AR
-
 Professor Jinah Park Received the Prime Minister's Award
Professor Jinah Park of the School of Computing received the Prime Minister’s Citation Ribbon on April 21 at a ceremony celebrating the Day of Science and ICT. The awardee was selected by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Korea Communications Commission.
Professor Park was recognized for her convergence R&D of a VR simulator for dental treatment with haptic feedback, in addition to her research on understanding 3D interaction behavior in VR environments. Her major academic contributions are in the field of medical imaging, where she developed a computational technique to analyze cardiac motion from tagging data.
Professor Park said she was very pleased to see her twenty-plus years of research on ways to converge computing into medical areas finally bear fruit. She also thanked her colleagues and students in her Computer Graphics and CGV Research Lab for working together to make this achievement possible.
2017.04.26 View 12476
Professor Jinah Park Received the Prime Minister's Award
Professor Jinah Park of the School of Computing received the Prime Minister’s Citation Ribbon on April 21 at a ceremony celebrating the Day of Science and ICT. The awardee was selected by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and Korea Communications Commission.
Professor Park was recognized for her convergence R&D of a VR simulator for dental treatment with haptic feedback, in addition to her research on understanding 3D interaction behavior in VR environments. Her major academic contributions are in the field of medical imaging, where she developed a computational technique to analyze cardiac motion from tagging data.
Professor Park said she was very pleased to see her twenty-plus years of research on ways to converge computing into medical areas finally bear fruit. She also thanked her colleagues and students in her Computer Graphics and CGV Research Lab for working together to make this achievement possible.
2017.04.26 View 12476 -
 KAIST Nanosatellite LINK Launched to the ISS
Courtesy: United Launch Alliance
The KAIST nanosatellite LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was successfully launched on an Atlas V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18 at Space Launch Complex 41, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The KAIST nanosatellite was developed by the research team led by Professor Hyochoong Bang of the Department of Aerospace Engineering.
Aboard the flight to the ISS (International Space Station) were 28 satellites including LINK. They are part of the QB50 Project, an international educational initiative which aims to deploy an array of CubeSat-mounted sensors into Earth’s thermosphere. The project is funded by the European Commission and managed by the von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics in Belgium.
The small satellites are hitching a lift into orbit aboard the unmanned resupply spacecraft Cygnus, with a total mass of 83 kilograms. Built to CubeSat specifications, Cygnus will deploy four of the spacecraft following its departure from the space station. LINK will conduct its scientific mission for three months at the station.
The majority of QB50 satellites carry one of three standard instrument packages, consisting of a primary instrument and an array of thermistors, thermocouples, and resistant temperature detectors. LINK is a two-unit CubeSat and weighs two kilograms. It carries an ion-neutral mass spectrometer (INMS), which measures the mass of ions and neutral atoms, as the primary payload of the QB50 project. The secondary payload is two Langmuir probes, which are in-house sensors (m-NLP) developed by Professor Kyong Wook Min’s team of the Department of Physics at KAIST. These are all geared toward collecting long-term continuous in-situ measurements of conditions in Earth’s lower thermosphere.
Professor Bang said, “The QB50 Project is being used for educational purposes. However, the LINK launch will bring a new breakthrough toward collecting information on Earth’s lower thermosphere. Building on these experiences of designing and launching the CubeSat will serve as an opportunity to verify the research results made in our lab firsthand in space.”
(Caption: LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was launched on an Atlast V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18.)
2017.04.25 View 9977
KAIST Nanosatellite LINK Launched to the ISS
Courtesy: United Launch Alliance
The KAIST nanosatellite LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was successfully launched on an Atlas V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18 at Space Launch Complex 41, Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida. The KAIST nanosatellite was developed by the research team led by Professor Hyochoong Bang of the Department of Aerospace Engineering.
Aboard the flight to the ISS (International Space Station) were 28 satellites including LINK. They are part of the QB50 Project, an international educational initiative which aims to deploy an array of CubeSat-mounted sensors into Earth’s thermosphere. The project is funded by the European Commission and managed by the von Karman Institute for Fluid Dynamics in Belgium.
The small satellites are hitching a lift into orbit aboard the unmanned resupply spacecraft Cygnus, with a total mass of 83 kilograms. Built to CubeSat specifications, Cygnus will deploy four of the spacecraft following its departure from the space station. LINK will conduct its scientific mission for three months at the station.
The majority of QB50 satellites carry one of three standard instrument packages, consisting of a primary instrument and an array of thermistors, thermocouples, and resistant temperature detectors. LINK is a two-unit CubeSat and weighs two kilograms. It carries an ion-neutral mass spectrometer (INMS), which measures the mass of ions and neutral atoms, as the primary payload of the QB50 project. The secondary payload is two Langmuir probes, which are in-house sensors (m-NLP) developed by Professor Kyong Wook Min’s team of the Department of Physics at KAIST. These are all geared toward collecting long-term continuous in-situ measurements of conditions in Earth’s lower thermosphere.
Professor Bang said, “The QB50 Project is being used for educational purposes. However, the LINK launch will bring a new breakthrough toward collecting information on Earth’s lower thermosphere. Building on these experiences of designing and launching the CubeSat will serve as an opportunity to verify the research results made in our lab firsthand in space.”
(Caption: LINK (Little Intelligent Nanosatellite of KAIST) was launched on an Atlast V booster aboard the NASA CRS-7 Mission on April 18.)
2017.04.25 View 9977 -
 FinTech Conference by KAIST, EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton, and Tsinghua
KAIST will partner with EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton University, and Tsinghua University to host a series of annual rotation conference on FinTech. The inaugural conference will be held in Princeton on April 26 and is entitled ‘Four-University Rotating FinTech Conference: Wealth Management Systems for Individual Investors.’
The conference will facilitate discussion among all interest parties of academics, practitioners, and regulators from around the world. Professor Woo Chang Kim of the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering will represent KAIST. Professor Kim is also the head of the Center for Wealth Management Technologies at KAIST.
In addition to Professor Kim, leading experts from the US, Asia, and Europe will present at the conference, including Andrew Yao (Turing Award recipient and founder of IIIS FinTech Center at Tsinghua University), John Bogle (founder of the Vanguard Group, and president of the Bogle Financial Markets Research Center), Lionel Martellini (director of EDHEC-Risk Institute), John Mashey (Bell Labs/Silicon Valley computer scientist/corporate executive), and John Mulvey (professor and founding member of the Bendheim Center for Finance at Princeton University).
This year’s conference will feature following sessions:
· Mass-Customization of Goal-Based Investment Solutions: The New Frontier in Digital Wealth Management Services
· Goal-Based Investment via Multi-Stage Stochastic Goal Programming for Robo-Advisor Services
· Big Data – Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
· Applying Machine Learning Concepts for Asset Allocation and ALM
· FinTech: Drawing Strengths from Computing Theories
· Savings and Investing to Achieve Retirement Goals: An Update Given Current Market Assumptions · The Rise of Robo-Advisors: A Threat or an Opportunity for the Wealth Management Industry?
The conference will include the participation of official partner Samsung Asset Management.
2017.04.20 View 11267
FinTech Conference by KAIST, EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton, and Tsinghua
KAIST will partner with EDHEC-Risk Institute, Princeton University, and Tsinghua University to host a series of annual rotation conference on FinTech. The inaugural conference will be held in Princeton on April 26 and is entitled ‘Four-University Rotating FinTech Conference: Wealth Management Systems for Individual Investors.’
The conference will facilitate discussion among all interest parties of academics, practitioners, and regulators from around the world. Professor Woo Chang Kim of the Department of Industrial & Systems Engineering will represent KAIST. Professor Kim is also the head of the Center for Wealth Management Technologies at KAIST.
In addition to Professor Kim, leading experts from the US, Asia, and Europe will present at the conference, including Andrew Yao (Turing Award recipient and founder of IIIS FinTech Center at Tsinghua University), John Bogle (founder of the Vanguard Group, and president of the Bogle Financial Markets Research Center), Lionel Martellini (director of EDHEC-Risk Institute), John Mashey (Bell Labs/Silicon Valley computer scientist/corporate executive), and John Mulvey (professor and founding member of the Bendheim Center for Finance at Princeton University).
This year’s conference will feature following sessions:
· Mass-Customization of Goal-Based Investment Solutions: The New Frontier in Digital Wealth Management Services
· Goal-Based Investment via Multi-Stage Stochastic Goal Programming for Robo-Advisor Services
· Big Data – Yesterday, Today and Tomorrow
· Applying Machine Learning Concepts for Asset Allocation and ALM
· FinTech: Drawing Strengths from Computing Theories
· Savings and Investing to Achieve Retirement Goals: An Update Given Current Market Assumptions · The Rise of Robo-Advisors: A Threat or an Opportunity for the Wealth Management Industry?
The conference will include the participation of official partner Samsung Asset Management.
2017.04.20 View 11267 -
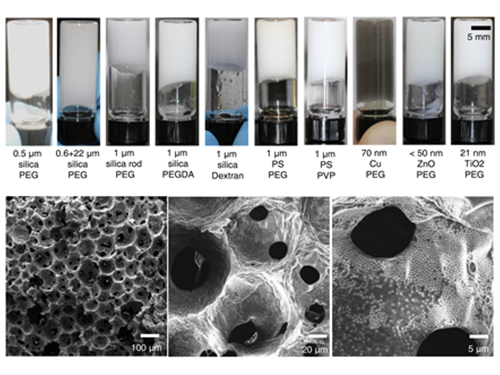 Processable High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsion Using Depletion Attraction
Professor Siyoung Choi’s research team from the KAIST Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering used physical force to successfully produce a stable emulsion.
Emulsions, commonly known as cosmetic products, refer to stably dispersed structures of oil droplets in water (or water droplets in oil). Pickering emulsions refer to emulsions stabilized using solid particles, instead of detergent. Traditionally, it is said that water and oil do not mix. Until recently, detergent was added to mix oil and water for dispersion. Emulsions have traditionally been produced using this technique and are currently used for products such as mayonnaise, sun block, and lotion.
On the other hand, Pickering emulsions have been used after stabilization of chemical treatments on solid particle surfaces to enhance adsorption power. However, there were limitations in its application, since the treatment process is complex and its applicable range remains limited. Instead of chemical treatment on Pickering emulsion surfaces, the research team mixed small macromolecules a few nanometer in size with larger solid particles (tens of nanometers to a few micrometers). This induced depletion force was used to successfully stabilize the emulsion.
Depletion force refers to the force a large number of small particles induces to aggregate the bigger particles, in order to secure free space for themselves. In short, the force induces an attraction between larger particles. Until now, depletion force could only be applied to solids and solid particles. However, the research team used macromolecules and large particles such as solid particles and oil droplets to show the applicability of depletion force between solids and liquids. By introducing macromolecules that act as smaller particles, hydrophilic solid particles enhanced the adsorption of solid particles to the oil droplet surface, while preventing dissociation from the particle surface, resulting in the maintenance of a stable state.
The research team confirmed the possibility of the simple production of various porous macromolecular materials using stable Pickering emulsions. Such porous macromolecules are expected to be applicable in separation film, systems engineering, drug delivery, and sensors, given their large surface area.
Professor KyuHan Kim, the first author said, “Until now, depletion force has only been used between solid colloid particles. This research has scientific significance since it is the first example of using depletion force between solid particles and liquid droplets.”
Professor Choi said, “Beyond its academic significance, this technology could contribute to industries and national competitiveness.” He continued, “Since this technology uses physical force, not chemical, to produce stable emulsion, it can be used regardless of the type of solid particle and macromolecule. Further, it could be used in customized porous material production for special purposes.”
The research was published in Nature Communications online on February 1. In particular, this research is significant since an undergraduate student, Subeen Kim, participated in the project as a second author through the KAIST Undergraduate Research Program (URP). This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
(Figure 1: Images of the inner structure of porous macromolecules produced using the new technology)
(Figure 2: Images showing the measurement of rheological properties of Pickering emulsions and system processability)
(Figure 3: Images showing a stable Pickering emulsion system)
2017.04.19 View 10401
Processable High Internal Phase Pickering Emulsion Using Depletion Attraction
Professor Siyoung Choi’s research team from the KAIST Department of Chemical & Biomolecular Engineering used physical force to successfully produce a stable emulsion.
Emulsions, commonly known as cosmetic products, refer to stably dispersed structures of oil droplets in water (or water droplets in oil). Pickering emulsions refer to emulsions stabilized using solid particles, instead of detergent. Traditionally, it is said that water and oil do not mix. Until recently, detergent was added to mix oil and water for dispersion. Emulsions have traditionally been produced using this technique and are currently used for products such as mayonnaise, sun block, and lotion.
On the other hand, Pickering emulsions have been used after stabilization of chemical treatments on solid particle surfaces to enhance adsorption power. However, there were limitations in its application, since the treatment process is complex and its applicable range remains limited. Instead of chemical treatment on Pickering emulsion surfaces, the research team mixed small macromolecules a few nanometer in size with larger solid particles (tens of nanometers to a few micrometers). This induced depletion force was used to successfully stabilize the emulsion.
Depletion force refers to the force a large number of small particles induces to aggregate the bigger particles, in order to secure free space for themselves. In short, the force induces an attraction between larger particles. Until now, depletion force could only be applied to solids and solid particles. However, the research team used macromolecules and large particles such as solid particles and oil droplets to show the applicability of depletion force between solids and liquids. By introducing macromolecules that act as smaller particles, hydrophilic solid particles enhanced the adsorption of solid particles to the oil droplet surface, while preventing dissociation from the particle surface, resulting in the maintenance of a stable state.
The research team confirmed the possibility of the simple production of various porous macromolecular materials using stable Pickering emulsions. Such porous macromolecules are expected to be applicable in separation film, systems engineering, drug delivery, and sensors, given their large surface area.
Professor KyuHan Kim, the first author said, “Until now, depletion force has only been used between solid colloid particles. This research has scientific significance since it is the first example of using depletion force between solid particles and liquid droplets.”
Professor Choi said, “Beyond its academic significance, this technology could contribute to industries and national competitiveness.” He continued, “Since this technology uses physical force, not chemical, to produce stable emulsion, it can be used regardless of the type of solid particle and macromolecule. Further, it could be used in customized porous material production for special purposes.”
The research was published in Nature Communications online on February 1. In particular, this research is significant since an undergraduate student, Subeen Kim, participated in the project as a second author through the KAIST Undergraduate Research Program (URP). This research was funded by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
(Figure 1: Images of the inner structure of porous macromolecules produced using the new technology)
(Figure 2: Images showing the measurement of rheological properties of Pickering emulsions and system processability)
(Figure 3: Images showing a stable Pickering emulsion system)
2017.04.19 View 10401 -
 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST announced its 30 scholarship recipients for the 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program on April 18. The six-week program, starting from July 10, will be run in Korea, Japan, and China.
The program provides young global scholars with focused and challenging nuclear nonproliferation studies. Young scholars will be exposed to diverse science and technology policies and practices concurrently conducted in many countries and the future direction for enhancing nuclear nonproliferation. They will participate in a series of seminars, projects, international conferences, and field trips.
Since its launch in 2014, the program has educated 71 young scholars. This year, more than 150 scholars from 37 countries applied for the program, reflecting the growing reputation of the program both at home and abroad. The director of the NEREC, Professor Man-Sung Yim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST said that young scholars from very prestigious foreign universities have shown strong interest in the program. According to Professor Yim, this year’s recipients are from 26 universities from 16 countries including Harvard University, Oxford University, the National Research Nuclear University of Russia, and the Tokyo Institute of Technology
2017.04.19 View 10775
2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program
The Nuclear Nonproliferation Education and Research Center (NEREC) at KAIST announced its 30 scholarship recipients for the 2017 Summer Nuclear Nonproliferation Education Program on April 18. The six-week program, starting from July 10, will be run in Korea, Japan, and China.
The program provides young global scholars with focused and challenging nuclear nonproliferation studies. Young scholars will be exposed to diverse science and technology policies and practices concurrently conducted in many countries and the future direction for enhancing nuclear nonproliferation. They will participate in a series of seminars, projects, international conferences, and field trips.
Since its launch in 2014, the program has educated 71 young scholars. This year, more than 150 scholars from 37 countries applied for the program, reflecting the growing reputation of the program both at home and abroad. The director of the NEREC, Professor Man-Sung Yim of the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering at KAIST said that young scholars from very prestigious foreign universities have shown strong interest in the program. According to Professor Yim, this year’s recipients are from 26 universities from 16 countries including Harvard University, Oxford University, the National Research Nuclear University of Russia, and the Tokyo Institute of Technology
2017.04.19 View 10775 -
 Tactile Sensor for Robot Skin Advanced by KAIST Team
The joint research team of Professors Jung Kim and Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a tactile sensor that can act as skin for robots using silicon and carbon materials. This technology produced a sensor that can absorb shock and distinguish various forms of touch, and it is hoped to be used as robot skin in the future.
Skin serves an important role as the largest organ of the human body. As well as protecting major organs from external shock, skin also measures and distinguishes delicate tactile information and transfer it to the nervous system.
Current robotic sensory technology allows robots to have visual and auditory systems at nearly similar levels to human capacity, but there are limitations in tactile sensors that can detect changes in the environment throughout the body. To apply skin with similar functions as humans to robots, it is essential to develop skin sensor technology with high flexibility and high shock absorption. Another limitation for developing robot skin was connecting numerous sensors all over the body using electric wiring.
To overcome this problem, the research team combined silicon and carbon nanotubes (CNT) to produce a composite, which was then used in combination with a medical imaging technique called electrical impedance tomography (EIT). This led to technology that can distinguish various forms of force over a large area without electrical wiring.
The sensing material can distinguish the location and the size of various forms by touch, and thus can be applied to robot skin that can absorb shock as well as serves as a 3D computer interface and tactile sensor. It can withstand strong force such as a hammer strike, and can be re-used even after partial damage to the sensor by filling and hardening the damaged region with composite. Further, the sensor can be made by filling a 3D shape frame with silicon-nanotube composite. Using this technology, new forms of computer interaces can be developed with both curbed and flat surfaces.
This research was conducted through a collaboration between Professor Park, an expert in nanostructures and sensors, and Professor Kim, an expert in bio-robotics. Hence, the technology is likely to be applied in real products.
Professor Kim said, “Flexible tactile sensors can not only be directly adhered to the body, but they also provides information on modified states in multiple dimensions”. He continued, “This technology will contribute to the soft robot industry in the areas of robot skin and the field of wearable medical appliances.”
Professor Park said, “This technology implemented a next-generation user interface through the integration of functional nano-composite material and computer tomography.”
This research was published in Scientific Reports, a sister journal of Nature, online on January 25. This research was conducted as joint research by first author Hyo-Sang Lee, as well as Donguk Kwon and Ji-seung Cho, and was funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
(Fiigrue 1: Robotic hand responding to resistance via a connection with the developed tactile sensor)
(Figure 2: Manufacturing process for pressure-resistant composite using silicon rubber and carbon nanotubes)
(Figure 3: Computer interface using pressure-resistant composite)
2017.04.17 View 14134
Tactile Sensor for Robot Skin Advanced by KAIST Team
The joint research team of Professors Jung Kim and Inkyu Park from the Department of Mechanical Engineering developed a tactile sensor that can act as skin for robots using silicon and carbon materials. This technology produced a sensor that can absorb shock and distinguish various forms of touch, and it is hoped to be used as robot skin in the future.
Skin serves an important role as the largest organ of the human body. As well as protecting major organs from external shock, skin also measures and distinguishes delicate tactile information and transfer it to the nervous system.
Current robotic sensory technology allows robots to have visual and auditory systems at nearly similar levels to human capacity, but there are limitations in tactile sensors that can detect changes in the environment throughout the body. To apply skin with similar functions as humans to robots, it is essential to develop skin sensor technology with high flexibility and high shock absorption. Another limitation for developing robot skin was connecting numerous sensors all over the body using electric wiring.
To overcome this problem, the research team combined silicon and carbon nanotubes (CNT) to produce a composite, which was then used in combination with a medical imaging technique called electrical impedance tomography (EIT). This led to technology that can distinguish various forms of force over a large area without electrical wiring.
The sensing material can distinguish the location and the size of various forms by touch, and thus can be applied to robot skin that can absorb shock as well as serves as a 3D computer interface and tactile sensor. It can withstand strong force such as a hammer strike, and can be re-used even after partial damage to the sensor by filling and hardening the damaged region with composite. Further, the sensor can be made by filling a 3D shape frame with silicon-nanotube composite. Using this technology, new forms of computer interaces can be developed with both curbed and flat surfaces.
This research was conducted through a collaboration between Professor Park, an expert in nanostructures and sensors, and Professor Kim, an expert in bio-robotics. Hence, the technology is likely to be applied in real products.
Professor Kim said, “Flexible tactile sensors can not only be directly adhered to the body, but they also provides information on modified states in multiple dimensions”. He continued, “This technology will contribute to the soft robot industry in the areas of robot skin and the field of wearable medical appliances.”
Professor Park said, “This technology implemented a next-generation user interface through the integration of functional nano-composite material and computer tomography.”
This research was published in Scientific Reports, a sister journal of Nature, online on January 25. This research was conducted as joint research by first author Hyo-Sang Lee, as well as Donguk Kwon and Ji-seung Cho, and was funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning.
(Fiigrue 1: Robotic hand responding to resistance via a connection with the developed tactile sensor)
(Figure 2: Manufacturing process for pressure-resistant composite using silicon rubber and carbon nanotubes)
(Figure 3: Computer interface using pressure-resistant composite)
2017.04.17 View 14134 -
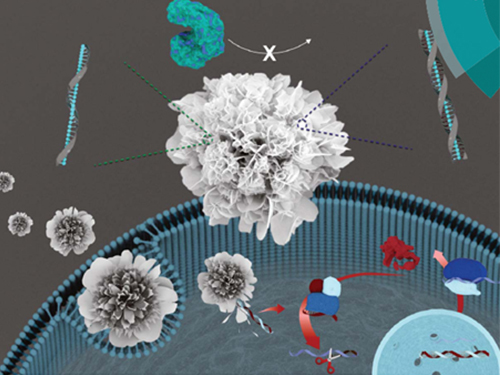 Nuclease-Resistant Hybrid Nanoflowers
An eco-friendly method to synthesize DNA-copper nanoflowers with high load efficiencies, low cytotoxicity, and strong resistance against nucleases has been developed by Professor Hyun Gyu Park in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his collaborators.
The research team successfully formed a flower-shaped nanostructure in an eco-friendly condition by using interactions between copper ions and DNA containing amide and amine groups. The resulting nanoflowers exhibit high DNA loading capacities in addition to low cytotoxicity.
Flower-shaped nanocrystals called nanoflowers have gained attention for their distinct features of high surface roughness and high surface area to volume ratios. The nanoflowers have been used in many areas including catalysis, electronics, and analytical chemistry.
Of late, research breakthroughs were made in the generation of hybrid inorganic-organic nanoflowers containing various enzymes as organic components. The hybridization with inorganic materials greatly enhanced enzymatic activity, stability, and durability compared to the corresponding free enzymes.
Generally, the formation of protein nanocrystals requires high heat treatment so it has limitations for achieving the high loading capacities of intact DNA.
The research team addressed the issue, focusing on the fact that nucleic acids with well-defined structures and selective recognition properties also contain amide and amine groups in their nucleobases. They proved that flower-like structures could be formed by using nucleic acids as a synthetic template, which paved the way to synthesize the hybrid nanoflowers containing DNA as an organic component in an eco-friendly condition.
The team also confirmed that this synthetic method can be universally applied to any DNA sequences containing amide and amine groups. They said their approach is quite unique considering that the majority of previous works focused on the utilization of DNA as a linker to assemble the nanomaterials. They said the method has several advantageous features. First, the ‘green’ synthetic procedure doesn’t involve any toxic chemicals, and shows low cytotoxicity and strong resistance against nucleases. Second, the obtained nanoflowers exhibit exceptionally high DNA loading capacities.
Above all, such superior features of hybrid nanoflowers enabled the sensitive detection of various molecules including phenol, hydrogen peroxide, and glucose. DNA-copper nanoflowers showed even higher peroxidase activity than those of protein-copper nanoflowers, which may be due to the larger surface area of the flower- shaped structures, creating a greater chance for applying them in the field of sensing of detection of hydrogen peroxide.
The research team expects that their research will create diverse applications in many areas including biosensors and will be further applied into therapeutic applications.
Professor Park said, “The inorganic component in the hybrid nanoflowers not only exhibits low cytotoxicity, but also protects the encapsulated DNA from being cleaved by endonuclease enzymes. Using this feature, the nanostructure will be applied into developing gene therapeutic carriers.”
This research was co-led by Professor Moon Il Kim at Gachon University and KAIST graduate Ki Soo Park, currently a professor at Konkuk University, is the first author. The research was featured as the front cover article of the Journal of Materials Chemistry B on March 28, Issue 12, published by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
The research was funded by the Mid-Career Researcher Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Global Frontier Project of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning.
(Figure: (A) Schematic illustration of the formation of nuclease-resistant DNA–inorganic nanoflowers. (B) SEM images showing time-dependent growth of DNA-nanoflowers. The concentration of A-rich ssDNA (Table S1, ESI†) was 0.25 mM.)
2017.04.14 View 10504
Nuclease-Resistant Hybrid Nanoflowers
An eco-friendly method to synthesize DNA-copper nanoflowers with high load efficiencies, low cytotoxicity, and strong resistance against nucleases has been developed by Professor Hyun Gyu Park in the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering and his collaborators.
The research team successfully formed a flower-shaped nanostructure in an eco-friendly condition by using interactions between copper ions and DNA containing amide and amine groups. The resulting nanoflowers exhibit high DNA loading capacities in addition to low cytotoxicity.
Flower-shaped nanocrystals called nanoflowers have gained attention for their distinct features of high surface roughness and high surface area to volume ratios. The nanoflowers have been used in many areas including catalysis, electronics, and analytical chemistry.
Of late, research breakthroughs were made in the generation of hybrid inorganic-organic nanoflowers containing various enzymes as organic components. The hybridization with inorganic materials greatly enhanced enzymatic activity, stability, and durability compared to the corresponding free enzymes.
Generally, the formation of protein nanocrystals requires high heat treatment so it has limitations for achieving the high loading capacities of intact DNA.
The research team addressed the issue, focusing on the fact that nucleic acids with well-defined structures and selective recognition properties also contain amide and amine groups in their nucleobases. They proved that flower-like structures could be formed by using nucleic acids as a synthetic template, which paved the way to synthesize the hybrid nanoflowers containing DNA as an organic component in an eco-friendly condition.
The team also confirmed that this synthetic method can be universally applied to any DNA sequences containing amide and amine groups. They said their approach is quite unique considering that the majority of previous works focused on the utilization of DNA as a linker to assemble the nanomaterials. They said the method has several advantageous features. First, the ‘green’ synthetic procedure doesn’t involve any toxic chemicals, and shows low cytotoxicity and strong resistance against nucleases. Second, the obtained nanoflowers exhibit exceptionally high DNA loading capacities.
Above all, such superior features of hybrid nanoflowers enabled the sensitive detection of various molecules including phenol, hydrogen peroxide, and glucose. DNA-copper nanoflowers showed even higher peroxidase activity than those of protein-copper nanoflowers, which may be due to the larger surface area of the flower- shaped structures, creating a greater chance for applying them in the field of sensing of detection of hydrogen peroxide.
The research team expects that their research will create diverse applications in many areas including biosensors and will be further applied into therapeutic applications.
Professor Park said, “The inorganic component in the hybrid nanoflowers not only exhibits low cytotoxicity, but also protects the encapsulated DNA from being cleaved by endonuclease enzymes. Using this feature, the nanostructure will be applied into developing gene therapeutic carriers.”
This research was co-led by Professor Moon Il Kim at Gachon University and KAIST graduate Ki Soo Park, currently a professor at Konkuk University, is the first author. The research was featured as the front cover article of the Journal of Materials Chemistry B on March 28, Issue 12, published by the Royal Society of Chemistry.
The research was funded by the Mid-Career Researcher Support Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea and the Global Frontier Project of the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning.
(Figure: (A) Schematic illustration of the formation of nuclease-resistant DNA–inorganic nanoflowers. (B) SEM images showing time-dependent growth of DNA-nanoflowers. The concentration of A-rich ssDNA (Table S1, ESI†) was 0.25 mM.)
2017.04.14 View 10504 -
 Improving Traffic Safety with a Crowdsourced Traffic Violation Reporting App
KAIST researchers revealed that crowdsourced traffic violation reporting with smartphone-based continuous video capturing can dramatically change the current practice of policing activities on the road and will significantly improve traffic safety.
Professor Uichin Lee of the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering and the Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering at KAIST and his research team designed and evaluated Mobile Roadwatch, a mobile app that helps citizen record traffic violation with their smartphones and report the recorded videos to the police.
This app supports continuous video recording just like onboard vehicle dashboard cameras. Mobile Roadwatch allows drivers to safely capture traffic violations by simply touching a smartphone screen while driving. The captured videos are automatically tagged with contextual information such as location and time. This information will be used as important evidence for the police to ticket the violators. All of the captured videos can be conveniently reviewed, allowing users to decide which events to report to the police.
The team conducted a two-week field study to understand how drivers use Mobile Roadwatch. They found that the drivers tended to capture all traffic risks regardless of the level of their involvement and the seriousness of the traffic risks. However, when it came to actual reporting, they tended to report only serious traffic violations, which could have led to car accidents, such as traffic signal violations and illegal U-turns. After receiving feedback about their reports from the police, drivers typically felt very good about their contributions to traffic safety.
At the same time, some drivers felt pleased to know that the offenders received tickets since they thought these offenders deserved to be ticketed. While participating in the Mobile Roadwatch campaign, drivers reported that they tried to drive as safely as possible and abide by traffic laws. This was because they wanted to be as fair as possible so that they could capture others’ violations without feeling guilty. They were also afraid that other drivers might capture their violations.
Professor Lee said, “Our study participants answered that Mobile Roadwatch served as a very useful tool for reporting traffic violations, and they were highly satisfied with its features. Beyond simple reporting, our tool can be extended to support online communities, which help people actively discuss various local safety issues and work with the police and local authorities to solve these safety issues.”
Korea and India were the early adaptors supporting video-based reporting of traffic violations to the police. In recent years, the number of reports has dramatically increased. For example, Korea’s ‘Looking for a Witness’ (released in April 2015) received more than half million reported violations as of November 2016. In the US, authorities started tapping into smartphone recordings by releasing video-based reporting apps such as ICE Blackbox and Mobile Justice. Professor Lee said that the existing services cannot be used while driving, because none of the existing services support continuous video recording and safe event capturing behind the wheel.
Professor Lee’s team has been incorporating advanced computer vision techniques into Mobile Roadwatch for automatically capturing traffic violations and safety risks, including potholes and obstacles. The researchers will present their results in May at the ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2017) in Denver, CO, USA. Their research was supported by the KAIST-KUSTAR fund.
(Caption: A driver is trying to capture an event by touching a screen. The Mobile Radwatch supports continuous video recording and safe event captureing behind the wheel.)
2017.04.10 View 12311
Improving Traffic Safety with a Crowdsourced Traffic Violation Reporting App
KAIST researchers revealed that crowdsourced traffic violation reporting with smartphone-based continuous video capturing can dramatically change the current practice of policing activities on the road and will significantly improve traffic safety.
Professor Uichin Lee of the Department of Industrial and Systems Engineering and the Graduate School of Knowledge Service Engineering at KAIST and his research team designed and evaluated Mobile Roadwatch, a mobile app that helps citizen record traffic violation with their smartphones and report the recorded videos to the police.
This app supports continuous video recording just like onboard vehicle dashboard cameras. Mobile Roadwatch allows drivers to safely capture traffic violations by simply touching a smartphone screen while driving. The captured videos are automatically tagged with contextual information such as location and time. This information will be used as important evidence for the police to ticket the violators. All of the captured videos can be conveniently reviewed, allowing users to decide which events to report to the police.
The team conducted a two-week field study to understand how drivers use Mobile Roadwatch. They found that the drivers tended to capture all traffic risks regardless of the level of their involvement and the seriousness of the traffic risks. However, when it came to actual reporting, they tended to report only serious traffic violations, which could have led to car accidents, such as traffic signal violations and illegal U-turns. After receiving feedback about their reports from the police, drivers typically felt very good about their contributions to traffic safety.
At the same time, some drivers felt pleased to know that the offenders received tickets since they thought these offenders deserved to be ticketed. While participating in the Mobile Roadwatch campaign, drivers reported that they tried to drive as safely as possible and abide by traffic laws. This was because they wanted to be as fair as possible so that they could capture others’ violations without feeling guilty. They were also afraid that other drivers might capture their violations.
Professor Lee said, “Our study participants answered that Mobile Roadwatch served as a very useful tool for reporting traffic violations, and they were highly satisfied with its features. Beyond simple reporting, our tool can be extended to support online communities, which help people actively discuss various local safety issues and work with the police and local authorities to solve these safety issues.”
Korea and India were the early adaptors supporting video-based reporting of traffic violations to the police. In recent years, the number of reports has dramatically increased. For example, Korea’s ‘Looking for a Witness’ (released in April 2015) received more than half million reported violations as of November 2016. In the US, authorities started tapping into smartphone recordings by releasing video-based reporting apps such as ICE Blackbox and Mobile Justice. Professor Lee said that the existing services cannot be used while driving, because none of the existing services support continuous video recording and safe event capturing behind the wheel.
Professor Lee’s team has been incorporating advanced computer vision techniques into Mobile Roadwatch for automatically capturing traffic violations and safety risks, including potholes and obstacles. The researchers will present their results in May at the ACM CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems (CHI 2017) in Denver, CO, USA. Their research was supported by the KAIST-KUSTAR fund.
(Caption: A driver is trying to capture an event by touching a screen. The Mobile Radwatch supports continuous video recording and safe event captureing behind the wheel.)
2017.04.10 View 12311 -
 Scholarship in Memory of Professor Shin Endowed by His Family
Professor Joong-Hoon Shin of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology was touted as a genius young scientist who would take the lead in nanoscience technology. After earning degrees from Harvard and the Caltech, he was appointed at KAIST at age 27. He was the youngest professor ever appointed in Korea.
Professor Shin’s outstanding research in the field of semiconductor nano-optics led him to be named as the ‘Scientist of the Year’ for three consecutive years from 2004 by the most prestigious scientist and technology organizations including the Korean Academy Science and Technology, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korean government. However, a fatal car accident last September on the way home from a seminar in Gangwon Province took his life and a promising scholar’s research was left unfinished. He was 47 years old.
Mrs. Young-Eun Hong, the widow of the late Professor Shin, made a 100 million KRW gift to KAIST to establish the ‘Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship’ on April 7. The scholarship will provide financial assistance to outstanding students of physics and nanoscience.
At the donation ceremony attended by President Sung-Chul Shin, Professor Shin’s colleagues and students, and family members, Mrs. Hong said, “My family would like to help young students achieve their dreams on behalf of my husband. I hope students will remember my husband’s passion and dedication toward his studies for a long time. He was a very hard worker.”
Working at KAIST, Professor Shin made significant achievements in field of semiconductor nano-optics, specializing in silicon photonics and silicon nanocrystal structures. In particular, his research team gained attention reproducing the structure of ‘Morpho butterfly’ wings, which produce the same colors from various angles, using external light as a light source without extra power. Their research led to the creation of original technology dubbed the biomimetics reflective display and was published in Nature in 2012.
Professor Shin’s legacy still endures. In February, a research team under Professor Shin-Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering includingthe late Professor Shin’s doctoral student Seung Yeol Lee, posthumously dedicated their research published on Advanced Materials to Professor Shin. ( click )
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a physicist, said “His passing is a great loss to the whole scientific and technology community, at home and abroad. But Joong-Hoon Shin scholarship will enable the growth and ensure the strength of nanoscience and its education at KAIST. We will uphold Professor Shin’s legacy by doing our best to make KAIST a world-leading university which can create global value.”
Mrs. Hong said she will continue her husband’s academic legacy at his alma maters, Harvard and the Caltech, where he earned his BS in physics and his Ph.D. in applied physics respectively. She said she will start fundraising to establish the Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship at Harvard and Caltech from July.
(Mrs. Hong poses with President Sung-Chul Shin after donating 100 million KRW for establishing 'Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship' in memory of her husband on April 7.)
2017.04.10 View 9468
Scholarship in Memory of Professor Shin Endowed by His Family
Professor Joong-Hoon Shin of the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology was touted as a genius young scientist who would take the lead in nanoscience technology. After earning degrees from Harvard and the Caltech, he was appointed at KAIST at age 27. He was the youngest professor ever appointed in Korea.
Professor Shin’s outstanding research in the field of semiconductor nano-optics led him to be named as the ‘Scientist of the Year’ for three consecutive years from 2004 by the most prestigious scientist and technology organizations including the Korean Academy Science and Technology, the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the Korean government. However, a fatal car accident last September on the way home from a seminar in Gangwon Province took his life and a promising scholar’s research was left unfinished. He was 47 years old.
Mrs. Young-Eun Hong, the widow of the late Professor Shin, made a 100 million KRW gift to KAIST to establish the ‘Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship’ on April 7. The scholarship will provide financial assistance to outstanding students of physics and nanoscience.
At the donation ceremony attended by President Sung-Chul Shin, Professor Shin’s colleagues and students, and family members, Mrs. Hong said, “My family would like to help young students achieve their dreams on behalf of my husband. I hope students will remember my husband’s passion and dedication toward his studies for a long time. He was a very hard worker.”
Working at KAIST, Professor Shin made significant achievements in field of semiconductor nano-optics, specializing in silicon photonics and silicon nanocrystal structures. In particular, his research team gained attention reproducing the structure of ‘Morpho butterfly’ wings, which produce the same colors from various angles, using external light as a light source without extra power. Their research led to the creation of original technology dubbed the biomimetics reflective display and was published in Nature in 2012.
Professor Shin’s legacy still endures. In February, a research team under Professor Shin-Hyun Kim of the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering includingthe late Professor Shin’s doctoral student Seung Yeol Lee, posthumously dedicated their research published on Advanced Materials to Professor Shin. ( click )
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a physicist, said “His passing is a great loss to the whole scientific and technology community, at home and abroad. But Joong-Hoon Shin scholarship will enable the growth and ensure the strength of nanoscience and its education at KAIST. We will uphold Professor Shin’s legacy by doing our best to make KAIST a world-leading university which can create global value.”
Mrs. Hong said she will continue her husband’s academic legacy at his alma maters, Harvard and the Caltech, where he earned his BS in physics and his Ph.D. in applied physics respectively. She said she will start fundraising to establish the Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship at Harvard and Caltech from July.
(Mrs. Hong poses with President Sung-Chul Shin after donating 100 million KRW for establishing 'Joong-Hoon Shin Scholarship' in memory of her husband on April 7.)
2017.04.10 View 9468 -
 Professor Won Do Heo Receives 'Scientist of the Month Award'
Professor Won Do Heo of the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the “Scientist of the Month” for April 2017 by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Heo was recognized for his suggestion of a new biological research method developing various optogenetics technology which controls cell function by using light. He developed the technology using lasers or LED light, without the need for surgery or drug administration, to identify the cause of diseases related to calcium ions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
The general technique used in optogenetics, that control cells in the body with light, is the simple activation and deactivation of neurons.
Professor Heo developed a calcium ion channel activation technique (OptoSTIM1) to activate calcium ions in the body using light. He also succeeded in increasing calcium concentrations with light to enhance the memory capacity of mice two-fold.
Using this technology, the desired amount and residing time of calcium ion influx can be controlled by changing light intensity and exposure periods, enabling the function of a single cell or various cells in animal tissue to be controlled remotely.
The experimental results showed that calcium ion influx can be activated in cells that are affected by calcium ions, such as normal cells, cancer cells, and human embryonic stem cells. By controlling calcium concentrations with light, it is possible to control biological phenomena, such as cellular growth, neurotransmitter transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone control.
Professor Heo said, “Until now, it was standard to use optogenetics to activate neurons using channelrhodopsin. The development of this new optogenetic technique using calcium ion channel activation can be applied to various biological studies, as well as become an essential research technique in neurobiology.
The “Scientist of the Month Award” is given every month to one researcher who made significant contributions to the advancement of science and technology with their outstanding research achievement. The awardee will receive prize money of ten million won.
2017.04.07 View 10672
Professor Won Do Heo Receives 'Scientist of the Month Award'
Professor Won Do Heo of the Department of Biological Sciences was selected as the “Scientist of the Month” for April 2017 by the Ministry of Science, ICT and Future Planning and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
Professor Heo was recognized for his suggestion of a new biological research method developing various optogenetics technology which controls cell function by using light. He developed the technology using lasers or LED light, without the need for surgery or drug administration, to identify the cause of diseases related to calcium ions such as Alzheimer’s disease and cancer.
The general technique used in optogenetics, that control cells in the body with light, is the simple activation and deactivation of neurons.
Professor Heo developed a calcium ion channel activation technique (OptoSTIM1) to activate calcium ions in the body using light. He also succeeded in increasing calcium concentrations with light to enhance the memory capacity of mice two-fold.
Using this technology, the desired amount and residing time of calcium ion influx can be controlled by changing light intensity and exposure periods, enabling the function of a single cell or various cells in animal tissue to be controlled remotely.
The experimental results showed that calcium ion influx can be activated in cells that are affected by calcium ions, such as normal cells, cancer cells, and human embryonic stem cells. By controlling calcium concentrations with light, it is possible to control biological phenomena, such as cellular growth, neurotransmitter transmission, muscle contraction, and hormone control.
Professor Heo said, “Until now, it was standard to use optogenetics to activate neurons using channelrhodopsin. The development of this new optogenetic technique using calcium ion channel activation can be applied to various biological studies, as well as become an essential research technique in neurobiology.
The “Scientist of the Month Award” is given every month to one researcher who made significant contributions to the advancement of science and technology with their outstanding research achievement. The awardee will receive prize money of ten million won.
2017.04.07 View 10672 -
 Improving Silver Nanowires for FTCEs with Flash Light Interactions
Flexible transparent conducting electrodes (FTCEs) are an essential element of flexible optoelectronics for next-generation wearable displays, augmented reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoTs). Silver nanowires (Ag NWs) have received a great deal of attention as future FTCEs due to their great flexibility, material stability, and large-scale productivity. Despite these advantages, Ag NWs have drawbacks such as high wire-to-wire contact resistance and poor adhesion to substrates, resulting in severe power consumption and the delamination of FTCEs.
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and Dr. Hong-Jin Park from BSP Inc., has developed high-performance Ag NWs (sheet resistance ~ 5 Ω/sq, transmittance 90 % at λ = 550 nm) with strong adhesion on plastic (interfacial energy of 30.7 J∙m-2) using flash light-material interactions.
The broad ultraviolet (UV) spectrum of a flash light enables the localized heating at the junctions of nanowires (NWs), which results in the fast and complete welding of Ag NWs. Consequently, the Ag NWs demonstrate six times higher conductivity than that of the pristine NWs. In addition, the near-infrared (NIR) of the flash lamp melted the interface between the Ag NWs and a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate, dramatically enhancing the adhesion force of the Ag NWs to the PET by 310 %.
Professor Lee said, “Light interaction with nanomaterials is an important field for future flexible electronics since it can overcome thermal limit of plastics, and we are currently expanding our research into light-inorganic interactions.”
Meanwhile, BSP Inc., a laser manufacturing company and a collaborator of this work, has launched new flash lamp equipment for flexible applications based on the Professor Lee’s research.
The results of this work entitled “Flash-Induced Self-Limited Plasmonic Welding of Ag NW Network for Transparent Flexible Energy Harvester (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201603473)” were published in the February 2, 2017 issue of Advanced Materials as the cover article.
Professor Lee also contributed an invited review in the same journal of the April 3, 2017 online issue, “Laser-Material Interactions for Flexible Applications (DOI:10.1002/adma.201606586),” overviewing the recent advances in light interactions with flexible nanomaterials.
References
[1] Advanced Materials, February 2, 2017, Flash-Induced Self-Limited Plasmonic Welding of Ag NW network for Transparent Flexible Energy Harvester http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201603473/epdf
[2] Advanced Materials, April 3, 2017, Laser-Material Interactions for Flexible Applications
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201606586/abstract
For further inquiries on research:
keonlee@kaist.ac.kr (Keon Jae Lee), hjpark@bsptech.co.kr (Hong-Jin Park)
Picture 1: Artistic Rendtition of Light Interaction with Nanomaterials
(This image shows flash-induced plasmonic interactions with nanowires to improve silver nanowires (Ag NWs).)
Picture 2: Ag NW/PET Film
(This picture shows the Ag NWs on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film after the flash-induced plasmonic thermal process.)
2017.04.05 View 12239
Improving Silver Nanowires for FTCEs with Flash Light Interactions
Flexible transparent conducting electrodes (FTCEs) are an essential element of flexible optoelectronics for next-generation wearable displays, augmented reality (AR), and the Internet of Things (IoTs). Silver nanowires (Ag NWs) have received a great deal of attention as future FTCEs due to their great flexibility, material stability, and large-scale productivity. Despite these advantages, Ag NWs have drawbacks such as high wire-to-wire contact resistance and poor adhesion to substrates, resulting in severe power consumption and the delamination of FTCEs.
A research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee of the Materials Science and Engineering Department at KAIST and Dr. Hong-Jin Park from BSP Inc., has developed high-performance Ag NWs (sheet resistance ~ 5 Ω/sq, transmittance 90 % at λ = 550 nm) with strong adhesion on plastic (interfacial energy of 30.7 J∙m-2) using flash light-material interactions.
The broad ultraviolet (UV) spectrum of a flash light enables the localized heating at the junctions of nanowires (NWs), which results in the fast and complete welding of Ag NWs. Consequently, the Ag NWs demonstrate six times higher conductivity than that of the pristine NWs. In addition, the near-infrared (NIR) of the flash lamp melted the interface between the Ag NWs and a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) substrate, dramatically enhancing the adhesion force of the Ag NWs to the PET by 310 %.
Professor Lee said, “Light interaction with nanomaterials is an important field for future flexible electronics since it can overcome thermal limit of plastics, and we are currently expanding our research into light-inorganic interactions.”
Meanwhile, BSP Inc., a laser manufacturing company and a collaborator of this work, has launched new flash lamp equipment for flexible applications based on the Professor Lee’s research.
The results of this work entitled “Flash-Induced Self-Limited Plasmonic Welding of Ag NW Network for Transparent Flexible Energy Harvester (DOI: 10.1002/adma.201603473)” were published in the February 2, 2017 issue of Advanced Materials as the cover article.
Professor Lee also contributed an invited review in the same journal of the April 3, 2017 online issue, “Laser-Material Interactions for Flexible Applications (DOI:10.1002/adma.201606586),” overviewing the recent advances in light interactions with flexible nanomaterials.
References
[1] Advanced Materials, February 2, 2017, Flash-Induced Self-Limited Plasmonic Welding of Ag NW network for Transparent Flexible Energy Harvester http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201603473/epdf
[2] Advanced Materials, April 3, 2017, Laser-Material Interactions for Flexible Applications
http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/adma.201606586/abstract
For further inquiries on research:
keonlee@kaist.ac.kr (Keon Jae Lee), hjpark@bsptech.co.kr (Hong-Jin Park)
Picture 1: Artistic Rendtition of Light Interaction with Nanomaterials
(This image shows flash-induced plasmonic interactions with nanowires to improve silver nanowires (Ag NWs).)
Picture 2: Ag NW/PET Film
(This picture shows the Ag NWs on a polyethylene terephthalate (PET) film after the flash-induced plasmonic thermal process.)
2017.04.05 View 12239 -
 Expanding the Genetic Code of Mus Musculus
Professor Hee-Sung Park of the Department of Chemistry, who garnered attention for his novel strategy of installing authentic post-translational modifications into recombinant proteins, expanded his research portfolio to another level. Professor Park’s team was the first to report the generation of a mouse strain with an expanded genetic code, allowing site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids.
Professor Park published the research on the new chemical biology method for achieving selective chemical modifications in proteins in Science last September. The research team, this time in collaboration with Professor Chan Bae Park of the Department of Physiology at the Ajou University School of Medicine, demonstrated temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation in various organs of the transgenic mouse using a recombinant green fluorescent protein as a model protein. This research was published in the online edition of Nature Communications on February 21.
This approach enables the rapid onset of position-specific acetylation of a target protein at any developmental stage, facilitating temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation in various organs of the transgenic mouse. Such temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation will be of prime importance for investigating many essential biological processes and human diseases at the tissue and organism level.
Almost all human proteins, the products of about 25,000 genes, are known to undergo various post-translational modifications during and after synthesis. Post-translation modifications regulate the function of cellular proteins, playing a key role in many essential processes such as delivering signals and body growth. However, the unusual protein modifications, aroused from genetic and/or environmental factors, trigger severe diseases including cancer, dementia, and diabetes.
The team inserted transgenes into the mouse genome to allocate the site-specific addition of unnatural amino acids. The researchers inserted a modified version of lysine into the house mice, which allowed for the control of the acetylation. They used recombinant green fluorescent proteins from transgenic house mice as models for control of the acetylation.
The team was also able to regulate the acetylation of specific temporal and spatial frames in the mice, restraining the abnormality in proteins to certain organs such as the liver and kidneys. The research team said the strategy will provide a powerful tool for systematic in vivo study of cellular proteins in the most commonly used mammalian model organisms for human physiology and disease. Professor Park said, “This method can be easily extended to generate a wide range of custom-made transgenic mouse strains for further investigating diverse proteins of interest.” He added, “This method can be further extended to generate a wide range of custom-made transgenic mouse strains, opening a new paradigm for investigating anti-cancer and cerebral disease treatments.
This work was supported by grants from KAIST Systems Healthcare and the Medicinal Bioconvergence Research Center and the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center of the Global Frontier Project funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.
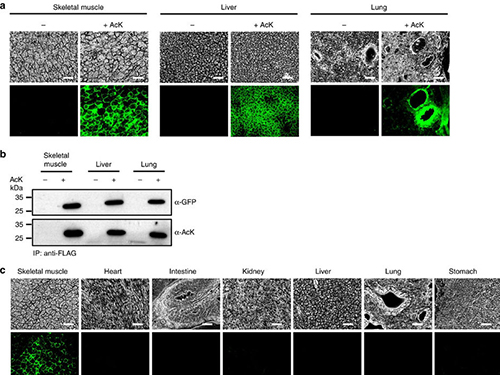
(Figure:Temporal and spatial control of in vivo protein acetylation)
(a) Temporal expression of acetylated GFPuv in the AcK-GFPamber mouse. The expression of GFPuv in skeletal muscle, liver, and lung tissues was detected only in the AcK-injected mouse. Scale bar, 200 µm. (b) Western blotting of anti-FLAG-immunoprecipitated proteins from tissues of the AcK-GFPamber mouse. Acetylated GFPuv was produced after AcK injection. (c) Spatial expression of acetylated GFPuv in the AcK-GFPamber mouse. Acetylated GFPuv was observed only in skeletal muscle when AcK was directly delivered to the tissues. Sacle bar, 200 µm.
2017.03.27 View 11189
Expanding the Genetic Code of Mus Musculus
Professor Hee-Sung Park of the Department of Chemistry, who garnered attention for his novel strategy of installing authentic post-translational modifications into recombinant proteins, expanded his research portfolio to another level. Professor Park’s team was the first to report the generation of a mouse strain with an expanded genetic code, allowing site-specific incorporation of unnatural amino acids.
Professor Park published the research on the new chemical biology method for achieving selective chemical modifications in proteins in Science last September. The research team, this time in collaboration with Professor Chan Bae Park of the Department of Physiology at the Ajou University School of Medicine, demonstrated temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation in various organs of the transgenic mouse using a recombinant green fluorescent protein as a model protein. This research was published in the online edition of Nature Communications on February 21.
This approach enables the rapid onset of position-specific acetylation of a target protein at any developmental stage, facilitating temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation in various organs of the transgenic mouse. Such temporal and spatial control of protein acetylation will be of prime importance for investigating many essential biological processes and human diseases at the tissue and organism level.
Almost all human proteins, the products of about 25,000 genes, are known to undergo various post-translational modifications during and after synthesis. Post-translation modifications regulate the function of cellular proteins, playing a key role in many essential processes such as delivering signals and body growth. However, the unusual protein modifications, aroused from genetic and/or environmental factors, trigger severe diseases including cancer, dementia, and diabetes.
The team inserted transgenes into the mouse genome to allocate the site-specific addition of unnatural amino acids. The researchers inserted a modified version of lysine into the house mice, which allowed for the control of the acetylation. They used recombinant green fluorescent proteins from transgenic house mice as models for control of the acetylation.
The team was also able to regulate the acetylation of specific temporal and spatial frames in the mice, restraining the abnormality in proteins to certain organs such as the liver and kidneys. The research team said the strategy will provide a powerful tool for systematic in vivo study of cellular proteins in the most commonly used mammalian model organisms for human physiology and disease. Professor Park said, “This method can be easily extended to generate a wide range of custom-made transgenic mouse strains for further investigating diverse proteins of interest.” He added, “This method can be further extended to generate a wide range of custom-made transgenic mouse strains, opening a new paradigm for investigating anti-cancer and cerebral disease treatments.
This work was supported by grants from KAIST Systems Healthcare and the Medicinal Bioconvergence Research Center and the Intelligent Synthetic Biology Center of the Global Frontier Project funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning and the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.
(Figure:Temporal and spatial control of in vivo protein acetylation)
(a) Temporal expression of acetylated GFPuv in the AcK-GFPamber mouse. The expression of GFPuv in skeletal muscle, liver, and lung tissues was detected only in the AcK-injected mouse. Scale bar, 200 µm. (b) Western blotting of anti-FLAG-immunoprecipitated proteins from tissues of the AcK-GFPamber mouse. Acetylated GFPuv was produced after AcK injection. (c) Spatial expression of acetylated GFPuv in the AcK-GFPamber mouse. Acetylated GFPuv was observed only in skeletal muscle when AcK was directly delivered to the tissues. Sacle bar, 200 µm.
2017.03.27 View 11189