AR
-
 Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho at KARI Receives the 16th Jeong Hun Cho Award
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho, a senior researcher at the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), was honored as the recipient of the 16th Jeong Hun Cho Award. The award recognizes young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering.
Dr. Cho earned his MS and PhD degrees from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2012, and served as a researcher at the Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, before joining the Future Convergence Research Division at KARI. He won this year’s award and received 25 million KRW in prize money.
Jeong Hun Cho, who was a PhD candidate in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, passed away in a tragic lab accident in May 2003 and was awarded an honorary doctorate posthumously. His family endowed the award and scholarship in his memory. Since 2005, the scholarship has selected three young scholars every year who specialize in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho was selected as this year’s awardee in recognition of his studies on the development and operation of KARISMA, a comprehensive software package for space debris collision risk management. Dr. Cho built a terrestrial testbed and produced a model for the development of a space debris elimination algorithm. He published six papers in SCI-level journals and wrote 35 symposium papers in the field of space development. He also applied or registered approximately 40 patents both in Korea and internationally.
The Award Committee also selected three students as scholarship recipients: PhD candidate Yongtae Yun from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST received 4 million KRW, MS-PhD candidate Haun-Min Lee from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University received 4 million KRW, and Seonju Yim from Kongju National University High School received 3 million KRW.
(END)
2020.05.13 View 13247
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho at KARI Receives the 16th Jeong Hun Cho Award
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho, a senior researcher at the Korea Aerospace Research Institute (KARI), was honored as the recipient of the 16th Jeong Hun Cho Award. The award recognizes young scientists in the field of aerospace engineering.
Dr. Cho earned his MS and PhD degrees from the KAIST Department of Aerospace Engineering in 2012, and served as a researcher at the Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, before joining the Future Convergence Research Division at KARI. He won this year’s award and received 25 million KRW in prize money.
Jeong Hun Cho, who was a PhD candidate in the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST, passed away in a tragic lab accident in May 2003 and was awarded an honorary doctorate posthumously. His family endowed the award and scholarship in his memory. Since 2005, the scholarship has selected three young scholars every year who specialize in aerospace engineering from Cho’s alma maters of KAIST, Korea University, and Kongju National University High School.
Dr. Dong-Hyun Cho was selected as this year’s awardee in recognition of his studies on the development and operation of KARISMA, a comprehensive software package for space debris collision risk management. Dr. Cho built a terrestrial testbed and produced a model for the development of a space debris elimination algorithm. He published six papers in SCI-level journals and wrote 35 symposium papers in the field of space development. He also applied or registered approximately 40 patents both in Korea and internationally.
The Award Committee also selected three students as scholarship recipients: PhD candidate Yongtae Yun from the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST received 4 million KRW, MS-PhD candidate Haun-Min Lee from the School of Mechanical Engineering at Korea University received 4 million KRW, and Seonju Yim from Kongju National University High School received 3 million KRW.
(END)
2020.05.13 View 13247 -
 Simple Molecular Reagents to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
- Researchers report minimalistic principles for designing small molecules with multiple reactivities against dementia. -
Sometimes the most complex problems actually have very simple solutions. A group of South Korean researchers reported an efficient and effective redox-based strategy for incorporating multiple functions into simple molecular reagents against neurodegenerative disorders. The team developed redox-active aromatic molecular reagents with a simple structural composition that can simultaneously target and modulate various pathogenic factors in complex neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, affecting one in ten people over the age of 65. Early-onset dementia also increasingly affects younger people.
A number of pathogenic elements such as reactive oxygen species, amyloid-beta, and metal ions have been suggested as potential causes of Alzheimer’s disease. Each element itself can lead to Alzheimer’s disease, but interactions between them may also aggravate the patient’s condition or interfere with the appropriate clinical care.
For example, when interacting with amyloid-beta, metal ions foster the aggregation and accumulation of amyloid-beta peptides that can induce oxidative stress and toxicity in the brain and lead to neurodegeneration.
Because these pathogenic factors of Alzheimer’s disease are intertwined, developing therapeutic agents that are capable of simultaneously regulating metal ion dyshomeostasis, amyloid-beta agglutination, and oxidative stress responses remains a key to halting the progression of the disease.
A research team led by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST demonstrated the feasibility of structure-mechanism-based molecular design for controlling a molecule’s chemical reactivity toward the various pathological factors of Alzheimer’s disease by tuning the redox properties of the molecule.
This study, featured as the ‘ACS Editors’ Choice’ in the May 6th issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), was conducted in conjunction with KAIST Professor Mu-Hyun Baik’s group and Professor Joo-Young Lee’s group at the Asan Medical Center.
Professor Lim and her collaborators rationally designed and generated 10 compact aromatic molecules presenting a range of redox potentials by adjusting the electronic distribution of the phenyl, phenylene, or pyridyl moiety to impart redox-dependent reactivities against the multiple pathogenic factors in Alzheimer’s disease.
During the team’s biochemical and biophysical studies, these designed molecular reagents displayed redox-dependent reactivities against numerous desirable targets that are associated with Alzheimer’s disease such as free radicals, metal-free amyloid-beta, and metal-bound amyloid-beta.
Further mechanistic results revealed that the redox properties of these designed molecular reagents were essential for their function. The team demonstrated that these reagents engaged in oxidative reactions with metal-free and metal-bound amyloid-beta and led to chemical modifications. The products of such oxidative transformations were observed to form covalent adducts with amyloid-beta and alter its aggregation.
Moreover, the administration of the most promising candidate molecule significantly attenuated the amyloid pathology in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice and improved their cognitive defects.
Professor Lim said, “This strategy is straightforward, time-saving, and cost-effective, and its effect is significant. We are excited to help enable the advancement of new therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative disorders, which can improve the lives of so many patients.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), and the Asan Institute for Life Sciences.
Image credit: Professor Mi Hee Lim, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of the news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kim, M. et al. (2020) ‘Minimalistic Principles for Designing Small Molecules with Multiple Reactivities against Pathological Factors in Dementia.’ Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), Volume 142, Issue 18, pp.8183-8193. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13100
Profile:
Mi Hee Lim
Professor
miheelim@kaist.ac.kr
http://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab
Lim Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
Profile:
Mu-Hyun Baik
Professor
mbaik2805@kaist.ac.kr
https://baik-laboratory.com/
Baik Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
Profile:
Joo-Yong Lee
Professor
jlee@amc.seoul.kr
Asan Institute for Life Sciences
Asan Medical Center
(END)
2020.05.11 View 19129
Simple Molecular Reagents to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease
- Researchers report minimalistic principles for designing small molecules with multiple reactivities against dementia. -
Sometimes the most complex problems actually have very simple solutions. A group of South Korean researchers reported an efficient and effective redox-based strategy for incorporating multiple functions into simple molecular reagents against neurodegenerative disorders. The team developed redox-active aromatic molecular reagents with a simple structural composition that can simultaneously target and modulate various pathogenic factors in complex neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the most prevalent neurodegenerative disorders, affecting one in ten people over the age of 65. Early-onset dementia also increasingly affects younger people.
A number of pathogenic elements such as reactive oxygen species, amyloid-beta, and metal ions have been suggested as potential causes of Alzheimer’s disease. Each element itself can lead to Alzheimer’s disease, but interactions between them may also aggravate the patient’s condition or interfere with the appropriate clinical care.
For example, when interacting with amyloid-beta, metal ions foster the aggregation and accumulation of amyloid-beta peptides that can induce oxidative stress and toxicity in the brain and lead to neurodegeneration.
Because these pathogenic factors of Alzheimer’s disease are intertwined, developing therapeutic agents that are capable of simultaneously regulating metal ion dyshomeostasis, amyloid-beta agglutination, and oxidative stress responses remains a key to halting the progression of the disease.
A research team led by Professor Mi Hee Lim from the Department of Chemistry at KAIST demonstrated the feasibility of structure-mechanism-based molecular design for controlling a molecule’s chemical reactivity toward the various pathological factors of Alzheimer’s disease by tuning the redox properties of the molecule.
This study, featured as the ‘ACS Editors’ Choice’ in the May 6th issue of the Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), was conducted in conjunction with KAIST Professor Mu-Hyun Baik’s group and Professor Joo-Young Lee’s group at the Asan Medical Center.
Professor Lim and her collaborators rationally designed and generated 10 compact aromatic molecules presenting a range of redox potentials by adjusting the electronic distribution of the phenyl, phenylene, or pyridyl moiety to impart redox-dependent reactivities against the multiple pathogenic factors in Alzheimer’s disease.
During the team’s biochemical and biophysical studies, these designed molecular reagents displayed redox-dependent reactivities against numerous desirable targets that are associated with Alzheimer’s disease such as free radicals, metal-free amyloid-beta, and metal-bound amyloid-beta.
Further mechanistic results revealed that the redox properties of these designed molecular reagents were essential for their function. The team demonstrated that these reagents engaged in oxidative reactions with metal-free and metal-bound amyloid-beta and led to chemical modifications. The products of such oxidative transformations were observed to form covalent adducts with amyloid-beta and alter its aggregation.
Moreover, the administration of the most promising candidate molecule significantly attenuated the amyloid pathology in the brains of Alzheimer’s disease transgenic mice and improved their cognitive defects.
Professor Lim said, “This strategy is straightforward, time-saving, and cost-effective, and its effect is significant. We are excited to help enable the advancement of new therapeutic agents for neurodegenerative disorders, which can improve the lives of so many patients.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea, the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), and the Asan Institute for Life Sciences.
Image credit: Professor Mi Hee Lim, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of the news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kim, M. et al. (2020) ‘Minimalistic Principles for Designing Small Molecules with Multiple Reactivities against Pathological Factors in Dementia.’ Journal of the American Chemical Society (JACS), Volume 142, Issue 18, pp.8183-8193. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13100
Profile:
Mi Hee Lim
Professor
miheelim@kaist.ac.kr
http://sites.google.com/site/miheelimlab
Lim Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
Profile:
Mu-Hyun Baik
Professor
mbaik2805@kaist.ac.kr
https://baik-laboratory.com/
Baik Laboratory
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
Profile:
Joo-Yong Lee
Professor
jlee@amc.seoul.kr
Asan Institute for Life Sciences
Asan Medical Center
(END)
2020.05.11 View 19129 -
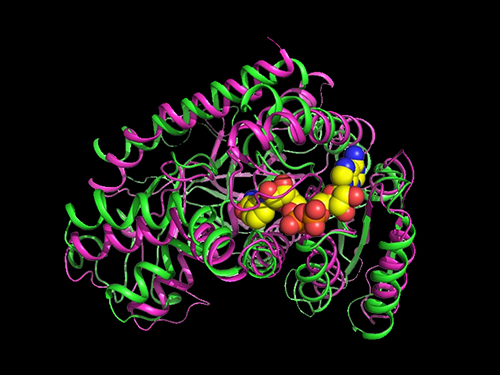 Researchers Present a Microbial Strain Capable of Massive Succinic Acid Production
A research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee reported the production of a microbial strain capable of the massive production of succinic acid with the highest production efficiency to date. This strategy of integrating systems metabolic engineering with enzyme engineering will be useful for the production of industrially competitive bio-based chemicals. Their strategy was described in Nature Communications on April 23.
The bio-based production of industrial chemicals from renewable non-food biomass has become increasingly important as a sustainable substitute for conventional petroleum-based production processes relying on fossil resources. Here, systems metabolic engineering, which is the key component for biorefinery technology, is utilized to effectively engineer the complex metabolic pathways of microorganisms to enable the efficient production of industrial chemicals.
Succinic acid, a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid, is one of the most promising platform chemicals serving as a precursor for industrially important chemicals. Among microorganisms producing succinic acid, Mannheimia succiniciproducens has been proven to be one of the best strains for succinic acid production.
The research team has developed a bio-based succinic acid production technology using the M. succiniciproducens strain isolated from the rumen of Korean cow for over 20 years and succeeded in developing a strain capable of producing succinic acid with the highest production efficiency.
They carried out systems metabolic engineering to optimize the succinic acid production pathway of the M. succiniciproducens strain by determining the crystal structure of key enzymes important for succinic acid production and performing protein engineering to develop enzymes with better catalytic performance.
As a result, 134 g per liter of succinic acid was produced from the fermentation of an engineered strain using glucose, glycerol, and carbon dioxide. They were able to achieve 21 g per liter per hour of succinic acid production, which is one of the key factors determining the economic feasibility of the overall production process. This is the world’s best succinic acid production efficiency reported to date. Previous production methods averaged 1~3 g per liter per hour.
Distinguished professor Sang Yup Lee explained that his team’s work will significantly contribute to transforming the current petrochemical-based industry into an eco-friendly bio-based one.
“Our research on the highly efficient bio-based production of succinic acid from renewable non-food resources and carbon dioxide has provided a basis for reducing our strong dependence on fossil resources, which is the main cause of the environmental crisis,” Professor Lee said.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes via Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries and the C1 Gas Refinery Program from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2020.05.06 View 11777
Researchers Present a Microbial Strain Capable of Massive Succinic Acid Production
A research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee reported the production of a microbial strain capable of the massive production of succinic acid with the highest production efficiency to date. This strategy of integrating systems metabolic engineering with enzyme engineering will be useful for the production of industrially competitive bio-based chemicals. Their strategy was described in Nature Communications on April 23.
The bio-based production of industrial chemicals from renewable non-food biomass has become increasingly important as a sustainable substitute for conventional petroleum-based production processes relying on fossil resources. Here, systems metabolic engineering, which is the key component for biorefinery technology, is utilized to effectively engineer the complex metabolic pathways of microorganisms to enable the efficient production of industrial chemicals.
Succinic acid, a four-carbon dicarboxylic acid, is one of the most promising platform chemicals serving as a precursor for industrially important chemicals. Among microorganisms producing succinic acid, Mannheimia succiniciproducens has been proven to be one of the best strains for succinic acid production.
The research team has developed a bio-based succinic acid production technology using the M. succiniciproducens strain isolated from the rumen of Korean cow for over 20 years and succeeded in developing a strain capable of producing succinic acid with the highest production efficiency.
They carried out systems metabolic engineering to optimize the succinic acid production pathway of the M. succiniciproducens strain by determining the crystal structure of key enzymes important for succinic acid production and performing protein engineering to develop enzymes with better catalytic performance.
As a result, 134 g per liter of succinic acid was produced from the fermentation of an engineered strain using glucose, glycerol, and carbon dioxide. They were able to achieve 21 g per liter per hour of succinic acid production, which is one of the key factors determining the economic feasibility of the overall production process. This is the world’s best succinic acid production efficiency reported to date. Previous production methods averaged 1~3 g per liter per hour.
Distinguished professor Sang Yup Lee explained that his team’s work will significantly contribute to transforming the current petrochemical-based industry into an eco-friendly bio-based one.
“Our research on the highly efficient bio-based production of succinic acid from renewable non-food resources and carbon dioxide has provided a basis for reducing our strong dependence on fossil resources, which is the main cause of the environmental crisis,” Professor Lee said.
This work was supported by the Technology Development Program to Solve Climate Changes via Systems Metabolic Engineering for Biorefineries and the C1 Gas Refinery Program from the Ministry of Science and ICT through the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2020.05.06 View 11777 -
 Professor Sukyung Park Named Presidential Science and Technology Adviser
Professor Sukyung Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was appointed as the science and technology adviser to the President Jae-in Moon on May 4. Professor Park, at the age of 47, became the youngest member of the president’s senior aide team at Chong Wa Dae.
A Chong Wa Dae spokesman said on May 4 while announcing the appointment, “Professor Park, a talent with a great deal of policymaking participation in science and technology, will contribute to accelerating the government’s push for science and technology innovation, especially in the information and communications technology (ICT) sector.”
Professor Park joined KAIST in 2004 as the first female professor of mechanical engineering. She is a biomechanics expert who has conducted extensive research on biometric mechanical behaviors. Professor Park is also a member of the KAIST Board of Trustees. Before that, she served as a senior researcher at the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) as well as a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology.
After graduating from Seoul Science High School as the first ever two-year graduate, Professor Park earned a bachelor and master’s degrees in mechanical engineering at KAIST. She then finished her Ph.D. from the University of Michigan.
(END)
2020.05.06 View 16539
Professor Sukyung Park Named Presidential Science and Technology Adviser
Professor Sukyung Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering was appointed as the science and technology adviser to the President Jae-in Moon on May 4. Professor Park, at the age of 47, became the youngest member of the president’s senior aide team at Chong Wa Dae.
A Chong Wa Dae spokesman said on May 4 while announcing the appointment, “Professor Park, a talent with a great deal of policymaking participation in science and technology, will contribute to accelerating the government’s push for science and technology innovation, especially in the information and communications technology (ICT) sector.”
Professor Park joined KAIST in 2004 as the first female professor of mechanical engineering. She is a biomechanics expert who has conducted extensive research on biometric mechanical behaviors. Professor Park is also a member of the KAIST Board of Trustees. Before that, she served as a senior researcher at the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (KIMM) as well as a member of the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology.
After graduating from Seoul Science High School as the first ever two-year graduate, Professor Park earned a bachelor and master’s degrees in mechanical engineering at KAIST. She then finished her Ph.D. from the University of Michigan.
(END)
2020.05.06 View 16539 -
 A Study Finds Neuropeptide Somatostatin Enhances Visual Processing
Researchers have confirmed that neuropeptide somatostatin can improve cognitive function in the brain. A research group of Professor Seung-Hee Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST found that the application of neuropeptide somatostatin improves visual processing and cognitive behaviors by reducing excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the cortex.
This study, reported at Science Advances on April 22nd (EST), sheds a new light on the therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. According to a recent study in Korea, one in ten seniors over 65 is experiencing dementia-related symptoms in their daily lives such like memory loss, cognitive decline, and motion function disorders. Professor Lee believes that somatostatin treatment can be directly applied to the recovery of cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s disease patients.
Professor Lee started this study noting the fact that the level of somatostatin expression was dramatically decreased in the cerebral cortex and cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients
Somatostatin-expressing neurons in the cortex are known to exert the dendritic inhibition of pyramidal neurons via GABAergic transmission. Previous studies focused on their inhibitory effects on cortical circuits, but somatostatin-expressing neurons can co-release somatostatin upon activation. Despite the abundant expression of somatostatin and its receptors in the cerebral cortex, it was not known if somatostatin could modulate cognitive processing in the cortex.
The research team demonstrated that the somatostatin treatment into the cerebral cortex could enhance visual processing and cognitive behaviors in mice. The research team combined behaviors, in vivo and in vitro electrophysiology, and electron microscopy techniques to reveal how the activation of somatostatin receptors in vivo enhanced the ability of visual recognition in animals. Interestingly, somatostatin release can reduce excitatory synaptic transmission to another subtype of GABAergic interneurons, parvalbumin (PV)-expressing neurons.
As somatostatin is a stable and safe neuropeptide expressed naturally in the mammalian brain, it was safe to be injected into the cortex and cerebrospinal fluid, showing a potential application to drug development for curing cognitive disorders in humans.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed the key role of the neuropeptide SST in modulating cortical function and enhancing cognitive ability in the mammalian brain. I hope new drugs can be developed based on the function of somatostatin to treat cognitive disabilities in many patients suffering from neurological disorders.”
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Song, Y. H et al. (2020) ‘Somatostatin enhances visual processing and perception by suppressing excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-positive interneurons in V1’, Science Advances, 6(17). Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz0517
Profile:
Seung-Hee Lee
Associate Professor
shlee1@kaist.ac.kr
https://sites.google.com/site/leelab2013/
Sensory Processing Lab (SPL)
Department of Biological Sciences (BIO)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Profile:
You-Hyang Song
Researcher (Ph.D.)
dbgidtm17@kaist.ac.kr
SPL, KAIST BIO
Profile:
Yang-Sun Hwang
Researcher (M.S.)
hys940129@kaist.ac.kr
SPL, KAIST BIO
(END)
2020.04.23 View 15620
A Study Finds Neuropeptide Somatostatin Enhances Visual Processing
Researchers have confirmed that neuropeptide somatostatin can improve cognitive function in the brain. A research group of Professor Seung-Hee Lee from the Department of Biological Sciences at KAIST found that the application of neuropeptide somatostatin improves visual processing and cognitive behaviors by reducing excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-positive interneurons in the cortex.
This study, reported at Science Advances on April 22nd (EST), sheds a new light on the therapeutics of neurodegenerative diseases. According to a recent study in Korea, one in ten seniors over 65 is experiencing dementia-related symptoms in their daily lives such like memory loss, cognitive decline, and motion function disorders. Professor Lee believes that somatostatin treatment can be directly applied to the recovery of cognitive functions in Alzheimer’s disease patients.
Professor Lee started this study noting the fact that the level of somatostatin expression was dramatically decreased in the cerebral cortex and cerebrospinal fluid of Alzheimer’s disease patients
Somatostatin-expressing neurons in the cortex are known to exert the dendritic inhibition of pyramidal neurons via GABAergic transmission. Previous studies focused on their inhibitory effects on cortical circuits, but somatostatin-expressing neurons can co-release somatostatin upon activation. Despite the abundant expression of somatostatin and its receptors in the cerebral cortex, it was not known if somatostatin could modulate cognitive processing in the cortex.
The research team demonstrated that the somatostatin treatment into the cerebral cortex could enhance visual processing and cognitive behaviors in mice. The research team combined behaviors, in vivo and in vitro electrophysiology, and electron microscopy techniques to reveal how the activation of somatostatin receptors in vivo enhanced the ability of visual recognition in animals. Interestingly, somatostatin release can reduce excitatory synaptic transmission to another subtype of GABAergic interneurons, parvalbumin (PV)-expressing neurons.
As somatostatin is a stable and safe neuropeptide expressed naturally in the mammalian brain, it was safe to be injected into the cortex and cerebrospinal fluid, showing a potential application to drug development for curing cognitive disorders in humans.
Professor Lee said, “Our research confirmed the key role of the neuropeptide SST in modulating cortical function and enhancing cognitive ability in the mammalian brain. I hope new drugs can be developed based on the function of somatostatin to treat cognitive disabilities in many patients suffering from neurological disorders.”
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Publication:
Song, Y. H et al. (2020) ‘Somatostatin enhances visual processing and perception by suppressing excitatory inputs to parvalbumin-positive interneurons in V1’, Science Advances, 6(17). Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.aaz0517
Profile:
Seung-Hee Lee
Associate Professor
shlee1@kaist.ac.kr
https://sites.google.com/site/leelab2013/
Sensory Processing Lab (SPL)
Department of Biological Sciences (BIO)
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Profile:
You-Hyang Song
Researcher (Ph.D.)
dbgidtm17@kaist.ac.kr
SPL, KAIST BIO
Profile:
Yang-Sun Hwang
Researcher (M.S.)
hys940129@kaist.ac.kr
SPL, KAIST BIO
(END)
2020.04.23 View 15620 -
 Highly Efficient and Stable Double Layer Solar Cell Developed
Solar cells convert light into energy, but they can be inefficient and vulnerable to the environment, degrading with, ironically, too much light or other factors, including moisture and low temperature. An international research team has developed a new type of solar cell that can both withstand environmental hazards and is 26.7% efficient in power conversion.
They published their results on March 26 in Science.
The researchers, led by Byungha Shin, a professor from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, focused on developing a new class of light-absorbing material, called a wide bandgap perovskite. The material has a highly effective crystal structure that can process the power needs, but it can become problematic when exposed to environmental hazards, such as moisture. Researchers have made some progress increasing the efficiency of solar cells based on perovskite, but the material has greater potential than what was previously achieved.
To achieve better performance, Shin and his team built a double layer solar cell, called tandem, in which two or more light absorbers are stacked together to better utilize solar energy. To use perovskite in these tandem devices, the scientists modified the material’s optical property, which allows it to absorb a wider range of solar energy. Without the adjustment, the material is not as useful in achieving high performing tandem solar cells. The modification of the optical property of perovskite, however, comes with a penalty — the material becomes hugely vulnerable to the environment, in particular, to light.
To counteract the wide bandgap perovskite’s delicate nature, the researchers engineered combinations of molecules composing a two-dimensional layer in the perovskite, stabilizing the solar cells.
“We developed a high-quality wide bandgap perovskite material and, in combination with silicon solar cells, achieved world-class perovskite-silicon tandem cells,” Shin said.
The development was only possible due to the engineering method, in which the mixing ratio of the molecules building the two-dimensional layer are carefully controlled. In this case, the perovskite material not only improved efficiency of the resulting solar cell but also gained durability, retaining 80% of its initial power conversion capability even after 1,000 hours of continuous illumination. This is the first time such a high efficiency has been achieved with a wide bandgap perovskite single layer alone, according to Shin.
“Such high-efficiency wide bandgap perovskite is an essential technology for achieving ultra-high efficiency of perovskite-silicon tandem (double layer) solar cells,” Shin said. “The results also show the importance of bandgap matching of upper and lower cells in these tandem solar cells.”
The researchers, having stabilized the wide bandgap perovskite material, are now focused on developing even more efficient tandem solar cells that are expected to have more than 30% of power conversion efficiency, something that no one has achieved yet,
“Our ultimate goal is to develop ultra-high-efficiency tandem solar cells that contribute to the increase of shared solar energy among all energy sources,” Shin said. “We want to contribute to making the planet healthier.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning, the Ministry of Trade Industry and Energy of Korea, and the U.S. Department of Energy.
Other contributors include Daehan Kim, Jekyung Kim, Passarut Boonmongkolras, Seong Ryul Pae and Minkyu Kim, all of whom affiliated with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST. Other authors include Byron W. Larson, Sean P. Dunfield, Chuanxiao Xiao, Jinhui Tong, Fei Zhang, Joseph J. Berry, Kai Zhu and Dong Hoe Kim, all of who are affiliated with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Colorado. Dunfield is also affiliated with the Materials Science and Engineering Program at the University of Colorado; Berry is also affiliated with the Department of Physics and the Renewable and Sustainable Energy Institute at the University of Colorado Boulder; and Kim is also affiliated with the Department of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Engineering at Sejong University. Hee Joon Jung and Vinayak Dravid of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Northwestern University; Ik Jae Park, Su Geun Ji and Jin Young Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Seoul National University; and Seok Beom Kang of the Department of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Engineering of Sejong University also contributed.
Image credit: Professor Byungha Shin, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication: Kim et al. (2020) “Efficient, stable silicon tandem cells enabled by anion-engineered wide band gap perovskites”. Science. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba3433
Profile:
Byungha Shin
Professor
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Daehan Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
zxzx4592@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.27 View 24784
Highly Efficient and Stable Double Layer Solar Cell Developed
Solar cells convert light into energy, but they can be inefficient and vulnerable to the environment, degrading with, ironically, too much light or other factors, including moisture and low temperature. An international research team has developed a new type of solar cell that can both withstand environmental hazards and is 26.7% efficient in power conversion.
They published their results on March 26 in Science.
The researchers, led by Byungha Shin, a professor from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, focused on developing a new class of light-absorbing material, called a wide bandgap perovskite. The material has a highly effective crystal structure that can process the power needs, but it can become problematic when exposed to environmental hazards, such as moisture. Researchers have made some progress increasing the efficiency of solar cells based on perovskite, but the material has greater potential than what was previously achieved.
To achieve better performance, Shin and his team built a double layer solar cell, called tandem, in which two or more light absorbers are stacked together to better utilize solar energy. To use perovskite in these tandem devices, the scientists modified the material’s optical property, which allows it to absorb a wider range of solar energy. Without the adjustment, the material is not as useful in achieving high performing tandem solar cells. The modification of the optical property of perovskite, however, comes with a penalty — the material becomes hugely vulnerable to the environment, in particular, to light.
To counteract the wide bandgap perovskite’s delicate nature, the researchers engineered combinations of molecules composing a two-dimensional layer in the perovskite, stabilizing the solar cells.
“We developed a high-quality wide bandgap perovskite material and, in combination with silicon solar cells, achieved world-class perovskite-silicon tandem cells,” Shin said.
The development was only possible due to the engineering method, in which the mixing ratio of the molecules building the two-dimensional layer are carefully controlled. In this case, the perovskite material not only improved efficiency of the resulting solar cell but also gained durability, retaining 80% of its initial power conversion capability even after 1,000 hours of continuous illumination. This is the first time such a high efficiency has been achieved with a wide bandgap perovskite single layer alone, according to Shin.
“Such high-efficiency wide bandgap perovskite is an essential technology for achieving ultra-high efficiency of perovskite-silicon tandem (double layer) solar cells,” Shin said. “The results also show the importance of bandgap matching of upper and lower cells in these tandem solar cells.”
The researchers, having stabilized the wide bandgap perovskite material, are now focused on developing even more efficient tandem solar cells that are expected to have more than 30% of power conversion efficiency, something that no one has achieved yet,
“Our ultimate goal is to develop ultra-high-efficiency tandem solar cells that contribute to the increase of shared solar energy among all energy sources,” Shin said. “We want to contribute to making the planet healthier.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Korea Institute of Energy Technology Evaluation and Planning, the Ministry of Trade Industry and Energy of Korea, and the U.S. Department of Energy.
Other contributors include Daehan Kim, Jekyung Kim, Passarut Boonmongkolras, Seong Ryul Pae and Minkyu Kim, all of whom affiliated with the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST. Other authors include Byron W. Larson, Sean P. Dunfield, Chuanxiao Xiao, Jinhui Tong, Fei Zhang, Joseph J. Berry, Kai Zhu and Dong Hoe Kim, all of who are affiliated with the National Renewable Energy Laboratory in Colorado. Dunfield is also affiliated with the Materials Science and Engineering Program at the University of Colorado; Berry is also affiliated with the Department of Physics and the Renewable and Sustainable Energy Institute at the University of Colorado Boulder; and Kim is also affiliated with the Department of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Engineering at Sejong University. Hee Joon Jung and Vinayak Dravid of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Northwestern University; Ik Jae Park, Su Geun Ji and Jin Young Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at Seoul National University; and Seok Beom Kang of the Department of Nanotechnology and Advanced Materials Engineering of Sejong University also contributed.
Image credit: Professor Byungha Shin, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication: Kim et al. (2020) “Efficient, stable silicon tandem cells enabled by anion-engineered wide band gap perovskites”. Science. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aba3433
Profile:
Byungha Shin
Professor
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Daehan Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
zxzx4592@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.27 View 24784 -
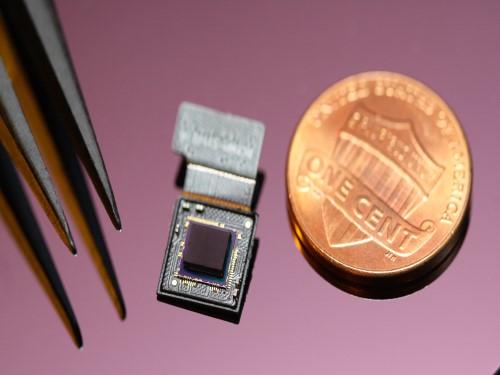 Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 22603
Ultrathin but Fully Packaged High-Resolution Camera
- Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera captures super-resolution images. -
The unique structures of biological vision systems in nature inspired scientists to design ultracompact imaging systems. A research group led by Professor Ki-Hun Jeong have made an ultracompact camera that captures high-contrast and high-resolution images. Fully packaged with micro-optical elements such as inverted micro-lenses, multilayered pinhole arrays, and gap spacers on the image sensor, the camera boasts a total track length of 740 μm and a field of view of 73°.
Inspired by the eye structures of the paper wasp species Xenos peckii, the research team completely suppressed optical noise between micro-lenses while reducing camera thickness. The camera has successfully demonstrated high-contrast clear array images acquired from tiny micro lenses. To further enhance the image quality of the captured image, the team combined the arrayed images into one image through super-resolution imaging.
An insect’s compound eye has superior visual characteristics, such as a wide viewing angle, high motion sensitivity, and a large depth of field while maintaining a small volume of visual structure with a small focal length. Among them, the eyes of Xenos peckii and an endoparasite found on paper wasps have hundreds of photoreceptors in a single lens unlike conventional compound eyes. In particular, the eye structures of an adult Xenos peckii exhibit hundreds of photoreceptors on an individual eyelet and offer engineering inspiration for ultrathin cameras or imaging applications because they have higher visual acuity than other compound eyes.
For instance, Xenos peckii’s eye-inspired cameras provide a 50 times higher spatial resolution than those based on arthropod eyes. In addition, the effective image resolution of the Xenos peckii’s eye can be further improved using the image overlaps between neighboring eyelets. This unique structure offers higher visual resolution than other insect eyes.
The team achieved high-contrast and super-resolution imaging through a novel arrayed design of micro-optical elements comprising multilayered aperture arrays and inverted micro-lens arrays directly stacked over an image sensor. This optical component was integrated with a complementary metal oxide semiconductor image sensor.
This is first demonstration of super-resolution imaging which acquires a single integrated image with high contrast and high resolving power reconstructed from high-contrast array images. It is expected that this ultrathin arrayed camera can be applied for further developing mobile devices, advanced surveillance vehicles, and endoscopes.
Professor Jeong said, “This research has led to technological advances in imaging technology. We will continue to strive to make significant impacts on multidisciplinary research projects in the fields of microtechnology and nanotechnology, seeking inspiration from natural photonic structures.”
This work was featured in Light Science & Applications last month and was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of and the Ministry of Health and Welfare (MOHW) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Ki-Hun Jeong, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Kisoo Kim, Kyung-Won Jang, Jae-Kwan Ryu, and Ki-Hun Jeong. (2020) “Biologically inspired ultrathin arrayed camera for high-contrast and high-resolution imaging”. Light Science & Applications. Volume 9. Article 28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-020-0261-8
Profile:
Ki-Hun Jeong
Professor
kjeong@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
Profile:
Kisoo Kim
Ph.D. Candidate
kisoo.kim1@kaist.ac.kr
http://biophotonics.kaist.ac.kr/
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
KAIST
(END)
2020.03.23 View 22603 -
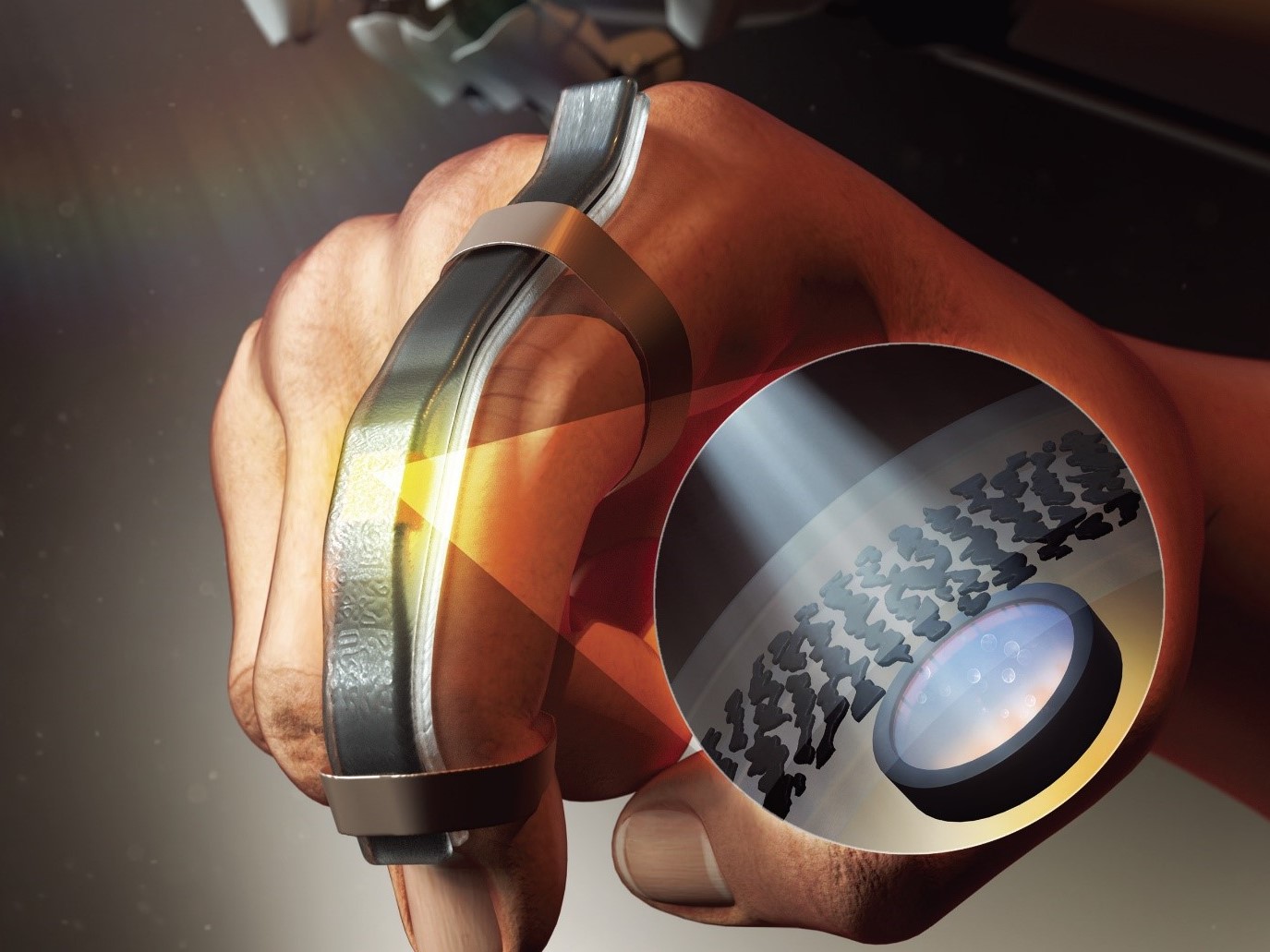 Wearable Strain Sensor Using Light Transmittance Helps Measure Physical Signals Better
KAIST researchers have developed a novel wearable strain sensor based on the modulation of optical transmittance of a carbon nanotube (CNT)-embedded elastomer. The sensor is capable of sensitive, stable, and continuous measurement of physical signals. This technology, featured in the March 4th issue of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces as a front cover article, shows great potential for the detection of subtle human motions and the real-time monitoring of body postures for healthcare applications.
A wearable strain sensor must have high sensitivity, flexibility, and stretchability, as well as low cost. Those used especially for health monitoring should also be tied to long-term solid performance, and be environmentally stable. Various stretchable strain sensors based on piezo-resistive and capacitive principles have been developed to meet all these requirements.
Conventional piezo-resistive strain sensors using functional nanomaterials, including CNTs as the most common example, have shown high sensitivity and great sensing performance. However, they suffer from poor long-term stability and linearity, as well as considerable signal hysteresis. As an alternative, piezo-capacitive strain sensors with better stability, lower hysteresis, and higher stretchability have been suggested. But due to the fact that piezo-capacitive strain sensors exhibit limited sensitivity and strong electromagnetic interference caused by the conductive objects in the surrounding environment, these conventional stretchable strain sensors are still facing limitations that are yet to be resolved.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering suggested that an optical-type stretchable strain sensor can be a good alternative to resolve the limitations of conventional piezo-resistive and piezo-capacitive strain sensors, because they have high stability and are less affected by environmental disturbances. The team then introduced an optical wearable strain sensor based on the light transmittance changes of a CNT-embedded elastomer, which further addresses the low sensitivity problem of conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
In order to achieve a large dynamic range for the sensor, Professor Park and his researchers chose Ecoflex as an elastomeric substrate with good mechanical durability, flexibility, and attachability on human skin, and the new optical wearable strain sensor developed by the research group actually shows a wide dynamic range of 0 to 400%.
In addition, the researchers propagated the microcracks under tensile strain within the film of multi-walled CNTs embedded in the Ecoflex substrate, changing the optical transmittance of the film. By doing so, it was possible for them to develop a wearable strain sensor having a sensitivity 10 times higher than conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
The proposed sensor has also passed the durability test with excellent results. The sensor’s response after 13,000 sets of cyclic loading was stable without any noticeable drift. This suggests that the sensor response can be used without degradation, even if the sensor is repeatedly used for a long time and in various environmental conditions.
Using the developed sensor, the research team could measure the finger bending motion and used it for robot control. They also developed a three-axes sensor array for body posture monitoring. The sensor was able to monitor human motions with small strains such as a pulse near the carotid artery and muscle movement around the mouth during pronunciation.
Professor Park said, “In this study, our group developed a new wearable strain sensor platform that overcomes many limitations of previously developed resistive, capacitive, and optical-type stretchable strain sensors. Our sensor could be widely used in a variety of fields including soft robotics, wearable electronics, electronic skin, healthcare, and even entertainment.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Jimin Gu, Donguk Kwon, Junseong Ahn, and Inkyu Park. (2020) “Wearable Strain sensors Using Light Transmittance Change of Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Elastomers with Microcracks” ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Volume 12. Issue 9. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18069
Profile:
Inkyu Park
Professor
inkyu@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
Micro/Nano Transducers Laboratory (MINT Lab)
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Profile:
Jimin Gu
Ph.D. Candidate
mint9411@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
MINT Lab
KAIST ME
(END)
2020.03.20 View 23478
Wearable Strain Sensor Using Light Transmittance Helps Measure Physical Signals Better
KAIST researchers have developed a novel wearable strain sensor based on the modulation of optical transmittance of a carbon nanotube (CNT)-embedded elastomer. The sensor is capable of sensitive, stable, and continuous measurement of physical signals. This technology, featured in the March 4th issue of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces as a front cover article, shows great potential for the detection of subtle human motions and the real-time monitoring of body postures for healthcare applications.
A wearable strain sensor must have high sensitivity, flexibility, and stretchability, as well as low cost. Those used especially for health monitoring should also be tied to long-term solid performance, and be environmentally stable. Various stretchable strain sensors based on piezo-resistive and capacitive principles have been developed to meet all these requirements.
Conventional piezo-resistive strain sensors using functional nanomaterials, including CNTs as the most common example, have shown high sensitivity and great sensing performance. However, they suffer from poor long-term stability and linearity, as well as considerable signal hysteresis. As an alternative, piezo-capacitive strain sensors with better stability, lower hysteresis, and higher stretchability have been suggested. But due to the fact that piezo-capacitive strain sensors exhibit limited sensitivity and strong electromagnetic interference caused by the conductive objects in the surrounding environment, these conventional stretchable strain sensors are still facing limitations that are yet to be resolved.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering suggested that an optical-type stretchable strain sensor can be a good alternative to resolve the limitations of conventional piezo-resistive and piezo-capacitive strain sensors, because they have high stability and are less affected by environmental disturbances. The team then introduced an optical wearable strain sensor based on the light transmittance changes of a CNT-embedded elastomer, which further addresses the low sensitivity problem of conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
In order to achieve a large dynamic range for the sensor, Professor Park and his researchers chose Ecoflex as an elastomeric substrate with good mechanical durability, flexibility, and attachability on human skin, and the new optical wearable strain sensor developed by the research group actually shows a wide dynamic range of 0 to 400%.
In addition, the researchers propagated the microcracks under tensile strain within the film of multi-walled CNTs embedded in the Ecoflex substrate, changing the optical transmittance of the film. By doing so, it was possible for them to develop a wearable strain sensor having a sensitivity 10 times higher than conventional optical stretchable strain sensors.
The proposed sensor has also passed the durability test with excellent results. The sensor’s response after 13,000 sets of cyclic loading was stable without any noticeable drift. This suggests that the sensor response can be used without degradation, even if the sensor is repeatedly used for a long time and in various environmental conditions.
Using the developed sensor, the research team could measure the finger bending motion and used it for robot control. They also developed a three-axes sensor array for body posture monitoring. The sensor was able to monitor human motions with small strains such as a pulse near the carotid artery and muscle movement around the mouth during pronunciation.
Professor Park said, “In this study, our group developed a new wearable strain sensor platform that overcomes many limitations of previously developed resistive, capacitive, and optical-type stretchable strain sensors. Our sensor could be widely used in a variety of fields including soft robotics, wearable electronics, electronic skin, healthcare, and even entertainment.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Publication:
Jimin Gu, Donguk Kwon, Junseong Ahn, and Inkyu Park. (2020) “Wearable Strain sensors Using Light Transmittance Change of Carbon Nanotube-Embedded Elastomers with Microcracks” ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces. Volume 12. Issue 9. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b18069
Profile:
Inkyu Park
Professor
inkyu@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
Micro/Nano Transducers Laboratory (MINT Lab)
Department of Mechanical Engineering (ME)Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Profile:
Jimin Gu
Ph.D. Candidate
mint9411@kaist.ac.kr
http://mintlab1.kaist.ac.kr
MINT Lab
KAIST ME
(END)
2020.03.20 View 23478 -
 ‘OSK Rising Stars 30’ Recognizes Four KAISTians
Four KAISTians were selected as star researchers to brighten the future of optics in commemoration of the 30th anniversary of the Optical Society of Korea (OSK). As ‘OSK Rising Stars 30’, the OSK named 27 domestic researchers under the age of 40 who have made significant contributions and will continue contributing to the development of Korea’s optics academia and industry.
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics was selected in recognition of his contributions to the field of biomedical optics. Professor Park focuses on developing novel optical methods for understanding, diagnosing, and treating human diseases, based on light scattering, light manipulation, and interferometry. As a member of numerous international optics societies including the OSA and the SPIE and a co-founder of two start-up companies, Professor Park continues to broaden his boundaries as a leading opticist and entrepreneur.
Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was recognized for blazing a trail in the field of broadband metamaterials. Professor Shin’s research on the broadband enhancement of the electric permittivity and refractive index of metamaterials has great potential in both academia and industry.
Professor Hongki Yoo from the Department of Mechanical Engineering is expected to create a significant ripple effect in the diagnosis of cardiovascular disorders through the development of new optical imaging techniques and applications.
Finally, Dr. Sejeong Kim, a KAIST graduate and a Chancellor’s postdoctoral research fellow at the University of Technology Sydney (UTS), was acknowledged for her optical device research utilizing two-dimensional materials. Dr. Kim’s research at UTS now focuses on the introduction of micro/nano cavities for new materials.
(END)
2020.03.16 View 13610
‘OSK Rising Stars 30’ Recognizes Four KAISTians
Four KAISTians were selected as star researchers to brighten the future of optics in commemoration of the 30th anniversary of the Optical Society of Korea (OSK). As ‘OSK Rising Stars 30’, the OSK named 27 domestic researchers under the age of 40 who have made significant contributions and will continue contributing to the development of Korea’s optics academia and industry.
Professor YongKeun Park from the Department of Physics was selected in recognition of his contributions to the field of biomedical optics. Professor Park focuses on developing novel optical methods for understanding, diagnosing, and treating human diseases, based on light scattering, light manipulation, and interferometry. As a member of numerous international optics societies including the OSA and the SPIE and a co-founder of two start-up companies, Professor Park continues to broaden his boundaries as a leading opticist and entrepreneur.
Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering was recognized for blazing a trail in the field of broadband metamaterials. Professor Shin’s research on the broadband enhancement of the electric permittivity and refractive index of metamaterials has great potential in both academia and industry.
Professor Hongki Yoo from the Department of Mechanical Engineering is expected to create a significant ripple effect in the diagnosis of cardiovascular disorders through the development of new optical imaging techniques and applications.
Finally, Dr. Sejeong Kim, a KAIST graduate and a Chancellor’s postdoctoral research fellow at the University of Technology Sydney (UTS), was acknowledged for her optical device research utilizing two-dimensional materials. Dr. Kim’s research at UTS now focuses on the introduction of micro/nano cavities for new materials.
(END)
2020.03.16 View 13610 -
 3D Hierarchically Porous Nanostructured Catalyst Helps Efficiently Reduce CO2
- This new catalyst will bring CO2 one step closer to serving as a sustainable energy source. -
KAIST researchers developed a three-dimensional (3D) hierarchically porous nanostructured catalyst with carbon dioxide (CO2) to carbon monoxide (CO) conversion rate up to 3.96 times higher than that of conventional nanoporous gold catalysts. This new catalyst helps overcome the existing limitations of the mass transport that has been a major cause of decreases in the CO2 conversion rate, holding a strong promise for the large-scale and cost-effective electrochemical conversion of CO2 into useful chemicals.
As CO2 emissions increase and fossil fuels deplete globally, reducing and converting CO2 to clean energy electrochemically has attracted a great deal of attention as a promising technology. Especially due to the fact that the CO2 reduction reaction occurs competitively with hydrogen evolution reactions (HER) at similar redox potentials, the development of an efficient electrocatalyst for selective and robust CO2 reduction reactions has remained a key technological issue.
Gold (Au) is one of the most commonly used catalysts in CO2 reduction reactions, but the high cost and scarcity of Au pose obstacles for mass commercial applications. The development of nanostructures has been extensively studied as a potential approach to improving the selectivity for target products and maximizing the number of active stable sites, thus enhancing the energy efficiency.
However, the nanopores of the previously reported complex nanostructures were easily blocked by gaseous CO bubbles during aqueous reactions. The CO bubbles hindered mass transport of the reactants through the electrolyte, resulting in low CO2 conversion rates.
In the study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA (PNAS) on March 4, a research group at KAIST led by Professor Seokwoo Jeon and Professor Jihun Oh from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering designed a 3D hierarchically porous Au nanostructure with two different sizes of macropores and nanopores. The team used proximity-field nanopatterning (PnP) and electroplating techniques that are effective for fabricating the 3D well-ordered nanostructures.
The proposed nanostructure, comprised of interconnected macroporous channels 200 to 300 nanometers (nm) wide and 10 nm nanopores, induces efficient mass transport through the interconnected macroporous channels as well as high selectivity by producing highly active stable sites from numerous nanopores.
As a result, its electrodes show a high CO selectivity of 85.8% at a low overpotential of 0.264 V and efficient mass activity that is up to 3.96 times higher than that of de-alloyed nanoporous Au electrodes.
“These results are expected to solve the problem of mass transfer in the field of similar electrochemical reactions and can be applied to a wide range of green energy applications for the efficient utilization of electrocatalysts,” said the researchers.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Seokwoo Jeon and Professor Jihun Oh, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Hyun et al. (2020) Hierarchically porous Au nanostructures with interconnected channels for efficient mass transport in electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA (PNAS). Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1918837117
Profile:
Seokwoo Jeon, PhD
Professor
jeon39@kaist.ac.kr
http://fdml.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile:
Jihun Oh, PhD
Associate Professor
jihun.oh@kaist.ac.kr
http://les.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
Department of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)
KAIST
Profile:
Gayea Hyun
PhD Candidate
cldywkd93@kaist.ac.kr
http://fdml.kaist.ac.kr
Flexible Devices and Metamaterials Laboratory (FDML)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
KAIST
Profile:
Jun Tae Song, PhD
Assistant Professor
song.juntae@cstf.kyushu-u.ac.jp
http://www.cstf.kyushu-u.ac.jp/~ishihara-lab/
Department of Applied Chemistry
https://www.kyushu-u.ac.jp
Kyushu UniversityFukuoka, Japan
(END)
2020.03.13 View 21022
3D Hierarchically Porous Nanostructured Catalyst Helps Efficiently Reduce CO2
- This new catalyst will bring CO2 one step closer to serving as a sustainable energy source. -
KAIST researchers developed a three-dimensional (3D) hierarchically porous nanostructured catalyst with carbon dioxide (CO2) to carbon monoxide (CO) conversion rate up to 3.96 times higher than that of conventional nanoporous gold catalysts. This new catalyst helps overcome the existing limitations of the mass transport that has been a major cause of decreases in the CO2 conversion rate, holding a strong promise for the large-scale and cost-effective electrochemical conversion of CO2 into useful chemicals.
As CO2 emissions increase and fossil fuels deplete globally, reducing and converting CO2 to clean energy electrochemically has attracted a great deal of attention as a promising technology. Especially due to the fact that the CO2 reduction reaction occurs competitively with hydrogen evolution reactions (HER) at similar redox potentials, the development of an efficient electrocatalyst for selective and robust CO2 reduction reactions has remained a key technological issue.
Gold (Au) is one of the most commonly used catalysts in CO2 reduction reactions, but the high cost and scarcity of Au pose obstacles for mass commercial applications. The development of nanostructures has been extensively studied as a potential approach to improving the selectivity for target products and maximizing the number of active stable sites, thus enhancing the energy efficiency.
However, the nanopores of the previously reported complex nanostructures were easily blocked by gaseous CO bubbles during aqueous reactions. The CO bubbles hindered mass transport of the reactants through the electrolyte, resulting in low CO2 conversion rates.
In the study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA (PNAS) on March 4, a research group at KAIST led by Professor Seokwoo Jeon and Professor Jihun Oh from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering designed a 3D hierarchically porous Au nanostructure with two different sizes of macropores and nanopores. The team used proximity-field nanopatterning (PnP) and electroplating techniques that are effective for fabricating the 3D well-ordered nanostructures.
The proposed nanostructure, comprised of interconnected macroporous channels 200 to 300 nanometers (nm) wide and 10 nm nanopores, induces efficient mass transport through the interconnected macroporous channels as well as high selectivity by producing highly active stable sites from numerous nanopores.
As a result, its electrodes show a high CO selectivity of 85.8% at a low overpotential of 0.264 V and efficient mass activity that is up to 3.96 times higher than that of de-alloyed nanoporous Au electrodes.
“These results are expected to solve the problem of mass transfer in the field of similar electrochemical reactions and can be applied to a wide range of green energy applications for the efficient utilization of electrocatalysts,” said the researchers.
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
Image credit: Professor Seokwoo Jeon and Professor Jihun Oh, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Hyun et al. (2020) Hierarchically porous Au nanostructures with interconnected channels for efficient mass transport in electrocatalytic CO2 reduction. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA (PNAS). Available online at https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1918837117
Profile:
Seokwoo Jeon, PhD
Professor
jeon39@kaist.ac.kr
http://fdml.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile:
Jihun Oh, PhD
Associate Professor
jihun.oh@kaist.ac.kr
http://les.kaist.ac.kr
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
Department of Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS)
KAIST
Profile:
Gayea Hyun
PhD Candidate
cldywkd93@kaist.ac.kr
http://fdml.kaist.ac.kr
Flexible Devices and Metamaterials Laboratory (FDML)
Department of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE)
KAIST
Profile:
Jun Tae Song, PhD
Assistant Professor
song.juntae@cstf.kyushu-u.ac.jp
http://www.cstf.kyushu-u.ac.jp/~ishihara-lab/
Department of Applied Chemistry
https://www.kyushu-u.ac.jp
Kyushu UniversityFukuoka, Japan
(END)
2020.03.13 View 21022 -
 Scientists Observe the Elusive Kondo Screening Cloud
Scientists ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon
An international research group of Professor Heung-Sun Sim has ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. This research, published in Nature on March 11, opens a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement. According to the research, the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This spin-spin interaction mediated by the Kondo cloud is unique since both its strength and sign (two spins favor either parallel or anti-parallel configuration) are electrically tunable, while conventional schemes cannot reverse the sign.
This phenomenon, which is important for many physical phenomena such as dilute magnetic impurities and spin glasses, is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed.
Magnetism arises from a property of electrons known as spin, meaning that they have angular momentum aligned in one of either two directions, conventionally known as up and down. However, due to a phenomenon known as the Kondo effect, the spins of conduction electrons—the electrons that flow freely in a material—become entangled with a localized magnetic impurity, and effectively screen it. The strength of this spin coupling, calibrated as a temperature, is known as the Kondo temperature.
The size of the cloud is another important parameter for a material containing multiple magnetic impurities because the spins in the cloud couple with one another and mediate the coupling between magnetic impurities when the clouds overlap. This happens in various materials such as Kondo lattices, spin glasses, and high temperature superconductors.
Although the Kondo effect for a single magnetic impurity is now a text-book subject in many-body physics, detection of its key object, the Kondo cloud and its length, has remained elusive despite many attempts during the past five decades. Experiments using nuclear magnetic resonance or scanning tunneling microscopy, two common methods for understanding the structure of matter, have either shown no signature of the cloud, or demonstrated a signature only at a very short distance, less than 1 nanometer, so much shorter than the predicted cloud size, which was in the micron range.
In the present study, the authors observed a Kondo screening cloud formed by an impurity defined as a localized electron spin in a quantum dot—a type of “artificial atom”—coupled to quasi-one-dimensional conduction electrons, and then used an interferometer to measure changes in the Kondo temperature, allowing them to investigate the presence of a cloud at the interferometer end.
Essentially, they slightly perturbed the conduction electrons at a location away from the quantum dot using an electrostatic gate. The wave of conducting electrons scattered by this perturbation returned back to the quantum dot and interfered with itself. This is similar to how a wave on a water surface being scattered by a wall forms a stripe pattern. The Kondo cloud is a quantum mechanical object which acts to preserve the wave nature of electrons inside the cloud.
Even though there is no direct electrostatic influence of the perturbation on the quantum dot, this interference modifies the Kondo signature measured by electron conductance through the quantum dot if the perturbation is present inside the cloud. In the study, the researchers found that the length as well as the shape of the cloud is universally scaled by the inverse of the Kondo temperature, and that the cloud’s size and shape were in good agreement with theoretical calculations.
Professor Sim at the Department of Physics proposed the method for detecting the Kondo cloud in the co-research with the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science, the City University of Hong Kong, the University of Tokyo, and Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
Professor Sim said, “The observed spin cloud is a micrometer-size object that has quantum mechanical wave nature and entanglement. This is why the spin cloud has not been observed despite a long search. It is remarkable in a fundamental and technical point of view that such a large quantum object can now be created, controlled, and detected.
Dr. Michihisa Yamamoto of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science also said, “It is very satisfying to have been able to obtain real space image of the Kondo cloud, as it is a real breakthrough for understanding various systems containing multiple magnetic impurities. The size of the Kondo cloud in semiconductors was found to be much larger than the typical size of semiconductor devices.”
Publication:
Borzenets et al. (2020) Observation of the Kondo screening cloud. Nature, 579. pp.210-213. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2058-6
Profile:
Heung-Sun Sim, PhD
Professor
hssim@kaist.ac.kr
https://qet.kaist.ac.kr/
Quantum Electron Correlation & Transport Theory Group (QECT Lab)
https://qc.kaist.ac.kr/index.php/group1/
Center for Quantum Coherence In COndensed Matter
Department of Physics
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2020.03.13 View 19312
Scientists Observe the Elusive Kondo Screening Cloud
Scientists ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon
An international research group of Professor Heung-Sun Sim has ended a 50-year quest by directly observing a quantum phenomenon known as a Kondo screening cloud. This research, published in Nature on March 11, opens a novel way to engineer spin screening and entanglement. According to the research, the cloud can mediate interactions between distant spins confined in quantum dots, which is a necessary protocol for semiconductor spin-based quantum information processing. This spin-spin interaction mediated by the Kondo cloud is unique since both its strength and sign (two spins favor either parallel or anti-parallel configuration) are electrically tunable, while conventional schemes cannot reverse the sign.
This phenomenon, which is important for many physical phenomena such as dilute magnetic impurities and spin glasses, is essentially a cloud that masks magnetic impurities in a material. It was known to exist but its spatial extension had never been observed, creating controversy over whether such an extension actually existed.
Magnetism arises from a property of electrons known as spin, meaning that they have angular momentum aligned in one of either two directions, conventionally known as up and down. However, due to a phenomenon known as the Kondo effect, the spins of conduction electrons—the electrons that flow freely in a material—become entangled with a localized magnetic impurity, and effectively screen it. The strength of this spin coupling, calibrated as a temperature, is known as the Kondo temperature.
The size of the cloud is another important parameter for a material containing multiple magnetic impurities because the spins in the cloud couple with one another and mediate the coupling between magnetic impurities when the clouds overlap. This happens in various materials such as Kondo lattices, spin glasses, and high temperature superconductors.
Although the Kondo effect for a single magnetic impurity is now a text-book subject in many-body physics, detection of its key object, the Kondo cloud and its length, has remained elusive despite many attempts during the past five decades. Experiments using nuclear magnetic resonance or scanning tunneling microscopy, two common methods for understanding the structure of matter, have either shown no signature of the cloud, or demonstrated a signature only at a very short distance, less than 1 nanometer, so much shorter than the predicted cloud size, which was in the micron range.
In the present study, the authors observed a Kondo screening cloud formed by an impurity defined as a localized electron spin in a quantum dot—a type of “artificial atom”—coupled to quasi-one-dimensional conduction electrons, and then used an interferometer to measure changes in the Kondo temperature, allowing them to investigate the presence of a cloud at the interferometer end.
Essentially, they slightly perturbed the conduction electrons at a location away from the quantum dot using an electrostatic gate. The wave of conducting electrons scattered by this perturbation returned back to the quantum dot and interfered with itself. This is similar to how a wave on a water surface being scattered by a wall forms a stripe pattern. The Kondo cloud is a quantum mechanical object which acts to preserve the wave nature of electrons inside the cloud.
Even though there is no direct electrostatic influence of the perturbation on the quantum dot, this interference modifies the Kondo signature measured by electron conductance through the quantum dot if the perturbation is present inside the cloud. In the study, the researchers found that the length as well as the shape of the cloud is universally scaled by the inverse of the Kondo temperature, and that the cloud’s size and shape were in good agreement with theoretical calculations.
Professor Sim at the Department of Physics proposed the method for detecting the Kondo cloud in the co-research with the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science, the City University of Hong Kong, the University of Tokyo, and Ruhr University Bochum in Germany.
Professor Sim said, “The observed spin cloud is a micrometer-size object that has quantum mechanical wave nature and entanglement. This is why the spin cloud has not been observed despite a long search. It is remarkable in a fundamental and technical point of view that such a large quantum object can now be created, controlled, and detected.
Dr. Michihisa Yamamoto of the RIKEN Center for Emergent Matter Science also said, “It is very satisfying to have been able to obtain real space image of the Kondo cloud, as it is a real breakthrough for understanding various systems containing multiple magnetic impurities. The size of the Kondo cloud in semiconductors was found to be much larger than the typical size of semiconductor devices.”
Publication:
Borzenets et al. (2020) Observation of the Kondo screening cloud. Nature, 579. pp.210-213. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-020-2058-6
Profile:
Heung-Sun Sim, PhD
Professor
hssim@kaist.ac.kr
https://qet.kaist.ac.kr/
Quantum Electron Correlation & Transport Theory Group (QECT Lab)
https://qc.kaist.ac.kr/index.php/group1/
Center for Quantum Coherence In COndensed Matter
Department of Physics
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
2020.03.13 View 19312 -
 A Single Biological Factor Predicts Distinct Cortical Organizations across Mammalian Species
-A KAIST team’s mathematical sampling model shows that retino-cortical mapping is a prime determinant in the topography of cortical organization.-
Researchers have explained how visual cortexes develop uniquely across the brains of different mammalian species. A KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has identified a single biological factor, the retino-cortical mapping ratio, that predicts distinct cortical organizations across mammalian species.
This new finding has resolved a long-standing puzzle in understanding visual neuroscience regarding the origin of functional architectures in the visual cortex. The study published in Cell Reports on March 10 demonstrates that the evolutionary variation of biological parameters may induce the development of distinct functional circuits in the visual cortex, even without species-specific developmental mechanisms.
In the primary visual cortex (V1) of mammals, neural tuning to visual stimulus orientation is organized into one of two distinct topographic patterns across species. While primates have columnar orientation maps, a salt-and-pepper type organization is observed in rodents.
For decades, this sharp contrast between cortical organizations has spawned fundamental questions about the origin of functional architectures in the V1. However, it remained unknown whether these patterns reflect disparate developmental mechanisms across mammalian taxa, or simply originate from variations in biological parameters under a universal development process.
To identify a determinant predicting distinct cortical organizations, Professor Paik and his researchers Jaeson Jang and Min Song examined the exact condition that generates columnar and salt-and-pepper organizations, respectively. Next, they applied a mathematical model to investigate how the topographic information of the underlying retinal mosaics pattern could be differently mapped onto a cortical space, depending on the mapping condition.
The research team proved that the retino-cortical feedforwarding mapping ratio appeared to be correlated to the cortical organization of each species. In the model simulations, the team found that distinct cortical circuitries can arise from different V1 areas and retinal ganglion cell (RGC) mosaic sizes. The team’s mathematical sampling model shows that retino-cortical mapping is a prime determinant in the topography of cortical organization, and this prediction was confirmed by neural parameter analysis of the data from eight phylogenetically distinct mammalian species.
Furthermore, the researchers proved that the Nyquist sampling theorem explains this parametric division of cortical organization with high accuracy. They showed that a mathematical model predicts that the organization of cortical orientation tuning makes a sharp transition around the Nyquist sampling frequency, explaining why cortical organizations can be observed in either columnar or salt-and-pepper organizations, but not in intermediates between these two stages.
Professor Paik said, “Our findings make a significant impact for understanding the origin of functional architectures in the visual cortex of the brain, and will provide a broad conceptual advancement as well as advanced insights into the mechanism underlying neural development in evolutionarily divergent species.”
He continued, “We believe that our findings will be of great interest to scientists working in a wide range of fields such as neuroscience, vision science, and developmental biology.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Image credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Jaeson Jang, Min Song, and Se-Bum Paik. (2020). Retino-cortical mapping ratio predicts columnar and salt-and-pepper organization in mammalian visual cortex. Cell Reports. Volume 30. Issue 10. pp. 3270-3279. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.038
Profile:
Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile:
Jaeson Jang
Ph.D. Candidate
jaesonjang@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST
Profile:
Min Song
Ph.D. Candidate
night@kaist.ac.kr
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering, KAIST
(END)
2020.03.11 View 16926
A Single Biological Factor Predicts Distinct Cortical Organizations across Mammalian Species
-A KAIST team’s mathematical sampling model shows that retino-cortical mapping is a prime determinant in the topography of cortical organization.-
Researchers have explained how visual cortexes develop uniquely across the brains of different mammalian species. A KAIST research team led by Professor Se-Bum Paik from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has identified a single biological factor, the retino-cortical mapping ratio, that predicts distinct cortical organizations across mammalian species.
This new finding has resolved a long-standing puzzle in understanding visual neuroscience regarding the origin of functional architectures in the visual cortex. The study published in Cell Reports on March 10 demonstrates that the evolutionary variation of biological parameters may induce the development of distinct functional circuits in the visual cortex, even without species-specific developmental mechanisms.
In the primary visual cortex (V1) of mammals, neural tuning to visual stimulus orientation is organized into one of two distinct topographic patterns across species. While primates have columnar orientation maps, a salt-and-pepper type organization is observed in rodents.
For decades, this sharp contrast between cortical organizations has spawned fundamental questions about the origin of functional architectures in the V1. However, it remained unknown whether these patterns reflect disparate developmental mechanisms across mammalian taxa, or simply originate from variations in biological parameters under a universal development process.
To identify a determinant predicting distinct cortical organizations, Professor Paik and his researchers Jaeson Jang and Min Song examined the exact condition that generates columnar and salt-and-pepper organizations, respectively. Next, they applied a mathematical model to investigate how the topographic information of the underlying retinal mosaics pattern could be differently mapped onto a cortical space, depending on the mapping condition.
The research team proved that the retino-cortical feedforwarding mapping ratio appeared to be correlated to the cortical organization of each species. In the model simulations, the team found that distinct cortical circuitries can arise from different V1 areas and retinal ganglion cell (RGC) mosaic sizes. The team’s mathematical sampling model shows that retino-cortical mapping is a prime determinant in the topography of cortical organization, and this prediction was confirmed by neural parameter analysis of the data from eight phylogenetically distinct mammalian species.
Furthermore, the researchers proved that the Nyquist sampling theorem explains this parametric division of cortical organization with high accuracy. They showed that a mathematical model predicts that the organization of cortical orientation tuning makes a sharp transition around the Nyquist sampling frequency, explaining why cortical organizations can be observed in either columnar or salt-and-pepper organizations, but not in intermediates between these two stages.
Professor Paik said, “Our findings make a significant impact for understanding the origin of functional architectures in the visual cortex of the brain, and will provide a broad conceptual advancement as well as advanced insights into the mechanism underlying neural development in evolutionarily divergent species.”
He continued, “We believe that our findings will be of great interest to scientists working in a wide range of fields such as neuroscience, vision science, and developmental biology.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF).
Image credit: Professor Se-Bum Paik, KAIST
Image usage restrictions: News organizations may use or redistribute this image, with proper attribution, as part of news coverage of this paper only.
Publication:
Jaeson Jang, Min Song, and Se-Bum Paik. (2020). Retino-cortical mapping ratio predicts columnar and salt-and-pepper organization in mammalian visual cortex. Cell Reports. Volume 30. Issue 10. pp. 3270-3279. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.02.038
Profile:
Se-Bum Paik
Assistant Professor
sbpaik@kaist.ac.kr
http://vs.kaist.ac.kr/
VSNN Laboratory
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering
http://kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
Profile:
Jaeson Jang
Ph.D. Candidate
jaesonjang@kaist.ac.kr
Department of Bio and Brain Engineering, KAIST
Profile:
Min Song
Ph.D. Candidate
night@kaist.ac.kr
Program of Brain and Cognitive Engineering, KAIST
(END)
2020.03.11 View 16926