ICA
-
 KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of immunotherapies that help immune cells attack cancer more effectively, have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, fewer than 20% of patients respond to these treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new strategies tailored to both responders and non-responders.
KAIST researchers have discovered that 'DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)', a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment. This breakthrough technology has been transferred to faculty startup BioRevert Inc., where it is currently being developed as a companion therapeutic and is expected to enter clinical trials by 2028.
< Photo 1. (From left) Researcher Jungeun Lee, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and Postdoctoral Researcher Jeong-Ryeol Gong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 8 that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had identified DDX54 as a critical factor that determines the immune evasion capacity of lung cancer cells. They demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 enhances immune cell infiltration into tumors and significantly improves the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy using anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies is considered a powerful approach in cancer treatment. However, its low response rate limits the number of patients who actually benefit.
To identify likely responders, tumor mutational burden (TMB) has recently been approved by the FDA as a key biomarker for immunotherapy. Cancers with high mutation rates are thought to be more responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, even tumors with high TMB can display an “immune-desert” phenotype—where immune cell infiltration is severely limited—resulting in poor treatment responses.
< Figure 1. DDX54 was identified as the master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy by orchestrating suppression of immune cell infiltration through cancer tissues as lung cancer cells become immune-evasive >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team compared transcriptome and genome data of lung cancer patients with immune evasion capabilities through gene regulatory network analysis (A) and discovered DDX54, a master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy (B-F).
This study is especially significant in that it successfully demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 in immune-desert lung tumors can overcome immunotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
The team used transcriptomic and genomic data from immune-evasive lung cancer patients and employed systems biology techniques to infer gene regulatory networks. Through this analysis, they identified DDX54 as a central regulator in the immune evasion of lung cancer cells.
In a syngeneic mouse model, the suppression of DDX54 led to significant increases in the infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells such as T cells and NK cells, and greatly improved the response to immunotherapy.
Single-cell transcriptomic and spatial transcriptomic analyses further showed that combination therapy targeting DDX54 promoted the differentiation of T cells and memory T cells that suppress tumors, while reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells and exhausted T cells that support tumor growth.
< Figure 2. In the syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells, it was confirmed that inhibiting DDX54 reversed the immune-evasion ability of cancer cells and enhanced the sensitivity to anti-PD-1 therapy >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells exhibiting immunotherapy resistance, the treatment applied after DDX54 inhibition resulted in statistically significant inhibition of lung cancer growth (B-D) and a significant increase in immune cell infiltration into the tumor tissue (E, F).
The mechanism is believed to involve DDX54 suppression inactivating signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT, MYC, and NF-κB, thereby downregulating immune-evasive proteins CD38 and CD47. This also reduced the infiltration of circulating monocytes—which promote tumor development—and promoted the differentiation of M1 macrophages that play anti-tumor roles.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho stated, “We have, for the first time, identified a master regulatory factor that enables immune evasion in lung cancer cells. By targeting this factor, we developed a new therapeutic strategy that can induce responsiveness to immunotherapy in previously resistant cancers.”
He added, “The discovery of DDX54—hidden within the complex molecular networks of cancer cells—was made possible through the systematic integration of systems biology, combining IT and BT.”
The study, led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 2, 2025, with Jeong-Ryeol Gong being the first author, Jungeun Lee, a co-first author, and Younghyun Han, a co-author of the article.
< Figure 3. Single-cell transcriptome and spatial transcriptome analysis confirmed that knockdown of DDX54 increased immune cell infiltration into cancer tissues >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells that underwent immunotherapy in combination with DDX54 inhibition, single-cell transcriptome (H-L) and spatial transcriptome (A-G) analysis of immune cells infiltrating inside cancer tissues were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that anticancer immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells actively infiltrated the core of lung cancer tissues when DDX54 inhibition and immunotherapy were concurrently administered.
(Paper title: “DDX54 downregulation enhances anti-PD1 therapy in immune-desert lung tumors with high tumor mutational burden,” DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2412310122)
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Research Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program.
< Figure 4. The identified master regulator DDX54 was confirmed to induce CD38 and CD47 expression through Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB activation. >
DDX54 activates the Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB pathways in lung cancer cells to increase CD38 and CD47 expression (A-G). This creates a cancer microenvironment that contributes to cancer development (H) and ultimately induces immune anticancer treatment resistance.
< Figure 5. It was confirmed that an immune-inflamed environment can be created by combining DDX54 inhibition and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. >
When DDX54 inhibition and ICI therapy are simultaneously administered, the cancer cell characteristics change, the immune evasion ability is restored, and the environment is transformed into an ‘immune-activated’ environment in which immune cells easily infiltrate cancer tissues. This strengthens the anticancer immune response, thereby increasing the sensitivity of immunotherapy even in lung cancer tissues that previously had low responsiveness to immunotherapy.
2025.04.08 View 7216
KAIST Identifies Master Regulator Blocking Immunotherapy, Paving the Way for a New Lung Cancer Treatment
Immune checkpoint inhibitors, a class of immunotherapies that help immune cells attack cancer more effectively, have revolutionized cancer treatment. However, fewer than 20% of patients respond to these treatments, highlighting the urgent need for new strategies tailored to both responders and non-responders.
KAIST researchers have discovered that 'DEAD-box helicases 54 (DDX54)', a type of RNA-binding protein, is the master regulator that hinders the effectiveness of immunotherapy—opening a new path for lung cancer treatment. This breakthrough technology has been transferred to faculty startup BioRevert Inc., where it is currently being developed as a companion therapeutic and is expected to enter clinical trials by 2028.
< Photo 1. (From left) Researcher Jungeun Lee, Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho and Postdoctoral Researcher Jeong-Ryeol Gong of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering at KAIST >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on April 8 that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering had identified DDX54 as a critical factor that determines the immune evasion capacity of lung cancer cells. They demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 enhances immune cell infiltration into tumors and significantly improves the efficacy of immunotherapy.
Immunotherapy using anti-PD-1 or anti-PD-L1 antibodies is considered a powerful approach in cancer treatment. However, its low response rate limits the number of patients who actually benefit.
To identify likely responders, tumor mutational burden (TMB) has recently been approved by the FDA as a key biomarker for immunotherapy. Cancers with high mutation rates are thought to be more responsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors. However, even tumors with high TMB can display an “immune-desert” phenotype—where immune cell infiltration is severely limited—resulting in poor treatment responses.
< Figure 1. DDX54 was identified as the master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy by orchestrating suppression of immune cell infiltration through cancer tissues as lung cancer cells become immune-evasive >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team compared transcriptome and genome data of lung cancer patients with immune evasion capabilities through gene regulatory network analysis (A) and discovered DDX54, a master regulator that induces resistance to immunotherapy (B-F).
This study is especially significant in that it successfully demonstrated that suppressing DDX54 in immune-desert lung tumors can overcome immunotherapy resistance and improve treatment outcomes.
The team used transcriptomic and genomic data from immune-evasive lung cancer patients and employed systems biology techniques to infer gene regulatory networks. Through this analysis, they identified DDX54 as a central regulator in the immune evasion of lung cancer cells.
In a syngeneic mouse model, the suppression of DDX54 led to significant increases in the infiltration of anti-cancer immune cells such as T cells and NK cells, and greatly improved the response to immunotherapy.
Single-cell transcriptomic and spatial transcriptomic analyses further showed that combination therapy targeting DDX54 promoted the differentiation of T cells and memory T cells that suppress tumors, while reducing the infiltration of regulatory T cells and exhausted T cells that support tumor growth.
< Figure 2. In the syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells, it was confirmed that inhibiting DDX54 reversed the immune-evasion ability of cancer cells and enhanced the sensitivity to anti-PD-1 therapy >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells exhibiting immunotherapy resistance, the treatment applied after DDX54 inhibition resulted in statistically significant inhibition of lung cancer growth (B-D) and a significant increase in immune cell infiltration into the tumor tissue (E, F).
The mechanism is believed to involve DDX54 suppression inactivating signaling pathways such as JAK-STAT, MYC, and NF-κB, thereby downregulating immune-evasive proteins CD38 and CD47. This also reduced the infiltration of circulating monocytes—which promote tumor development—and promoted the differentiation of M1 macrophages that play anti-tumor roles.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho stated, “We have, for the first time, identified a master regulatory factor that enables immune evasion in lung cancer cells. By targeting this factor, we developed a new therapeutic strategy that can induce responsiveness to immunotherapy in previously resistant cancers.”
He added, “The discovery of DDX54—hidden within the complex molecular networks of cancer cells—was made possible through the systematic integration of systems biology, combining IT and BT.”
The study, led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, was published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America (PNAS) on April 2, 2025, with Jeong-Ryeol Gong being the first author, Jungeun Lee, a co-first author, and Younghyun Han, a co-author of the article.
< Figure 3. Single-cell transcriptome and spatial transcriptome analysis confirmed that knockdown of DDX54 increased immune cell infiltration into cancer tissues >
In a syngeneic mouse model made of lung cancer cells that underwent immunotherapy in combination with DDX54 inhibition, single-cell transcriptome (H-L) and spatial transcriptome (A-G) analysis of immune cells infiltrating inside cancer tissues were performed. As a result, it was confirmed that anticancer immune cells such as T cells, B cells, and NK cells actively infiltrated the core of lung cancer tissues when DDX54 inhibition and immunotherapy were concurrently administered.
(Paper title: “DDX54 downregulation enhances anti-PD1 therapy in immune-desert lung tumors with high tumor mutational burden,” DOI: https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2412310122)
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Research Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program.
< Figure 4. The identified master regulator DDX54 was confirmed to induce CD38 and CD47 expression through Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB activation. >
DDX54 activates the Jak-Stat3, MYC, and NF-κB pathways in lung cancer cells to increase CD38 and CD47 expression (A-G). This creates a cancer microenvironment that contributes to cancer development (H) and ultimately induces immune anticancer treatment resistance.
< Figure 5. It was confirmed that an immune-inflamed environment can be created by combining DDX54 inhibition and immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. >
When DDX54 inhibition and ICI therapy are simultaneously administered, the cancer cell characteristics change, the immune evasion ability is restored, and the environment is transformed into an ‘immune-activated’ environment in which immune cells easily infiltrate cancer tissues. This strengthens the anticancer immune response, thereby increasing the sensitivity of immunotherapy even in lung cancer tissues that previously had low responsiveness to immunotherapy.
2025.04.08 View 7216 -
 KAIST Innovates Mid-Infrared Photodetectors for Exoplanet Detection, Expanding Applications to Environmental and Medical Fields
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) utilizes mid-infrared spectroscopy to precisely analyze molecular components such as water vapor and sulfur dioxide in exoplanet atmospheres. The key to this analysis, where each molecule exhibits a unique spectral "fingerprint," lies in highly sensitive photodetector technology capable of measuring extremely weak light intensities. Recently, KAIST researchers have developed an innovative photodetector capable of detecting a broad range of mid-infrared spectra, garnering significant attention.
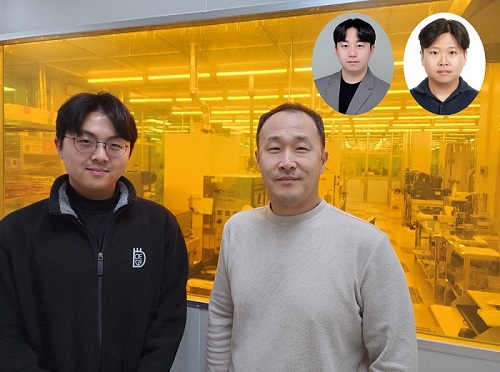
< Photo 1. (from the left) Ph.D. candidate Inki Kim (co-author), Professor SangHyeon Kim (corresponding author), Dr. Joonsup Shim (first author), and Dr. Jinha Lim (co-author) of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering. >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th of March that a research team led by Professor SangHyeon Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a mid-infrared photodetector that operates stably at room temperature, marking a major turning point for the commercialization of ultra-compact optical sensors.
The newly developed photodetector utilizes conventional silicon-based CMOS processes, enabling low-cost mass production while maintaining stable operation at room temperature. Notably, the research team successfully demonstrated the real-time detection of carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas using ultra-compact and ultra-thin optical sensors equipped with this photodetector, proving its potential for environmental monitoring and hazardous gas analysis.
Existing mid-infrared photodetectors generally require cooling systems due to high thermal noise at room temperature. These cooling systems increase the size and cost of equipment, making miniaturization and integration into portable devices challenging. Furthermore, conventional mid-infrared photodetectors are incompatible with silicon-based CMOS processes, limiting large-scale production and commercialization.
To address these limitations, the research team developed a waveguide-integrated photodetector using germanium (Ge), a Group IV element like silicon. This approach enables broad-spectrum mid-infrared detection while ensuring stable operation at room temperature.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a room-temperature mid-infrared waveguide-integrated photodetector based on the Ge-on-insulator optical platform proposed in this study (top). Optical microscope image of the integrated photodetector connected with the sensing unit (bottom). >
A waveguide is a structure designed to efficiently guide light along a specific path with minimal loss. To implement various optical functions on a chip (on-chip), the development of waveguide-integrated photodetectors and waveguide-based optical components is essential.
Unlike conventional photodetectors that primarily rely on bandgap absorption principles, this new technology leverages the bolometric effect*, allowing it to detect the entire mid-infrared spectral range. As a result, it can be widely applied to the real-time sensing of various molecular species.
*Bolometric effect: A principle in which light absorption leads to an increase in temperature, causing electrical signals to change accordingly.
The waveguide-integrated mid-infrared photodetector developed by the research team is considered a groundbreaking innovation that overcomes the limitations of existing mid-infrared sensor technologies, including the need for cooling, difficulties in mass production, and high costs.
< Figure 2. Room temperature photoresponse characteristics of the mid-infrared waveguide photodetector proposed in this study (left) and real-time carbon dioxide (CO2) gas sensing results using the photodetector (right). >
This breakthrough technology is expected to be applicable across diverse fields, including environmental monitoring, medical diagnostics, industrial process management, national defense and security, and smart devices. It also paves the way for next-generation mid-infrared sensor advancements.
Professor SangHyeon Kim from KAIST stated, "This research represents a novel approach that overcomes the limitations of existing mid-infrared photodetector technologies and has great potential for practical applications in various fields." He further emphasized, "Since this sensor technology is compatible with CMOS processes, it enables low-cost mass production, making it highly suitable for next-generation environmental monitoring systems and smart manufacturing sites."
< Figure 3. Performance comparison image of a room-temperature mid-infrared waveguide photodetector fabricated with the technology proposed in this study. It achieves the world’s highest performance compared to existing technologies utilizing the Bolometric effect, and is the only solution compatible with CMOS processes. The technology proposed by our research team is characterized by its ability to respond to a wide spectrum of the mid-infrared band without limitations. >
The study, with Dr. Joonsup Shim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard University) as the first author, was published on March 19, 2025 in the internationally renowned journal Light: Science & Applications (JCR 2.9%, IF=20.6).
(Paper title: “Room-temperature waveguide-integrated photodetector using bolometric effect for mid-infrared spectroscopy applications,” https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-025-01803-3)
2025.03.27 View 4525
KAIST Innovates Mid-Infrared Photodetectors for Exoplanet Detection, Expanding Applications to Environmental and Medical Fields
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) utilizes mid-infrared spectroscopy to precisely analyze molecular components such as water vapor and sulfur dioxide in exoplanet atmospheres. The key to this analysis, where each molecule exhibits a unique spectral "fingerprint," lies in highly sensitive photodetector technology capable of measuring extremely weak light intensities. Recently, KAIST researchers have developed an innovative photodetector capable of detecting a broad range of mid-infrared spectra, garnering significant attention.
< Photo 1. (from the left) Ph.D. candidate Inki Kim (co-author), Professor SangHyeon Kim (corresponding author), Dr. Joonsup Shim (first author), and Dr. Jinha Lim (co-author) of KAIST School of Electrical Engineering. >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th of March that a research team led by Professor SangHyeon Kim from the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a mid-infrared photodetector that operates stably at room temperature, marking a major turning point for the commercialization of ultra-compact optical sensors.
The newly developed photodetector utilizes conventional silicon-based CMOS processes, enabling low-cost mass production while maintaining stable operation at room temperature. Notably, the research team successfully demonstrated the real-time detection of carbon dioxide (CO₂) gas using ultra-compact and ultra-thin optical sensors equipped with this photodetector, proving its potential for environmental monitoring and hazardous gas analysis.
Existing mid-infrared photodetectors generally require cooling systems due to high thermal noise at room temperature. These cooling systems increase the size and cost of equipment, making miniaturization and integration into portable devices challenging. Furthermore, conventional mid-infrared photodetectors are incompatible with silicon-based CMOS processes, limiting large-scale production and commercialization.
To address these limitations, the research team developed a waveguide-integrated photodetector using germanium (Ge), a Group IV element like silicon. This approach enables broad-spectrum mid-infrared detection while ensuring stable operation at room temperature.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of a room-temperature mid-infrared waveguide-integrated photodetector based on the Ge-on-insulator optical platform proposed in this study (top). Optical microscope image of the integrated photodetector connected with the sensing unit (bottom). >
A waveguide is a structure designed to efficiently guide light along a specific path with minimal loss. To implement various optical functions on a chip (on-chip), the development of waveguide-integrated photodetectors and waveguide-based optical components is essential.
Unlike conventional photodetectors that primarily rely on bandgap absorption principles, this new technology leverages the bolometric effect*, allowing it to detect the entire mid-infrared spectral range. As a result, it can be widely applied to the real-time sensing of various molecular species.
*Bolometric effect: A principle in which light absorption leads to an increase in temperature, causing electrical signals to change accordingly.
The waveguide-integrated mid-infrared photodetector developed by the research team is considered a groundbreaking innovation that overcomes the limitations of existing mid-infrared sensor technologies, including the need for cooling, difficulties in mass production, and high costs.
< Figure 2. Room temperature photoresponse characteristics of the mid-infrared waveguide photodetector proposed in this study (left) and real-time carbon dioxide (CO2) gas sensing results using the photodetector (right). >
This breakthrough technology is expected to be applicable across diverse fields, including environmental monitoring, medical diagnostics, industrial process management, national defense and security, and smart devices. It also paves the way for next-generation mid-infrared sensor advancements.
Professor SangHyeon Kim from KAIST stated, "This research represents a novel approach that overcomes the limitations of existing mid-infrared photodetector technologies and has great potential for practical applications in various fields." He further emphasized, "Since this sensor technology is compatible with CMOS processes, it enables low-cost mass production, making it highly suitable for next-generation environmental monitoring systems and smart manufacturing sites."
< Figure 3. Performance comparison image of a room-temperature mid-infrared waveguide photodetector fabricated with the technology proposed in this study. It achieves the world’s highest performance compared to existing technologies utilizing the Bolometric effect, and is the only solution compatible with CMOS processes. The technology proposed by our research team is characterized by its ability to respond to a wide spectrum of the mid-infrared band without limitations. >
The study, with Dr. Joonsup Shim (currently a postdoctoral researcher at Harvard University) as the first author, was published on March 19, 2025 in the internationally renowned journal Light: Science & Applications (JCR 2.9%, IF=20.6).
(Paper title: “Room-temperature waveguide-integrated photodetector using bolometric effect for mid-infrared spectroscopy applications,” https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-025-01803-3)
2025.03.27 View 4525 -
 KAIST Develops Eco-Friendly, Nylon-Like Plastic Using Microorganisms
Poly(ester amide) amide is a next-generation material that combines the advantages of PET (polyester) and nylon (polyamide), two widely used plastics. However, it could only be produced from fossil fuels, which posed environmental concerns. Using microorganisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a new bio-based plastic to replace conventional plastic.
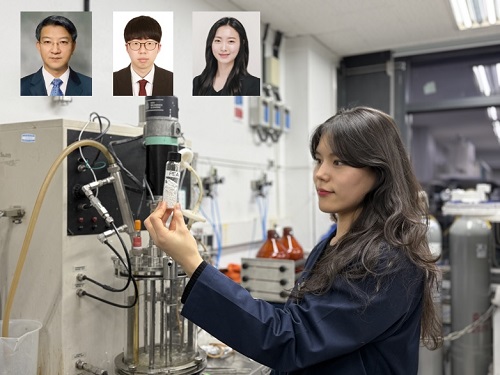
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed microbial strains through systems metabolic engineering to produce various eco-friendly, bio-based poly(ester amide)s. The team collaborated with researchers from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young-Kook Lee) to analyze and confirm the properties of the resulting plastic.
Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team designed new metabolic pathways that do not naturally exist in microorganisms, and developed a platform microbial strain capable of producing nine different types of poly(ester amide)s, including poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-3-aminopropionate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-4-aminobutyrate).
Using glucose derived from abundant biomass sources such as waste wood and weeds, the team successfully produced poly(ester amide)s in an eco-friendly manner. The researchers also confirmed the potential for industrial-scale production by demonstrating high production efficiency (54.57 g/L) using fed-batch fermentation of the engineered strain.
In collaboration with researchers Haemin Jeong and Jihoon Shin from KRICT, the KAIST team analyzed the properties of the bio-based plastic and found that it exhibited characteristics similar to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This means the new plastic is not only eco-friendly but also strong and durable enough to replace conventional plastics.
The engineered strains and strategies developed in this study are expected to be useful not only for producing various poly(ester amide)s but also for constructing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of other types of polymers.
Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, “This study is the first to demonstrate the possibility of producing poly(ester amide)s (plastics) through a renewable bio-based chemical process rather than relying on the petroleum-based chemical industry. We plan to further enhance the production yield and efficiency through continued research.”
The study was published online on March 17 in the international journal Nature Chemical Biology.
·Title: Biosynthesis of poly(ester amide)s in engineered Escherichia coli
·DOI: 10.1038/s41589-025-01842-2
·Authors: A total of seven authors including Tong Un Chae (KAIST, first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, second author), Da-Hee Ahn (KAIST, third author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, fourth author), Haemin Jeong (KRICT, fifth author), Jihoon Shin (KRICT, sixth author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author).
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) under the Eco-Friendly Chemical Technology Development Project as part of the "Next-Generation Biorefinery Technology Development to Lead the Bio-Chemical Industry" initiative (project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST).
2025.03.24 View 6743
KAIST Develops Eco-Friendly, Nylon-Like Plastic Using Microorganisms
Poly(ester amide) amide is a next-generation material that combines the advantages of PET (polyester) and nylon (polyamide), two widely used plastics. However, it could only be produced from fossil fuels, which posed environmental concerns. Using microorganisms, KAIST researchers have successfully developed a new bio-based plastic to replace conventional plastic.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of March that a research team led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering has developed microbial strains through systems metabolic engineering to produce various eco-friendly, bio-based poly(ester amide)s. The team collaborated with researchers from the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young-Kook Lee) to analyze and confirm the properties of the resulting plastic.
Professor Sang Yup Lee’s research team designed new metabolic pathways that do not naturally exist in microorganisms, and developed a platform microbial strain capable of producing nine different types of poly(ester amide)s, including poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-3-aminopropionate) and poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-ran-4-aminobutyrate).
Using glucose derived from abundant biomass sources such as waste wood and weeds, the team successfully produced poly(ester amide)s in an eco-friendly manner. The researchers also confirmed the potential for industrial-scale production by demonstrating high production efficiency (54.57 g/L) using fed-batch fermentation of the engineered strain.
In collaboration with researchers Haemin Jeong and Jihoon Shin from KRICT, the KAIST team analyzed the properties of the bio-based plastic and found that it exhibited characteristics similar to high-density polyethylene (HDPE). This means the new plastic is not only eco-friendly but also strong and durable enough to replace conventional plastics.
The engineered strains and strategies developed in this study are expected to be useful not only for producing various poly(ester amide)s but also for constructing metabolic pathways for the biosynthesis of other types of polymers.
Professor Sang Yup Lee stated, “This study is the first to demonstrate the possibility of producing poly(ester amide)s (plastics) through a renewable bio-based chemical process rather than relying on the petroleum-based chemical industry. We plan to further enhance the production yield and efficiency through continued research.”
The study was published online on March 17 in the international journal Nature Chemical Biology.
·Title: Biosynthesis of poly(ester amide)s in engineered Escherichia coli
·DOI: 10.1038/s41589-025-01842-2
·Authors: A total of seven authors including Tong Un Chae (KAIST, first author), So Young Choi (KAIST, second author), Da-Hee Ahn (KAIST, third author), Woo Dae Jang (KAIST, fourth author), Haemin Jeong (KRICT, fifth author), Jihoon Shin (KRICT, sixth author), and Sang Yup Lee (KAIST, corresponding author).
This research was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) under the Eco-Friendly Chemical Technology Development Project as part of the "Next-Generation Biorefinery Technology Development to Lead the Bio-Chemical Industry" initiative (project led by Distinguished Professor Sang Yup Lee at KAIST).
2025.03.24 View 6743 -
 No More Touch Issues on Rainy Days! KAIST Develops Human-Like Tactile Sensor
Recent advancements in robotics have enabled machines to handle delicate objects like eggs with precision, thanks to highly integrated pressure sensors that provide detailed tactile feedback. However, even the most advanced robots struggle to accurately detect pressure in complex environments involving water, bending, or electromagnetic interference. A research team at KAIST has successfully developed a pressure sensor that operates stably without external interference, even on wet surfaces like a smartphone screen covered in water, achieving human-level tactile sensitivity.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th of March that a research team led by Professor Jun-Bo Yoon from the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a high-resolution pressure sensor that remains unaffected by external interference such as "ghost touches" caused by moisture on touchscreens.
Capacitive pressure sensors, widely used in touch systems due to their simple structure and durability, are essential components of human-machine interface (HMI) technologies in smartphones, wearable devices, and robots. However, they are prone to malfunctions caused by water droplets, electromagnetic interference, and curves.
To address these issues, the research team investigated the root causes of interference in capacitive pressure sensors. They identified that the "fringe field" generated at the sensor’s edges is particularly susceptible to external disturbances.
The researchers concluded that, to fundamentally resolve this issue, suppressing the fringe field was necessary. Through theoretical analysis, they determined that reducing the electrode spacing to the nanometer scale could effectively minimize the fringe field to below a few percent.
Utilizing proprietary micro/nanofabrication techniques, the team developed a nanogap pressure sensor with an electrode spacing of 900 nanometers (nm). This newly developed sensor reliably detected pressure regardless of the material exerting force and remained unaffected by bending or electromagnetic interference.
Furthermore, the team successfully implemented an artificial tactile system utilizing the developed sensor’s characteristics. Human skin contains specialized pressure receptors called Merkel’s disks. To artificially mimic them, the exclusive detection of pressure was necessary, but hadn’t been achieved by conventional sensors.
Professor Yoon’s research team overcame these challenges, developing a sensor achieving a density comparable to Merkel’s discs and enabling wireless, high-precision pressure sensing.
To explore potential applications, the researcher also developed a force touch pad system, demonstrating its ability to capture pressure magnitude and distribution with high resolution and without interference.
Professor Yoon stated, “Our nanogap pressure sensor operates reliably even in rainy conditions or sweaty environments, eliminating common touch malfunctions. We believe this innovation will significantly enhance everyday user experiences.”
He added, “This technology has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including precision tactile sensors for robotics, medical wearable devices, and next-generation augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) interfaces.”
The study was led by Jae-Soon Yang (Ph.D.), Myung-Kun Chung (Ph.D. candidate), and Jae-Young Yoo (Assistant Professor at Sungkyunkwan University, a KAIST Ph.D. graduate). The research findings were published in Nature Communications on February 27, 2025. (Paper title: “Interference-Free Nanogap Pressure Sensor Array with High Spatial Resolution for Wireless Human-Machine Interface Applications”, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57232-8)
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and Leading Research Center Support Program.
2025.03.14 View 4897
No More Touch Issues on Rainy Days! KAIST Develops Human-Like Tactile Sensor
Recent advancements in robotics have enabled machines to handle delicate objects like eggs with precision, thanks to highly integrated pressure sensors that provide detailed tactile feedback. However, even the most advanced robots struggle to accurately detect pressure in complex environments involving water, bending, or electromagnetic interference. A research team at KAIST has successfully developed a pressure sensor that operates stably without external interference, even on wet surfaces like a smartphone screen covered in water, achieving human-level tactile sensitivity.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 10th of March that a research team led by Professor Jun-Bo Yoon from the School of Electrical Engineering has developed a high-resolution pressure sensor that remains unaffected by external interference such as "ghost touches" caused by moisture on touchscreens.
Capacitive pressure sensors, widely used in touch systems due to their simple structure and durability, are essential components of human-machine interface (HMI) technologies in smartphones, wearable devices, and robots. However, they are prone to malfunctions caused by water droplets, electromagnetic interference, and curves.
To address these issues, the research team investigated the root causes of interference in capacitive pressure sensors. They identified that the "fringe field" generated at the sensor’s edges is particularly susceptible to external disturbances.
The researchers concluded that, to fundamentally resolve this issue, suppressing the fringe field was necessary. Through theoretical analysis, they determined that reducing the electrode spacing to the nanometer scale could effectively minimize the fringe field to below a few percent.
Utilizing proprietary micro/nanofabrication techniques, the team developed a nanogap pressure sensor with an electrode spacing of 900 nanometers (nm). This newly developed sensor reliably detected pressure regardless of the material exerting force and remained unaffected by bending or electromagnetic interference.
Furthermore, the team successfully implemented an artificial tactile system utilizing the developed sensor’s characteristics. Human skin contains specialized pressure receptors called Merkel’s disks. To artificially mimic them, the exclusive detection of pressure was necessary, but hadn’t been achieved by conventional sensors.
Professor Yoon’s research team overcame these challenges, developing a sensor achieving a density comparable to Merkel’s discs and enabling wireless, high-precision pressure sensing.
To explore potential applications, the researcher also developed a force touch pad system, demonstrating its ability to capture pressure magnitude and distribution with high resolution and without interference.
Professor Yoon stated, “Our nanogap pressure sensor operates reliably even in rainy conditions or sweaty environments, eliminating common touch malfunctions. We believe this innovation will significantly enhance everyday user experiences.”
He added, “This technology has the potential to revolutionize various fields, including precision tactile sensors for robotics, medical wearable devices, and next-generation augmented reality (AR) and virtual reality (VR) interfaces.”
The study was led by Jae-Soon Yang (Ph.D.), Myung-Kun Chung (Ph.D. candidate), and Jae-Young Yoo (Assistant Professor at Sungkyunkwan University, a KAIST Ph.D. graduate). The research findings were published in Nature Communications on February 27, 2025. (Paper title: “Interference-Free Nanogap Pressure Sensor Array with High Spatial Resolution for Wireless Human-Machine Interface Applications”, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-025-57232-8)
This study was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and Leading Research Center Support Program.
2025.03.14 View 4897 -
 KAIST develops a new, bone-like material that strengthens with use in collaboration with GIT
Materials used in apartment buildings, vehicles, and other structures deteriorate over time under repeated loads, leading to failure and breakage. A joint research team from Korea and the United States has successfully developed a bioinspired material that becomes stronger with use, taking inspiration from the way bones synthesize minerals from bodily fluids under stress, increasing bone density.
< (From left) Professor Sung Hoon Kang of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University Ph.D. candidates Bohan Sun and Grant Kitchen, Professor Yuhang Hu and Ph.D. candidate Dongjung He of Georgia Institute of Technology >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of February that a research team led by Professor Sung Hoon Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Johns Hopkins University and the Georgia Institute of Technology, had developed a new material that strengthens with repeated use, similar to how bones become stronger with exercise.
Professor Kang’s team sought to address the issue of conventional materials degrading with repeated use. Inspired by the biological process where stress triggers cells to form minerals that strengthen bones, the team developed a material that synthesizes minerals under stress without relying on cellular activity. This innovation is expected to enable applications in a variety of fields.
To replace the function of cells, the research team created a porous piezoelectric substrate that converts mechanical force into electricity and actually generates more charge under greater force. They then synthesized a composite material by infusing it with an electrolyte containing mineral components similar to those in blood.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the biomimetic concept based on bone and pitcher plants, the reversible strengthening mechanism, the process of fabricating porous composites, the mechanical property changes with increasing stiffness and energy dissipation after cyclic loading, and the reprogrammable self-folding mechanism and applications >
After subjecting the material to periodic forces and measuring changes in its properties, they observed that its stiffness increased proportionally with the frequency and magnitude of stress and that its energy dissipation capability improved.
The reason for such properties was found to be due to minerals forming inside the porous material under repeated stress, as observed through micro-CT imaging of its internal structure. When subjected to large forces, these minerals fractured and dissipated energy, only to reform under further cyclic stress.
Unlike conventional materials that weaken with repeated use, this new material simultaneously enhances stiffness and impact absorption over time.
< Figure 2. Comparison of the changes in properties of the newly developed new material (LIPPS) with other materials under cyclic loading. (A) Graph showing the relative change rate of energy dissipation after cyclic loading and the relative change rate of elastic modulus upon unloading. LIPPS is in a new area that existing materials have not reached, and shows the characteristics of simultaneous increases in elastic modulus and energy dissipation. (B) Graph comparing the performance of LIPPS with current state-of-the-art mechanically adaptive materials. (Left) The maximum property change rate compared to the baseline after cyclic loading, LIPPS shows much higher changes in elastic modulus, dissipated energy density and ratio, toughness (impact resistance), and stored energy density than the existing adaptive materials. (Right) The absolute value range of the reported properties before and after cyclic loading shows that LIPPS has higher elastic modulus and toughness than the existing adaptive materials. >
Moreover, because its properties improve in proportion to the magnitude and frequency of applied stress, it can self-adjust to achieve mechanical property distributions suitable for different structural applications. It also possesses self-healing capabilities.
Professor Kang stated, "This newly developed material, which strengthens and absorbs impact better with repeated use compared to conventional materials, holds great potential for applications in artificial joints, as well as in aircraft, ships, automobiles, and structural engineering."
This study, with Professor Sung Hoon Kang as the corresponding author, was published in Science Advances (Vol. 11, Issue 6, February).
(Paper title: “A material dynamically enhancing both load-bearing and energy-dissipation capability under cyclic loading”) DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt3979
This research was conducted as a joint effort with Johns Hopkins University's Extreme Materials Institute and the Georgia Institute of Technology, supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Brain Pool Plus program.
2025.02.22 View 4579
KAIST develops a new, bone-like material that strengthens with use in collaboration with GIT
Materials used in apartment buildings, vehicles, and other structures deteriorate over time under repeated loads, leading to failure and breakage. A joint research team from Korea and the United States has successfully developed a bioinspired material that becomes stronger with use, taking inspiration from the way bones synthesize minerals from bodily fluids under stress, increasing bone density.
< (From left) Professor Sung Hoon Kang of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Johns Hopkins University Ph.D. candidates Bohan Sun and Grant Kitchen, Professor Yuhang Hu and Ph.D. candidate Dongjung He of Georgia Institute of Technology >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of February that a research team led by Professor Sung Hoon Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Johns Hopkins University and the Georgia Institute of Technology, had developed a new material that strengthens with repeated use, similar to how bones become stronger with exercise.
Professor Kang’s team sought to address the issue of conventional materials degrading with repeated use. Inspired by the biological process where stress triggers cells to form minerals that strengthen bones, the team developed a material that synthesizes minerals under stress without relying on cellular activity. This innovation is expected to enable applications in a variety of fields.
To replace the function of cells, the research team created a porous piezoelectric substrate that converts mechanical force into electricity and actually generates more charge under greater force. They then synthesized a composite material by infusing it with an electrolyte containing mineral components similar to those in blood.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the biomimetic concept based on bone and pitcher plants, the reversible strengthening mechanism, the process of fabricating porous composites, the mechanical property changes with increasing stiffness and energy dissipation after cyclic loading, and the reprogrammable self-folding mechanism and applications >
After subjecting the material to periodic forces and measuring changes in its properties, they observed that its stiffness increased proportionally with the frequency and magnitude of stress and that its energy dissipation capability improved.
The reason for such properties was found to be due to minerals forming inside the porous material under repeated stress, as observed through micro-CT imaging of its internal structure. When subjected to large forces, these minerals fractured and dissipated energy, only to reform under further cyclic stress.
Unlike conventional materials that weaken with repeated use, this new material simultaneously enhances stiffness and impact absorption over time.
< Figure 2. Comparison of the changes in properties of the newly developed new material (LIPPS) with other materials under cyclic loading. (A) Graph showing the relative change rate of energy dissipation after cyclic loading and the relative change rate of elastic modulus upon unloading. LIPPS is in a new area that existing materials have not reached, and shows the characteristics of simultaneous increases in elastic modulus and energy dissipation. (B) Graph comparing the performance of LIPPS with current state-of-the-art mechanically adaptive materials. (Left) The maximum property change rate compared to the baseline after cyclic loading, LIPPS shows much higher changes in elastic modulus, dissipated energy density and ratio, toughness (impact resistance), and stored energy density than the existing adaptive materials. (Right) The absolute value range of the reported properties before and after cyclic loading shows that LIPPS has higher elastic modulus and toughness than the existing adaptive materials. >
Moreover, because its properties improve in proportion to the magnitude and frequency of applied stress, it can self-adjust to achieve mechanical property distributions suitable for different structural applications. It also possesses self-healing capabilities.
Professor Kang stated, "This newly developed material, which strengthens and absorbs impact better with repeated use compared to conventional materials, holds great potential for applications in artificial joints, as well as in aircraft, ships, automobiles, and structural engineering."
This study, with Professor Sung Hoon Kang as the corresponding author, was published in Science Advances (Vol. 11, Issue 6, February).
(Paper title: “A material dynamically enhancing both load-bearing and energy-dissipation capability under cyclic loading”) DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.adt3979
This research was conducted as a joint effort with Johns Hopkins University's Extreme Materials Institute and the Georgia Institute of Technology, supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Brain Pool Plus program.
2025.02.22 View 4579 -
 KAIST Research Team Develops an AI Framework Capable of Overcoming the Strength-Ductility Dilemma in Additive-manufactured Titanium Alloys
<(From Left) Ph.D. Student Jaejung Park and Professor Seungchul Lee of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and , Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, and M.S.–Ph.D. Integrated Program Student Jeong Ah Lee of POSTECH. >
The KAIST research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee from Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyoung Seop Kim’s team at POSTECH, successfully overcame the strength–ductility dilemma of Ti 6Al 4V alloy using artificial intelligence, enabling the production of high strength, high ductility metal products. The AI developed by the team accurately predicts mechanical properties based on various 3D printing process parameters while also providing uncertainty information, and it uses both to recommend process parameters that hold high promise for 3D printing.
Among various 3D printing technologies, laser powder bed fusion is an innovative method for manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy, renowned for its high strength and bio-compatibility. However, this alloy made via 3D printing has traditionally faced challenges in simultaneously achieving high strength and high ductility. Although there have been attempts to address this issue by adjusting both the printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, the vast number of possible combinations made it difficult to explore them all through experiments and simulations alone.
The active learning framework developed by the team quickly explores a wide range of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions to recommend those expected to improve both strength and ductility of the alloy. These recommendations are based on the AI model’s predictions of ultimate tensile strength and total elongation along with associated uncertainty information for each set of process parameters and heat treatment conditions. The recommended conditions are then validated by performing 3D printing and tensile tests to obtain the true mechanical property values. These new data are incorporated into further AI model training, and through iterative exploration, the optimal process parameters and heat treatment conditions for producing high-performance alloys were determined in only five iterations. With these optimized conditions, the 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy achieved an ultimate tensile strength of 1190 MPa and a total elongation of 16.5%, successfully overcoming the strength–ductility dilemma.
Professor Seungchul Lee commented, “In this study, by optimizing the 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, we were able to develop a high-strength, high-ductility Ti-6Al-4V alloy with minimal experimentation trials. Compared to previous studies, we produced an alloy with a similar ultimate tensile strength but higher total elongation, as well as that with a similar elongation but greater ultimate tensile strength.” He added, “Furthermore, if our approach is applied not only to mechanical properties but also to other properties such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, we anticipate that it will enable efficient exploration of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions.”
This study was published in Nature Communications on January 22 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56267-1), and the research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Nano & Material Technology Development Program and the Leading Research Center Program.
2025.02.21 View 7016
KAIST Research Team Develops an AI Framework Capable of Overcoming the Strength-Ductility Dilemma in Additive-manufactured Titanium Alloys
<(From Left) Ph.D. Student Jaejung Park and Professor Seungchul Lee of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering and , Professor Hyoung Seop Kim of POSTECH, and M.S.–Ph.D. Integrated Program Student Jeong Ah Lee of POSTECH. >
The KAIST research team led by Professor Seungchul Lee from Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Hyoung Seop Kim’s team at POSTECH, successfully overcame the strength–ductility dilemma of Ti 6Al 4V alloy using artificial intelligence, enabling the production of high strength, high ductility metal products. The AI developed by the team accurately predicts mechanical properties based on various 3D printing process parameters while also providing uncertainty information, and it uses both to recommend process parameters that hold high promise for 3D printing.
Among various 3D printing technologies, laser powder bed fusion is an innovative method for manufacturing Ti-6Al-4V alloy, renowned for its high strength and bio-compatibility. However, this alloy made via 3D printing has traditionally faced challenges in simultaneously achieving high strength and high ductility. Although there have been attempts to address this issue by adjusting both the printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, the vast number of possible combinations made it difficult to explore them all through experiments and simulations alone.
The active learning framework developed by the team quickly explores a wide range of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions to recommend those expected to improve both strength and ductility of the alloy. These recommendations are based on the AI model’s predictions of ultimate tensile strength and total elongation along with associated uncertainty information for each set of process parameters and heat treatment conditions. The recommended conditions are then validated by performing 3D printing and tensile tests to obtain the true mechanical property values. These new data are incorporated into further AI model training, and through iterative exploration, the optimal process parameters and heat treatment conditions for producing high-performance alloys were determined in only five iterations. With these optimized conditions, the 3D printed Ti-6Al-4V alloy achieved an ultimate tensile strength of 1190 MPa and a total elongation of 16.5%, successfully overcoming the strength–ductility dilemma.
Professor Seungchul Lee commented, “In this study, by optimizing the 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions, we were able to develop a high-strength, high-ductility Ti-6Al-4V alloy with minimal experimentation trials. Compared to previous studies, we produced an alloy with a similar ultimate tensile strength but higher total elongation, as well as that with a similar elongation but greater ultimate tensile strength.” He added, “Furthermore, if our approach is applied not only to mechanical properties but also to other properties such as thermal conductivity and thermal expansion, we anticipate that it will enable efficient exploration of 3D printing process parameters and heat treatment conditions.”
This study was published in Nature Communications on January 22 (https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-025-56267-1), and the research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Nano & Material Technology Development Program and the Leading Research Center Program.
2025.02.21 View 7016 -
 Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
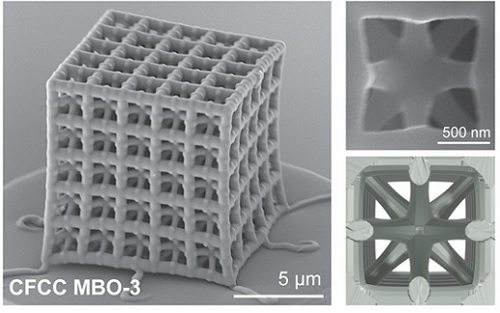
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 6818
Ultralight advanced material developed by KAIST and U of Toronto
< (From left) Professor Seunghwa Ryu of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering, Professor Tobin Filleter of the University of Toronto, Dr. Jinwook Yeo of KAIST, and Dr. Peter Serles of the University of Toronto >
Recently, in advanced industries such as automobiles, aerospace, and mobility, there has been increasing demand for materials that achieve weight reduction while maintaining excellent mechanical properties. An international joint research team has developed an ultralight, high-strength material utilizing nanostructures, presenting the potential for various industrial applications through customized design in the future.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 18th of February that a research team led by Professor Seunghwa Ryu from the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Tobin Filleter from the University of Toronto, has developed a nano-lattice structure that maximizes lightweight properties while maintaining high stiffness and strength.
In this study, the research team optimized the beam shape of the lattice structure to maintain its lightweight characteristics while maximizing stiffness and strength.
Particularly, using a multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm*, the team conducted an optimal design process that simultaneously considers tensile and shear stiffness improvement and weight reduction. They demonstrated that the optimal lattice structure could be predicted and designed with significantly less data (about 400 data points) compared to conventional methods.
*Multi-objective Bayesian optimization algorithm: A method that finds the optimal solution while considering multiple objectives simultaneously. It efficiently collects data and predicts results even under conditions of uncertainty.
< Figure 1. Multi-objective Bayesian optimization for generative design of carbon nanolattices with high compressive stiffness and strength at low density. The upper is the illustration of process workflow. The lower part shows top four MBO CFCC geometries with their 2D Bézier curves. (The optimized structure is predicted and designed with much less data (approximately 400) than the conventional method >
Furthermore, to maximize the effect where mechanical properties improve as size decreases at the nanoscale, the research team utilized pyrolytic carbon* material to implement an ultralight, high-strength, high-stiffness nano-lattice structure.
*Pyrolytic carbon: A carbon material obtained by decomposing organic substances at high temperatures. It has excellent heat resistance and strength, making it widely used in industries such as semiconductor equipment coatings and artificial joint coatings, where it must withstand high temperatures without deformation.
For this, the team applied two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology* to precisely fabricate complex nano-lattice structures, and mechanical performance evaluations confirmed that the developed structure simultaneously possesses strength comparable to steel and the lightness of Styrofoam.
*Two-photon polymerization (2PP) technology: An advanced optical manufacturing technique based on the principle that polymerization occurs only when two photons of a specific wavelength are absorbed simultaneously.
Additionally, the research team demonstrated that multi-focus two-photon polymerization (multi-focus 2PP) technology enables the fabrication of millimeter-scale structures while maintaining nanoscale precision.
Professor Seunghwa Ryu explained, "This technology innovatively solves the stress concentration issue, which has been a limitation of conventional design methods, through three-dimensional nano-lattice structures, achieving both ultralight weight and high strength in material development."
< Figure 2. FESEM image of the fabricated nano-lattice structure and (bottom right) the macroscopic nanolattice resting on a bubble >
He further emphasized, "By integrating data-driven optimal design with precision 3D printing technology, this development not only meets the demand for lightweight materials in the aerospace and automotive industries but also opens possibilities for various industrial applications through customized design."
This study was led by Dr. Peter Serles of the Department of Mechanical & Industrial Engineering at University of Toronto and Dr. Jinwook Yeo from KAIST as co-first authors, with Professor Seunghwa Ryu and Professor Tobin Filleter as corresponding authors.
The research was published on January 23, 2025 in the international journal Advanced Materials (Paper title: “Ultrahigh Specific Strength by Bayesian Optimization of Lightweight Carbon Nanolattices”).
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202410651
This research was supported by the Multiphase Materials Innovation Manufacturing Research Center (an ERC program) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, the M3DT (Medical Device Digital Development Tool) project funded by the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety, and the KAIST International Collaboration Program.
2025.02.18 View 6818 -
 Formosa Group of Taiwan to Establish Bio R&D Center at KAIST Investing 12.5 M USD
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 17th that it signed an agreement for cooperation in the bio-medical field with Formosa Group, one of the three largest companies in Taiwan.
< Formosa Group Chairman Sandy Wang and KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee at the signing ceremony >
Formosa Group Executive Committee member and Chairman Sandy Wang, who leads the group's bio and eco-friendly energy sectors, decided to establish a bio-medical research center within KAIST and invest approximately KRW 18 billion or more over 5 years. In addition, to commercialize the research results, KAIST and Formosa Group will establish a joint venture in Korea with KAIST Holdings, a KAIST-funded company.
The cooperation between the two organizations began in early 2023 when KAIST signed a comprehensive exchange and cooperation agreement (MOU) with Ming Chi University of Science and Technology (明志科技大學), Chang Gung University (長庚大學), and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (長庚記念醫院), which are established and supported by Formosa Group. Afterwards, Chairman Sandy Wang visited KAIST in May 2024 and signed a more specific business agreement (MOA).
KAIST Holdings is a holding company established by KAIST, a government-funded organization, to attract investment and conduct business, and will pursue the establishment of a joint venture with a 50:50 equity structure in cooperation with Formosa Group. KAIST Holdings will invest KAIST’s intellectual property rights, and Formosa Group will invest a corresponding amount of funds.
The KAIST-Formosa joint venture will provide research funds to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center to be established in the future, secure the right to implement the intellectual property rights generated, and promote full-scale business.
The KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center will establish a ‘brain organoid bank’ created by obtaining tissues from hundreds of patients with degenerative brain diseases, thereby securing high-dimensional data that will reveal the fundamental causes of aging and disease. It is expected that KAIST’s world-class artificial intelligence technology will analyze large-scale patient data to find the causes of aging and disease.
Through this business, it is expected that by 2030, five years from now, it will discover more than 10 types of intractable brain disease treatments and expand to more than 20 businesses, including human cell-centered diagnostics and preclinical businesses, and secure infrastructure and intellectual property rights that can create value worth approximately KRW 250 billion.
The Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan has 10,000 beds and handles 35,000 patients per day, and systematically accumulates patient tissue and clinical data. Chang Gung Memorial Hospital will differentiate the tissues of patients with degenerative brain diseases and send them to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center, which will then produce brain organoids to be used for disease research and new drug development. This will allow the world’s largest patient tissue data bank to be established.
Dean Daesoo Kim of the College of Life Science and Bioengineering at KAIST said, “This collaboration between KAIST and Formosa Group is a new research collaboration model that goes beyond joint research to establish a joint venture and global commercialization of developed technologies, and it is significant in that it can serve as an opportunity to promote biomedical research and development.”
With this agreement, KAIST, which has been promoting the KAIST Advanced Regenerative Medicine Engineering Center in Osong K-Bio Square, has secured a practical global partner.
< Representatives of the Formosa Group and KAIST >
KAIST’s Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget, Professor Kyung-Soo Kim emphasized, “KAIST has made great efforts to secure an edge in state-of-the-art biomedical fields such as stem cells and gene editing technology, by attracting the world’s best experts and discovering global cooperation partners, and these results can ultimately be linked to the Osong K-Bio Square project.”
SVP Kim then predicted, “In particular, the practical cooperation with Taiwan’s best Formosa Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, which has abundant clinical experience in stem cell treatment, will be an important axis of KAIST’s bio innovation strategy.”
Formosa Chairman Sandy Wang emphasized that this investment and cooperation is built on trust in KAIST’s R&D capabilities and the passion of its researchers. And added that through this, the Formosa Group will practice corporate social responsibility and take an important first step together with KAIST to protect the welfare and health of humanity. She also went on the say that she expects to see the cooperation expanded to various fields such as mobility and semiconductors based on the successes begotten from the cooperation in the bio field.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “I evaluate this agreement as one of the most important events that will spearhead KAIST into overseas biotechnology stages,” and added, “I expect that this cooperation will be an opportunity for Taiwan and Korea, both of which have IT industry-centered structures, to create new growth engines in the bio industry.” Meanwhile, Formosa Group is a company founded by Chairman Sandy Wang’s father, Chairman Yung-Ching Wang. It is the world’s No. 1 plastic PVC producer and is leading core industries of the Taiwanese economy, including semiconductors, steel, heavy industry, bio, and batteries. Chairman Yung-Ching Wang was respected by the Taiwanese people for his exemplary return of wealth to society under the belief that the companies and assets he founded “belong to the people.”
2025.02.17 View 5320
Formosa Group of Taiwan to Establish Bio R&D Center at KAIST Investing 12.5 M USD
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 17th that it signed an agreement for cooperation in the bio-medical field with Formosa Group, one of the three largest companies in Taiwan.
< Formosa Group Chairman Sandy Wang and KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee at the signing ceremony >
Formosa Group Executive Committee member and Chairman Sandy Wang, who leads the group's bio and eco-friendly energy sectors, decided to establish a bio-medical research center within KAIST and invest approximately KRW 18 billion or more over 5 years. In addition, to commercialize the research results, KAIST and Formosa Group will establish a joint venture in Korea with KAIST Holdings, a KAIST-funded company.
The cooperation between the two organizations began in early 2023 when KAIST signed a comprehensive exchange and cooperation agreement (MOU) with Ming Chi University of Science and Technology (明志科技大學), Chang Gung University (長庚大學), and Chang Gung Memorial Hospital (長庚記念醫院), which are established and supported by Formosa Group. Afterwards, Chairman Sandy Wang visited KAIST in May 2024 and signed a more specific business agreement (MOA).
KAIST Holdings is a holding company established by KAIST, a government-funded organization, to attract investment and conduct business, and will pursue the establishment of a joint venture with a 50:50 equity structure in cooperation with Formosa Group. KAIST Holdings will invest KAIST’s intellectual property rights, and Formosa Group will invest a corresponding amount of funds.
The KAIST-Formosa joint venture will provide research funds to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center to be established in the future, secure the right to implement the intellectual property rights generated, and promote full-scale business.
The KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center will establish a ‘brain organoid bank’ created by obtaining tissues from hundreds of patients with degenerative brain diseases, thereby securing high-dimensional data that will reveal the fundamental causes of aging and disease. It is expected that KAIST’s world-class artificial intelligence technology will analyze large-scale patient data to find the causes of aging and disease.
Through this business, it is expected that by 2030, five years from now, it will discover more than 10 types of intractable brain disease treatments and expand to more than 20 businesses, including human cell-centered diagnostics and preclinical businesses, and secure infrastructure and intellectual property rights that can create value worth approximately KRW 250 billion.
The Chang Gung Memorial Hospital in Taiwan has 10,000 beds and handles 35,000 patients per day, and systematically accumulates patient tissue and clinical data. Chang Gung Memorial Hospital will differentiate the tissues of patients with degenerative brain diseases and send them to the KAIST-Formosa Bio-Medical Research Center, which will then produce brain organoids to be used for disease research and new drug development. This will allow the world’s largest patient tissue data bank to be established.
Dean Daesoo Kim of the College of Life Science and Bioengineering at KAIST said, “This collaboration between KAIST and Formosa Group is a new research collaboration model that goes beyond joint research to establish a joint venture and global commercialization of developed technologies, and it is significant in that it can serve as an opportunity to promote biomedical research and development.”
With this agreement, KAIST, which has been promoting the KAIST Advanced Regenerative Medicine Engineering Center in Osong K-Bio Square, has secured a practical global partner.
< Representatives of the Formosa Group and KAIST >
KAIST’s Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget, Professor Kyung-Soo Kim emphasized, “KAIST has made great efforts to secure an edge in state-of-the-art biomedical fields such as stem cells and gene editing technology, by attracting the world’s best experts and discovering global cooperation partners, and these results can ultimately be linked to the Osong K-Bio Square project.”
SVP Kim then predicted, “In particular, the practical cooperation with Taiwan’s best Formosa Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, which has abundant clinical experience in stem cell treatment, will be an important axis of KAIST’s bio innovation strategy.”
Formosa Chairman Sandy Wang emphasized that this investment and cooperation is built on trust in KAIST’s R&D capabilities and the passion of its researchers. And added that through this, the Formosa Group will practice corporate social responsibility and take an important first step together with KAIST to protect the welfare and health of humanity. She also went on the say that she expects to see the cooperation expanded to various fields such as mobility and semiconductors based on the successes begotten from the cooperation in the bio field.
KAIST President Kwang-Hyung Lee said, “I evaluate this agreement as one of the most important events that will spearhead KAIST into overseas biotechnology stages,” and added, “I expect that this cooperation will be an opportunity for Taiwan and Korea, both of which have IT industry-centered structures, to create new growth engines in the bio industry.” Meanwhile, Formosa Group is a company founded by Chairman Sandy Wang’s father, Chairman Yung-Ching Wang. It is the world’s No. 1 plastic PVC producer and is leading core industries of the Taiwanese economy, including semiconductors, steel, heavy industry, bio, and batteries. Chairman Yung-Ching Wang was respected by the Taiwanese people for his exemplary return of wealth to society under the belief that the companies and assets he founded “belong to the people.”
2025.02.17 View 5320 -
 KAIST Develops Wearable Carbon Dioxide Sensor to Enable Real-time Apnea Diagnosis
- Professor Seunghyup Yoo’s research team of the School of Electrical Engineering developed an ultralow-power carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor using a flexible and thin organic photodiode, and succeeded in real-time breathing monitoring by attaching it to a commercial mask
- Wearable devices with features such as low power, high stability, and flexibility can be utilized for early diagnosis of various diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea
< Photo 1. From the left, School of Electrical Engineering, Ph.D. candidate DongHo Choi, Professor Seunghyup Yoo, and Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Bachelor’s candidate MinJae Kim >
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major respiratory metabolite, and continuous monitoring of CO2 concentration in exhaled breath is not only an important indicator for early detection and diagnosis of respiratory and circulatory system diseases, but can also be widely used for monitoring personal exercise status. KAIST researchers succeeded in accurately measuring CO2 concentration by attaching it to the inside of a mask.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 10th that Professor Seunghyup Yoo's research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering developed a low-power, high-speed wearable CO2 sensor capable of stable breathing monitoring in real time.
Existing non-invasive CO2 sensors had limitations in that they were large in size and consumed high power. In particular, optochemical CO2 sensors using fluorescent molecules have the advantage of being miniaturized and lightweight, but due to the photodegradation phenomenon of dye molecules, they are difficult to use stably for a long time, which limits their use as wearable healthcare sensors.
Optochemical CO2 sensors utilize the fact that the intensity of fluorescence emitted from fluorescent molecules decreases depending on the concentration of CO2, and it is important to effectively detect changes in fluorescence light.
To this end, the research team developed a low-power CO2 sensor consisting of an LED and an organic photodiode surrounding it. Based on high light collection efficiency, the sensor, which minimizes the amount of excitation light irradiated on fluorescent molecules, achieved a device power consumption of 171 μW, which is tens of times lower than existing sensors that consume several mW.
< Figure 1. Structure and operating principle of the developed optochemical carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor. Light emitted from the LED is converted into fluorescence through the fluorescent film, reflected from the light scattering layer, and incident on the organic photodiode. CO2 reacts with a small amount of water inside the fluorescent film to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), and the fluorescence intensity due to 470 nm excitation light decreases. The circular organic photodiode with high light collection efficiency effectively detects changes in fluorescence intensity, lowers the power required light up the LED, and reduces light-induced deterioration. >
The research team also elucidated the photodegradation path of fluorescent molecules used in CO2 sensors, revealed the cause of the increase in error over time in photochemical sensors, and suggested an optical design method to suppress the occurrence of errors.
Based on this, the research team developed a sensor that effectively reduces errors caused by photodegradation, which was a chronic problem of existing photochemical sensors, and can be used continuously for up to 9 hours while existing technologies based on the same material can be used for less than 20 minutes, and can be used multiple times when replacing the CO2 detection fluorescent film.
< Figure 2. Wearable smart mask and real-time breathing monitoring. The fabricated sensor module consists of four elements (①: gas-permeable light-scattering layer, ②: color filter and organic photodiode, ③: light-emitting diode, ④: CO2-detecting fluorescent film). The thin and light sensor (D1: 400 nm, D2: 470 nm) is attached to the inside of the mask to monitor the wearer's breathing in real time. >
The developed sensor accurately measured CO2 concentration by being attached to the inside of a mask based on the advantages of being light (0.12 g), thin (0.7 mm), and flexible. In addition, it showed fast speed and high resolution that can monitor respiratory rate by distinguishing between inhalation and exhalation in real time.
< Photo 2. The developed sensor attached to the inside of the mask >
Professor Seunghyup Yoo said, "The developed sensor has excellent characteristics such as low power, high stability, and flexibility, so it can be widely applied to wearable devices, and can be used for the early diagnosis of various diseases such as hypercapnia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and sleep apnea." He added, "In particular, it is expected to be used to improve side effects caused by rebreathing in environments where dust is generated or where masks are worn for long periods of time, such as during seasonal changes."
This study, in which KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering's undergraduate student Minjae Kim and School of Electrical Engineering's doctoral student Dongho Choi participated as joint first authors, was published in the online version of Cell's sister journal, Device, on the 22nd of last month. (Paper title: Ultralow-power carbon dioxide sensor for real-time breath monitoring) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.device.2024.100681
< Photo 3. From the left, Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering, MinJae Kim, an undergraduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dongho Choi, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering >
This study was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy's Materials and Components Technology Development Project, the National Research Foundation of Korea's Original Technology Development Project, and the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation Project. This work was supported by the (URP) program.
2025.02.13 View 9196
KAIST Develops Wearable Carbon Dioxide Sensor to Enable Real-time Apnea Diagnosis
- Professor Seunghyup Yoo’s research team of the School of Electrical Engineering developed an ultralow-power carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor using a flexible and thin organic photodiode, and succeeded in real-time breathing monitoring by attaching it to a commercial mask
- Wearable devices with features such as low power, high stability, and flexibility can be utilized for early diagnosis of various diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and sleep apnea
< Photo 1. From the left, School of Electrical Engineering, Ph.D. candidate DongHo Choi, Professor Seunghyup Yoo, and Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Bachelor’s candidate MinJae Kim >
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a major respiratory metabolite, and continuous monitoring of CO2 concentration in exhaled breath is not only an important indicator for early detection and diagnosis of respiratory and circulatory system diseases, but can also be widely used for monitoring personal exercise status. KAIST researchers succeeded in accurately measuring CO2 concentration by attaching it to the inside of a mask.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on February 10th that Professor Seunghyup Yoo's research team in the Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering developed a low-power, high-speed wearable CO2 sensor capable of stable breathing monitoring in real time.
Existing non-invasive CO2 sensors had limitations in that they were large in size and consumed high power. In particular, optochemical CO2 sensors using fluorescent molecules have the advantage of being miniaturized and lightweight, but due to the photodegradation phenomenon of dye molecules, they are difficult to use stably for a long time, which limits their use as wearable healthcare sensors.
Optochemical CO2 sensors utilize the fact that the intensity of fluorescence emitted from fluorescent molecules decreases depending on the concentration of CO2, and it is important to effectively detect changes in fluorescence light.
To this end, the research team developed a low-power CO2 sensor consisting of an LED and an organic photodiode surrounding it. Based on high light collection efficiency, the sensor, which minimizes the amount of excitation light irradiated on fluorescent molecules, achieved a device power consumption of 171 μW, which is tens of times lower than existing sensors that consume several mW.
< Figure 1. Structure and operating principle of the developed optochemical carbon dioxide (CO2) sensor. Light emitted from the LED is converted into fluorescence through the fluorescent film, reflected from the light scattering layer, and incident on the organic photodiode. CO2 reacts with a small amount of water inside the fluorescent film to form carbonic acid (H2CO3), which increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H+), and the fluorescence intensity due to 470 nm excitation light decreases. The circular organic photodiode with high light collection efficiency effectively detects changes in fluorescence intensity, lowers the power required light up the LED, and reduces light-induced deterioration. >
The research team also elucidated the photodegradation path of fluorescent molecules used in CO2 sensors, revealed the cause of the increase in error over time in photochemical sensors, and suggested an optical design method to suppress the occurrence of errors.
Based on this, the research team developed a sensor that effectively reduces errors caused by photodegradation, which was a chronic problem of existing photochemical sensors, and can be used continuously for up to 9 hours while existing technologies based on the same material can be used for less than 20 minutes, and can be used multiple times when replacing the CO2 detection fluorescent film.
< Figure 2. Wearable smart mask and real-time breathing monitoring. The fabricated sensor module consists of four elements (①: gas-permeable light-scattering layer, ②: color filter and organic photodiode, ③: light-emitting diode, ④: CO2-detecting fluorescent film). The thin and light sensor (D1: 400 nm, D2: 470 nm) is attached to the inside of the mask to monitor the wearer's breathing in real time. >
The developed sensor accurately measured CO2 concentration by being attached to the inside of a mask based on the advantages of being light (0.12 g), thin (0.7 mm), and flexible. In addition, it showed fast speed and high resolution that can monitor respiratory rate by distinguishing between inhalation and exhalation in real time.
< Photo 2. The developed sensor attached to the inside of the mask >
Professor Seunghyup Yoo said, "The developed sensor has excellent characteristics such as low power, high stability, and flexibility, so it can be widely applied to wearable devices, and can be used for the early diagnosis of various diseases such as hypercapnia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and sleep apnea." He added, "In particular, it is expected to be used to improve side effects caused by rebreathing in environments where dust is generated or where masks are worn for long periods of time, such as during seasonal changes."
This study, in which KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering's undergraduate student Minjae Kim and School of Electrical Engineering's doctoral student Dongho Choi participated as joint first authors, was published in the online version of Cell's sister journal, Device, on the 22nd of last month. (Paper title: Ultralow-power carbon dioxide sensor for real-time breath monitoring) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.device.2024.100681
< Photo 3. From the left, Professor Seunghyup Yoo of the School of Electrical Engineering, MinJae Kim, an undergraduate student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dongho Choi, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering >
This study was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy's Materials and Components Technology Development Project, the National Research Foundation of Korea's Original Technology Development Project, and the KAIST Undergraduate Research Participation Project. This work was supported by the (URP) program.
2025.02.13 View 9196 -
 KAIST Discovers Molecular Switch that Reverses Cancerous Transformation at the Critical Moment of Transition
< (From left) PhD student Seoyoon D. Jeong, (bottom) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, (top) Dr. Dongkwan Shin, Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.
The research team discovered that normal cells can enter an unstable critical transition state where normal cells and cancer cells coexist just before they change into cancer cells during tumorigenesis, the production or development of tumors, and analyzed this critical transition state using a systems biology method to develop a cancer reversal molecular switch identification technology that can reverse the cancerization process. They then applied this to colon cancer cells and confirmed through molecular cell experiments that cancer cells can recover the characteristics of normal cells.
This is an original technology that automatically infers a computer model of the genetic network that controls the critical transition of cancer development from single-cell RNA sequencing data, and systematically finds molecular switches for cancer reversion by simulation analysis. It is expected that this technology will be applied to the development of reversion therapies for other cancers in the future.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "We have discovered a molecular switch that can revert the fate of cancer cells back to a normal state by capturing the moment of critical transition right before normal cells are changed into an irreversible cancerous state."
< Figure 1. Overall conceptual framework of the technology that automatically constructs a molecular regulatory network from single-cell RNA sequencing data of colon cancer cells to discover molecular switches for cancer reversion through computer simulation analysis. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a fundamental technology for automatic construction of a computer model of a core gene network by analyzing the entire process of tumorigenesis of colon cells turning into cancer cells, and developed an original technology for discovering the molecular switches that can induce cancer cell reversal through attractor landscape analysis. >
He continued, "In particular, this study has revealed in detail, at the genetic network level, what changes occur within cells behind the process of cancer development, which has been considered a mystery until now." He emphasized, "This is the first study to reveal that an important clue that can revert the fate of tumorigenesis is hidden at this very critical moment of change."
< Figure 2. Identification of tumor transition state using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids for normal and cancerous tissues, a critical transition was identified in which normal and cancerous cells coexist and instability increases (a-d). The critical transition was confirmed to show intermediate levels of major phenotypic features related to cancer or normal tissues that are indicative of the states between the normal and cancerous cells (e). >
The results of this study, conducted by KAIST Dr. Dongkwan Shin (currently at the National Cancer Center), Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong, and doctoral student Seoyoon D. Jeong jointly with a research team at Seoul National University that provided the organoids (in vitro cultured tissues) from colon cancer patient, were published as an online paper in the international journal ‘Advanced Science’ published by Wiley on January 22nd.
(Paper title: Attractor landscape analysis reveals a reversion switch in the transition of colorectal tumorigenesis) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202412503)
< Figure 3. Reconstruction of a dynamic network model for the transition state of colorectal cancer.
A new technology was established to build a gene network computer model that can simulate the dynamic changes between genes by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing data and existing experimental results on gene-to-gene interactions in the critical transition of cancer. (a). Using this technology, a gene network computer model for the critical transition of colorectal cancer was constructed, and the distribution of attractors representing normal and cancer cell phenotypes was investigated through attractor landscape analysis (b-e). >
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program and the Disease-Centered Translational Research Project of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
< Figure 4. Quantification of attractor landscapes and discovery of transcription factors for cancer reversibility through perturbation simulation analysis. A methodology for implementing discontinuous attractor landscapes continuously from a computer model of gene networks and quantifying them as cancer scores was introduced (a), and attractor landscapes for the critical transition of colorectal cancer were secured (b-d). By tracking the change patterns of normal and cancer cell attractors through perturbation simulation analysis for each gene, the optimal combination of transcription factors for cancer reversion was discovered (e-h). This was confirmed in various parameter combinations as well (i). >
< Figure 5. Identification and experimental validation of the optimal target gene for cancer reversion. Among the common target genes of the discovered transcription factor combinations, we identified cancer reversing molecular switches that are predicted to suppress cancer cell proliferation and restore the characteristics of normal colon cells (a-d). When inhibitors for the molecular switches were treated to organoids derived from colon cancer patients, it was confirmed that cancer cell proliferation was suppressed and the expression of key genes related to cancer development was inhibited (e-h), and a group of genes related to normal colon epithelium was activated and transformed into a state similar to normal colon cells (i-j). >
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed an original technology to systematically discover key molecular switches that can induce reversion of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach using an attractor landscape analysis of a genetic network model for the critical transition at the moment of transformation from normal cells to cancer cells, and verified the reversing effect of actual colon cancer through cellular experiments. >
2025.02.05 View 30118
KAIST Discovers Molecular Switch that Reverses Cancerous Transformation at the Critical Moment of Transition
< (From left) PhD student Seoyoon D. Jeong, (bottom) Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho, (top) Dr. Dongkwan Shin, Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho’s research team has recently been highlighted for their work on developing an original technology for cancer reversal treatment that does not kill cancer cells but only changes their characteristics to reverse them to a state similar to normal cells. This time, they have succeeded in revealing for the first time that a molecular switch that can induce cancer reversal at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells is hidden in the genetic network.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of February that Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team of the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has succeeded in developing a fundamental technology to capture the critical transition phenomenon at the moment when normal cells change into cancer cells and analyze it to discover a molecular switch that can revert cancer cells back into normal cells.
A critical transition is a phenomenon in which a sudden change in state occurs at a specific point in time, like water changing into steam at 100℃. This critical transition phenomenon also occurs in the process in which normal cells change into cancer cells at a specific point in time due to the accumulation of genetic and epigenetic changes.
The research team discovered that normal cells can enter an unstable critical transition state where normal cells and cancer cells coexist just before they change into cancer cells during tumorigenesis, the production or development of tumors, and analyzed this critical transition state using a systems biology method to develop a cancer reversal molecular switch identification technology that can reverse the cancerization process. They then applied this to colon cancer cells and confirmed through molecular cell experiments that cancer cells can recover the characteristics of normal cells.
This is an original technology that automatically infers a computer model of the genetic network that controls the critical transition of cancer development from single-cell RNA sequencing data, and systematically finds molecular switches for cancer reversion by simulation analysis. It is expected that this technology will be applied to the development of reversion therapies for other cancers in the future.
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho said, "We have discovered a molecular switch that can revert the fate of cancer cells back to a normal state by capturing the moment of critical transition right before normal cells are changed into an irreversible cancerous state."
< Figure 1. Overall conceptual framework of the technology that automatically constructs a molecular regulatory network from single-cell RNA sequencing data of colon cancer cells to discover molecular switches for cancer reversion through computer simulation analysis. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team established a fundamental technology for automatic construction of a computer model of a core gene network by analyzing the entire process of tumorigenesis of colon cells turning into cancer cells, and developed an original technology for discovering the molecular switches that can induce cancer cell reversal through attractor landscape analysis. >
He continued, "In particular, this study has revealed in detail, at the genetic network level, what changes occur within cells behind the process of cancer development, which has been considered a mystery until now." He emphasized, "This is the first study to reveal that an important clue that can revert the fate of tumorigenesis is hidden at this very critical moment of change."
< Figure 2. Identification of tumor transition state using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer. Using single-cell RNA sequencing data from colorectal cancer patient-derived organoids for normal and cancerous tissues, a critical transition was identified in which normal and cancerous cells coexist and instability increases (a-d). The critical transition was confirmed to show intermediate levels of major phenotypic features related to cancer or normal tissues that are indicative of the states between the normal and cancerous cells (e). >
The results of this study, conducted by KAIST Dr. Dongkwan Shin (currently at the National Cancer Center), Dr. Jeong-Ryeol Gong, and doctoral student Seoyoon D. Jeong jointly with a research team at Seoul National University that provided the organoids (in vitro cultured tissues) from colon cancer patient, were published as an online paper in the international journal ‘Advanced Science’ published by Wiley on January 22nd.
(Paper title: Attractor landscape analysis reveals a reversion switch in the transition of colorectal tumorigenesis) (DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202412503)
< Figure 3. Reconstruction of a dynamic network model for the transition state of colorectal cancer.
A new technology was established to build a gene network computer model that can simulate the dynamic changes between genes by integrating single-cell RNA sequencing data and existing experimental results on gene-to-gene interactions in the critical transition of cancer. (a). Using this technology, a gene network computer model for the critical transition of colorectal cancer was constructed, and the distribution of attractors representing normal and cancer cell phenotypes was investigated through attractor landscape analysis (b-e). >
This study was conducted with the support of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program and the Disease-Centered Translational Research Project of the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI) of the Ministry of Health and Welfare.
< Figure 4. Quantification of attractor landscapes and discovery of transcription factors for cancer reversibility through perturbation simulation analysis. A methodology for implementing discontinuous attractor landscapes continuously from a computer model of gene networks and quantifying them as cancer scores was introduced (a), and attractor landscapes for the critical transition of colorectal cancer were secured (b-d). By tracking the change patterns of normal and cancer cell attractors through perturbation simulation analysis for each gene, the optimal combination of transcription factors for cancer reversion was discovered (e-h). This was confirmed in various parameter combinations as well (i). >
< Figure 5. Identification and experimental validation of the optimal target gene for cancer reversion. Among the common target genes of the discovered transcription factor combinations, we identified cancer reversing molecular switches that are predicted to suppress cancer cell proliferation and restore the characteristics of normal colon cells (a-d). When inhibitors for the molecular switches were treated to organoids derived from colon cancer patients, it was confirmed that cancer cell proliferation was suppressed and the expression of key genes related to cancer development was inhibited (e-h), and a group of genes related to normal colon epithelium was activated and transformed into a state similar to normal colon cells (i-j). >
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed an original technology to systematically discover key molecular switches that can induce reversion of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach using an attractor landscape analysis of a genetic network model for the critical transition at the moment of transformation from normal cells to cancer cells, and verified the reversing effect of actual colon cancer through cellular experiments. >
2025.02.05 View 30118 -
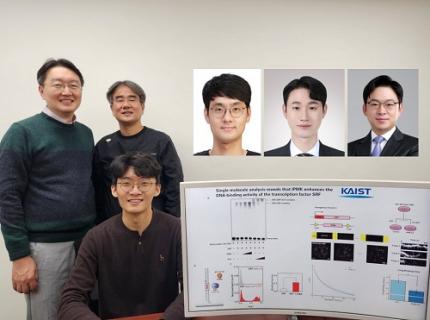 KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 12271
KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 12271 -
 KAIST Alumni Association to Honor Alumni of the Year Award Winners
Photo 1. Photo of the KAIST Alumni of the Year Award Recipients
(From left) UST President Lee-whan Kim, CEO Han Chung of iThree Systems Co., Ltd., CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd., and Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on Monday, the 13th of January that the Alumni Association (President Yun-Tae Lee) has selected its Alumni of the Year.
This year’s honorees are: ▴ President Lee-whan Kim of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), ▴ CEO Han Chung of i3 Systems, ▴ CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution, and ▴ Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The honorees were selected based on their achievements over the past year, and the award ceremony will be held at the 2025 KAIST Alumni Association New Year’s Gathering to be held at the L Tower in Seoul at 5 PM on Friday the 17th.
The KAIST Alumni of the Year Award is an award presented by the Alumni Association to alumni who have contributed to the development of the country and the society or have brought honor to their alma mater through outstanding academic achievements and community service. Since its establishment in 1992, 126 recipients have been awarded.
Lee-whan Kim (Master's graduate of Mechanical Engineering, 82), the President of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), established a leading foundation for national science and technology policy and strategy, and played a leading role in innovating national science and technology capabilities through the advancement of the national research and development system and the advancement of science and technology personnel training. In particular, he played a pivotal role in the establishment of UST and the Korea Science Academy (KSA), and greatly contributed to establishing a foundation for the training and utilization of science and technology personnel.
Han Chung (Master's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 91, with Ph.D. degree in 96), the CEO of i3 Systems, is a first-generation researcher in the field of domestic infrared detectors. He developed military detectors for over 30 years and founded i3 Systems, a specialized infrared detector company, in 1998. Currently, he supplies more than 80% of the infrared detectors used by the Korean military, and has also achieved export results to over 20 countries.
Dong Myung Kim (Master's graduate of Materials Science and Engineering, 94, with Ph.D. degree in 98) the CEO of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd. has led innovation in the battery field with his ceaseless exploration and challenging spirit, and is known as an authority in the secondary battery industry. He played a leading role in establishing K-Battery as a global leader, strengthened the country's future industrial competitiveness, and greatly contributed to the development of science and technology.
Hyun Myung (Bachelor's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 92, with Master's degree in 94, and Ph.D. degree in 98) a Professor of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, won first place in the world at the Quadruped Robot Challenge (QRC) hosted by the IEEE’s International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2023 with the 'DreamWaQ' system, an AI walking technology based on deep reinforcement learning that utilizes non-video sensory technologies. He contributed to enhancing the competitiveness of the domestic robot industry by developing his own fully autonomous walking technology that recognizes the environment around the robot and finds the optimal path.
Yun-Tae Lee, the 27th president of the KAIST Alumni Association, said, “KAIST alumni have been the driving force behind the growth of industries in all walks of life by continuously conducting research and development in the field of advanced science and technology for a long time,” and added, “I am very proud of the KAIST alumni award recipients who are leading science and technology on the world stage beyond Korea, and I sincerely thank them for their efforts and achievements.”
2025.01.15 View 7242
KAIST Alumni Association to Honor Alumni of the Year Award Winners
Photo 1. Photo of the KAIST Alumni of the Year Award Recipients
(From left) UST President Lee-whan Kim, CEO Han Chung of iThree Systems Co., Ltd., CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd., and Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on Monday, the 13th of January that the Alumni Association (President Yun-Tae Lee) has selected its Alumni of the Year.
This year’s honorees are: ▴ President Lee-whan Kim of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), ▴ CEO Han Chung of i3 Systems, ▴ CEO Dong Myung Kim of LG Energy Solution, and ▴ Professor Hyun Myung of the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST.
The honorees were selected based on their achievements over the past year, and the award ceremony will be held at the 2025 KAIST Alumni Association New Year’s Gathering to be held at the L Tower in Seoul at 5 PM on Friday the 17th.
The KAIST Alumni of the Year Award is an award presented by the Alumni Association to alumni who have contributed to the development of the country and the society or have brought honor to their alma mater through outstanding academic achievements and community service. Since its establishment in 1992, 126 recipients have been awarded.
Lee-whan Kim (Master's graduate of Mechanical Engineering, 82), the President of the Korea National University of Science and Technology (UST), established a leading foundation for national science and technology policy and strategy, and played a leading role in innovating national science and technology capabilities through the advancement of the national research and development system and the advancement of science and technology personnel training. In particular, he played a pivotal role in the establishment of UST and the Korea Science Academy (KSA), and greatly contributed to establishing a foundation for the training and utilization of science and technology personnel.
Han Chung (Master's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 91, with Ph.D. degree in 96), the CEO of i3 Systems, is a first-generation researcher in the field of domestic infrared detectors. He developed military detectors for over 30 years and founded i3 Systems, a specialized infrared detector company, in 1998. Currently, he supplies more than 80% of the infrared detectors used by the Korean military, and has also achieved export results to over 20 countries.
Dong Myung Kim (Master's graduate of Materials Science and Engineering, 94, with Ph.D. degree in 98) the CEO of LG Energy Solution Co., Ltd. has led innovation in the battery field with his ceaseless exploration and challenging spirit, and is known as an authority in the secondary battery industry. He played a leading role in establishing K-Battery as a global leader, strengthened the country's future industrial competitiveness, and greatly contributed to the development of science and technology.
Hyun Myung (Bachelor's graduate of Electrical Engineering, 92, with Master's degree in 94, and Ph.D. degree in 98) a Professor of Electrical Engineering, KAIST, won first place in the world at the Quadruped Robot Challenge (QRC) hosted by the IEEE’s International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA) 2023 with the 'DreamWaQ' system, an AI walking technology based on deep reinforcement learning that utilizes non-video sensory technologies. He contributed to enhancing the competitiveness of the domestic robot industry by developing his own fully autonomous walking technology that recognizes the environment around the robot and finds the optimal path.
Yun-Tae Lee, the 27th president of the KAIST Alumni Association, said, “KAIST alumni have been the driving force behind the growth of industries in all walks of life by continuously conducting research and development in the field of advanced science and technology for a long time,” and added, “I am very proud of the KAIST alumni award recipients who are leading science and technology on the world stage beyond Korea, and I sincerely thank them for their efforts and achievements.”
2025.01.15 View 7242