EC
-
 Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 11189
Professor Kwon to Represent the Asia-Pacific Region of the IEEE RAS
Professor Dong-Soon Kwon of the Mechanical Engineering Department at KAIST has been reappointed to the Administrative Committee of the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE) Robotics and Automation Society (IEEE RAS). Beginning January 1, 2017, he will serve his second three-year term, which will end in 2019. In 2014, he was the first Korean appointed to the committee, representing the Asia-Pacific community of the IEEE Society.
Professor Kwon said, “I feel thankful but, at the same time, it is a great responsibility to serve the Asian research community within the Society. I hope I can contribute to the development of robotics engineering in the region and in Korea as well.”
Consisted of 18 elected members, the administrative committee manages the major activities of IEEE RAS including hosting its annual flagship meeting, the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.
The IEEE RAS fosters the advancement in the theory and practice of robotics and automation engineering and facilitates the exchange of scientific and technological knowledge that supports the maintenance of high professional standards among its members.
2016.12.06 View 11189 -
 Mystery of Biological Plastic Synthesis Machinery Unveiled
Plastics and other polymers are used every day. These polymers are mostly made from fossil resources by refining petrochemicals. On the other hand, many microorganisms naturally synthesize polyesters known as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) as distinct granules inside cells.
PHAs are a family of microbial polyesters that have attracted much attention as biodegradable and biocompatible plastics and elastomers that can substitute petrochemical counterparts. There have been numerous papers and patents on gene cloning and metabolic engineering of PHA biosynthetic machineries, biochemical studies, and production of PHAs; simple Google search with “polyhydroxyalkanoates” yielded returns of 223,000 document pages. PHAs have always been considered amazing examples of biological polymer synthesis. It is astounding to see PHAs of 500 kDa to sometimes as high as 10,000 kDa can be synthesized in vivo by PHA synthase, the key polymerizing enzyme in PHA biosynthesis. They have attracted great interest in determining the crystal structure of PHA synthase over the last 30 years, but unfortunately without success. Thus, the characteristics and molecular mechanisms of PHA synthase were under a dark veil.
In two papers published back-to-back in Biotechnology Journal online on November 30, 2016, a Korean research team led by Professor Kyung-Jin Kim at Kyungpook National University and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) described the crystal structure of PHA synthase from Ralstonia eutropha, the best studied bacterium for PHA production, and reported the structural basis for the detailed molecular mechanisms of PHA biosynthesis. The crystal structure has been deposited to Protein Data Bank in February 2016. After deciphering the crystal structure of the catalytic domain of PHA synthase, in addition to other structural studies on whole enzyme and related proteins, the research team also performed experiments to elucidate the mechanisms of the enzyme reaction, validating detailed structures, enzyme engineering, and also N-terminal domain studies among others.
Through several biochemical studies based on crystal structure, the authors show that PHA synthase exists as a dimer and is divided into two distinct domains, the N-terminal domain (RePhaC1ND) and the C-terminal domain (RePhaC1CD). The RePhaC1CD catalyzes the polymerization reaction via a non-processive ping-pong mechanism using a Cys-His-Asp catalytic triad. The two catalytic sites of the RePhaC1CD dimer are positioned 33.4 Å apart, suggesting that the polymerization reaction occurs independently at each site. This study also presents the structure-based mechanisms for substrate specificities of various PHA synthases from different classes.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, who has worked on this topic for more than 20 years, said,
“The results and information presented in these two papers have long been awaited not only in the PHA community, but also metabolic engineering, bacteriology/microbiology, and in general biological sciences communities. The structural information on PHA synthase together with the recently deciphered reaction mechanisms will be valuable for understanding the detailed mechanisms of biosynthesizing this important energy/redox storage material, and also for the rational engineering of PHA synthases to produce designer bioplastics from various monomers more efficiently.”
Indeed, these two papers published in Biotechnology Journal finally reveal the 30-year mystery of machinery of biological polyester synthesis, and will serve as the essential compass in creating designer and more efficient bioplastic machineries.
References:
Jieun Kim, Yeo-Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Sang Yup Lee and Kyung-Jin Kim. “Crystal structure of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase C-terminal domain and reaction mechanisms” Biotechnology Journal DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600648
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/biot.201600648/abstract
Yeo-Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Jieun Kim, Kyeong Sik Jin, Sang Yup Lee and Kyung-Jin Kim. “Structure and function of the N-terminal domain of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, and the proposed structure and mechanisms of the whole enzyme” Biotechnology Journal DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600649
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/biot.201600649/abstract
2016.12.02 View 11172
Mystery of Biological Plastic Synthesis Machinery Unveiled
Plastics and other polymers are used every day. These polymers are mostly made from fossil resources by refining petrochemicals. On the other hand, many microorganisms naturally synthesize polyesters known as polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) as distinct granules inside cells.
PHAs are a family of microbial polyesters that have attracted much attention as biodegradable and biocompatible plastics and elastomers that can substitute petrochemical counterparts. There have been numerous papers and patents on gene cloning and metabolic engineering of PHA biosynthetic machineries, biochemical studies, and production of PHAs; simple Google search with “polyhydroxyalkanoates” yielded returns of 223,000 document pages. PHAs have always been considered amazing examples of biological polymer synthesis. It is astounding to see PHAs of 500 kDa to sometimes as high as 10,000 kDa can be synthesized in vivo by PHA synthase, the key polymerizing enzyme in PHA biosynthesis. They have attracted great interest in determining the crystal structure of PHA synthase over the last 30 years, but unfortunately without success. Thus, the characteristics and molecular mechanisms of PHA synthase were under a dark veil.
In two papers published back-to-back in Biotechnology Journal online on November 30, 2016, a Korean research team led by Professor Kyung-Jin Kim at Kyungpook National University and Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) described the crystal structure of PHA synthase from Ralstonia eutropha, the best studied bacterium for PHA production, and reported the structural basis for the detailed molecular mechanisms of PHA biosynthesis. The crystal structure has been deposited to Protein Data Bank in February 2016. After deciphering the crystal structure of the catalytic domain of PHA synthase, in addition to other structural studies on whole enzyme and related proteins, the research team also performed experiments to elucidate the mechanisms of the enzyme reaction, validating detailed structures, enzyme engineering, and also N-terminal domain studies among others.
Through several biochemical studies based on crystal structure, the authors show that PHA synthase exists as a dimer and is divided into two distinct domains, the N-terminal domain (RePhaC1ND) and the C-terminal domain (RePhaC1CD). The RePhaC1CD catalyzes the polymerization reaction via a non-processive ping-pong mechanism using a Cys-His-Asp catalytic triad. The two catalytic sites of the RePhaC1CD dimer are positioned 33.4 Å apart, suggesting that the polymerization reaction occurs independently at each site. This study also presents the structure-based mechanisms for substrate specificities of various PHA synthases from different classes.
Professor Sang Yup Lee, who has worked on this topic for more than 20 years, said,
“The results and information presented in these two papers have long been awaited not only in the PHA community, but also metabolic engineering, bacteriology/microbiology, and in general biological sciences communities. The structural information on PHA synthase together with the recently deciphered reaction mechanisms will be valuable for understanding the detailed mechanisms of biosynthesizing this important energy/redox storage material, and also for the rational engineering of PHA synthases to produce designer bioplastics from various monomers more efficiently.”
Indeed, these two papers published in Biotechnology Journal finally reveal the 30-year mystery of machinery of biological polyester synthesis, and will serve as the essential compass in creating designer and more efficient bioplastic machineries.
References:
Jieun Kim, Yeo-Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Sang Yup Lee and Kyung-Jin Kim. “Crystal structure of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase C-terminal domain and reaction mechanisms” Biotechnology Journal DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600648
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/biot.201600648/abstract
Yeo-Jin Kim, So Young Choi, Jieun Kim, Kyeong Sik Jin, Sang Yup Lee and Kyung-Jin Kim. “Structure and function of the N-terminal domain of Ralstonia eutropha polyhydroxyalkanoate synthase, and the proposed structure and mechanisms of the whole enzyme” Biotechnology Journal DOI: 10.1002/biot.201600649
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/biot.201600649/abstract
2016.12.02 View 11172 -
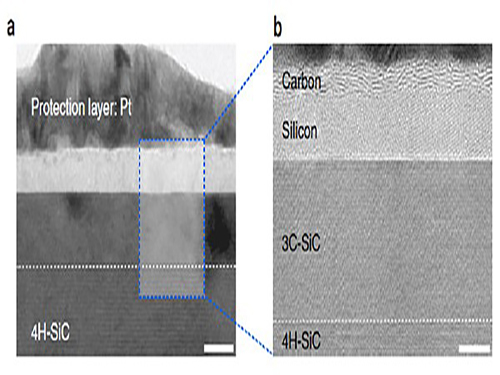 Making Graphene Using Laser-induced Phase Separation
IBS & KAIST researchers clarify how laser annealing technology can lead to the production of ultrathin nanomaterials
All our smart phones have shiny flat AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays. Behind each single pixel of these displays hides at least two silicon transistors which are mass-manufactured using laser annealing technology. While the traditional methods to make the transistors use temperature above 1,000°C, the laser technique reaches the same results at low temperatures even on plastic substrates (melting temperature below 300°C). Interestingly, a similar procedure can be used to generate crystals of graphene. Graphene is a strong and thin nano-material made of carbon, its electric and heat-conductive properties have attracted the attention of scientists worldwide.
Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and his research group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), as well as Professor Sung-Yool Choi of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team discovered graphene synthesis mechanism using laser-induced solid-state phase separation of single-crystal silicon carbide (SiC). This study, available in Nature Communications, clarifies how this laser technology can separate a complex compound (SiC) into its ultrathin elements of carbon and silicon.
Although several fundamental studies presented the effect of excimer lasers in transforming elemental materials like silicon, the laser interaction with more complex compounds like SiC has rarely been studied due to the complexity of compound phase transition and ultra-short processing time.
With high resolution microscope images and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists found that a single-pulse irradiation of xenon chloride excimer laser of 30 nanoseconds melts SiC, leading to the separation of a liquid SiC layer, a disordered carbon layer with graphitic domains (about 2.5 nm thick) on top surface and a polycrystalline silicon layer (about 5 nm) below carbon layer. Giving additional pulses causes the sublimation of the separated silicon, while the disordered carbon layer is transformed into a multilayer graphene.
"This research shows that the laser material interaction technology can be a powerful tool for the next generation of two dimensional nanomaterials," said Professor Lee.
Professor Choi added: "Using laser-induced phase separation of complex compounds, new types of two dimensional materials can be synthesized in the future."
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that after just one laser pulse of 30 nanoseconds, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrate is melted and separates into a carbon and a silicon layer. More pulses cause the carbon layer to organize into graphene and the silicon to leave as gas.
Molecular dynamics simulates the graphene formation mechanism. The carbon layer on the top forms because the laser-induced liquid SiC (SiC (l)) is unstable.
(Press Release by Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS))
2016.12.01 View 12397
Making Graphene Using Laser-induced Phase Separation
IBS & KAIST researchers clarify how laser annealing technology can lead to the production of ultrathin nanomaterials
All our smart phones have shiny flat AMOLED (active-matrix organic light-emitting diode) displays. Behind each single pixel of these displays hides at least two silicon transistors which are mass-manufactured using laser annealing technology. While the traditional methods to make the transistors use temperature above 1,000°C, the laser technique reaches the same results at low temperatures even on plastic substrates (melting temperature below 300°C). Interestingly, a similar procedure can be used to generate crystals of graphene. Graphene is a strong and thin nano-material made of carbon, its electric and heat-conductive properties have attracted the attention of scientists worldwide.
Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and his research group at the Center for Multidimensional Carbon Materials within the Institute for Basic Science (IBS), as well as Professor Sung-Yool Choi of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team discovered graphene synthesis mechanism using laser-induced solid-state phase separation of single-crystal silicon carbide (SiC). This study, available in Nature Communications, clarifies how this laser technology can separate a complex compound (SiC) into its ultrathin elements of carbon and silicon.
Although several fundamental studies presented the effect of excimer lasers in transforming elemental materials like silicon, the laser interaction with more complex compounds like SiC has rarely been studied due to the complexity of compound phase transition and ultra-short processing time.
With high resolution microscope images and molecular dynamic simulations, scientists found that a single-pulse irradiation of xenon chloride excimer laser of 30 nanoseconds melts SiC, leading to the separation of a liquid SiC layer, a disordered carbon layer with graphitic domains (about 2.5 nm thick) on top surface and a polycrystalline silicon layer (about 5 nm) below carbon layer. Giving additional pulses causes the sublimation of the separated silicon, while the disordered carbon layer is transformed into a multilayer graphene.
"This research shows that the laser material interaction technology can be a powerful tool for the next generation of two dimensional nanomaterials," said Professor Lee.
Professor Choi added: "Using laser-induced phase separation of complex compounds, new types of two dimensional materials can be synthesized in the future."
High-resolution transmission electron microscopy shows that after just one laser pulse of 30 nanoseconds, the silicon carbide (SiC) substrate is melted and separates into a carbon and a silicon layer. More pulses cause the carbon layer to organize into graphene and the silicon to leave as gas.
Molecular dynamics simulates the graphene formation mechanism. The carbon layer on the top forms because the laser-induced liquid SiC (SiC (l)) is unstable.
(Press Release by Courtesy of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS))
2016.12.01 View 12397 -
 Aerospace Engineering Students Win the Minister's Award
On November 11, 2016, students from KAIST’s Aerospace Engineering Department won the Minister’s Award of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea at the 14th Research Paper Competition hosted by Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI). The award came with a cash prize of USD 1,200 as well as opportunities to visit international airshows held abroad.
The KAIST students' paper introduced a novel design concept for "a virtual-fighter-pilot system for unmanned combat aerial vehicles to enable them to engage in mass aerial combat."
This was one of the two highest honors given to contestants. A group of students from Korea Aerospace University received the other grand prize from the Minister of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korea.
The KAIST team consisted of two doctoral students, Hee-Min Shin and Jae-Hyun Lee, and one Master’s student, Hyun-Gi Kim. Their advisor, Professor “David” Hyunchul Shim, received the Special Achievement Award for his contribution to the paper.
KAI’s competition was established in 2003 to spur academic interest and research in aerospace engineering. Over the past 14 years, contestants have submitted 376 papers, and KAI has published 88 papers. KAI has positioned itself as the host of one of the most prestigious research paper competitions held in Korea in the area of aerospace engineering.
The Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, the Korea Aerospace Industries Association, and the Korea Civil Aviation Development Association also sponsored the competition, with the Ministries of Trade, Industry and Energy and of Land, Infrastructure and Transport.
Professor Shim said, “This represents a great honor for our students. In recent years, research in unmanned aerial systems has increased tremendously throughout the world, and I hope KAIST will continue to inspire and innovate research in this field.”
Pictured from left to right are Hee-Min Shin, Jae-Hyun Lee, and Hyun-Gi Kim.
Pictured from right to left are Professor Hyunchul Shim, Hyun-Gi Kim, Hee-Min Shin, and Vice President Sung-Sup Chang of Korea Aerospace Industries.
2016.11.22 View 13037
Aerospace Engineering Students Win the Minister's Award
On November 11, 2016, students from KAIST’s Aerospace Engineering Department won the Minister’s Award of Trade, Industry and Energy of Korea at the 14th Research Paper Competition hosted by Korea Aerospace Industries (KAI). The award came with a cash prize of USD 1,200 as well as opportunities to visit international airshows held abroad.
The KAIST students' paper introduced a novel design concept for "a virtual-fighter-pilot system for unmanned combat aerial vehicles to enable them to engage in mass aerial combat."
This was one of the two highest honors given to contestants. A group of students from Korea Aerospace University received the other grand prize from the Minister of Land, Infrastructure and Transport of Korea.
The KAIST team consisted of two doctoral students, Hee-Min Shin and Jae-Hyun Lee, and one Master’s student, Hyun-Gi Kim. Their advisor, Professor “David” Hyunchul Shim, received the Special Achievement Award for his contribution to the paper.
KAI’s competition was established in 2003 to spur academic interest and research in aerospace engineering. Over the past 14 years, contestants have submitted 376 papers, and KAI has published 88 papers. KAI has positioned itself as the host of one of the most prestigious research paper competitions held in Korea in the area of aerospace engineering.
The Korean Society for Aeronautical and Space Sciences, the Korea Aerospace Industries Association, and the Korea Civil Aviation Development Association also sponsored the competition, with the Ministries of Trade, Industry and Energy and of Land, Infrastructure and Transport.
Professor Shim said, “This represents a great honor for our students. In recent years, research in unmanned aerial systems has increased tremendously throughout the world, and I hope KAIST will continue to inspire and innovate research in this field.”
Pictured from left to right are Hee-Min Shin, Jae-Hyun Lee, and Hyun-Gi Kim.
Pictured from right to left are Professor Hyunchul Shim, Hyun-Gi Kim, Hee-Min Shin, and Vice President Sung-Sup Chang of Korea Aerospace Industries.
2016.11.22 View 13037 -
 Professor Lee Co-chairs the Global Future Councils on Biotechnology of the WEF
The World Economic Forum (WEF) established a new global network of the world’s leading experts, “The Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils,” to explore innovative solutions for the most pressing global challenges. The Councils’ first meeting took place on November 13-14, 2016, in Dubai, the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Some 25 nations joined as member states. The Councils have 35 committees.
Over 700 global leaders in business, government, civil society and academia gathered at the inaugural meeting to “develop ideas and strategies to prepare the world for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, with topics including smart cities, robotics, and the future of mobility,” according to a statement issued by the WEF.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was appointed to co-chair one of the Councils' committees, The Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils on Biotechnology, for two years. The other chairperson is Dr. Feng Zhang, a professor of Biomedical Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), who played a critical role in the development of optogenetics and CRISPR technologies.
The Biotechnology Committee consists of 24 globally recognized professionals in life sciences, law, ethics and policy including Thomas Connelly, the executive director of the American Chemical Society, Tina Fano, the executive vice president of Novozymes, and Mostafa Ronaghi, the chief technology officer of Illumina.
Professor Lee also serves as a committee member of The Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils on the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
“Life sciences and engineering will receive more attention as a key element of the Fourth Industrial Revolution that the global society as a whole has been experiencing now. Together with thought leaders gathered worldwide, I will join the international community’s concerted efforts to address issues of importance that impact greatly on the future of humanity,” Professor Lee said.
In addition, Professor Lee received the James E. Bailey Award 2016 from The Society for Biological Engineering on November 15, 2016. He is the first Asian researcher to be recognized for his contributions to the field of biotechnology.
2016.11.15 View 10414
Professor Lee Co-chairs the Global Future Councils on Biotechnology of the WEF
The World Economic Forum (WEF) established a new global network of the world’s leading experts, “The Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils,” to explore innovative solutions for the most pressing global challenges. The Councils’ first meeting took place on November 13-14, 2016, in Dubai, the United Arab Emirates (UAE). Some 25 nations joined as member states. The Councils have 35 committees.
Over 700 global leaders in business, government, civil society and academia gathered at the inaugural meeting to “develop ideas and strategies to prepare the world for the Fourth Industrial Revolution, with topics including smart cities, robotics, and the future of mobility,” according to a statement issued by the WEF.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST was appointed to co-chair one of the Councils' committees, The Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils on Biotechnology, for two years. The other chairperson is Dr. Feng Zhang, a professor of Biomedical Engineering at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), who played a critical role in the development of optogenetics and CRISPR technologies.
The Biotechnology Committee consists of 24 globally recognized professionals in life sciences, law, ethics and policy including Thomas Connelly, the executive director of the American Chemical Society, Tina Fano, the executive vice president of Novozymes, and Mostafa Ronaghi, the chief technology officer of Illumina.
Professor Lee also serves as a committee member of The Annual Meeting of the Global Future Councils on the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
“Life sciences and engineering will receive more attention as a key element of the Fourth Industrial Revolution that the global society as a whole has been experiencing now. Together with thought leaders gathered worldwide, I will join the international community’s concerted efforts to address issues of importance that impact greatly on the future of humanity,” Professor Lee said.
In addition, Professor Lee received the James E. Bailey Award 2016 from The Society for Biological Engineering on November 15, 2016. He is the first Asian researcher to be recognized for his contributions to the field of biotechnology.
2016.11.15 View 10414 -
 Professor Shin's Team Receives the Best Software Defined Network Solution Showcase Award
Professor Seungwon Shin of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team won the Best Software Defined Networking (SDN) Solution Showcase Award hosted by the SDN World Congress, one of the biggest network summits held in Europe with over 2,000 participants. This year the conference took place in The Hague, the Netherlands, October 10-14, 2016.
SDN is an approach to computer networking that allows network administrators to respond quickly to changing business requirements via a centralized control console and to support the dynamic, scalable computing and storage needs of more modern computing environments such as data centers.
Collaborating with researchers from Queen’s University in the United Kingdom and Huawei, a global information and communications technology solutions provider in China, Professor Shin’s team, which is led by doctoral students Seungsoo Lee, Changhoon Yoon, and Jaehyun Nam, implemented a SDN security project called “DELTA.” ATTORESEARCH, a Korean SDN architecture and applications provider, conducted testing and verification for the project.
DELTA is a new SDN security evaluation framework with two main functions. It can automatically recognize attack cases against SDN elements across diverse environments and can assist in identifying unknown security problems within a SDN deployment.
The DELTA project consists of a control plane, the part of a network that carries signaling traffic and is responsible for routing; a data plane, the part of a network that carries user traffic; and a control channel that connects the two aforementioned planes. These three components have their own agents installed, which are all controlled by an agent manger. The agent manger can automatically detect any spots where the network security is weak.
Specifically, the project aimes to defense attacks against OpenFlow protocol, one of the first SDN standards; SDN controllers, a network operating system that is based on protocols; and network switch devices that use OpenFlow protocol.
The DELTA project was registered with the Open Networking Foundation, a user-driven organization dedicated to the promotion and adoption of SDN through open standards development, as an open source SDN security evaluation tool. This project is the only open source SDN which has been led by Korean researchers.
The SDN World Congress 2016 recognized the need for and importance of the DELTA project by conferring upon it the Best Solution Showcase Award. The Open Networking Foundation also widely publicized this award news.
Professor Shin said:
“In recent years, SDN has been attracting a large amount of interest as an emerging technology, but there still have not many SDN projects in Korea. This award acknowledges the advancement of Korean SDN technology, showing the potential for Korea to become a leader in SDN research.”
Picture: Major Components of the DELTA Project: Agents and Agent Manger
2016.10.25 View 9615
Professor Shin's Team Receives the Best Software Defined Network Solution Showcase Award
Professor Seungwon Shin of the Electrical Engineering School at KAIST and his research team won the Best Software Defined Networking (SDN) Solution Showcase Award hosted by the SDN World Congress, one of the biggest network summits held in Europe with over 2,000 participants. This year the conference took place in The Hague, the Netherlands, October 10-14, 2016.
SDN is an approach to computer networking that allows network administrators to respond quickly to changing business requirements via a centralized control console and to support the dynamic, scalable computing and storage needs of more modern computing environments such as data centers.
Collaborating with researchers from Queen’s University in the United Kingdom and Huawei, a global information and communications technology solutions provider in China, Professor Shin’s team, which is led by doctoral students Seungsoo Lee, Changhoon Yoon, and Jaehyun Nam, implemented a SDN security project called “DELTA.” ATTORESEARCH, a Korean SDN architecture and applications provider, conducted testing and verification for the project.
DELTA is a new SDN security evaluation framework with two main functions. It can automatically recognize attack cases against SDN elements across diverse environments and can assist in identifying unknown security problems within a SDN deployment.
The DELTA project consists of a control plane, the part of a network that carries signaling traffic and is responsible for routing; a data plane, the part of a network that carries user traffic; and a control channel that connects the two aforementioned planes. These three components have their own agents installed, which are all controlled by an agent manger. The agent manger can automatically detect any spots where the network security is weak.
Specifically, the project aimes to defense attacks against OpenFlow protocol, one of the first SDN standards; SDN controllers, a network operating system that is based on protocols; and network switch devices that use OpenFlow protocol.
The DELTA project was registered with the Open Networking Foundation, a user-driven organization dedicated to the promotion and adoption of SDN through open standards development, as an open source SDN security evaluation tool. This project is the only open source SDN which has been led by Korean researchers.
The SDN World Congress 2016 recognized the need for and importance of the DELTA project by conferring upon it the Best Solution Showcase Award. The Open Networking Foundation also widely publicized this award news.
Professor Shin said:
“In recent years, SDN has been attracting a large amount of interest as an emerging technology, but there still have not many SDN projects in Korea. This award acknowledges the advancement of Korean SDN technology, showing the potential for Korea to become a leader in SDN research.”
Picture: Major Components of the DELTA Project: Agents and Agent Manger
2016.10.25 View 9615 -
 2016 KAIST EEWS Workshop
The Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS) Graduate School of KAIST hosted a workshop entitled “Progress and Perspectives of Energy Science and Technology” on October 20, 2016. The workshop took place at the Fusion Hall of the KAIST Institute on campus.
About 400 experts in energy science and engineering participated in the event. Eight globally recognized scientists introduced the latest research trends in nanomaterials, energy theory, catalysts, and photocatalysts and led discussions on the current status and prospects of EEWS.
Professors Yi Cui of Stanford University, an expert in nanomaterials, and William A. Goddard of California Institute of Technology presented their research experiments on materials design and recent results on the direction of theory under the topics of energy and environment.
Dr. Miquel Salmeron, a former head of the Material Science Division of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and Professor Yuichi Ikuhara of Tokyo University introduced their analysis of catalysts and energy matters at an atomic scale.
Professor Sukbok Chang of the Chemistry Department at KAIST, a deputy editor of ACS Catalysis and the head of the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute of Basic Science, and Professor Yang-Kook Sun of Energy Engineering at Hanyang University, who is also a deputy editor of ACS Energy Letters, presented their latest research results on new catalytic reaction development and energy storage.
The workshop consisted of three sections which addressed the design of energy and environment materials; analysis of energy and catalytic materials; and energy conversion and catalysts.
The EEWS Graduate School was established in 2008 with the sponsorship of the Korean government’s World Class University (WCU) project to support science education in Korea. Professor J. Fraser Stoddart, the winner of the 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, was previously worked at the KAIST EEWS Graduate School as a WCU visiting professor for two years, from 2011 to 2013. Professor Ali Coskun, who was a postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Professor Stoddart, now teaches and conducts research as a full-time professor at the graduate school.
Dean Yousung Jung of the EEWS Graduate School said:
“This workshop has provided us with a meaningful opportunity to engage in discussions on energy science and technology with world-class scholars from all around the world. It is also a good venue for our graduate school to share with them what we have been doing in research and education.”
2016.10.20 View 14075
2016 KAIST EEWS Workshop
The Energy, Environment, Water and Sustainability (EEWS) Graduate School of KAIST hosted a workshop entitled “Progress and Perspectives of Energy Science and Technology” on October 20, 2016. The workshop took place at the Fusion Hall of the KAIST Institute on campus.
About 400 experts in energy science and engineering participated in the event. Eight globally recognized scientists introduced the latest research trends in nanomaterials, energy theory, catalysts, and photocatalysts and led discussions on the current status and prospects of EEWS.
Professors Yi Cui of Stanford University, an expert in nanomaterials, and William A. Goddard of California Institute of Technology presented their research experiments on materials design and recent results on the direction of theory under the topics of energy and environment.
Dr. Miquel Salmeron, a former head of the Material Science Division of Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, and Professor Yuichi Ikuhara of Tokyo University introduced their analysis of catalysts and energy matters at an atomic scale.
Professor Sukbok Chang of the Chemistry Department at KAIST, a deputy editor of ACS Catalysis and the head of the Center for Catalytic Hydrocarbon Functionalizations at the Institute of Basic Science, and Professor Yang-Kook Sun of Energy Engineering at Hanyang University, who is also a deputy editor of ACS Energy Letters, presented their latest research results on new catalytic reaction development and energy storage.
The workshop consisted of three sections which addressed the design of energy and environment materials; analysis of energy and catalytic materials; and energy conversion and catalysts.
The EEWS Graduate School was established in 2008 with the sponsorship of the Korean government’s World Class University (WCU) project to support science education in Korea. Professor J. Fraser Stoddart, the winner of the 2016 Nobel Prize in Chemistry, was previously worked at the KAIST EEWS Graduate School as a WCU visiting professor for two years, from 2011 to 2013. Professor Ali Coskun, who was a postdoctoral researcher in the laboratory of Professor Stoddart, now teaches and conducts research as a full-time professor at the graduate school.
Dean Yousung Jung of the EEWS Graduate School said:
“This workshop has provided us with a meaningful opportunity to engage in discussions on energy science and technology with world-class scholars from all around the world. It is also a good venue for our graduate school to share with them what we have been doing in research and education.”
2016.10.20 View 14075 -
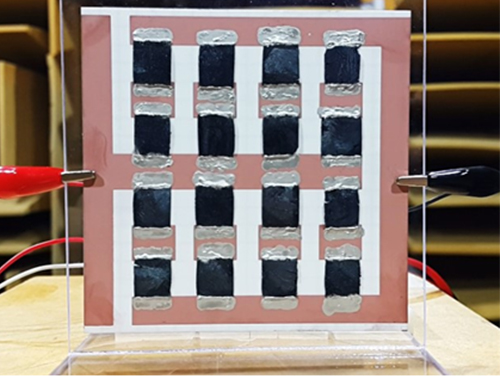 Extremely Thin and Highly Flexible Graphene-Based Thermoacoustic Speakers
A joint research team led by Professors Jung-Woo Choi and Byung Jin Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim of the Material Science and Engineering Department, all on the faculty of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has developed a simpler way to mass-produce ultra-thin graphene thermosacoustic speakers.
Their research results were published online on August 17, 2016 in a journal called Applied Materials & Interfaces. The IEEE Spectrum, a monthly magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, reported on the research on September 9, 2016, in an article titled, “Graphene Enables Flat Speakers for Mobile Audio Systems.” The American Chemical Society also drew attention to the team’s work in its article dated September 7, 2016, “Bringing Graphene Speakers to the Mobile Market.”
Thermoacoustic speakers generate sound waves from temperature fluctuations by rapidly heating and cooling conducting materials. Unlike conventional voice-coil speakers, thermoacoustic speakers do not rely on vibrations to produce sound, and thus do not need bulky acoustic boxes to keep complicated mechanical parts for sound production. They also generate good quality sound in all directions, enabling them to be placed on any surface including curved ones without canceling out sounds generated from opposite sides.
Based on a two-step, template-free fabrication method that involved freeze-drying a solution of graphene oxide flakes and the reduction/doping of oxidized graphene to improve electrical properties, the research team produced a N-doped, three-dimensional (3D), reduced graphene oxide aerogel (N-rGOA) with a porous macroscopic structure that permitted easy modulation for many potential applications.
Using 3D graphene aerogels, the team succeeded in fabricating an array of loudspeakers that were able to withstand over 40 W input power and that showed excellent sound pressure level (SPL), comparable to those of previously reported 2D and 3D graphene loudspeakers.
Choong Sun Kim, the lead author of the research paper and a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, said:
“Thermoacoustic speakers have a higher efficiency when conducting materials have a smaller heat capacity. Nanomaterials such as graphene are an ideal candidate for conductors, but they require a substrate to support their extremely thinness. The substrate’s tendency to lose heat lowers the speakers’ efficiency. Here, we developed 3D graphene aerogels without a substrate by using a simple two-step process. With graphene aerogels, we have fabricated an array of loudspeakers that demonstrated stable performance. This is a practical technology that will enable mass-production of thermosacoustic speakers including on mobile platforms.”
The research paper is entitled “Application of N-Doped Three-Dimensional Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel to Thin Film Loudspeaker.” (DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03618)
Figure 1: A Thermoacoustic Loudspeaker Consisted of an Array of 16 3D Graphene Aerogels
Figure 2: Two-step Fabrication Process of 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel Using Freeze-Drying and Reduction/Doping
Figure 3: X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Graph of the 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel and Its Scanning Electron Microscope Image
2016.10.05 View 15077
Extremely Thin and Highly Flexible Graphene-Based Thermoacoustic Speakers
A joint research team led by Professors Jung-Woo Choi and Byung Jin Cho of the School of Electrical Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim of the Material Science and Engineering Department, all on the faculty of the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST), has developed a simpler way to mass-produce ultra-thin graphene thermosacoustic speakers.
Their research results were published online on August 17, 2016 in a journal called Applied Materials & Interfaces. The IEEE Spectrum, a monthly magazine published by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers, reported on the research on September 9, 2016, in an article titled, “Graphene Enables Flat Speakers for Mobile Audio Systems.” The American Chemical Society also drew attention to the team’s work in its article dated September 7, 2016, “Bringing Graphene Speakers to the Mobile Market.”
Thermoacoustic speakers generate sound waves from temperature fluctuations by rapidly heating and cooling conducting materials. Unlike conventional voice-coil speakers, thermoacoustic speakers do not rely on vibrations to produce sound, and thus do not need bulky acoustic boxes to keep complicated mechanical parts for sound production. They also generate good quality sound in all directions, enabling them to be placed on any surface including curved ones without canceling out sounds generated from opposite sides.
Based on a two-step, template-free fabrication method that involved freeze-drying a solution of graphene oxide flakes and the reduction/doping of oxidized graphene to improve electrical properties, the research team produced a N-doped, three-dimensional (3D), reduced graphene oxide aerogel (N-rGOA) with a porous macroscopic structure that permitted easy modulation for many potential applications.
Using 3D graphene aerogels, the team succeeded in fabricating an array of loudspeakers that were able to withstand over 40 W input power and that showed excellent sound pressure level (SPL), comparable to those of previously reported 2D and 3D graphene loudspeakers.
Choong Sun Kim, the lead author of the research paper and a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST, said:
“Thermoacoustic speakers have a higher efficiency when conducting materials have a smaller heat capacity. Nanomaterials such as graphene are an ideal candidate for conductors, but they require a substrate to support their extremely thinness. The substrate’s tendency to lose heat lowers the speakers’ efficiency. Here, we developed 3D graphene aerogels without a substrate by using a simple two-step process. With graphene aerogels, we have fabricated an array of loudspeakers that demonstrated stable performance. This is a practical technology that will enable mass-production of thermosacoustic speakers including on mobile platforms.”
The research paper is entitled “Application of N-Doped Three-Dimensional Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel to Thin Film Loudspeaker.” (DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b03618)
Figure 1: A Thermoacoustic Loudspeaker Consisted of an Array of 16 3D Graphene Aerogels
Figure 2: Two-step Fabrication Process of 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel Using Freeze-Drying and Reduction/Doping
Figure 3: X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Graph of the 3D Reduced Graphene Oxide Aerogel and Its Scanning Electron Microscope Image
2016.10.05 View 15077 -
 Professor Lee to Head the Addis Ababa Institute of Technology
Emeritus Professor In Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST was appointed to the post of President of the Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (AAiT) in Ethiopia. His term will begin on August 1, 2016 and end on July 31, 2018, which can be extended up to five years.
AAiT is an affiliated institute of Addis Ababa University, a distinguished national university in Ethiopia, and specializes in education and research in engineering and technology. There are currently 5,500 undergraduate and 4,500 graduate students enrolled at the institute.
The Ethiopian government has recognized the importance of science and technology for the future of the country. The government intends to develop AAiT into a distinguished research university similar to KAIST, and thus sought advice from KAIST to recommend an administrator who will head AAiT. Upon recommendation by KAIST President Steve Kang, Professor Lee was appointed.
Professor Lee graduated from Seoul National University with bachelor's and master’s degrees in aeronautical engineering and earned his Ph.D. in aeronautics from Stanford University.
He has served as the President of The Korean Society for Aeronautics and Space Sciences, the Director of the KAIST Satellite Technology Research Center, and a Research Associate at NASA Ames Research Center.
2016.08.03 View 9536
Professor Lee to Head the Addis Ababa Institute of Technology
Emeritus Professor In Lee of the Department of Aerospace Engineering at KAIST was appointed to the post of President of the Addis Ababa Institute of Technology (AAiT) in Ethiopia. His term will begin on August 1, 2016 and end on July 31, 2018, which can be extended up to five years.
AAiT is an affiliated institute of Addis Ababa University, a distinguished national university in Ethiopia, and specializes in education and research in engineering and technology. There are currently 5,500 undergraduate and 4,500 graduate students enrolled at the institute.
The Ethiopian government has recognized the importance of science and technology for the future of the country. The government intends to develop AAiT into a distinguished research university similar to KAIST, and thus sought advice from KAIST to recommend an administrator who will head AAiT. Upon recommendation by KAIST President Steve Kang, Professor Lee was appointed.
Professor Lee graduated from Seoul National University with bachelor's and master’s degrees in aeronautical engineering and earned his Ph.D. in aeronautics from Stanford University.
He has served as the President of The Korean Society for Aeronautics and Space Sciences, the Director of the KAIST Satellite Technology Research Center, and a Research Associate at NASA Ames Research Center.
2016.08.03 View 9536 -
 Doctoral Student Receives the Best Paper Award from the International Metabolic Engineering Conference 2016
So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, received the Student and Young Investigator Poster Award at the 11th International Metabolic Engineering Conference held in Awaji, Japan on June 26-30.
Choi received the award for her research on one-step fermentative production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli, which was published in the April 2016 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
In her paper, she presented a novel technology to synthesize PLGA, a non-natural copolymer, through a biological production process. Because of its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility, PLGA is widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications, including surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Employing a metabolic engineering approach, Choi manipulated the metabolic pathway of an Escherichia coli bacterium to convert glucose and xylose into the biosynthesis of PLGA within the cell. Previously, PLGA could be obtained only through chemical synthesis.
Choi said, “I’m thrilled to receive an award from a flagship conference of my research field. Mindful of this recognition, I will continue my research to produce meaningful results, thereby contributing to the development of science and technology in Korea.”
The International Metabolic Engineering Conference is a leading professional gathering where state-of-the-art developments and achievements made in the field of metabolic engineering are shared. With the participation of about 400 professionals from all around the world, the conference participants discussed this year’s theme of “Design, Synthesis and System Integration for Metabolic Engineering.”
2016.07.07 View 11856
Doctoral Student Receives the Best Paper Award from the International Metabolic Engineering Conference 2016
So Young Choi, a Ph.D. candidate at the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST, received the Student and Young Investigator Poster Award at the 11th International Metabolic Engineering Conference held in Awaji, Japan on June 26-30.
Choi received the award for her research on one-step fermentative production of Poly(lactate-co-glycolate) (PLGA) from carbohydrates in Escherichia coli, which was published in the April 2016 issue of Nature Biotechnology.
In her paper, she presented a novel technology to synthesize PLGA, a non-natural copolymer, through a biological production process. Because of its biodegradability, non-toxicity, and biocompatibility, PLGA is widely used in biomedical and therapeutic applications, including surgical sutures, prosthetic devices, drug delivery, and tissue engineering.
Employing a metabolic engineering approach, Choi manipulated the metabolic pathway of an Escherichia coli bacterium to convert glucose and xylose into the biosynthesis of PLGA within the cell. Previously, PLGA could be obtained only through chemical synthesis.
Choi said, “I’m thrilled to receive an award from a flagship conference of my research field. Mindful of this recognition, I will continue my research to produce meaningful results, thereby contributing to the development of science and technology in Korea.”
The International Metabolic Engineering Conference is a leading professional gathering where state-of-the-art developments and achievements made in the field of metabolic engineering are shared. With the participation of about 400 professionals from all around the world, the conference participants discussed this year’s theme of “Design, Synthesis and System Integration for Metabolic Engineering.”
2016.07.07 View 11856 -
 Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 12105
Top 10 Emerging Technologies by World Economic Forum
The World Economic Forum’s Meta-Council on Emerging Technologies announced its annual list of breakthrough technologies, the “Top 10 Emerging Technologies of 2016,” on June 23, 2016. The Meta-Council chose the top ten technologies based on the technologies’ potential to improve lives, transform industries, and safeguard the planet. The research field of systems metabolic engineering, founded by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department at KAIST, was also citied. Systems metabolic engineering, which combines elements of synthetic biology, systems biology, and evolutionary engineering, offers a sustainable process for the production of useful chemicals in an environmentally friendly way from plants such as inedible biomass, reducing the need of using fossil fuels. Details about the list follow below:
https://www.weforum.org/press/2016/06/battery-powered-villages-sociable-robots-rank-among-top-10-emerging-technologies-of-2016
The picture below shows the “systems metabolic engineering of E. coli for the production of PLGA." PLGA is poly(lactate-co-glycolate), which is widely used for biomedical applications, and has been made by chemical synthesis. Now it is possible to produce PLGA eco-friendly by one-step fermentation of a gut bacterium which is developed through systems metabolic engineering.
2016.06.27 View 12105 -
 KAIST to Participate in Summer Davos Forum 2016 in China
A group of KAIST researchers will share their insights on the future and challenges of the current technological innovations impacting all aspects of society, while showcasing their research excellence in artificial intelligence and robotics.
Scientific and technological breakthroughs are more important than ever as key agents to drive social, economic, and political changes and advancements in today’s world. The World Economic Forum (WEF), an international organization that provides one of the broadest engagement platforms to address issues of major concern to the global community, will discuss the effects of these breakthroughs at its 10th Annual Meeting of the New Champions, a.k.a., the Summer Davos Forum, in Tianjin, China, June 26-28, 2016.
Three professors from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) will join the Annual Meeting and offer their expertise in the fields of biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and robotics to explore the conference theme, “The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Its Transformational Impact.” The Fourth Industrial Revolution, a term coined by WEF founder, Klaus Schwab, is characterized by a range of new technologies that fuse the physical, digital, and biological worlds, such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and automation.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will speak at the Experts Reception to be held on June 25, 2016 on the topic of “The Summer Davos Forum and Science and Technology in Asia.” On June 27, 2016, he will participate in two separate discussion sessions.
In the first session entitled “What If Drugs Are Printed from the Internet?,” Professor Lee will discuss the impacts of advancements in biotechnology and 3D printing technology on the future of medicine with Nita A. Farahany, a Duke University professor. Clare Matterson, the Director of Strategy at Wellcome Trust in the United Kingdom, will serve as the moderator. The discussants will note recent developments made in the way patients receive their medicine, for example, downloading drugs directly from the internet and the production of yeast strains to make opioids for pain treatment through systems metabolic engineering. They will also suggest how these emerging technologies will transform the landscape of the pharmaceutical industry in the years to come.
In the second session, “Lessons for Life,” Professor Lee will talk about how to nurture life-long learning and creativity to support personal and professional growth necessary in an era of the new industrial revolution.
During the Annual Meeting, Professors Jong-Hwan Kim of the Electrical Engineering School and David Hyunchul Shim of the Aerospace Department will host, together with researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and AnthroTronix, an engineering research and development company, a technological exhibition on robotics. Professor Kim, the founder of the internally renowned Robot World Cup, will showcase his humanoid soccer-playing micro-robots and display their various cutting-edge technologies such as imaging processing, artificial intelligence, walking, and balancing. Professor Shim will present a human-like robotic piloting system, PIBOT, which autonomously operates a simulated flight program by employing control sticks and guiding an airplane from takeoff to landing.
In addition, the two professors will join Professor Lee, who is also a moderator, to host a KAIST-led session on June 26, 2016, entitled “Science in Depth: From Deep Learning to Autonomous Machines.” Professors Kim and Shim will explore new opportunities and challenges in their fields from machine learning to autonomous robotics, including unmanned vehicles and drones.
Since 2011, KAIST has participated in the World Economic Forum’s two flagship conferences, the January and June Davos Forums, to introduce outstanding talents, share their latest research achievements, and interact with global leaders.
KAIST President Steve Kang said, “It is important for KAIST to be involved in global forums that identify issues critical to humanity and seek answers to solve them, and where our skills and knowledge in science and technology can play a meaningful role. The Annual Meeting in China will become another venue to accomplish this.”
2016.06.27 View 13651
KAIST to Participate in Summer Davos Forum 2016 in China
A group of KAIST researchers will share their insights on the future and challenges of the current technological innovations impacting all aspects of society, while showcasing their research excellence in artificial intelligence and robotics.
Scientific and technological breakthroughs are more important than ever as key agents to drive social, economic, and political changes and advancements in today’s world. The World Economic Forum (WEF), an international organization that provides one of the broadest engagement platforms to address issues of major concern to the global community, will discuss the effects of these breakthroughs at its 10th Annual Meeting of the New Champions, a.k.a., the Summer Davos Forum, in Tianjin, China, June 26-28, 2016.
Three professors from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) will join the Annual Meeting and offer their expertise in the fields of biotechnology, artificial intelligence, and robotics to explore the conference theme, “The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Its Transformational Impact.” The Fourth Industrial Revolution, a term coined by WEF founder, Klaus Schwab, is characterized by a range of new technologies that fuse the physical, digital, and biological worlds, such as the Internet of Things, cloud computing, and automation.
Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee of the Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Department will speak at the Experts Reception to be held on June 25, 2016 on the topic of “The Summer Davos Forum and Science and Technology in Asia.” On June 27, 2016, he will participate in two separate discussion sessions.
In the first session entitled “What If Drugs Are Printed from the Internet?,” Professor Lee will discuss the impacts of advancements in biotechnology and 3D printing technology on the future of medicine with Nita A. Farahany, a Duke University professor. Clare Matterson, the Director of Strategy at Wellcome Trust in the United Kingdom, will serve as the moderator. The discussants will note recent developments made in the way patients receive their medicine, for example, downloading drugs directly from the internet and the production of yeast strains to make opioids for pain treatment through systems metabolic engineering. They will also suggest how these emerging technologies will transform the landscape of the pharmaceutical industry in the years to come.
In the second session, “Lessons for Life,” Professor Lee will talk about how to nurture life-long learning and creativity to support personal and professional growth necessary in an era of the new industrial revolution.
During the Annual Meeting, Professors Jong-Hwan Kim of the Electrical Engineering School and David Hyunchul Shim of the Aerospace Department will host, together with researchers from Carnegie Mellon University and AnthroTronix, an engineering research and development company, a technological exhibition on robotics. Professor Kim, the founder of the internally renowned Robot World Cup, will showcase his humanoid soccer-playing micro-robots and display their various cutting-edge technologies such as imaging processing, artificial intelligence, walking, and balancing. Professor Shim will present a human-like robotic piloting system, PIBOT, which autonomously operates a simulated flight program by employing control sticks and guiding an airplane from takeoff to landing.
In addition, the two professors will join Professor Lee, who is also a moderator, to host a KAIST-led session on June 26, 2016, entitled “Science in Depth: From Deep Learning to Autonomous Machines.” Professors Kim and Shim will explore new opportunities and challenges in their fields from machine learning to autonomous robotics, including unmanned vehicles and drones.
Since 2011, KAIST has participated in the World Economic Forum’s two flagship conferences, the January and June Davos Forums, to introduce outstanding talents, share their latest research achievements, and interact with global leaders.
KAIST President Steve Kang said, “It is important for KAIST to be involved in global forums that identify issues critical to humanity and seek answers to solve them, and where our skills and knowledge in science and technology can play a meaningful role. The Annual Meeting in China will become another venue to accomplish this.”
2016.06.27 View 13651