, and has played a significant role in improving the quality of life of ordinary citizens by supplying 230,000 households out of 383 complexes and approximately 300,000 households nationwide as rental housing, thereby contributing greatly to the stability of national housing.
< Chairman Joong Keun Lee giving his acceptance speech for his honorary Doctorate >
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who has been offering hope for a sustainable future, said, “I am honored to receive an honorary doctorate from KAIST, and I hope that KAIST students will nurture their dreams and talents and grow into global talents who will contribute to national development.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee has been carrying out various social contribution activities, and in particular, through supporting academic infrastructure, which is the core of national competitiveness, we can see his deep interest in and sense of responsibility for the development of science and technology in our country.” He added, “I am truly delighted to have him as a member of the KAIST family, and I congratulate him on behalf of all members, including our students.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee also delivered a message of encouragement at the ceremony to charge the graduates to, “Find and keep a dream of your own, be on the lookout for opportunities, don’t be afraid of making mistakes, and do not shy away from taking on challenging tasks.” He added, “Even if you fail, don’t give up. Keep on trying so that you will get to that stage of radiate your own light on the stages where anything is possible.” (End)
2025.02.14 View 3211
KAIST Holds 2025 Commencement Ceremony
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) held its 2025 Commencement Ceremony at the Lyu Keun-Chul Sports Complex on the Daejeon Main Campus at 2 p.m. on the 14th of February.
< A scene from KAIST Commencement 2025 - Guests of Honor and Administrative Professors Entering the Stage headed by the color guards of the ELKA (Encouraging Leaders of KAIST) >
At this ceremony, a total of 3,144 degrees were conferred, including 785 doctorates, 1,643 masters, and 716 bachelors. With this, KAIST has produced a total of 81,156 advanced science and technology personnel, including 17,313 doctorates, 41,566 masters, and 22,277 bachelors since its establishment in 1971.
Changyu Lee from the School of Computing received the Minister of Science and ICT Award, and the Chairman of the KAIST Board of Trustees Award went to Lance Khizner Dabu Gragasin, an international student from the Philippines of the Department of Chemical and Biological Engineering. The President’s Award was given to Seoyeong Yang of the Department of Biological Sciences, and the Alumni Association President’s Award and the Development Foundation Chairman’s Award was given to Gahyeon Bae of the Department of Industrial Design and Buyeon Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, respectively.
Minister of Science and ICT Sang-Im Yoo joined the ceremony to deliver a congratulatory speech and to present the awards to outstanding graduates.
< Minister Sang-Im Yoo of the Ministry of Science, Technology and ICT giving his congratulatory message at KAIST Commencement 2025 >
The valedictorian speeches were given by Minjae Kim of the School of Computing, who has practiced the value of sharing that learning is not competition but cooperation, and Mohammed Haruna Hamza of the Department of Aerospace Engineering, a Nigerian international student. Mr. Hamza is the first foreign student to represent the graduating class as valedictorian since the founding of KAIST.
Hamza lost his home and school in his home country due to a terrorist group’s bombing and moved south, but despite the adversity, he continued his studies while pursuing his dream of becoming an aerospace engineer. As a result of his efforts, Hamza was invited by the Korean government to study at KAIST. He expressed his determination to pursue his dream by saying, “I am grateful for the people and experiences that helped me overcome my adversity. The future is the result of the decisions we make today.”
A Pakistani international student was chosen as one of this year's "Most Talked about Graduates of the Year". It is Ali Syed Sheraz who wore his doctoral cap at this year’s commencement ceremony. Ali, a single father who left his one-year-old son behind in his home country, working as a university lecturer. He joined the Ph.D. program in mechanical engineering in 2019 with a passion for mechanical energy.
Ali’s academic journey was full of challenges and growth. Due to COVID-19, his research was suspended for six months, and he had difficulty continuing his studies undergoing three surgeries after a bicycle accident, including a surgery for a fractured elbow, a nose surgery, and removal of kidney stones.
However, he accepted these failure and hardship as a process of growth and participated in the ‘Failed Project Showcase’ and ‘Failure Essay Contest’ held by the KAIST Failure Society, sharing his experiences and growing into a more solid researcher.
< Most Talked about Graduate Graduate of the Year - Syed Sheraz Ali >
Despite experiencing various hardships, he found lessons to learn from them and changed his perspective, which made him unafraid of taking on new challenges. He showed through his own example that failure is not just stumbling blocks but can be a stepping stone to success by looking at his studies and personal life positively.
Furthermore, after becoming the president of the Muslim Student Association, Ali introduced halal menus to the cafeteria on campus so that more Muslim students could eat comfortably. Thanks to this change, his time at KAIST has become an opportunity to understand and experience various cultures more.
Ali is researching artificial muscles (soft actuators) with the world's highest bending strain using MXene, an artificial muscle nanomaterial that can move smoothly, in Professor Il-kwon Oh's lab.
Ali said, "After completing my Ph.D., I plan to develop soft robots, healthcare electronics, and next-generation tactile technology based on MXene, a next-generation 2D material. It is important for my juniors not to be afraid of failure and to have a challenging attitude."
Another 'Most Talked about Graduate of the Year', Mr. Sung-Hyun Jung, who graduated with a master's degree from the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management, is the CEO of Promedius, a medical AI startup, and has commercialized an osteoporosis diagnosis software based on chest X-rays using AI, and grown it into a leading company in the bone health field.
CEO Jung's challenge shows that KAIST's management education is not just theoretical but practical enough to be applied immediately in the field. CEO Jung, who is also the father of three daughters, experienced business failure in China during the period when the conflict between Korea and China was intensifying.
He moved to Silicon Valley in the United States to revive his business and tried to acquire even small businesses, but the reality was not easy. He worked hard, standing 14 hours a day in a kimchi factory and a restaurant kitchen to make a living. After finishing his life in the United States, CEO Jung returned to Korea and had the opportunity to join Lunit, a global medical AI leader founded by KAIST graduates. CEO Jung experienced the growth of the global medical AI market firsthand with unit Chairman Seungwook Paek.
When he entered the Master's Program at the Graduate School of Bio Innvation Management in 2023 to acquire more specialized knowledge, CEO Jung had just transferred to Promedius and was in a crisis situation with only about 6 months left before the company's funds were exhausted.
While considering a change in business direction because he judged that it would be difficult to survive with existing business items, he learned keywords and investment review perspectives that venture capital (VC) pays attention to in Professor Hoonje Cho’s ‘Bio-innovation Business Startup Strategy and Practice’ class. He attracted 11.4 billion won in investment by applying the investment proposal he wrote based on what he learned from the class to actual practice.
< Most Talked about Graduate of the Year - Sung-Hyun Jung >
In addition, he applied the innovation strategy in the medical field he learned in Professor Kihwan Park’s ‘Innovation and Marketing in Bio and Pharmaceutics’ to the field of osteoporosis, and achieved the result of being selected as the first Asian company to be a corporate advisory committee member of the International Osteoporosis Foundation (IOF). Through this, he established the company as a representative global entity in the osteoporosis field in just one year.
CEO Jung, who applied what he learned from KAIST to actual management and achieved results in the global market in a short period of time, said, “I want to prove that KAIST education is not limited to theory, but is very practical.” He said, “I want to let people know that my life, once full of hardship, got on the track toward success after encountering KAIST,” and expressed his ambition, saying, “My long-term goal is to create a world-class company that is recognized globally.”
In addition, an honorary doctorate was awarded to Chairman Joong Keun Lee of Booyoung Group at the commencement ceremony.
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who is an entrepreneur that led Booyoung Group, a leading general construction company, received the honorary doctorate in business administration, for leading the development of domestic housing welfare, education, and culture.
KAIST Provost Gyunmin Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee spared no effort in providing dedicated support for the development of domestic science and technology and the cultivation of future talents. He is awarded the honorary doctorate in recognition of his social responsibility in various fields, including scholarships and support for educational facilities, as well as domestic and international education, culture, veterans affairs, and overseas support.”
Since founding Booyoung Group in 1983, Chairman Lee has boldly entered the rental housing business, a field that large construction companies had avoided, and has played a significant role in improving the quality of life of ordinary citizens by supplying 230,000 households out of 383 complexes and approximately 300,000 households nationwide as rental housing, thereby contributing greatly to the stability of national housing.
< Chairman Joong Keun Lee giving his acceptance speech for his honorary Doctorate >
Chairman Joong Keun Lee, who has been offering hope for a sustainable future, said, “I am honored to receive an honorary doctorate from KAIST, and I hope that KAIST students will nurture their dreams and talents and grow into global talents who will contribute to national development.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “Chairman Joong Keun Lee has been carrying out various social contribution activities, and in particular, through supporting academic infrastructure, which is the core of national competitiveness, we can see his deep interest in and sense of responsibility for the development of science and technology in our country.” He added, “I am truly delighted to have him as a member of the KAIST family, and I congratulate him on behalf of all members, including our students.”
President Kwang-Hyung Lee also delivered a message of encouragement at the ceremony to charge the graduates to, “Find and keep a dream of your own, be on the lookout for opportunities, don’t be afraid of making mistakes, and do not shy away from taking on challenging tasks.” He added, “Even if you fail, don’t give up. Keep on trying so that you will get to that stage of radiate your own light on the stages where anything is possible.” (End)
2025.02.14 View 3211 -
 KAIST Develops AI-Driven Performance Prediction Model to Advance Space Electric Propulsion Technology
< (From left) PhD candidate Youngho Kim, Professor Wonho Choe, and PhD candidate Jaehong Park from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering >
Hall thrusters, a key space technology for missions like SpaceX's Starlink constellation and NASA's Psyche asteroid mission, are high-efficiency electric propulsion devices using plasma technology*. The KAIST research team announced that the AI-designed Hall thruster developed for CubeSats will be installed on the KAIST-Hall Effect Rocket Orbiter (K-HERO) CubeSat to demonstrate its in-orbit performance during the fourth launch of the Korean Launch Vehicle called Nuri rocket (KSLV-2) scheduled for November this year.
*Plasma is one of the four states of matter, where gases are heated to high energies, causing them to separate into charged ions and electrons. Plasma is used not only in space electric propulsion but also in semiconductor manufacturing, display processes, and sterilization devices.
On February 3rd, the research team from the KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering’s Electric Propulsion Laboratory, led by Professor Wonho Choe, announced the development of an AI-based technique to accurately predict the performance of Hall thrusters, the engines of satellites and space probes.
Hall thrusters provide high fuel efficiency, requiring minimal propellant to achieve significant acceleration of spacecrafts or satellites while producing substantial thrust relative to power consumption. Due to these advantages, Hall thrusters are widely used in various space missions, including the formation flight of satellite constellations, deorbiting maneuvers for space debris mitigation, and deep space missions such as asteroid exploration.
As the space industry continues to grow during the NewSpace era, the demand for Hall thrusters suited to diverse missions is increasing. To rapidly develop highly efficient, mission-optimized Hall thrusters, it is essential to predict thruster performance accurately from the design phase.
However, conventional methods have limitations, as they struggle to handle the complex plasma phenomena within Hall thrusters or are only applicable under specific conditions, leading to lower prediction accuracy.
The research team developed an AI-based performance prediction technique with high accuracy, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with the iterative design, fabrication, and testing of thrusters. Since 2003, Professor Wonho Choe’s team has been leading research on electric propulsion development in Korea. The team applied a neural network ensemble model to predict thruster performance using 18,000 Hall thruster training data points generated from their in-house numerical simulation tool.
The in-house numerical simulation tool, developed to model plasma physics and thrust performance, played a crucial role in providing high-quality training data. The simulation’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with experimental data from ten KAIST in-house Hall thrusters, with an average prediction error of less than 10%.
< Figure 1. This research has been selected as the cover article for the March 2025 issue (Volume 7, Issue 3) of the AI interdisciplinary journal, Advanced Intelligent Systems. >
The trained neural network ensemble model acts as a digital twin, accurately predicting the Hall thruster performance within seconds based on thruster design variables.
Notably, it offers detailed analyses of performance parameters such as thrust and discharge current, accounting for Hall thruster design variables like propellant flow rate and magnetic field—factors that are challenging to evaluate using traditional scaling laws.
This AI model demonstrated an average prediction error of less than 5% for the in-house 700 W and 1 kW KAIST Hall thrusters and less than 9% for a 5 kW high-power Hall thruster developed by the University of Michigan and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory. This confirms the broad applicability of the AI prediction method across different power levels of Hall thrusters.
Professor Wonho Choe stated, “The AI-based prediction technique developed by our team is highly accurate and is already being utilized in the analysis of thrust performance and the development of highly efficient, low-power Hall thrusters for satellites and spacecraft. This AI approach can also be applied beyond Hall thrusters to various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, surface processing, and coating, through ion beam sources.”
< Figure 2. The AI-based prediction technique developed by the research team accurately predicts thrust performance based on design variables, making it highly valuable for the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. The neural network ensemble processes design variables, such as channel geometry and magnetic field information, and outputs key performance metrics like thrust and prediction accuracy, enabling efficient thruster design and performance analysis. >
Additionally, Professor Choe mentioned, “The CubeSat Hall thruster, developed using the AI technique in collaboration with our lab startup—Cosmo Bee, an electric propulsion company—will be tested in orbit this November aboard the K-HERO 3U (30 x 10 x 10 cm) CubeSat, scheduled for launch on the fourth flight of the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket.”
This research was published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems on December 25, 2024 with PhD candidate Jaehong Park as the first author and was selected as the journal’s cover article, highlighting its innovation.
< Figure 3. Image of the 150 W low-power Hall thruster for small and micro satellites, developed in collaboration with Cosmo Bee and the KAIST team. The thruster will be tested in orbit on the K-HERO CubeSat during the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket’s fourth launch in Q4 2025. >
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Space Pioneer Program (200mN High Thrust Electric Propulsion System Development).
(Paper Title: Predicting Performance of Hall Effect Ion Source Using Machine Learning, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202400555 )
< Figure 4. Graphs of the predicted thrust and discharge current of KAIST’s 700 W Hall thruster using the AI model (HallNN). The left image shows the Hall thruster operating in KAIST Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s vacuum chamber, while the center and right graphs present the prediction results for thrust and discharge current based on anode mass flow rate. The red lines represent AI predictions, and the blue dots represent experimental results, with a prediction error of less than 5%. >
2025.02.03 View 3367
KAIST Develops AI-Driven Performance Prediction Model to Advance Space Electric Propulsion Technology
< (From left) PhD candidate Youngho Kim, Professor Wonho Choe, and PhD candidate Jaehong Park from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering >
Hall thrusters, a key space technology for missions like SpaceX's Starlink constellation and NASA's Psyche asteroid mission, are high-efficiency electric propulsion devices using plasma technology*. The KAIST research team announced that the AI-designed Hall thruster developed for CubeSats will be installed on the KAIST-Hall Effect Rocket Orbiter (K-HERO) CubeSat to demonstrate its in-orbit performance during the fourth launch of the Korean Launch Vehicle called Nuri rocket (KSLV-2) scheduled for November this year.
*Plasma is one of the four states of matter, where gases are heated to high energies, causing them to separate into charged ions and electrons. Plasma is used not only in space electric propulsion but also in semiconductor manufacturing, display processes, and sterilization devices.
On February 3rd, the research team from the KAIST Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering’s Electric Propulsion Laboratory, led by Professor Wonho Choe, announced the development of an AI-based technique to accurately predict the performance of Hall thrusters, the engines of satellites and space probes.
Hall thrusters provide high fuel efficiency, requiring minimal propellant to achieve significant acceleration of spacecrafts or satellites while producing substantial thrust relative to power consumption. Due to these advantages, Hall thrusters are widely used in various space missions, including the formation flight of satellite constellations, deorbiting maneuvers for space debris mitigation, and deep space missions such as asteroid exploration.
As the space industry continues to grow during the NewSpace era, the demand for Hall thrusters suited to diverse missions is increasing. To rapidly develop highly efficient, mission-optimized Hall thrusters, it is essential to predict thruster performance accurately from the design phase.
However, conventional methods have limitations, as they struggle to handle the complex plasma phenomena within Hall thrusters or are only applicable under specific conditions, leading to lower prediction accuracy.
The research team developed an AI-based performance prediction technique with high accuracy, significantly reducing the time and cost associated with the iterative design, fabrication, and testing of thrusters. Since 2003, Professor Wonho Choe’s team has been leading research on electric propulsion development in Korea. The team applied a neural network ensemble model to predict thruster performance using 18,000 Hall thruster training data points generated from their in-house numerical simulation tool.
The in-house numerical simulation tool, developed to model plasma physics and thrust performance, played a crucial role in providing high-quality training data. The simulation’s accuracy was validated through comparisons with experimental data from ten KAIST in-house Hall thrusters, with an average prediction error of less than 10%.
< Figure 1. This research has been selected as the cover article for the March 2025 issue (Volume 7, Issue 3) of the AI interdisciplinary journal, Advanced Intelligent Systems. >
The trained neural network ensemble model acts as a digital twin, accurately predicting the Hall thruster performance within seconds based on thruster design variables.
Notably, it offers detailed analyses of performance parameters such as thrust and discharge current, accounting for Hall thruster design variables like propellant flow rate and magnetic field—factors that are challenging to evaluate using traditional scaling laws.
This AI model demonstrated an average prediction error of less than 5% for the in-house 700 W and 1 kW KAIST Hall thrusters and less than 9% for a 5 kW high-power Hall thruster developed by the University of Michigan and the U.S. Air Force Research Laboratory. This confirms the broad applicability of the AI prediction method across different power levels of Hall thrusters.
Professor Wonho Choe stated, “The AI-based prediction technique developed by our team is highly accurate and is already being utilized in the analysis of thrust performance and the development of highly efficient, low-power Hall thrusters for satellites and spacecraft. This AI approach can also be applied beyond Hall thrusters to various industries, including semiconductor manufacturing, surface processing, and coating, through ion beam sources.”
< Figure 2. The AI-based prediction technique developed by the research team accurately predicts thrust performance based on design variables, making it highly valuable for the development of high-efficiency Hall thrusters. The neural network ensemble processes design variables, such as channel geometry and magnetic field information, and outputs key performance metrics like thrust and prediction accuracy, enabling efficient thruster design and performance analysis. >
Additionally, Professor Choe mentioned, “The CubeSat Hall thruster, developed using the AI technique in collaboration with our lab startup—Cosmo Bee, an electric propulsion company—will be tested in orbit this November aboard the K-HERO 3U (30 x 10 x 10 cm) CubeSat, scheduled for launch on the fourth flight of the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket.”
This research was published online in Advanced Intelligent Systems on December 25, 2024 with PhD candidate Jaehong Park as the first author and was selected as the journal’s cover article, highlighting its innovation.
< Figure 3. Image of the 150 W low-power Hall thruster for small and micro satellites, developed in collaboration with Cosmo Bee and the KAIST team. The thruster will be tested in orbit on the K-HERO CubeSat during the KSLV-2 Nuri rocket’s fourth launch in Q4 2025. >
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Space Pioneer Program (200mN High Thrust Electric Propulsion System Development).
(Paper Title: Predicting Performance of Hall Effect Ion Source Using Machine Learning, DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/aisy.202400555 )
< Figure 4. Graphs of the predicted thrust and discharge current of KAIST’s 700 W Hall thruster using the AI model (HallNN). The left image shows the Hall thruster operating in KAIST Electric Propulsion Laboratory’s vacuum chamber, while the center and right graphs present the prediction results for thrust and discharge current based on anode mass flow rate. The red lines represent AI predictions, and the blue dots represent experimental results, with a prediction error of less than 5%. >
2025.02.03 View 3367 -
 KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 7040
KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 7040 -
 KAIST Develops Neuromorphic Semiconductor Chip that Learns and Corrects Itself
< Photo. The research team of the School of Electrical Engineering posed by the newly deveoped processor. (From center to the right) Professor Young-Gyu Yoon, Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program Students Seungjae Han and Hakcheon Jeong and Professor Shinhyun Choi >
- Professor Shinhyun Choi and Professor Young-Gyu Yoon’s Joint Research Team from the School of Electrical Engineering developed a computing chip that can learn, correct errors, and process AI tasks
- Equipping a computing chip with high-reliability memristor devices with self-error correction functions for real-time learning and image processing
Existing computer systems have separate data processing and storage devices, making them inefficient for processing complex data like AI. A KAIST research team has developed a memristor-based integrated system similar to the way our brain processes information. It is now ready for application in various devices including smart security cameras, allowing them to recognize suspicious activity immediately without having to rely on remote cloud servers, and medical devices with which it can help analyze health data in real time.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of January that the joint research team of Professor Shinhyun Choi and Professor Young-Gyu Yoon of the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based ultra-small computing chip that can learn and correct errors on its own.
< Figure 1. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of a computing chip equipped with a highly reliable selector-less 32×32 memristor crossbar array (left). Hardware system developed for real-time artificial intelligence implementation (right). >
What is special about this computing chip is that it can learn and correct errors that occur due to non-ideal characteristics that were difficult to solve in existing neuromorphic devices. For example, when processing a video stream, the chip learns to automatically separate a moving object from the background, and it becomes better at this task over time.
This self-learning ability has been proven by achieving accuracy comparable to ideal computer simulations in real-time image processing. The research team's main achievement is that it has completed a system that is both reliable and practical, beyond the development of brain-like components.
The research team has developed the world's first memristor-based integrated system that can adapt to immediate environmental changes, and has presented an innovative solution that overcomes the limitations of existing technology.
< Figure 2. Background and foreground separation results of an image containing non-ideal characteristics of memristor devices (left). Real-time image separation results through on-device learning using the memristor computing chip developed by our research team (right). >
At the heart of this innovation is a next-generation semiconductor device called a memristor*. The variable resistance characteristics of this device can replace the role of synapses in neural networks, and by utilizing it, data storage and computation can be performed simultaneously, just like our brain cells.
*Memristor: A compound word of memory and resistor, next-generation electrical device whose resistance value is determined by the amount and direction of charge that has flowed between the two terminals in the past.
The research team designed a highly reliable memristor that can precisely control resistance changes and developed an efficient system that excludes complex compensation processes through self-learning. This study is significant in that it experimentally verified the commercialization possibility of a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based integrated system that supports real-time learning and inference.
This technology will revolutionize the way artificial intelligence is used in everyday devices, allowing AI tasks to be processed locally without relying on remote cloud servers, making them faster, more privacy-protected, and more energy-efficient.
“This system is like a smart workspace where everything is within arm’s reach instead of having to go back and forth between desks and file cabinets,” explained KAIST researchers Hakcheon Jeong and Seungjae Han, who led the development of this technology. “This is similar to the way our brain processes information, where everything is processed efficiently at once at one spot.”
The research was conducted with Hakcheon Jeong and Seungjae Han, the students of Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program at KAIST School of Electrical Engineering being the co-first authors, the results of which was published online in the international academic journal, Nature Electronics, on January 8, 2025.
*Paper title: Self-supervised video processing with self-calibration on an analogue computing platform based on a selector-less memristor array ( https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01318-6 )
This research was supported by the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, Excellent New Researcher Project and PIM AI Semiconductor Core Technology Development Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute Research and Development Support Project of the Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2025.01.17 View 4401
KAIST Develops Neuromorphic Semiconductor Chip that Learns and Corrects Itself
< Photo. The research team of the School of Electrical Engineering posed by the newly deveoped processor. (From center to the right) Professor Young-Gyu Yoon, Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program Students Seungjae Han and Hakcheon Jeong and Professor Shinhyun Choi >
- Professor Shinhyun Choi and Professor Young-Gyu Yoon’s Joint Research Team from the School of Electrical Engineering developed a computing chip that can learn, correct errors, and process AI tasks
- Equipping a computing chip with high-reliability memristor devices with self-error correction functions for real-time learning and image processing
Existing computer systems have separate data processing and storage devices, making them inefficient for processing complex data like AI. A KAIST research team has developed a memristor-based integrated system similar to the way our brain processes information. It is now ready for application in various devices including smart security cameras, allowing them to recognize suspicious activity immediately without having to rely on remote cloud servers, and medical devices with which it can help analyze health data in real time.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of January that the joint research team of Professor Shinhyun Choi and Professor Young-Gyu Yoon of the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based ultra-small computing chip that can learn and correct errors on its own.
< Figure 1. Scanning electron microscope (SEM) image of a computing chip equipped with a highly reliable selector-less 32×32 memristor crossbar array (left). Hardware system developed for real-time artificial intelligence implementation (right). >
What is special about this computing chip is that it can learn and correct errors that occur due to non-ideal characteristics that were difficult to solve in existing neuromorphic devices. For example, when processing a video stream, the chip learns to automatically separate a moving object from the background, and it becomes better at this task over time.
This self-learning ability has been proven by achieving accuracy comparable to ideal computer simulations in real-time image processing. The research team's main achievement is that it has completed a system that is both reliable and practical, beyond the development of brain-like components.
The research team has developed the world's first memristor-based integrated system that can adapt to immediate environmental changes, and has presented an innovative solution that overcomes the limitations of existing technology.
< Figure 2. Background and foreground separation results of an image containing non-ideal characteristics of memristor devices (left). Real-time image separation results through on-device learning using the memristor computing chip developed by our research team (right). >
At the heart of this innovation is a next-generation semiconductor device called a memristor*. The variable resistance characteristics of this device can replace the role of synapses in neural networks, and by utilizing it, data storage and computation can be performed simultaneously, just like our brain cells.
*Memristor: A compound word of memory and resistor, next-generation electrical device whose resistance value is determined by the amount and direction of charge that has flowed between the two terminals in the past.
The research team designed a highly reliable memristor that can precisely control resistance changes and developed an efficient system that excludes complex compensation processes through self-learning. This study is significant in that it experimentally verified the commercialization possibility of a next-generation neuromorphic semiconductor-based integrated system that supports real-time learning and inference.
This technology will revolutionize the way artificial intelligence is used in everyday devices, allowing AI tasks to be processed locally without relying on remote cloud servers, making them faster, more privacy-protected, and more energy-efficient.
“This system is like a smart workspace where everything is within arm’s reach instead of having to go back and forth between desks and file cabinets,” explained KAIST researchers Hakcheon Jeong and Seungjae Han, who led the development of this technology. “This is similar to the way our brain processes information, where everything is processed efficiently at once at one spot.”
The research was conducted with Hakcheon Jeong and Seungjae Han, the students of Integrated Master's and Doctoral Program at KAIST School of Electrical Engineering being the co-first authors, the results of which was published online in the international academic journal, Nature Electronics, on January 8, 2025.
*Paper title: Self-supervised video processing with self-calibration on an analogue computing platform based on a selector-less memristor array ( https://doi.org/10.1038/s41928-024-01318-6 )
This research was supported by the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Project, Excellent New Researcher Project and PIM AI Semiconductor Core Technology Development Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute Research and Development Support Project of the Institute of Information & communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2025.01.17 View 4401 -
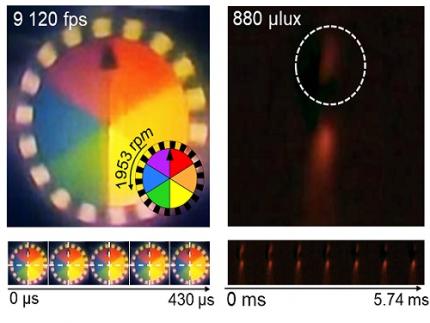 KAIST Develops Insect-Eye-Inspired Camera Capturing 9,120 Frames Per Second
< (From left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD Student Jae-Myeong Kwon, Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, PhD Student Hyun-Kyung Kim, PhD Student Young-Gil Cha, and Professor Min H. Kim of the School of Computing >
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of January that a research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
< Figure 1. (A) Vision in a fast-eyed insect. Reflected light from swiftly moving objects sequentially stimulates the photoreceptors along the individual optical channels called ommatidia, of which the visual signals are separately and parallelly processed via the lamina and medulla. Each neural response is temporally summed to enhance the visual signals. The parallel processing and temporal summation allow fast and low-light imaging in dim light. (B) High-speed and high-sensitivity microlens array camera (HS-MAC). A rolling shutter image sensor is utilized to simultaneously acquire multiple frames by channel division, and temporal summation is performed in parallel to realize high speed and sensitivity even in a low-light environment. In addition, the frame components of a single fragmented array image are stitched into a single blurred frame, which is subsequently deblurred by compressive image reconstruction. >
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
The team also introduced a "channel-splitting" technique to significantly enhance the camera's speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a "compressed image restoration" algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than one millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
< Figure 2. A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. >
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study's first author, stated, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
< Figure 3. Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. >
This research was published in the international journal Science Advances in January 2025 (Paper Title: “Biologically-inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
This study was supported by the Korea Research Institute for Defense Technology Planning and Advancement (KRIT) of the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
2025.01.16 View 5003
KAIST Develops Insect-Eye-Inspired Camera Capturing 9,120 Frames Per Second
< (From left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD Student Jae-Myeong Kwon, Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, PhD Student Hyun-Kyung Kim, PhD Student Young-Gil Cha, and Professor Min H. Kim of the School of Computing >
The compound eyes of insects can detect fast-moving objects in parallel and, in low-light conditions, enhance sensitivity by integrating signals over time to determine motion. Inspired by these biological mechanisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a low-cost, high-speed camera that overcomes the limitations of frame rate and sensitivity faced by conventional high-speed cameras.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 16th of January that a research team led by Professors Ki-Hun Jeong (Department of Bio and Brain Engineering) and Min H. Kim (School of Computing) has developed a novel bio-inspired camera capable of ultra-high-speed imaging with high sensitivity by mimicking the visual structure of insect eyes.
High-quality imaging under high-speed and low-light conditions is a critical challenge in many applications. While conventional high-speed cameras excel in capturing fast motion, their sensitivity decreases as frame rates increase because the time available to collect light is reduced.
To address this issue, the research team adopted an approach similar to insect vision, utilizing multiple optical channels and temporal summation. Unlike traditional monocular camera systems, the bio-inspired camera employs a compound-eye-like structure that allows for the parallel acquisition of frames from different time intervals.
< Figure 1. (A) Vision in a fast-eyed insect. Reflected light from swiftly moving objects sequentially stimulates the photoreceptors along the individual optical channels called ommatidia, of which the visual signals are separately and parallelly processed via the lamina and medulla. Each neural response is temporally summed to enhance the visual signals. The parallel processing and temporal summation allow fast and low-light imaging in dim light. (B) High-speed and high-sensitivity microlens array camera (HS-MAC). A rolling shutter image sensor is utilized to simultaneously acquire multiple frames by channel division, and temporal summation is performed in parallel to realize high speed and sensitivity even in a low-light environment. In addition, the frame components of a single fragmented array image are stitched into a single blurred frame, which is subsequently deblurred by compressive image reconstruction. >
During this process, light is accumulated over overlapping time periods for each frame, increasing the signal-to-noise ratio. The researchers demonstrated that their bio-inspired camera could capture objects up to 40 times dimmer than those detectable by conventional high-speed cameras.
The team also introduced a "channel-splitting" technique to significantly enhance the camera's speed, achieving frame rates thousands of times faster than those supported by the image sensors used in packaging. Additionally, a "compressed image restoration" algorithm was employed to eliminate blur caused by frame integration and reconstruct sharp images.
The resulting bio-inspired camera is less than one millimeter thick and extremely compact, capable of capturing 9,120 frames per second while providing clear images in low-light conditions.
< Figure 2. A high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera packaged in an image sensor. It is made small enough to fit on a finger, with a thickness of less than 1 mm. >
The research team plans to extend this technology to develop advanced image processing algorithms for 3D imaging and super-resolution imaging, aiming for applications in biomedical imaging, mobile devices, and various other camera technologies.
Hyun-Kyung Kim, a doctoral student in the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST and the study's first author, stated, “We have experimentally validated that the insect-eye-inspired camera delivers outstanding performance in high-speed and low-light imaging despite its small size. This camera opens up possibilities for diverse applications in portable camera systems, security surveillance, and medical imaging.”
< Figure 3. Rotating plate and flame captured using the high-speed, high-sensitivity biomimetic camera. The rotating plate at 1,950 rpm was accurately captured at 9,120 fps. In addition, the pinch-off of the flame with a faint intensity of 880 µlux was accurately captured at 1,020 fps. >
This research was published in the international journal Science Advances in January 2025 (Paper Title: “Biologically-inspired microlens array camera for high-speed and high-sensitivity imaging”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.ads3389
This study was supported by the Korea Research Institute for Defense Technology Planning and Advancement (KRIT) of the Defense Acquisition Program Administration (DAPA), the Ministry of Science and ICT, and the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE).
2025.01.16 View 5003 -
 KAIST Alumni Association to Honor Alumni of the Year Award Winners
Photo 1. Photo of the KAIST Alumni of the Year Award Recipients
(From left) UST President Lee-whan Kim, CEO Han Chung of iThree Systems Co., Ltd., CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd., and Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on Monday, the 13th of January that the Alumni Association (President Yun-Tae Lee) has selected its Alumni of the Year.
This year’s honorees are: ▴ President Lee-whan Kim of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), ▴ CEO Han Chung of i3 Systems, ▴ CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution, and ▴ Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The honorees were selected based on their achievements over the past year, and the award ceremony will be held at the 2025 KAIST Alumni Association New Year’s Gathering to be held at the L Tower in Seoul at 5 PM on Friday the 17th.
The KAIST Alumni of the Year Award is an award presented by the Alumni Association to alumni who have contributed to the development of the country and the society or have brought honor to their alma mater through outstanding academic achievements and community service. Since its establishment in 1992, 126 recipients have been awarded.
Lee-whan Kim (Master's graduate of Mechanical Engineering, 82), the President of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), established a leading foundation for national science and technology policy and strategy, and played a leading role in innovating national science and technology capabilities through the advancement of the national research and development system and the advancement of science and technology personnel training. In particular, he played a pivotal role in the establishment of UST and the Korea Science Academy (KSA), and greatly contributed to establishing a foundation for the training and utilization of science and technology personnel.
Han Chung (Master's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 91, with Ph.D. degree in 96), the CEO of i3 Systems, is a first-generation researcher in the field of domestic infrared detectors. He developed military detectors for over 30 years and founded i3 Systems, a specialized infrared detector company, in 1998. Currently, he supplies more than 80% of the infrared detectors used by the Korean military, and has also achieved export results to over 20 countries.
Dong Myung Kim (Master's graduate of Materials Science and Engineering, 94, with Ph.D. degree in 98) the CEO of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd. has led innovation in the battery field with his ceaseless exploration and challenging spirit, and is known as an authority in the secondary battery industry. He played a leading role in establishing K-Battery as a global leader, strengthened the country's future industrial competitiveness, and greatly contributed to the development of science and technology.
Hyun Myung (Bachelor's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 92, with Master's degree in 94, and Ph.D. degree in 98) a Professor of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, won first place in the world at the Quadruped Robot Challenge (QRC) hosted by the IEEE’s International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2023 with the 'DreamWaQ' system, an AI walking technology based on deep reinforcement learning that utilizes non-video sensory technologies. He contributed to enhancing the competitiveness of the domestic robot industry by developing his own fully autonomous walking technology that recognizes the environment around the robot and finds the optimal path.
Yun-Tae Lee, the 27th president of the KAIST Alumni Association, said, “KAIST alumni have been the driving force behind the growth of industries in all walks of life by continuously conducting research and development in the field of advanced science and technology for a long time,” and added, “I am very proud of the KAIST alumni award recipients who are leading science and technology on the world stage beyond Korea, and I sincerely thank them for their efforts and achievements.”
2025.01.15 View 2894
KAIST Alumni Association to Honor Alumni of the Year Award Winners
Photo 1. Photo of the KAIST Alumni of the Year Award Recipients
(From left) UST President Lee-whan Kim, CEO Han Chung of iThree Systems Co., Ltd., CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd., and Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on Monday, the 13th of January that the Alumni Association (President Yun-Tae Lee) has selected its Alumni of the Year.
This year’s honorees are: ▴ President Lee-whan Kim of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), ▴ CEO Han Chung of i3 Systems, ▴ CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution, and ▴ Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The honorees were selected based on their achievements over the past year, and the award ceremony will be held at the 2025 KAIST Alumni Association New Year’s Gathering to be held at the L Tower in Seoul at 5 PM on Friday the 17th.
The KAIST Alumni of the Year Award is an award presented by the Alumni Association to alumni who have contributed to the development of the country and the society or have brought honor to their alma mater through outstanding academic achievements and community service. Since its establishment in 1992, 126 recipients have been awarded.
Lee-whan Kim (Master's graduate of Mechanical Engineering, 82), the President of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), established a leading foundation for national science and technology policy and strategy, and played a leading role in innovating national science and technology capabilities through the advancement of the national research and development system and the advancement of science and technology personnel training. In particular, he played a pivotal role in the establishment of UST and the Korea Science Academy (KSA), and greatly contributed to establishing a foundation for the training and utilization of science and technology personnel.
Han Chung (Master's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 91, with Ph.D. degree in 96), the CEO of i3 Systems, is a first-generation researcher in the field of domestic infrared detectors. He developed military detectors for over 30 years and founded i3 Systems, a specialized infrared detector company, in 1998. Currently, he supplies more than 80% of the infrared detectors used by the Korean military, and has also achieved export results to over 20 countries.
Dong Myung Kim (Master's graduate of Materials Science and Engineering, 94, with Ph.D. degree in 98) the CEO of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd. has led innovation in the battery field with his ceaseless exploration and challenging spirit, and is known as an authority in the secondary battery industry. He played a leading role in establishing K-Battery as a global leader, strengthened the country's future industrial competitiveness, and greatly contributed to the development of science and technology.
Hyun Myung (Bachelor's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 92, with Master's degree in 94, and Ph.D. degree in 98) a Professor of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, won first place in the world at the Quadruped Robot Challenge (QRC) hosted by the IEEE’s International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2023 with the 'DreamWaQ' system, an AI walking technology based on deep reinforcement learning that utilizes non-video sensory technologies. He contributed to enhancing the competitiveness of the domestic robot industry by developing his own fully autonomous walking technology that recognizes the environment around the robot and finds the optimal path.
Yun-Tae Lee, the 27th president of the KAIST Alumni Association, said, “KAIST alumni have been the driving force behind the growth of industries in all walks of life by continuously conducting research and development in the field of advanced science and technology for a long time,” and added, “I am very proud of the KAIST alumni award recipients who are leading science and technology on the world stage beyond Korea, and I sincerely thank them for their efforts and achievements.”
2025.01.15 View 2894 -
 KAIST Research Team Develops Stretchable Microelectrodes Array for Organoid Signal Monitoring
< Photo 1. (From top left) Professor Hyunjoo J. Lee, Dr. Mi-Young Son, Dr. Mi-Ok Lee(In the front row from left) Doctoral student Kiup Kim, Doctoral student Youngsun Lee >
On January 14th, the KAIST research team led by Professor Hyunjoo J. Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering in collaboration with Dr. Mi-Young Son and Dr. Mi-Ok Lee at Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) announced the development of a highly stretchable microelectrode array (sMEA) designed for non-invasive electrophysiological signal measurement of organoids.
Organoids* are highly promising models for human biology and are expected to replace many animal experiments. Their potential applications include disease modeling, drug screening, and personalized medicine as they closely mimic the structure and function of humans.
*Organoids: three-dimensional in vitro tissue models derived from human stem cells
Despite these advantages, existing organoid research has primarily focused on genetic analysis, with limited studies on organoid functionality. For effective drug evaluation and precise biological research, technology that preserves the three-dimensional structure of organoids while enabling real-time monitoring of their functions is needed. However, it’s challenging to provide non-invasive ways to evaluate the functionalities without incurring damage to the tissues. This challenge is particularly significant for electrophysiological signal measurement in cardiac and brain organoids since the sensor needs to be in direct contact with organoids of varying size and irregular shape. Achieving tight contact between electrodes and the external surface of the organoids without damaging the organoids has been a persistent challenge.
< Figure 1. Schematic image of highly stretchable MEA (sMEA) with protruding microelectrodes. >
The KAIST research team developed a highly stretchable microelectrode array with a unique serpentine structure that contacts the surface of organoids in a highly conformal fashion. They successfully demonstrated real-time measurement and analysis of electrophysiological signals from two types of electrogenic organoids (heart and brain). By employing a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS)-based process, the team fabricated the serpentine-structured microelectrode array and used an electrochemical deposition process to develop PEDOT:PSS-based protruding microelectrodes. These innovations demonstrated exceptional stretchability and close surface adherence to various organoid sizes. The protruding microelectrodes improved contact between organoids and the electrodes, ensuring stable and reliable electrophysiological signal measurements with high signal-to-noise ratios (SNR).
< Figure 2. Conceptual illustration, optical image, and fluorescence images of an organoid captured by the sMEA with protruding microelectrodes.>
Using this technology, the team successfully monitored and analyzed electrophysiological signals from cardiac spheroids of various sizes, revealing three-dimensional signal propagation patterns and identifying changes in signal characteristics according to size. They also measured electrophysiological signals in midbrain organoids, demonstrating the versatility of the technology. Additionally, they monitored signal modulations induced by various drugs, showcasing the potential of this technology for drug screening applications.
< Figure 3. SNR improvement effect by protruding PEDOT:PSS microelectrodes. >
Prof. Hyunjoo Jenny Lee stated, “By integrating MEMS technology and electrochemical deposition techniques, we successfully developed a stretchable microelectrode array adaptable to organoids of diverse sizes and shapes. The high practicality is a major advantage of this system since the fabrication is based on semiconductor fabrication with high volume production, reliability, and accuracy. This technology that enables in situ, real-time analysis of states and functionalities of organoids will be a game changer in high-through drug screening.”
This study led by Ph.D. candidate Kiup Kim from KAIST and Ph.D. candidate Youngsun Lee from KRIBB, with significant contributions from Dr. Kwang Bo Jung, was published online on December 15, 2024 in Advanced Materials (IF: 27.4).
< Figure 4. Drug screening using cardiac spheroids and midbrain organoids.>
This research was supported by a grant from 3D-TissueChip Based Drug Discovery Platform Technology Development Program (No. 20009209) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea), by the Commercialization Promotion Agency for R&D Outcomes (COMPA) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (RS-2024-00415902), by the K-Brain Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (RS-2023-00262568), by BK21 FOUR (Connected AI Education & Research Program for Industry and Society Innovation, KAIST EE, No. 4120200113769), and by Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) Research Initiative Program (KGM4722432).
2025.01.14 View 2289
KAIST Research Team Develops Stretchable Microelectrodes Array for Organoid Signal Monitoring
< Photo 1. (From top left) Professor Hyunjoo J. Lee, Dr. Mi-Young Son, Dr. Mi-Ok Lee(In the front row from left) Doctoral student Kiup Kim, Doctoral student Youngsun Lee >
On January 14th, the KAIST research team led by Professor Hyunjoo J. Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering in collaboration with Dr. Mi-Young Son and Dr. Mi-Ok Lee at Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) announced the development of a highly stretchable microelectrode array (sMEA) designed for non-invasive electrophysiological signal measurement of organoids.
Organoids* are highly promising models for human biology and are expected to replace many animal experiments. Their potential applications include disease modeling, drug screening, and personalized medicine as they closely mimic the structure and function of humans.
*Organoids: three-dimensional in vitro tissue models derived from human stem cells
Despite these advantages, existing organoid research has primarily focused on genetic analysis, with limited studies on organoid functionality. For effective drug evaluation and precise biological research, technology that preserves the three-dimensional structure of organoids while enabling real-time monitoring of their functions is needed. However, it’s challenging to provide non-invasive ways to evaluate the functionalities without incurring damage to the tissues. This challenge is particularly significant for electrophysiological signal measurement in cardiac and brain organoids since the sensor needs to be in direct contact with organoids of varying size and irregular shape. Achieving tight contact between electrodes and the external surface of the organoids without damaging the organoids has been a persistent challenge.
< Figure 1. Schematic image of highly stretchable MEA (sMEA) with protruding microelectrodes. >
The KAIST research team developed a highly stretchable microelectrode array with a unique serpentine structure that contacts the surface of organoids in a highly conformal fashion. They successfully demonstrated real-time measurement and analysis of electrophysiological signals from two types of electrogenic organoids (heart and brain). By employing a micro-electromechanical system (MEMS)-based process, the team fabricated the serpentine-structured microelectrode array and used an electrochemical deposition process to develop PEDOT:PSS-based protruding microelectrodes. These innovations demonstrated exceptional stretchability and close surface adherence to various organoid sizes. The protruding microelectrodes improved contact between organoids and the electrodes, ensuring stable and reliable electrophysiological signal measurements with high signal-to-noise ratios (SNR).
< Figure 2. Conceptual illustration, optical image, and fluorescence images of an organoid captured by the sMEA with protruding microelectrodes.>
Using this technology, the team successfully monitored and analyzed electrophysiological signals from cardiac spheroids of various sizes, revealing three-dimensional signal propagation patterns and identifying changes in signal characteristics according to size. They also measured electrophysiological signals in midbrain organoids, demonstrating the versatility of the technology. Additionally, they monitored signal modulations induced by various drugs, showcasing the potential of this technology for drug screening applications.
< Figure 3. SNR improvement effect by protruding PEDOT:PSS microelectrodes. >
Prof. Hyunjoo Jenny Lee stated, “By integrating MEMS technology and electrochemical deposition techniques, we successfully developed a stretchable microelectrode array adaptable to organoids of diverse sizes and shapes. The high practicality is a major advantage of this system since the fabrication is based on semiconductor fabrication with high volume production, reliability, and accuracy. This technology that enables in situ, real-time analysis of states and functionalities of organoids will be a game changer in high-through drug screening.”
This study led by Ph.D. candidate Kiup Kim from KAIST and Ph.D. candidate Youngsun Lee from KRIBB, with significant contributions from Dr. Kwang Bo Jung, was published online on December 15, 2024 in Advanced Materials (IF: 27.4).
< Figure 4. Drug screening using cardiac spheroids and midbrain organoids.>
This research was supported by a grant from 3D-TissueChip Based Drug Discovery Platform Technology Development Program (No. 20009209) funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry & Energy (MOTIE, Korea), by the Commercialization Promotion Agency for R&D Outcomes (COMPA) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) (RS-2024-00415902), by the K-Brain Project of the National Research Foundation (NRF) funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (RS-2023-00262568), by BK21 FOUR (Connected AI Education & Research Program for Industry and Society Innovation, KAIST EE, No. 4120200113769), and by Korea Research Institute of Bioscience and Biotechnology (KRIBB) Research Initiative Program (KGM4722432).
2025.01.14 View 2289