EC
-
 Newdin Contents Donates 'Strikezon'
Newdin Contents, an online and mobile game maker, made a gift of ‘Strikezon' to KAIST on April 19. The screen game valued at 100 million KRW will be placed in the lobby of the School of Computing, enriching the diverse physical activity options for the KAIST community. The donation was made at a ceremony attended by KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, the CEO of the Newdin, Hyo-Kyum Kim, and Head of the School of Computing Professor Myoung Ho Kim.
At the Strikezon, students can enjoy mini baseball games indoors including a batting challenge and a pitching mode indoors for free.
President Shin thanked Mr. Kim of Newdin Contents, saying the donation will be a stepping stone for possible mutual collaborations which will play a synergistic role for technological development. Mr. Kim noted, “We are very pleased to donate the program to KAIST, which is the alma mater of Joon-Mo Hwang, the developer of Strikezon.” He added that Newdin Contents will make every effort to produce advanced game products with state of the art technology.
(Photo caption:President Sung-Chul Shin hits the ball at the Strikezon on April 19.)
2017.04.19 View 5712
Newdin Contents Donates 'Strikezon'
Newdin Contents, an online and mobile game maker, made a gift of ‘Strikezon' to KAIST on April 19. The screen game valued at 100 million KRW will be placed in the lobby of the School of Computing, enriching the diverse physical activity options for the KAIST community. The donation was made at a ceremony attended by KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, the CEO of the Newdin, Hyo-Kyum Kim, and Head of the School of Computing Professor Myoung Ho Kim.
At the Strikezon, students can enjoy mini baseball games indoors including a batting challenge and a pitching mode indoors for free.
President Shin thanked Mr. Kim of Newdin Contents, saying the donation will be a stepping stone for possible mutual collaborations which will play a synergistic role for technological development. Mr. Kim noted, “We are very pleased to donate the program to KAIST, which is the alma mater of Joon-Mo Hwang, the developer of Strikezon.” He added that Newdin Contents will make every effort to produce advanced game products with state of the art technology.
(Photo caption:President Sung-Chul Shin hits the ball at the Strikezon on April 19.)
2017.04.19 View 5712 -
 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST announced its 30 scholarship recipients for the 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program on April 18. The six-week program, starting from July 10, will be run in Korea, Japan, and China.
The program provides young global scholars with focused and challenging nuclear nonproliferation studies. Young scholars will be exposed to diverse science and technology policies and practices concurrently conducted in many countries and the future direction for enhancing nuclear nonproliferation. They will participate in a series of seminars, projects, international conferences, and field trips.
Since its launch in 2014, the program has educated 71 young scholars. This year, more than 150 scholars from 37 countries applied for the program, reflecting the growing reputation of the program both at home and abroad. The director of the NEREC, Professor Man-Sung Yim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST said that young scholars from very prestigious foreign universities have shown strong interest in the program. According to Professor Yim, this year’s recipients are from 26 universities from 16 countries including Harvard University, Oxford University, the National Research Nuclear University of Russia, and the Tokyo Institute of Technology
2017.04.19 View 9790
2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST announced its 30 scholarship recipients for the 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program on April 18. The six-week program, starting from July 10, will be run in Korea, Japan, and China.
The program provides young global scholars with focused and challenging nuclear nonproliferation studies. Young scholars will be exposed to diverse science and technology policies and practices concurrently conducted in many countries and the future direction for enhancing nuclear nonproliferation. They will participate in a series of seminars, projects, international conferences, and field trips.
Since its launch in 2014, the program has educated 71 young scholars. This year, more than 150 scholars from 37 countries applied for the program, reflecting the growing reputation of the program both at home and abroad. The director of the NEREC, Professor Man-Sung Yim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST said that young scholars from very prestigious foreign universities have shown strong interest in the program. According to Professor Yim, this year’s recipients are from 26 universities from 16 countries including Harvard University, Oxford University, the National Research Nuclear University of Russia, and the Tokyo Institute of Technology
2017.04.19 View 9790 -
 Scholarship in Memory of Professor Shin Endowed by His Family
Professor Joong-Hoon Shin of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology was touted as a genius young scientist who would take the lead in nanoscience technology. After earning degrees from Harvard and the Caltech, he was appointed at KAIST at age 27. He was the youngest professor ever appointed in Korea.
Professor Shin’s outstanding research in the field of semiconductor nano-optics led him to be named as the ‘Scientist of the Year’ for three consecutive years from 2004 by the most prestigious scientist and technology organizations including the Korean Academy Science and Technology, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korean government. However, a fatal car accident last September on the way home from a seminar in Gangwon Province took his life and a promising scholar’s research was left unfinished. He was 47 years old.
Mrs. Young-Eun Hong, the widow of the late Professor Shin, made a 100 million KRW gift to KAIST to establish the ‘Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship’ on April 7. The scholarship will provide financial assistance to outstanding students of physics and nanoscience.
At the donation ceremony attended by President Sung-Chul Shin, Professor Shin’s colleagues and students, and family members, Mrs. Hong said, “My family would like to help young students achieve their dreams on behalf of my husband. I hope students will remember my husband’s passion and dedication toward his studies for a long time. He was a very hard worker.”
Working at KAIST, Professor Shin made significant achievements in field of semiconductor nano-optics, specializing in silicon photonics and silicon nanocrystal structures. In particular, his research team gained attention reproducing the structure of ‘Morpho butterfly’ wings, which produce the same colors from various angles, using external light as a light source without extra power. Their research led to the creation of original technology dubbed the biomimetics reflective display and was published in Nature in 2012.
Professor Shin’s legacy still endures. In February, a research team under Professor Shin-Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering includingthe late Professor Shin’s doctoral student Seung Yeol Lee, posthumously dedicated their research published on Advanced Materials to Professor Shin. ( click )
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a physicist, said “His passing is a great loss to the whole scientific and technology community, at home and abroad. But Joong-Hoon Shin scholarship will enable the growth and ensure the strength of nanoscience and its education at KAIST. We will uphold Professor Shin’s legacy by doing our best to make KAIST a world-leading university which can create global value.”
Mrs. Hong said she will continue her husband’s academic legacy at his alma maters, Harvard and the Caltech, where he earned his BS in physics and his Ph.D. in applied physics respectively. She said she will start fundraising to establish the Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship at Harvard and Caltech from July.
(Mrs. Hong poses with President Sung-Chul Shin after donating 100 million KRW for establishing 'Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship' in memory of her husband on April 7.)
2017.04.10 View 8763
Scholarship in Memory of Professor Shin Endowed by His Family
Professor Joong-Hoon Shin of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology was touted as a genius young scientist who would take the lead in nanoscience technology. After earning degrees from Harvard and the Caltech, he was appointed at KAIST at age 27. He was the youngest professor ever appointed in Korea.
Professor Shin’s outstanding research in the field of semiconductor nano-optics led him to be named as the ‘Scientist of the Year’ for three consecutive years from 2004 by the most prestigious scientist and technology organizations including the Korean Academy Science and Technology, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korean government. However, a fatal car accident last September on the way home from a seminar in Gangwon Province took his life and a promising scholar’s research was left unfinished. He was 47 years old.
Mrs. Young-Eun Hong, the widow of the late Professor Shin, made a 100 million KRW gift to KAIST to establish the ‘Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship’ on April 7. The scholarship will provide financial assistance to outstanding students of physics and nanoscience.
At the donation ceremony attended by President Sung-Chul Shin, Professor Shin’s colleagues and students, and family members, Mrs. Hong said, “My family would like to help young students achieve their dreams on behalf of my husband. I hope students will remember my husband’s passion and dedication toward his studies for a long time. He was a very hard worker.”
Working at KAIST, Professor Shin made significant achievements in field of semiconductor nano-optics, specializing in silicon photonics and silicon nanocrystal structures. In particular, his research team gained attention reproducing the structure of ‘Morpho butterfly’ wings, which produce the same colors from various angles, using external light as a light source without extra power. Their research led to the creation of original technology dubbed the biomimetics reflective display and was published in Nature in 2012.
Professor Shin’s legacy still endures. In February, a research team under Professor Shin-Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering includingthe late Professor Shin’s doctoral student Seung Yeol Lee, posthumously dedicated their research published on Advanced Materials to Professor Shin. ( click )
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a physicist, said “His passing is a great loss to the whole scientific and technology community, at home and abroad. But Joong-Hoon Shin scholarship will enable the growth and ensure the strength of nanoscience and its education at KAIST. We will uphold Professor Shin’s legacy by doing our best to make KAIST a world-leading university which can create global value.”
Mrs. Hong said she will continue her husband’s academic legacy at his alma maters, Harvard and the Caltech, where he earned his BS in physics and his Ph.D. in applied physics respectively. She said she will start fundraising to establish the Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship at Harvard and Caltech from July.
(Mrs. Hong poses with President Sung-Chul Shin after donating 100 million KRW for establishing 'Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship' in memory of her husband on April 7.)
2017.04.10 View 8763 -
 Professor Won Do Heo Receives 'Scientist of the Month Award'
Professor Won Do Heo of the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the “Scientist of the Month” for April 2017 by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Heo was recognized for his suggestion of a new biological research method developing various optogenetics technology which controls cell function by using light. He developed the technology using lasers or LED light, without the need for surgery or drug administration, to identify the cause of diseases related to calcium ions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
The general technique used in optogenetics, that control cells in the body with light, is the simple activation and deactivation of neurons.
Professor Heo developed a calcium ion channel activation technique (OptoSTIM1) to activate calcium ions in the body using light. He also succeeded in increasing calcium concentrations with light to enhance the memory capacity of mice two-fold.
Using this technology, the desired amount and residing time of calcium ion influx can be controlled by changing light intensity and exposure periods, enabling the function of a single cell or various cells in animal tissue to be controlled remotely.
The experimental results showed that calcium ion influx can be activated in cells that are affected by calcium ions, such as normal cells, cancer cells, and human embryonic stem cells. By controlling calcium concentrations with light, it is possible to control biological phenomena, such as cellular growth, neurotransmitter transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone control.
Professor Heo said, “Until now, it was standard to use optogenetics to activate neurons using channelrhodopsin. The development of this new optogenetic technique using calcium ion channel activation can be applied to various biological studies, as well as become an essential research technique in neurobiology.
The “Scientist of the Month Award” is given every month to one researcher who made significant contributions to the advancement of science and technology with their outstanding research achievement. The awardee will receive prize money of ten million won.
2017.04.07 View 9606
Professor Won Do Heo Receives 'Scientist of the Month Award'
Professor Won Do Heo of the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the “Scientist of the Month” for April 2017 by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Heo was recognized for his suggestion of a new biological research method developing various optogenetics technology which controls cell function by using light. He developed the technology using lasers or LED light, without the need for surgery or drug administration, to identify the cause of diseases related to calcium ions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
The general technique used in optogenetics, that control cells in the body with light, is the simple activation and deactivation of neurons.
Professor Heo developed a calcium ion channel activation technique (OptoSTIM1) to activate calcium ions in the body using light. He also succeeded in increasing calcium concentrations with light to enhance the memory capacity of mice two-fold.
Using this technology, the desired amount and residing time of calcium ion influx can be controlled by changing light intensity and exposure periods, enabling the function of a single cell or various cells in animal tissue to be controlled remotely.
The experimental results showed that calcium ion influx can be activated in cells that are affected by calcium ions, such as normal cells, cancer cells, and human embryonic stem cells. By controlling calcium concentrations with light, it is possible to control biological phenomena, such as cellular growth, neurotransmitter transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone control.
Professor Heo said, “Until now, it was standard to use optogenetics to activate neurons using channelrhodopsin. The development of this new optogenetic technique using calcium ion channel activation can be applied to various biological studies, as well as become an essential research technique in neurobiology.
The “Scientist of the Month Award” is given every month to one researcher who made significant contributions to the advancement of science and technology with their outstanding research achievement. The awardee will receive prize money of ten million won.
2017.04.07 View 9606 -
 ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 9905
ANSYS Korea Donates Engineering Simulation Software
ANSYS Korea made an in-kind donation of engineering simulation software, Multiphysics Campus Solution, to KAIST on March 24. ANSYS Korea donated 10,000 copies for education and 1,000 copies for research valued at about 4 billion KRW (about 200 billion KRW commercially).
The ANSYS software will benefit the engineering simulation work in nine departments and 60 labs for three years, including the departments of mechanical engineering, aerospace engineering, electrical engineering, civil and environmental engineering, nuclear and quantum engineering, chemical and bimolecular engineering, bio and brain engineering, materials science and engineering, and the Cho Chun Shik Graduate School of Green Transportation.
ANSYS is a global engineering simulation company. It provides ANSYS CAE (Computer Aided Engineering) software products in various industries in the world as well as various support, training, and consulting services. Deemed an exemplary model of university-industry R&D collaboration especially in the Industry 4.0 era, their donation will help create the best engineering education environment possible at KAIST.
ANSYS's multi-physics campus solution is a comprehensive software suite that spans the entire range of physics, providing access to virtually any field of engineering simulation that a design process requires. It expands the fields of fluids, structures, electromagnetics, and semiconductors. Undergraduates use it to learn physics principles and gain hands-on, real-world experience that can lead to a deeper understanding of engineering concepts. Postgraduate researchers apply simulation tools to solve complex engineering problems and produce data for their theses.
"Engineering simulations are playing a stronger role in science and engineering. ANSYS software will help our undergraduates and our researchers learn the principles of physics and deepen their understanding of engineering concepts. We hope this will serve as an instrumental tool for multidisciplinary studies, critical to fostering our students," said President Sung-Chul Shin.
ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho added, "We sincerely hope our software will help KAIST students and researchers experience the best engineering education and achieve significant research results."
(Photo caption: President Shin (left) poses with ANSYS Korea CEO Yong-Won Cho at the donation ceremony on March 24 at KAIST)
2017.03.24 View 9905 -
 Professor Kwangjo Kim Named as Fellow of IACR
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security has been selected as a fellow of the International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR).
The IACR has honored outstanding scholars who have achieved academic excellence in cryptologic research since 2004. He is the first Korean scholar to receive an IACR fellowship.
The IACR, established in 1981, is responsible for organizing international cryptologic conferences every year including the three major cryptologic academic conferences Eurocrypt, Crypto, and Asiacript. The IACR also sponsors workshop series such as the Theory of Cryptography Conference (TCC), the Workshop on Fast Software Encryption (FSE), the Public Key Cryptography Workshop (PKC), and Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES).
Professor Kim, an internationally acclaimed scholar in the fields of cryptology and information security theory and its applications, was recognized for his outstanding academic achievements and leadership. He has made significant contributions to cryptology in Korea by hosting Asiacript in 1996 and 2001 as well as CHES in 2014. During his 34 years of academic activities, he has published more than 80 SCI journal papers and garnered more than 20,000 citations.
Professor Kim served on the board of the directors of the IACR from 2000 to 2004 and was the chairperson of the Asiacript Steering Committee from 2005 to 2008. He is on the editorial board of the online journal Cryptography.
Professor Kim said, “I am so humbled and honored to be named as a fellow of such a prestigious academic association. I will continue to strive to assist highly educated information security personnel with further research in cryptology.”
2017.03.16 View 9511
Professor Kwangjo Kim Named as Fellow of IACR
Professor Kwangjo Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security has been selected as a fellow of the International Association for Cryptologic Research (IACR).
The IACR has honored outstanding scholars who have achieved academic excellence in cryptologic research since 2004. He is the first Korean scholar to receive an IACR fellowship.
The IACR, established in 1981, is responsible for organizing international cryptologic conferences every year including the three major cryptologic academic conferences Eurocrypt, Crypto, and Asiacript. The IACR also sponsors workshop series such as the Theory of Cryptography Conference (TCC), the Workshop on Fast Software Encryption (FSE), the Public Key Cryptography Workshop (PKC), and Cryptographic Hardware and Embedded Systems (CHES).
Professor Kim, an internationally acclaimed scholar in the fields of cryptology and information security theory and its applications, was recognized for his outstanding academic achievements and leadership. He has made significant contributions to cryptology in Korea by hosting Asiacript in 1996 and 2001 as well as CHES in 2014. During his 34 years of academic activities, he has published more than 80 SCI journal papers and garnered more than 20,000 citations.
Professor Kim served on the board of the directors of the IACR from 2000 to 2004 and was the chairperson of the Asiacript Steering Committee from 2005 to 2008. He is on the editorial board of the online journal Cryptography.
Professor Kim said, “I am so humbled and honored to be named as a fellow of such a prestigious academic association. I will continue to strive to assist highly educated information security personnel with further research in cryptology.”
2017.03.16 View 9511 -
 Global Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies
The Center for Science, Policy and Society (CSPS) at the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy of KAIST will host the 2017 Global Expert Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution March 17-18 at the Plaza Hotel in Seoul.
At the workshop, experts from public and private sectors at home and abroad will address the socio-economic impacts and implications of the emergence of new technologies that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about. The workshop will be hosted in collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Global Future Council (GFC) on Technology, Values and Policy. The World Economic Forum’s network of GFCs is the world’s foremost interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking about the future.
Four keynote speakers, including Professor Wendell Wallach of the Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics at Yale University and Dean of the School of Public Policy and Management at Tsinghua University Lan Xue, will deliver speeches. Professor Wallach is the leader of an AI/Robotics Global Governance Project sponsored by the World Economic Forum and will make a speech entitled “Build the Global Infrastructure to Make Sure that AI and Robotics Will Be Beneficial.” Dean Xue, a member of the World Economic Forum’s GFC on Tech, Values, and Policy, is well known for his analysis of the social implications of the risks brought about by emerging technologies. He will speak on “Global Risk Governance of Disruptive 4IR Technologies.”
More than thirty experts will participate in the workshop. Speakers include the KAIST Vice President for Planning and Budget Soohyun Kim, Dean of KAIST Institute San Yup Lee, Professor Jaeseung Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, Dr. Sung Chul Kang of the KIST Healthcare Robotics Research Group, and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Program Director Kyong Hoon Kim.
The CSPS of KAIST will continue to make collaborative research efforts with the GFC for developing new insights and perspectives on key global systems as well as study the impact and governance of key emerging technologies.
2017.03.16 View 11394
Global Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies
The Center for Science, Policy and Society (CSPS) at the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy of KAIST will host the 2017 Global Expert Workshop on the Risks of Emerging Technologies Driving the Fourth Industrial Revolution March 17-18 at the Plaza Hotel in Seoul.
At the workshop, experts from public and private sectors at home and abroad will address the socio-economic impacts and implications of the emergence of new technologies that the Fourth Industrial Revolution will bring about. The workshop will be hosted in collaboration with the World Economic Forum’s Global Future Council (GFC) on Technology, Values and Policy. The World Economic Forum’s network of GFCs is the world’s foremost interdisciplinary knowledge network dedicated to promoting innovative thinking about the future.
Four keynote speakers, including Professor Wendell Wallach of the Interdisciplinary Center for Bioethics at Yale University and Dean of the School of Public Policy and Management at Tsinghua University Lan Xue, will deliver speeches. Professor Wallach is the leader of an AI/Robotics Global Governance Project sponsored by the World Economic Forum and will make a speech entitled “Build the Global Infrastructure to Make Sure that AI and Robotics Will Be Beneficial.” Dean Xue, a member of the World Economic Forum’s GFC on Tech, Values, and Policy, is well known for his analysis of the social implications of the risks brought about by emerging technologies. He will speak on “Global Risk Governance of Disruptive 4IR Technologies.”
More than thirty experts will participate in the workshop. Speakers include the KAIST Vice President for Planning and Budget Soohyun Kim, Dean of KAIST Institute San Yup Lee, Professor Jaeseung Jeong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST, Dr. Sung Chul Kang of the KIST Healthcare Robotics Research Group, and Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology Program Director Kyong Hoon Kim.
The CSPS of KAIST will continue to make collaborative research efforts with the GFC for developing new insights and perspectives on key global systems as well as study the impact and governance of key emerging technologies.
2017.03.16 View 11394 -
 Dr.Sung-Chul Shin Inaugurated as the 16th President of KAIST
(President Shin delivers his inaugural address at the inauguration ceremony on March 15.)
Professor Sung-Chul Shin was officially inaugurated as its 16th president of KAIST on March 15 in a ceremony at the KAIST Auditorium.
The celebration began with a procession by dignitaries including the KAIST Board of Trustees Chairman Jang-Moo Lee, the National Academy of Sciences of Korea President Sook-Il Kwun, Daejeon City Mayor Sun-Taik Kwon, National Assemblyman Sangmin Lee, KAIST Alumni Association President Jungsik Koh. Academic leaders, foreign envoys, faculty, students, and staff members of KAIST joined the ceremony.
In his inaugural speech, President Shin presented a new vision for KAIST to become a global value creator in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He said that KAIST has played a pivotal role in the nation’s industrialization and information revolution over the past half century and, with the advent of the new industry paradigm, KAIST should be now responsible for being a new value creator, not only serving the nation but pursuing global betterment. “KAIST should be a global hub of new knowledge and technology creation,” he emphasized.
Envisioning a “Global Value-Creative World-Leading University,” President Shin aims for KAIST to be an institution which can create global value as an innovative global leading research university. To realize this vision, he pledged to continue innovation in five areas of education, research & development, technology commercialization, globalization of the campus, and future strategy for the university and the nation.
In the educational innovation, he emphasized multidisciplinary studies, team work, and leadership training for students. To this end, KAIST will expand the non-departmental courses toward entire 4-year course while concurrently operating the existing system of declaring a major in students’ second year. KAIST will offer mandatory courses in humanities, social sciences, and arts and most classes will be run by team-based learning and group research activities. “KAIST Global Leadership Center” will support students to develop the qualities required for collaboration and the global leaderships.
With respect to the research innovation, President Shin said KAIST will establish “Convergence Research Matrix” system to foster strategic research groups for interdisciplinary and convergence collaboration across a wide range of divisions and departments. “Based on the CRMS, we will identify 10 flagship future-oriented convergence research areas for KAIST to truly claim its reputation as a world-leading research university,” he said. He added he will also introduce the “Collaborative Research Lab” system to better retain the academic successes without interruption, and to improve the continuity of research. “We will strive to organize teams of professors in diverse age groups to work together in mutually complementary fields,” he added.
In terms of technological commercialization, he hopes that KAIST to be a role model. He said he will make every effort to establish a resilient R&DB environment with ideas, technologies, and entrepreneurship. KAIST will rev up a new university-industry cooperation, fully sponsoring the creation of “Technology in-Kind Investment Companies.”
KAIST will continue to take initiative for globalization. He said KAIST will create an ‘English-Only Zone’ at the campus, saying that his ultimate goal is to create Korean-English bilingual campus. He also asked the foreign community to make their effort to learn Korean and Korean culture while staying at KAIST, in an effort to embrace diversity at the campus. He plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from nine percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of five percent.
As for the future strategy for the university and the nation, he will soon finalize the long-term strategic plan of “Vision 2031” that will lay out a roadmap for KAIST future direction toward its 60th anniversary. KAIST will also play a fundamental role in shaping national policies and strategies for science and technology by operating think-tank groups that consist of KAIST beyond disciplines. These think-tanks will design detailed development plans for KAIST as well as for national strategies for the advancement of science and technology.
He said that such institutional innovation will not be completed without the support, dedication, and passion of all KAIST members, adding that he will strive to serve them with 3Cs (Change, Communication, and Care).
For the full text of President Shin’s inaugural address, please click.
2017.03.15 View 12280
Dr.Sung-Chul Shin Inaugurated as the 16th President of KAIST
(President Shin delivers his inaugural address at the inauguration ceremony on March 15.)
Professor Sung-Chul Shin was officially inaugurated as its 16th president of KAIST on March 15 in a ceremony at the KAIST Auditorium.
The celebration began with a procession by dignitaries including the KAIST Board of Trustees Chairman Jang-Moo Lee, the National Academy of Sciences of Korea President Sook-Il Kwun, Daejeon City Mayor Sun-Taik Kwon, National Assemblyman Sangmin Lee, KAIST Alumni Association President Jungsik Koh. Academic leaders, foreign envoys, faculty, students, and staff members of KAIST joined the ceremony.
In his inaugural speech, President Shin presented a new vision for KAIST to become a global value creator in the Fourth Industrial Revolution. He said that KAIST has played a pivotal role in the nation’s industrialization and information revolution over the past half century and, with the advent of the new industry paradigm, KAIST should be now responsible for being a new value creator, not only serving the nation but pursuing global betterment. “KAIST should be a global hub of new knowledge and technology creation,” he emphasized.
Envisioning a “Global Value-Creative World-Leading University,” President Shin aims for KAIST to be an institution which can create global value as an innovative global leading research university. To realize this vision, he pledged to continue innovation in five areas of education, research & development, technology commercialization, globalization of the campus, and future strategy for the university and the nation.
In the educational innovation, he emphasized multidisciplinary studies, team work, and leadership training for students. To this end, KAIST will expand the non-departmental courses toward entire 4-year course while concurrently operating the existing system of declaring a major in students’ second year. KAIST will offer mandatory courses in humanities, social sciences, and arts and most classes will be run by team-based learning and group research activities. “KAIST Global Leadership Center” will support students to develop the qualities required for collaboration and the global leaderships.
With respect to the research innovation, President Shin said KAIST will establish “Convergence Research Matrix” system to foster strategic research groups for interdisciplinary and convergence collaboration across a wide range of divisions and departments. “Based on the CRMS, we will identify 10 flagship future-oriented convergence research areas for KAIST to truly claim its reputation as a world-leading research university,” he said. He added he will also introduce the “Collaborative Research Lab” system to better retain the academic successes without interruption, and to improve the continuity of research. “We will strive to organize teams of professors in diverse age groups to work together in mutually complementary fields,” he added.
In terms of technological commercialization, he hopes that KAIST to be a role model. He said he will make every effort to establish a resilient R&DB environment with ideas, technologies, and entrepreneurship. KAIST will rev up a new university-industry cooperation, fully sponsoring the creation of “Technology in-Kind Investment Companies.”
KAIST will continue to take initiative for globalization. He said KAIST will create an ‘English-Only Zone’ at the campus, saying that his ultimate goal is to create Korean-English bilingual campus. He also asked the foreign community to make their effort to learn Korean and Korean culture while staying at KAIST, in an effort to embrace diversity at the campus. He plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from nine percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of five percent.
As for the future strategy for the university and the nation, he will soon finalize the long-term strategic plan of “Vision 2031” that will lay out a roadmap for KAIST future direction toward its 60th anniversary. KAIST will also play a fundamental role in shaping national policies and strategies for science and technology by operating think-tank groups that consist of KAIST beyond disciplines. These think-tanks will design detailed development plans for KAIST as well as for national strategies for the advancement of science and technology.
He said that such institutional innovation will not be completed without the support, dedication, and passion of all KAIST members, adding that he will strive to serve them with 3Cs (Change, Communication, and Care).
For the full text of President Shin’s inaugural address, please click.
2017.03.15 View 12280 -
 13 KAIST Faculty Named as Inaugural Members of Y-KAST
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) launched the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology (Y-KAST) and selected 73 scientists as its inaugural members on February 24. Among them, 13 KAIST faculty were recognized as the inaugural members of Y-KAST.
Y-KAIST, made up of distinguished mid-career scientists under the age of 45, will take the leading role in international collaboration as well as innovative agenda-making in science and technology.
The inaugural members include Professor Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry and Dr. Sung-Jin Oh of the Center for Mathematical Challenges at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), affiliated with KAIST. Professor Ihee is gaining wide acclaim in the fields of physics and chemistry, and in 2016, Dr. Oh was the youngest ever awardee of the Presidential Award of Young Scientist.
The other Y-KAIST members are as follows: Professors Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry; Mi Young Kim, Byung-Kwan Cho, and Ji-Joon Song of the Department of Biological Sciences; Song-Yong Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering; Sang-il Oum of the Department of Mathematical Sciences; Jung Kyoon Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering; Seokwoo Jeon, Sang Ouk Kim, and Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Jang Wook Choi of the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability); and Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering.
The leading countries of the Academy of Science, which include Germany, Sweden, Belgium, Canada, and Japan, have established the Young Academy of Science since 2010 in order to encourage the research activities of their young scientists and to establish a global platform for collaborative research projects through their active networking at home and abroad.
President Myung-Chul Lee of KAST said, “We will spare no effort to connect these outstanding mid-career researchers for their future collaboration. Their networking will make significant impacts toward their own research activities as well as the global stature of Korea’s science and technology R&D.
(Photo caption: Members of Y-KAST pose at the inaugural ceremony of Y-KAST on February 24.)
2017.03.02 View 19442
13 KAIST Faculty Named as Inaugural Members of Y-KAST
The Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) launched the Young Korean Academy of Science and Technology (Y-KAST) and selected 73 scientists as its inaugural members on February 24. Among them, 13 KAIST faculty were recognized as the inaugural members of Y-KAST.
Y-KAIST, made up of distinguished mid-career scientists under the age of 45, will take the leading role in international collaboration as well as innovative agenda-making in science and technology.
The inaugural members include Professor Hyotcherl Ihee of the Department of Chemistry and Dr. Sung-Jin Oh of the Center for Mathematical Challenges at the Korea Institute for Advanced Study (KIAS), affiliated with KAIST. Professor Ihee is gaining wide acclaim in the fields of physics and chemistry, and in 2016, Dr. Oh was the youngest ever awardee of the Presidential Award of Young Scientist.
The other Y-KAIST members are as follows: Professors Haeshin Lee of the Department of Chemistry; Mi Young Kim, Byung-Kwan Cho, and Ji-Joon Song of the Department of Biological Sciences; Song-Yong Kim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering; Sang-il Oum of the Department of Mathematical Sciences; Jung Kyoon Choi of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering; Seokwoo Jeon, Sang Ouk Kim, and Il-Doo Kim of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering; Jang Wook Choi of the Graduate School of EEWS (Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability); and Jeong Ho Lee of the Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering.
The leading countries of the Academy of Science, which include Germany, Sweden, Belgium, Canada, and Japan, have established the Young Academy of Science since 2010 in order to encourage the research activities of their young scientists and to establish a global platform for collaborative research projects through their active networking at home and abroad.
President Myung-Chul Lee of KAST said, “We will spare no effort to connect these outstanding mid-career researchers for their future collaboration. Their networking will make significant impacts toward their own research activities as well as the global stature of Korea’s science and technology R&D.
(Photo caption: Members of Y-KAST pose at the inaugural ceremony of Y-KAST on February 24.)
2017.03.02 View 19442 -
 Semiconductor Photonic Nanocavities on Paper Substrates
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics and his team at KAIST have developed a semiconductor photonic nanocavity laser that can operate on a paper substrate.
The researchers hope that this novel method, which involves transferring nano-sized photonic crystal particles onto a paper substrate with high absorptiveness, will enable the diagnoses of various diseases by using high-tech semiconductor sensors at low cost.
The results of this research were published in the November 17th, 2016, issue of Advanced Materials.
Photonic crystals, which utilize light as a medium to provide high bandwidths, can transfer large amounts of information. Compared with their electronic counterparts, photonic crystals also consume less energy to operate.
Normally, semiconductor photonic particles require substrates, which play only a passive role in the assembly and endurance of individual, functional photonic components. These substrates, however, are bulky and environmentally hazardous as they are made up of non-biodegradable materials.
The research team overcame these two shortcomings by replacing a semiconductor substrate with standard paper. The substrate’s mass was reduced considerably, and because paper is made from trees, it degrades. Paper can be easily and cheaply acquired from our surroundings, which drastically reduces the unit cost of semiconductors.
In addition, paper possesses superior mechanical characteristics. It is flexible and can be repeatedly folded and unfolded without being torn. These are traits that have long been sought by researchers for existing flexible substrates.
The research team used a micro-sized stamp to detach photonic crystal nanobeam cavities selectively from their original substrate and transfer them onto a new paper substrate. Using this technique, the team removed nanophotonic crystals that had been patterned (using a process of selectively etching circuits onto a substrate) onto a semiconductor substrate with a high degree of integration, and realigned them as desired on a paper substrate.
The nanophotonic crystals that the team combined with paper in this research were 0.5 micrometers in width, 6 micrometers in length, and 0.3 micrometers in height—about one-hundredth of the width of a single hair (0.1 millimeter).
The team also transferred their photonic crystals onto paper with a fluid channel, which proved that it could be used as a refractive index sensor. As can be seen in current commercial pregnancy diagnosis kits, paper has high absorptiveness. Since photonic crystal particles have high sensitivity, they are highly suitable for applications such as sensors.
Professor Cho stated that “by using paper substrates, this technology can greatly contribute to the rising field of producing environmentally-friendly photonic particles” and “by combining inexpensive paper and high-performance photonic crystal sensors, we can obtain low prices as well as designing appropriate technologies with high performance.”
Dr. Sejeong Kim of the Department of Physics participated in this study as the first author, and Professor Kwanwoo Shin of Sogang University and Professor Yong-Hee Lee of KAIST also took part in this research. The research was supported by the National Research Foundation’s Mid-Career Researcher Program, and the Climate Change Research Hub of KAIST.
Figure 1. Illustration of photonic crystal lasers on paper substrates
Figure 2. Photonic crystal resonator laser and refractive index sensor operating on paper substrates
2017.03.01 View 8030
Semiconductor Photonic Nanocavities on Paper Substrates
Professor Yong-Hoon Cho of the Department of Physics and his team at KAIST have developed a semiconductor photonic nanocavity laser that can operate on a paper substrate.
The researchers hope that this novel method, which involves transferring nano-sized photonic crystal particles onto a paper substrate with high absorptiveness, will enable the diagnoses of various diseases by using high-tech semiconductor sensors at low cost.
The results of this research were published in the November 17th, 2016, issue of Advanced Materials.
Photonic crystals, which utilize light as a medium to provide high bandwidths, can transfer large amounts of information. Compared with their electronic counterparts, photonic crystals also consume less energy to operate.
Normally, semiconductor photonic particles require substrates, which play only a passive role in the assembly and endurance of individual, functional photonic components. These substrates, however, are bulky and environmentally hazardous as they are made up of non-biodegradable materials.
The research team overcame these two shortcomings by replacing a semiconductor substrate with standard paper. The substrate’s mass was reduced considerably, and because paper is made from trees, it degrades. Paper can be easily and cheaply acquired from our surroundings, which drastically reduces the unit cost of semiconductors.
In addition, paper possesses superior mechanical characteristics. It is flexible and can be repeatedly folded and unfolded without being torn. These are traits that have long been sought by researchers for existing flexible substrates.
The research team used a micro-sized stamp to detach photonic crystal nanobeam cavities selectively from their original substrate and transfer them onto a new paper substrate. Using this technique, the team removed nanophotonic crystals that had been patterned (using a process of selectively etching circuits onto a substrate) onto a semiconductor substrate with a high degree of integration, and realigned them as desired on a paper substrate.
The nanophotonic crystals that the team combined with paper in this research were 0.5 micrometers in width, 6 micrometers in length, and 0.3 micrometers in height—about one-hundredth of the width of a single hair (0.1 millimeter).
The team also transferred their photonic crystals onto paper with a fluid channel, which proved that it could be used as a refractive index sensor. As can be seen in current commercial pregnancy diagnosis kits, paper has high absorptiveness. Since photonic crystal particles have high sensitivity, they are highly suitable for applications such as sensors.
Professor Cho stated that “by using paper substrates, this technology can greatly contribute to the rising field of producing environmentally-friendly photonic particles” and “by combining inexpensive paper and high-performance photonic crystal sensors, we can obtain low prices as well as designing appropriate technologies with high performance.”
Dr. Sejeong Kim of the Department of Physics participated in this study as the first author, and Professor Kwanwoo Shin of Sogang University and Professor Yong-Hee Lee of KAIST also took part in this research. The research was supported by the National Research Foundation’s Mid-Career Researcher Program, and the Climate Change Research Hub of KAIST.
Figure 1. Illustration of photonic crystal lasers on paper substrates
Figure 2. Photonic crystal resonator laser and refractive index sensor operating on paper substrates
2017.03.01 View 8030 -
 Prof. Woo Chang Kim Is Appointed as Managing Editor of Quantitative Finance
Professor Woo Chang Kim of the Industrial and Systems Engineering Department has been elected as the Managing Editor of Quantitative Finance.
Founded in 2001, Quantitative Finance has been an internationally-acclaimed peer-reviewed journal in the field of financial engineering, along with Mathematical Finance.
This is the first time for a Korean researcher to be named for the editorial board, which consists of eminent scholars from around the world, including four Nobel laureates.
Professor Kim’s expertise lies in financial optimization, portfolio management, and asset liability management. In recent years, he has focused his research on robo-advisors in the area of FinTech, and for this contribution, he was appointed as managing editor.
Professor Kim also served as an editor, deputy editor, and a member of the editorial boards for various journals, including the Journal of Portfolio Management and Optimization and Engineering. Currently, he serves as a member of the Korean National Pension Fund’s Electoral Commission, an adviser to Samsung Asset Management Co., Ltd., and the director of the KAIST Asset Management for Future Technology Research Center that was opened in October 2016.
2017.02.23 View 8922
Prof. Woo Chang Kim Is Appointed as Managing Editor of Quantitative Finance
Professor Woo Chang Kim of the Industrial and Systems Engineering Department has been elected as the Managing Editor of Quantitative Finance.
Founded in 2001, Quantitative Finance has been an internationally-acclaimed peer-reviewed journal in the field of financial engineering, along with Mathematical Finance.
This is the first time for a Korean researcher to be named for the editorial board, which consists of eminent scholars from around the world, including four Nobel laureates.
Professor Kim’s expertise lies in financial optimization, portfolio management, and asset liability management. In recent years, he has focused his research on robo-advisors in the area of FinTech, and for this contribution, he was appointed as managing editor.
Professor Kim also served as an editor, deputy editor, and a member of the editorial boards for various journals, including the Journal of Portfolio Management and Optimization and Engineering. Currently, he serves as a member of the Korean National Pension Fund’s Electoral Commission, an adviser to Samsung Asset Management Co., Ltd., and the director of the KAIST Asset Management for Future Technology Research Center that was opened in October 2016.
2017.02.23 View 8922 -
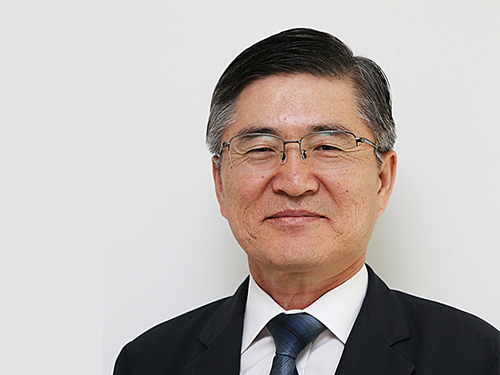
 Dr. Sung-Chul Shin Selected 16th President of KAIST
(President Sung-Chul Shin)
The KAIST Board of Trustees elected Professor Sung-Chul Shin of the Department of Physics the 16th president of KAIST on February 21. Professor Shin succeeds President Sung-Mo Kang whose four-year term will end on February 23. He is the first KAIST alumnus to serve as its president.
The Board of Trustees announced, “We believe that Professor Shin’s scientific achievement, outstanding leadership, and clear vision will serve KAIST faculty, students, and staff very well. He will be the best person to help KAIST leap forward in the four years ahead.”
The newly-elected president said, “I am humbled and honored to have been elected to lead such a prestigious institute of Korea. Aiming to be one of the top ten global universities, KAIST will continue to innovate its systems.” Previously, Dr. Shin led the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) for six years as president since 2011.
Professor Shin joined the KAIST faculty in 1989. He graduated from Seoul National University and then earned his MS degree in condensed matter physics at KAIST in 1977. After earning his Ph.D. in material physics at Northwestern University in 1984, he worked at Eastman Kodak Research Labs as a senior research scientist for five years.
Before heading to DGIST, President Shin held key administrative positions at KAIST from the early 1990s including dean of planning, dean of the international office, and vice-dean of student affairs. During President Robert Laughlin’s tenure, the first foreign president at KAIST, he served as vice-president for two years from 2004. He also served on the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology of the Korean government as vice chairperson from 2015 to 2016.
A renowned scholar in the field of nanoscience, President Shin’s research focuses on the artificial synthesis and characterization of nonmagnetic materials, magnetic anisotropy, and magneto-optical phenomena. He leads the Laboratory for Nanospinics of Spintronic Materials at KAIST and has published in 290 journals while holding 37 patents.
A fellow in the American Physical Society (APS) since 2008, he was the president of the Korean Physical Society from 2011 to 2012. He has been on the editorial board of J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials from 2009 and was the first Korean recipient of the Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (AUMS) Award, which recognizes outstanding scientists in the field of magnetics.
President Shin envisions making KAIST’s research and education more competitive through continuing innovation. His innovation efforts will extend to the five key areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future planning.
Among his priorities, he emphasizes multidisciplinary studies and leadership training for students. He plans to focus on undeclared major courses for undergraduates to help them expand their experience and exposure to diverse disciplines. This approach will help create well-rounded engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs by enabling them to develop skills while leveraging a strong connection to the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
To better respond to Industry 4.0, which calls for convergence studies and collaborative work, he proposed establishing a ‘Convergence Innovation System’ by strategically selecting 10 flagship convergence research groups. In order to accelerate the technology commercialization and ecosystem of start-ups, he will strengthen entrepreneurship education, making it a prerequisite requirement for students. President Shin said he will spare no effort to incubate and spin-off ventures in which KAIST technology is being transferred. For globalization efforts, he plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from 9 percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of 5 percent. For future strategic innovation, he will implement a long-term innovation strategic plan dubbed ‘Vision 2031.’
2017.02.22 View 12778
Dr. Sung-Chul Shin Selected 16th President of KAIST
(President Sung-Chul Shin)
The KAIST Board of Trustees elected Professor Sung-Chul Shin of the Department of Physics the 16th president of KAIST on February 21. Professor Shin succeeds President Sung-Mo Kang whose four-year term will end on February 23. He is the first KAIST alumnus to serve as its president.
The Board of Trustees announced, “We believe that Professor Shin’s scientific achievement, outstanding leadership, and clear vision will serve KAIST faculty, students, and staff very well. He will be the best person to help KAIST leap forward in the four years ahead.”
The newly-elected president said, “I am humbled and honored to have been elected to lead such a prestigious institute of Korea. Aiming to be one of the top ten global universities, KAIST will continue to innovate its systems.” Previously, Dr. Shin led the Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology (DGIST) for six years as president since 2011.
Professor Shin joined the KAIST faculty in 1989. He graduated from Seoul National University and then earned his MS degree in condensed matter physics at KAIST in 1977. After earning his Ph.D. in material physics at Northwestern University in 1984, he worked at Eastman Kodak Research Labs as a senior research scientist for five years.
Before heading to DGIST, President Shin held key administrative positions at KAIST from the early 1990s including dean of planning, dean of the international office, and vice-dean of student affairs. During President Robert Laughlin’s tenure, the first foreign president at KAIST, he served as vice-president for two years from 2004. He also served on the Presidential Advisory Council on Science and Technology of the Korean government as vice chairperson from 2015 to 2016.
A renowned scholar in the field of nanoscience, President Shin’s research focuses on the artificial synthesis and characterization of nonmagnetic materials, magnetic anisotropy, and magneto-optical phenomena. He leads the Laboratory for Nanospinics of Spintronic Materials at KAIST and has published in 290 journals while holding 37 patents.
A fellow in the American Physical Society (APS) since 2008, he was the president of the Korean Physical Society from 2011 to 2012. He has been on the editorial board of J. Magnetism and Magnetic Materials from 2009 and was the first Korean recipient of the Asian Union of Magnetics Societies (AUMS) Award, which recognizes outstanding scientists in the field of magnetics.
President Shin envisions making KAIST’s research and education more competitive through continuing innovation. His innovation efforts will extend to the five key areas of education, research, technology commercialization, globalization, and future planning.
Among his priorities, he emphasizes multidisciplinary studies and leadership training for students. He plans to focus on undeclared major courses for undergraduates to help them expand their experience and exposure to diverse disciplines. This approach will help create well-rounded engineers, scientists, and entrepreneurs by enabling them to develop skills while leveraging a strong connection to the arts, humanities, and social sciences.
To better respond to Industry 4.0, which calls for convergence studies and collaborative work, he proposed establishing a ‘Convergence Innovation System’ by strategically selecting 10 flagship convergence research groups. In order to accelerate the technology commercialization and ecosystem of start-ups, he will strengthen entrepreneurship education, making it a prerequisite requirement for students. President Shin said he will spare no effort to incubate and spin-off ventures in which KAIST technology is being transferred. For globalization efforts, he plans to increase the ratio of foreign faculty from 9 percent to 15 percent, while doubling the current foreign student enrollment ratio of 5 percent. For future strategic innovation, he will implement a long-term innovation strategic plan dubbed ‘Vision 2031.’
2017.02.22 View 12778