research
A KAIST research team has developed a new context-awareness technology that enables AI assistants to determine when to talk to their users based on user circumstances. This technology can contribute to developing advanced AI assistants that can offer pre-emptive services such as reminding users to take medication on time or modifying schedules based on the actual progress of planned tasks.
Unlike conventional AI assistants that used to act passively upon users’ commands, today’s AI assistants are evolving to provide more proactive services through self-reasoning of user circumstances. This opens up new opportunities for AI assistants to better support users in their daily lives. However, if AI assistants do not talk at the right time, they could rather interrupt their users instead of helping them.
The right time for talking is more difficult for AI assistants to determine than it appears. This is because the context can differ depending on the state of the user or the surrounding environment.
A group of researchers led by Professor Uichin Lee from the KAIST School of Computing identified key contextual factors in user circumstances that determine when the AI assistant should start, stop, or resume engaging in voice services in smart home environments. Their findings were published in the Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT) in September.
The group conducted this study in collaboration with Professor Jae-Gil Lee’s group in the KAIST School of Computing, Professor Sangsu Lee’s group in the KAIST Department of Industrial Design, and Professor Auk Kim’s group at Kangwon National University.
After developing smart speakers equipped with AI assistant function for experimental use, the researchers installed them in the rooms of 40 students who live in double-occupancy campus dormitories and collected a total of 3,500 in-situ user response data records over a period of a week.
The smart speakers repeatedly asked the students a question, “Is now a good time to talk?” at random intervals or whenever a student’s movement was detected. Students answered with either “yes” or “no” and then explained why, describing what they had been doing before being questioned by the smart speakers.
Data analysis revealed that 47% of user responses were “no” indicating they did not want to be interrupted. The research team then created 19 home activity categories to cross-analyze the key contextual factors that determine opportune moments for AI assistants to talk, and classified these factors into ‘personal,’ ‘movement,’ and ‘social’ factors respectively.
Personal factors, for instance, include:
1. the degree of concentration on or engagement in activities,
2. the degree urgency and busyness,
3. the state of user’s mental or physical condition, and
4. the state of being able to talk or listen while multitasking.
While users were busy concentrating on studying, tired, or drying hair, they found it difficult to engage in conversational interactions with the smart speakers.
Some representative movement factors include departure, entrance, and physical activity transitions. Interestingly, in movement scenarios, the team found that the communication range was an important factor. Departure is an outbound movement from the smart speaker, and entrance is an inbound movement. Users were much more available during inbound movement scenarios as opposed to outbound movement scenarios.
In general, smart speakers are located in a shared place at home, such as a living room, where multiple family members gather at the same time. In Professor Lee’s group’s experiment, almost half of the in-situ user responses were collected when both roommates were present. The group found social presence also influenced interruptibility. Roommates often wanted to minimize possible interpersonal conflicts, such as disturbing their roommates' sleep or work.
Narae Cha, the lead author of this study, explained, “By considering personal, movement, and social factors, we can envision a smart speaker that can intelligently manage the timing of conversations with users.”
She believes that this work lays the foundation for the future of AI assistants, adding, “Multi-modal sensory data can be used for context sensing, and this context information will help smart speakers proactively determine when it is a good time to start, stop, or resume conversations with their users.”
This work was supported by the National Research Foundation (NRF) of Korea.
< Image 1. In-situ experience sampling of user availability for conversations with AI assistants >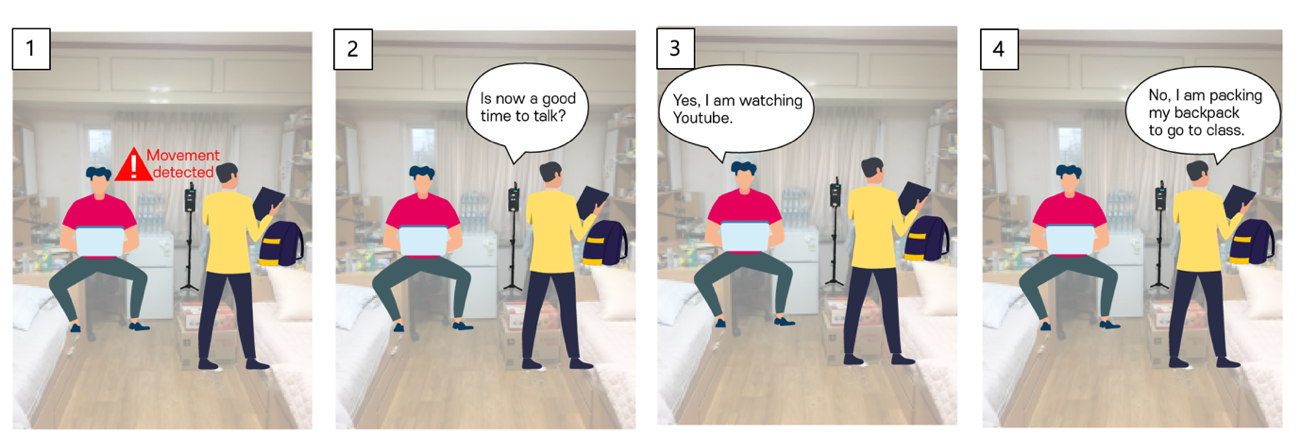
< Image 2. Key Contextual Factors that Determine Optimal Timing for AI Assistants to Talk >
Publication:
Cha, N, et al. (2020) “Hello There! Is Now a Good Time to Talk?”: Opportune Moments for Proactive Interactions with Smart Speakers. Proceedings of the ACM on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), Vol. 4, No. 3, Article No. 74, pp. 1-28. Available online at https://doi.org/10.1145/3411810
Link to Introductory Video:
https://youtu.be/AA8CTi2hEf0
Profile:
Uichin Lee
Associate Professor
uclee@kaist.ac.kr
http://ic.kaist.ac.kr
Interactive Computing Lab.
School of Computing
https://www.kaist.ac.kr
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
Daejeon, Republic of Korea
(END)
-
research KAIST Develops AI That Automatically Designs Optimal Drug Candidates for Cancer-Targeting Mutations
< (From left) Ph.D candidate Wonho Zhung, Ph.D cadidate Joongwon Lee , Prof. Woo Young Kim , Ph.D candidate Jisu Seo > Traditional drug development methods involve identifying a target protin (e.g., a cancer cell receptor) that causes disease, and then searching through countless molecular candidates (potential drugs) that could bind to that protein and block its function. This process is costly, time-consuming, and has a low success rate. KAIST researchers have developed an AI model th
2025-08-12 -
event 2025 APEC Youth STEM Science Exchange Program Successfully Completed
<Photo1. Group photo at the end of the program> KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 11thof August that it successfully hosted the 'APEC Youth STEM Conference KAIST Academic Program,' a global science exchange program for 28 youth researchers from 10 countries and over 30 experts who participated in the '2025 APEC Youth STEM* Collaborative Research and Competition.' The event was held at the main campus in Daejeon on Saturday, August 9. STEM (Science, Technology, Eng
2025-08-11 -
event 'Team Atlanta', in which KAIST Professor Insu Yun research team participated, won the DARPA AI Cyber Challenge in the US, with a prize of 5.5 billion KRW
<Photo1. Group Photo of Team Atlanta> Team Atlanta, led by Professor Insu Yun of the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering at KAIST and Tae-soo Kim, an executive from Samsung Research, along with researchers from POSTECH and Georgia Tech, won the final championship at the AI Cyber Challenge (AIxCC) hosted by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA). The final was held at the world's largest hacking conference, DEF CON 33, in Las Vegas on August 8 (local time)
2025-08-10 -
research Material Innovation Realized with Robotic Arms and AI, Without Human Researchers
<(From Left) M.S candidate Dongwoo Kim from KAIST, Ph.D candidate Hyun-Gi Lee from KAIST, Intern Yeham Kang from KAIST, M.S candidate Seongjae Bae from KAIST, Professor Dong-Hwa Seo from KAIST, (From top right, from left) Senior Researcher Inchul Park from POSCO Holdings, Senior Researcher Jung Woo Park, senior researcher from POSCO Holdings> A joint research team from industry and academia in Korea has successfully developed an autonomous lab that uses AI and automation to create ne
2025-08-06 -
event KAIST Successfully Presents the Future of AI Transformation and Physical AI Strategy at the 1st National Strategic Technology Forum
<(Front row, fourth from the right) President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST, (back row, fifth from the right) Forum co-host Representative Hyung-Doo Choi, (back row, sixth from the left) Forum co-host Representative Han-Kyu Kim, along with ruling and opposition party members of the Science, ICT, Broadcasting, and Communications Committee and the Trade, Industry, Energy, SMEs, and Startups Committee, as well as Professors Hoe-Jun Yoo and Jung Kim from KAIST)> KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee)
2025-07-31