EC
-
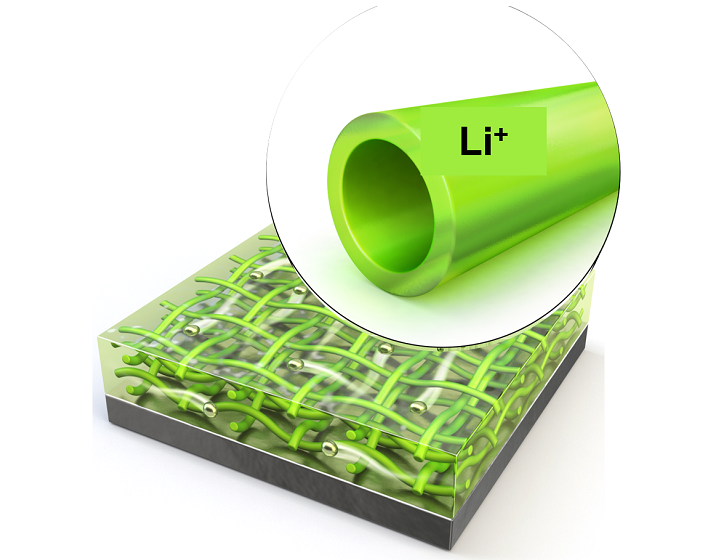 KAIST Extends Lithium Metal Battery Lifespan by 750% Using Water
Lithium metal, a next-generation anode material, has been highlighted for overcoming the performance limitations of commercial batteries. However, issues inherent to lithium metal have caused shortened battery lifespans and increased fire risks. KAIST researchers have achieved a world-class breakthrough by extending the lifespan of lithium metal anodes by approximately 750% only using water.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 2nd of December that Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Jiyoung Lee from Ajou University, successfully stabilized lithium growth and significantly enhanced the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries using eco-friendly hollow nanofibers as protective layers.
Conventional protective layer technologies, which involve applying a surface coating onto lithium metal in order to create an artificial interface with the electrolyte, have relied on toxic processes and expensive materials, with limited improvements in the lifespan of lithium metal anodes.
< Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of the newly developed protective membrane by eco-friendly electrospinning process using water >
To address these limitations, Professor Kim’s team proposed a hollow nanofiber protective layer capable of controlling lithium-ion growth through both physical and chemical means. This protective layer was manufactured through an environmentally friendly electrospinning process* using guar gum** extracted from plants as the primary material and utilizing water as the sole solvent.
*Electrospinning process: A method where polymer solutions are subjected to an electric field, producing continuous fibers with diameters ranging from tens of nanometers to several micrometers.
**Guar gum: A natural polymer extracted from guar beans, composed mainly of monosaccharides. Its oxidized functional groups regulate interactions with lithium ions.
< Figure 2. Physical and chemical control of Lithium dendrite by the newly developed protective membrane >
The nanofiber protective layer effectively controlled reversible chemical reactions between the electrolyte and lithium ions. The hollow spaces within the fibers suppressed the random accumulation of lithium ions on the metal surface, stabilizing the interface between the lithium metal surface and the electrolyte.
< Figure 3. Performance of Lithium metal battery full cells with the newly developed protective membrane >
As a result, the lithium metal anodes with this protective layer demonstrated approximately a 750% increase in lifespan compared to conventional lithium metal anodes. The battery retained 93.3% of its capacity even after 300 charge-discharge cycles, achieving world-class performance.
The researchers also verified that this natural protective layer decomposes entirely within about a month in soil, proving its eco-friendly nature throughout the manufacturing and disposal process.
< Figure 4. Excellent decomposition rate of the newly developed protective membrane >
Professor Il-Doo Kim explained, “By leveraging both physical and chemical protective functions, we were able to guide reversible reactions between lithium metal and the electrolyte more effectively and suppress dendrite growth, resulting in lithium metal anodes with unprecedented lifespan characteristics.”
He added, “As the environmental burden caused by battery production and disposal becomes a pressing issue due to surging battery demand, this water-based manufacturing method with biodegradable properties will significantly contribute to the commercialization of next-generation eco-friendly batteries.”
This study was led by Dr. Jiyoung Lee (now a professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Ajou University) and Dr. Hyunsub Song (currently at Samsung Electronics), both graduates of KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering. The findings were published as a front cover article in Advanced Materials, Volume 36, Issue 47, on November 21.
(Paper title: “Overcoming Chemical and Mechanical Instabilities in Lithium Metal Anodes with Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Artificial SEI Layer”)
The research was supported by the KAIST-LG Energy Solution Frontier Research Lab (FRL), the Alchemist Project funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and the Top-Tier Research Support Program from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2024.12.12 View 5966
KAIST Extends Lithium Metal Battery Lifespan by 750% Using Water
Lithium metal, a next-generation anode material, has been highlighted for overcoming the performance limitations of commercial batteries. However, issues inherent to lithium metal have caused shortened battery lifespans and increased fire risks. KAIST researchers have achieved a world-class breakthrough by extending the lifespan of lithium metal anodes by approximately 750% only using water.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 2nd of December that Professor Il-Doo Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Professor Jiyoung Lee from Ajou University, successfully stabilized lithium growth and significantly enhanced the lifespan of next-generation lithium metal batteries using eco-friendly hollow nanofibers as protective layers.
Conventional protective layer technologies, which involve applying a surface coating onto lithium metal in order to create an artificial interface with the electrolyte, have relied on toxic processes and expensive materials, with limited improvements in the lifespan of lithium metal anodes.
< Figure 1. Schematic illustration of the fabrication process of the newly developed protective membrane by eco-friendly electrospinning process using water >
To address these limitations, Professor Kim’s team proposed a hollow nanofiber protective layer capable of controlling lithium-ion growth through both physical and chemical means. This protective layer was manufactured through an environmentally friendly electrospinning process* using guar gum** extracted from plants as the primary material and utilizing water as the sole solvent.
*Electrospinning process: A method where polymer solutions are subjected to an electric field, producing continuous fibers with diameters ranging from tens of nanometers to several micrometers.
**Guar gum: A natural polymer extracted from guar beans, composed mainly of monosaccharides. Its oxidized functional groups regulate interactions with lithium ions.
< Figure 2. Physical and chemical control of Lithium dendrite by the newly developed protective membrane >
The nanofiber protective layer effectively controlled reversible chemical reactions between the electrolyte and lithium ions. The hollow spaces within the fibers suppressed the random accumulation of lithium ions on the metal surface, stabilizing the interface between the lithium metal surface and the electrolyte.
< Figure 3. Performance of Lithium metal battery full cells with the newly developed protective membrane >
As a result, the lithium metal anodes with this protective layer demonstrated approximately a 750% increase in lifespan compared to conventional lithium metal anodes. The battery retained 93.3% of its capacity even after 300 charge-discharge cycles, achieving world-class performance.
The researchers also verified that this natural protective layer decomposes entirely within about a month in soil, proving its eco-friendly nature throughout the manufacturing and disposal process.
< Figure 4. Excellent decomposition rate of the newly developed protective membrane >
Professor Il-Doo Kim explained, “By leveraging both physical and chemical protective functions, we were able to guide reversible reactions between lithium metal and the electrolyte more effectively and suppress dendrite growth, resulting in lithium metal anodes with unprecedented lifespan characteristics.”
He added, “As the environmental burden caused by battery production and disposal becomes a pressing issue due to surging battery demand, this water-based manufacturing method with biodegradable properties will significantly contribute to the commercialization of next-generation eco-friendly batteries.”
This study was led by Dr. Jiyoung Lee (now a professor in the Department of Chemical Engineering at Ajou University) and Dr. Hyunsub Song (currently at Samsung Electronics), both graduates of KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering. The findings were published as a front cover article in Advanced Materials, Volume 36, Issue 47, on November 21.
(Paper title: “Overcoming Chemical and Mechanical Instabilities in Lithium Metal Anodes with Sustainable and Eco-Friendly Artificial SEI Layer”)
The research was supported by the KAIST-LG Energy Solution Frontier Research Lab (FRL), the Alchemist Project funded by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and the Top-Tier Research Support Program from the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2024.12.12 View 5966 -
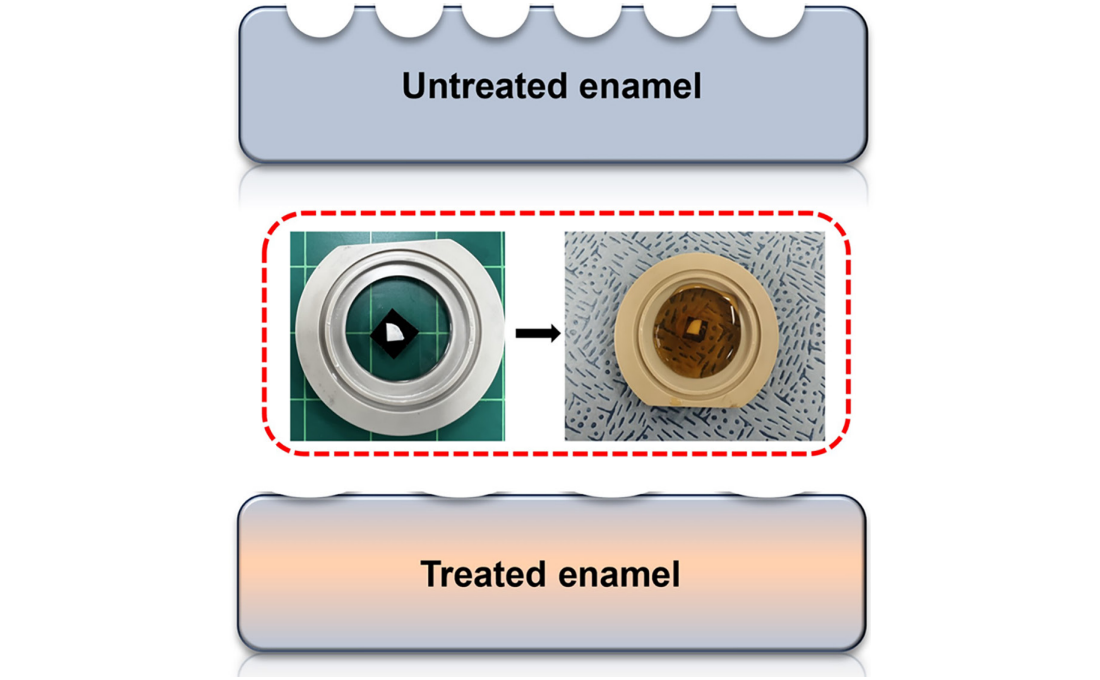 KAIST Scientifically Identifies a Method to Prevent Dental Erosion from Carbonated Drinks
A Korean research team, which had previously visualized and scientifically proven the harmful effects of carbonated drinks like cola on dental health using nanotechnology, has now identified a mechanism for an effective method to prevent tooth damage caused by these beverages.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of December that a team led by Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Seoul National University's School of Dentistry (Departments of Pediatric Dentistry and Oral Microbiology) and Professor Hye Ryung Byon’s research team from the Department of Chemistry, has revealed through nanotechnology that silver diamine fluoride (SDF)* forms a fluoride-containing protective layer on the tooth surface, effectively inhibiting cola-induced erosion.
*SDF (Silver Diamine Fluoride): A dental agent primarily used for the treatment and prevention of tooth decay. SDF strengthens carious lesions, suppresses bacterial growth, and halts the progression of cavities.
The team analyzed the surface morphology and mechanical properties of tooth enamel on a nanoscale using atomic force microscopy (AFM). They also examined the chemical properties of the nano-film formed by SDF treatment using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)* and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)*.
*XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy): A powerful surface analysis technique used to investigate the chemical composition and electronic structure of materials.
*FTIR (Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy): An analytical method that identifies the molecular structure and composition of materials by analyzing how they absorb or transmit infrared light.
The findings showed significant differences in surface roughness and elastic modulus between teeth exposed to cola with and without SDF treatment. Teeth treated with SDF exhibited minimal changes in surface roughness due to erosion (from 64 nm to 70 nm) and maintained a high elastic modulus (from 215 GPa to 205 GPa).
This was attributed to the formation of a fluoroapatite* layer by SDF, which acted as a protective shield.
*Fluoroapatite: A phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Ca₅(PO₄)₃F (calcium fluoro-phosphate). It can occur naturally or be synthesized biologically/artificially and plays a crucial role in strengthening teeth and bones.
< Figure 1. Schematic of the workflow. Surface morphology and mechanical properties of untreated and treated silver diamine fluoride (SDF) treated enamel exposed to cola were analyzed over time using atomic force microscopy (AFM). >
Professor Young J. Kim from Seoul National University's Department of Pediatric Dentistry noted, "This technology could be applied to prevent dental erosion and strengthen teeth for both children and adults. It is a cost-effective and accessible dental treatment."
< Figure 2. Changes in surface roughness and elastic modulus according to time of exposure to cola for SDF untreated and treated teeth. After 1 hour, the surface roughness of the SDF untreated teeth rapidly became rougher from 83 nm to 287 nm and the elastic modulus weakened from 125 GPa to 13 GPa, whereas the surface roughness of the SDF treated teeth changed only slightly from 64 nm to 70 nm and the elastic modulus barely changed from 215 GPa to 205 GPa, maintaining a similar state to the initial state. >
Professor Seungbum Hong emphasized, "Dental health significantly impacts quality of life. This research offers an effective non-invasive method to prevent early dental erosion, moving beyond traditional surgical treatments. By simply applying SDF, dental erosion can be prevented and enamel strengthened, potentially reducing pain and costs associated with treatment."
This study, led by the first author Aditi Saha, a PhD student in KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering, was published in the international journal Biomaterials Research on November 7 under the title "Nanoscale Study on Noninvasive Prevention of Dental Erosion of Enamel by Silver Diamine Fluoride". The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.12.11 View 4371
KAIST Scientifically Identifies a Method to Prevent Dental Erosion from Carbonated Drinks
A Korean research team, which had previously visualized and scientifically proven the harmful effects of carbonated drinks like cola on dental health using nanotechnology, has now identified a mechanism for an effective method to prevent tooth damage caused by these beverages.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th of December that a team led by Professor Seungbum Hong from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, in collaboration with Seoul National University's School of Dentistry (Departments of Pediatric Dentistry and Oral Microbiology) and Professor Hye Ryung Byon’s research team from the Department of Chemistry, has revealed through nanotechnology that silver diamine fluoride (SDF)* forms a fluoride-containing protective layer on the tooth surface, effectively inhibiting cola-induced erosion.
*SDF (Silver Diamine Fluoride): A dental agent primarily used for the treatment and prevention of tooth decay. SDF strengthens carious lesions, suppresses bacterial growth, and halts the progression of cavities.
The team analyzed the surface morphology and mechanical properties of tooth enamel on a nanoscale using atomic force microscopy (AFM). They also examined the chemical properties of the nano-film formed by SDF treatment using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS)* and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR)*.
*XPS (X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy): A powerful surface analysis technique used to investigate the chemical composition and electronic structure of materials.
*FTIR (Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy): An analytical method that identifies the molecular structure and composition of materials by analyzing how they absorb or transmit infrared light.
The findings showed significant differences in surface roughness and elastic modulus between teeth exposed to cola with and without SDF treatment. Teeth treated with SDF exhibited minimal changes in surface roughness due to erosion (from 64 nm to 70 nm) and maintained a high elastic modulus (from 215 GPa to 205 GPa).
This was attributed to the formation of a fluoroapatite* layer by SDF, which acted as a protective shield.
*Fluoroapatite: A phosphate mineral with the chemical formula Ca₅(PO₄)₃F (calcium fluoro-phosphate). It can occur naturally or be synthesized biologically/artificially and plays a crucial role in strengthening teeth and bones.
< Figure 1. Schematic of the workflow. Surface morphology and mechanical properties of untreated and treated silver diamine fluoride (SDF) treated enamel exposed to cola were analyzed over time using atomic force microscopy (AFM). >
Professor Young J. Kim from Seoul National University's Department of Pediatric Dentistry noted, "This technology could be applied to prevent dental erosion and strengthen teeth for both children and adults. It is a cost-effective and accessible dental treatment."
< Figure 2. Changes in surface roughness and elastic modulus according to time of exposure to cola for SDF untreated and treated teeth. After 1 hour, the surface roughness of the SDF untreated teeth rapidly became rougher from 83 nm to 287 nm and the elastic modulus weakened from 125 GPa to 13 GPa, whereas the surface roughness of the SDF treated teeth changed only slightly from 64 nm to 70 nm and the elastic modulus barely changed from 215 GPa to 205 GPa, maintaining a similar state to the initial state. >
Professor Seungbum Hong emphasized, "Dental health significantly impacts quality of life. This research offers an effective non-invasive method to prevent early dental erosion, moving beyond traditional surgical treatments. By simply applying SDF, dental erosion can be prevented and enamel strengthened, potentially reducing pain and costs associated with treatment."
This study, led by the first author Aditi Saha, a PhD student in KAIST’s Department of Materials Science and Engineering, was published in the international journal Biomaterials Research on November 7 under the title "Nanoscale Study on Noninvasive Prevention of Dental Erosion of Enamel by Silver Diamine Fluoride". The research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.12.11 View 4371 -
 KAIST Awarded Presidential Commendation for Contributions in Software Industry
- At the “25th Software Industry Day” celebration held in the afternoon on Monday, December 2nd, 2024 at Yangjae L Tower in Seoul
- KAIST was awarded the “Presidential Commendation” for its contributions for the advancement of the Software Industry in the Group Category
- Korea’s first AI master’s and doctoral degree program opened at KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI
- Focus on training non-major developers through SW Officer Training Academy "Jungle", Machine Learning Engineer Bootcamp, etc., talents who can integrate development and collaboration, and advanced talents in the latest AI technologies.
- Professor Minjoon Seo of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI received Prime Minister’s Commendation for his contributions for the advancement of the software industry.
< Photo 1. Professor Kyung-soo Kim, the Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget (second from the left) and the Manager of Planning Team, Mr. Sunghoon Jung, stand at the stage after receiving the Presidential Commendation as KAIST was selected as one of the groups that contributed to the advancement of the software industry at the "25th Software Industry Day" celebration. >
“KAIST has been leading the way in achieving the grand goal of fostering 1 million AI talents in Korea by services that pan from providing various educational opportunities, from developing the capabilities of experts with no computer science specialty to fostering advanced professionals. I would like to thank all members of KAIST community who worked hard to achieve the great feat of receiving the Presidential Commendations.” (KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on December 3rd that it was selected as a group that contributed to the advancement of the software industry at the “2024 Software Industry Day” celebration held at the Yangjae El Tower in Seoul on the 2nd of December and received a presidential commendation.
The “Software Industry Day”, hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the National IT Industry Promotion Agency and the Korea Software Industry Association, is an event designed to promote the status of software industry workers in Korea and to honor their achievements.
Every year, those who have made significant contributions to policy development, human resource development, and export growth for industry revitalization are selected and awarded the ‘Software Industry Development Contribution Award.’
KAIST was recognized for its contribution to developing a demand-based, industrial field-centric curriculum and fostering non-major developers and convergence talents with the goal of expanding software value and fostering excellent human resources.
< Photo 2. Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget Kyung-soo Kim receiving the commendation as the representative of KAIST >
Specifically, it first opened the SW Officer Training Academy "Jungle" to foster convergent program developers equipped with the abilities to handle both the computer coding and human interactions for collaborations. This is a non-degree program that provides intensive study and assignments for 5 months for graduates and intellectuals without prior knowledge of computer science.
KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI opened and operated Korea’s first master's and doctoral degree program in the field of artificial intelligence. In addition, it planned a “Machine Learning Engineers’ Boot Camp” and conducted lectures and practical training for a total of 16 weeks on the latest AI technologies such as deep learning basics and large language models. It aims to strengthen the practical capabilities of start-up companies while lowering the threshold for companies to introduce AI technology.
Also, KAIST was selected to participate in the 1st and 2nd stages of the Software-centered University Project and has been taking part in the project since 2016. Through this, it was highly evaluated for promoting curriculum based on latest technology, an autonomous system where students directly select integrated education, and expansion of internships.
< Photo 3. Professor Minjoon Seo of Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI, who received the Prime Minister's Commendation for his contribution to the advancement of the software industry on the same day >
At the awards ceremony that day, Professor Minjoon Seo of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI also received the Prime Minister's Commendation for his contribution to the advancement of the software industry. Professor Seo was recognized for his leading research achievements in the fields of AI and natural language processing by publishing 28 papers in top international AI conferences over the past four years.
At the same time, he was noted for his contributions to enhancing the originality and innovation of language model research, such as △knowledge encoding, △knowledge access and utilization, and △high-dimensional inference performance, and for demonstrating leadership in the international academic community.
President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST stated, “Our university will continue to do its best to foster software talents with global competitiveness through continuous development of cutting-edge curriculum and innovative degree systems.”
2024.12.03 View 5434
KAIST Awarded Presidential Commendation for Contributions in Software Industry
- At the “25th Software Industry Day” celebration held in the afternoon on Monday, December 2nd, 2024 at Yangjae L Tower in Seoul
- KAIST was awarded the “Presidential Commendation” for its contributions for the advancement of the Software Industry in the Group Category
- Korea’s first AI master’s and doctoral degree program opened at KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI
- Focus on training non-major developers through SW Officer Training Academy "Jungle", Machine Learning Engineer Bootcamp, etc., talents who can integrate development and collaboration, and advanced talents in the latest AI technologies.
- Professor Minjoon Seo of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI received Prime Minister’s Commendation for his contributions for the advancement of the software industry.
< Photo 1. Professor Kyung-soo Kim, the Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget (second from the left) and the Manager of Planning Team, Mr. Sunghoon Jung, stand at the stage after receiving the Presidential Commendation as KAIST was selected as one of the groups that contributed to the advancement of the software industry at the "25th Software Industry Day" celebration. >
“KAIST has been leading the way in achieving the grand goal of fostering 1 million AI talents in Korea by services that pan from providing various educational opportunities, from developing the capabilities of experts with no computer science specialty to fostering advanced professionals. I would like to thank all members of KAIST community who worked hard to achieve the great feat of receiving the Presidential Commendations.” (KAIST President Kwang Hyung Lee)
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on December 3rd that it was selected as a group that contributed to the advancement of the software industry at the “2024 Software Industry Day” celebration held at the Yangjae El Tower in Seoul on the 2nd of December and received a presidential commendation.
The “Software Industry Day”, hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the National IT Industry Promotion Agency and the Korea Software Industry Association, is an event designed to promote the status of software industry workers in Korea and to honor their achievements.
Every year, those who have made significant contributions to policy development, human resource development, and export growth for industry revitalization are selected and awarded the ‘Software Industry Development Contribution Award.’
KAIST was recognized for its contribution to developing a demand-based, industrial field-centric curriculum and fostering non-major developers and convergence talents with the goal of expanding software value and fostering excellent human resources.
< Photo 2. Senior Vice President for Planning and Budget Kyung-soo Kim receiving the commendation as the representative of KAIST >
Specifically, it first opened the SW Officer Training Academy "Jungle" to foster convergent program developers equipped with the abilities to handle both the computer coding and human interactions for collaborations. This is a non-degree program that provides intensive study and assignments for 5 months for graduates and intellectuals without prior knowledge of computer science.
KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI opened and operated Korea’s first master's and doctoral degree program in the field of artificial intelligence. In addition, it planned a “Machine Learning Engineers’ Boot Camp” and conducted lectures and practical training for a total of 16 weeks on the latest AI technologies such as deep learning basics and large language models. It aims to strengthen the practical capabilities of start-up companies while lowering the threshold for companies to introduce AI technology.
Also, KAIST was selected to participate in the 1st and 2nd stages of the Software-centered University Project and has been taking part in the project since 2016. Through this, it was highly evaluated for promoting curriculum based on latest technology, an autonomous system where students directly select integrated education, and expansion of internships.
< Photo 3. Professor Minjoon Seo of Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI, who received the Prime Minister's Commendation for his contribution to the advancement of the software industry on the same day >
At the awards ceremony that day, Professor Minjoon Seo of KAIST Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI also received the Prime Minister's Commendation for his contribution to the advancement of the software industry. Professor Seo was recognized for his leading research achievements in the fields of AI and natural language processing by publishing 28 papers in top international AI conferences over the past four years.
At the same time, he was noted for his contributions to enhancing the originality and innovation of language model research, such as △knowledge encoding, △knowledge access and utilization, and △high-dimensional inference performance, and for demonstrating leadership in the international academic community.
President Kwang Hyung Lee of KAIST stated, “Our university will continue to do its best to foster software talents with global competitiveness through continuous development of cutting-edge curriculum and innovative degree systems.”
2024.12.03 View 5434 -
 KAIST Develops a Multifunctional Structural Battery Capable of Energy Storage and Load Support
Structural batteries are used in industries such as eco-friendly, energy-based automobiles, mobility, and aerospace, and they must simultaneously meet the requirements of high energy density for energy storage and high load-bearing capacity. Conventional structural battery technology has struggled to enhance both functions concurrently. However, KAIST researchers have succeeded in developing foundational technology to address this issue.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim, PhD candidates Sangyoon Bae and Su Hyun Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering >
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim and Master's Graduate Mohamad A. Raja of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th of November that Professor Seong Su Kim's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a thin, uniform, high-density, multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite battery* capable of supporting loads, and that is free from fire risks while offering high energy density.
*Multifunctional structural batteries: Refers to the ability of each material in the composite to simultaneously serve as a load-bearing structure and an energy storage element.
Early structural batteries involved embedding commercial lithium-ion batteries into layered composite materials. These batteries suffered from low integration of their mechanical and electrochemical properties, leading to challenges in material processing, assembly, and design optimization, making commercialization difficult.
To overcome these challenges, Professor Kim's team explored the concept of "energy-storing composite materials," focusing on interface and curing properties, which are critical in traditional composite design. This led to the development of high-density multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite batteries that maximize multifunctionality.
The team analyzed the curing mechanisms of epoxy resin, known for its strong mechanical properties, combined with ionic liquid and carbonate electrolyte-based solid polymer electrolytes. By controlling temperature and pressure, they were able to optimize the curing process.
The newly developed structural battery was manufactured through vacuum compression molding, increasing the volume fraction of carbon fibers—serving as both electrodes and current collectors—by over 160% compared to previous carbon-fiber-based batteries.
This greatly increased the contact area between electrodes and electrolytes, resulting in a high-density structural battery with improved electrochemical performance. Furthermore, the team effectively controlled air bubbles within the structural battery during the curing process, simultaneously enhancing the battery's mechanical properties.
Professor Seong Su Kim, the lead researcher, explained, “We proposed a framework for designing solid polymer electrolytes, a core material for high-stiffness, ultra-thin structural batteries, from both material and structural perspectives. These material-based structural batteries can serve as internal components in cars, drones, airplanes, and robots, significantly extending their operating time with a single charge. This represents a foundational technology for next-generation multifunctional energy storage applications.”
< Figure 2. Supplementary cover of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces >
Mohamad A. Raja, a master’s graduate of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, participated as the first author of this research, which was published in the prestigious journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on September 10. The paper was recognized for its excellence and selected as a supplementary cover article. (Paper title: “Thin, Uniform, and Highly Packed Multifunctional Structural Carbon Fiber Composite Battery Lamina Informed by Solid Polymer Electrolyte Cure Kinetics.” https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08698)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Development Program.
2024.11.27 View 5097
KAIST Develops a Multifunctional Structural Battery Capable of Energy Storage and Load Support
Structural batteries are used in industries such as eco-friendly, energy-based automobiles, mobility, and aerospace, and they must simultaneously meet the requirements of high energy density for energy storage and high load-bearing capacity. Conventional structural battery technology has struggled to enhance both functions concurrently. However, KAIST researchers have succeeded in developing foundational technology to address this issue.
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim, PhD candidates Sangyoon Bae and Su Hyun Lim of the Department of Mechanical Engineering >
< Photo 2. (From left) Professor Seong Su Kim and Master's Graduate Mohamad A. Raja of KAIST Department of Mechanical Engineering >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 19th of November that Professor Seong Su Kim's team from the Department of Mechanical Engineering has developed a thin, uniform, high-density, multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite battery* capable of supporting loads, and that is free from fire risks while offering high energy density.
*Multifunctional structural batteries: Refers to the ability of each material in the composite to simultaneously serve as a load-bearing structure and an energy storage element.
Early structural batteries involved embedding commercial lithium-ion batteries into layered composite materials. These batteries suffered from low integration of their mechanical and electrochemical properties, leading to challenges in material processing, assembly, and design optimization, making commercialization difficult.
To overcome these challenges, Professor Kim's team explored the concept of "energy-storing composite materials," focusing on interface and curing properties, which are critical in traditional composite design. This led to the development of high-density multifunctional structural carbon fiber composite batteries that maximize multifunctionality.
The team analyzed the curing mechanisms of epoxy resin, known for its strong mechanical properties, combined with ionic liquid and carbonate electrolyte-based solid polymer electrolytes. By controlling temperature and pressure, they were able to optimize the curing process.
The newly developed structural battery was manufactured through vacuum compression molding, increasing the volume fraction of carbon fibers—serving as both electrodes and current collectors—by over 160% compared to previous carbon-fiber-based batteries.
This greatly increased the contact area between electrodes and electrolytes, resulting in a high-density structural battery with improved electrochemical performance. Furthermore, the team effectively controlled air bubbles within the structural battery during the curing process, simultaneously enhancing the battery's mechanical properties.
Professor Seong Su Kim, the lead researcher, explained, “We proposed a framework for designing solid polymer electrolytes, a core material for high-stiffness, ultra-thin structural batteries, from both material and structural perspectives. These material-based structural batteries can serve as internal components in cars, drones, airplanes, and robots, significantly extending their operating time with a single charge. This represents a foundational technology for next-generation multifunctional energy storage applications.”
< Figure 2. Supplementary cover of ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces >
Mohamad A. Raja, a master’s graduate of KAIST’s Department of Mechanical Engineering, participated as the first author of this research, which was published in the prestigious journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces on September 10. The paper was recognized for its excellence and selected as a supplementary cover article. (Paper title: “Thin, Uniform, and Highly Packed Multifunctional Structural Carbon Fiber Composite Battery Lamina Informed by Solid Polymer Electrolyte Cure Kinetics.” https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.4c08698)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Mid-Career Researcher Program and the National Semiconductor Research Laboratory Development Program.
2024.11.27 View 5097 -
 KAIST Unveils New Possibilities for Treating Intractable Brain Tumors
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Heung Kyu Lee, KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, and Dr. Keun Bon Ku >
Immunotherapy, which enhances the immune system's T cell response to eliminate cancer cells, has emerged as a key approach in cancer treatment. However, in the case of glioblastoma, an aggressive and treatment-resistant brain tumor, numerous clinical trials have failed to confirm their efficacy. Korean researchers have recently analyzed the mechanisms that cause T cell exhaustion, which is characterized by a loss of function or a weakened response following prolonged exposure to antigens in such intractable cancers, identifying key control factors in T cell activation and clarifying the mechanisms that enhance therapeutic effectiveness.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th of November that Professor Heung Kyu Lee’s team from the Department of Biological Sciences, in collaboration with the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (represented by President Young Kuk Lee), has confirmed improved survival rates in a glioblastoma mouse model. By removing the inhibitory Fc gamma receptor (FcγRIIB), the research team was able to restore the responsiveness of cytotoxic T cells to immune checkpoint inhibitors, leading to enhanced anticancer activity.
The research team examined the effect of FcγRIIB, an inhibitory receptor recently found in cytotoxic T cells, on tumor-infiltrating T cells and the therapeutic effectiveness of the anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor.
< Figure 1. Study results on improved survival rate due to increased antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 treatment in inhibitory Fc gamma receptor(Fcgr2b) ablation mice with murine glioblastoma. >
Their findings showed that deleting FcγRIIB induced the increase of tumor antigen-specific memory T cells, which helps to suppress exhaustion, enhances stem-like qualities, and reactivates T cell-mediated antitumor immunity, particularly in response to anti-PD-1 treatment. Furthermore, FcγRIIB deletion led to an increase in antigen-specific memory T cells that maintained continuous infiltration into the tumor tissue.
This study presents a new therapeutic target for tumors unresponsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors and demonstrates that combining FcγRIIB inhibition with anti-PD-1 treatment can produce synergistic effects, potentially improving therapeutic outcomes for tumors like glioblastoma, which typically show resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy.
< Figure 2. Overview of the study on the enhanced response to anti-PD-1 therapy for glioblastoma brain tumors upon deletion of the inhibitory Fc gamma receptor (FcγRIIB) in tumor microenvironment. When the inhibitory Fc gamma receptor (FcγRIIB) of cytotoxic T cells is deleted, an increase in tumor-specific memory T cells (Ttsms) was observed. In addition, this T cell subset is identified as originating from the tumor-draining lymph nodes(TdLNs) and leads to persistent infiltration into the tumor tissue. Anti-PD-1 therapy leads to an increased anti-tumor immune response via Ttsms, which is confirmed by increased tumor cell toxicity and increased cell division and decreased cell de-migration indices. Ultimately, the increased cytotoxic T cell immune response leads to an increase in the survival rate of glioblastoma. >
Professor Heung Kyu Lee explained, "This study offers a way to overcome clinical failures in treating brain tumors with immune checkpoint therapy and opens possibilities for broader applications to other intractable cancers. It also highlights the potential of utilizing cytotoxic T cells for tumor cell therapy."
The study, led by Dr. Keun Bon Ku of KAIST (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology's Center for Infectious Disease Diagnosis and Prevention), along with Chae Won Kim, Yumin Kim, Byeong Hoon Kang, Jeongwoo La, In Kang, Won Hyung Park, Stephen Ahn, and Sung Ki Lee, was published online on October 26 in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, an international journal in tumor immunology and therapy from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer. (Paper title: “Inhibitory Fcγ receptor deletion enhances CD8 T cell stemness increasing anti-PD-1 therapy responsiveness against glioblastoma,” http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2024-009449).
This research received support from the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program, and the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation.
2024.11.15 View 4753
KAIST Unveils New Possibilities for Treating Intractable Brain Tumors
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Heung Kyu Lee, KAIST Department of Biological Sciences, and Dr. Keun Bon Ku >
Immunotherapy, which enhances the immune system's T cell response to eliminate cancer cells, has emerged as a key approach in cancer treatment. However, in the case of glioblastoma, an aggressive and treatment-resistant brain tumor, numerous clinical trials have failed to confirm their efficacy. Korean researchers have recently analyzed the mechanisms that cause T cell exhaustion, which is characterized by a loss of function or a weakened response following prolonged exposure to antigens in such intractable cancers, identifying key control factors in T cell activation and clarifying the mechanisms that enhance therapeutic effectiveness.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 6th of November that Professor Heung Kyu Lee’s team from the Department of Biological Sciences, in collaboration with the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (represented by President Young Kuk Lee), has confirmed improved survival rates in a glioblastoma mouse model. By removing the inhibitory Fc gamma receptor (FcγRIIB), the research team was able to restore the responsiveness of cytotoxic T cells to immune checkpoint inhibitors, leading to enhanced anticancer activity.
The research team examined the effect of FcγRIIB, an inhibitory receptor recently found in cytotoxic T cells, on tumor-infiltrating T cells and the therapeutic effectiveness of the anti-PD-1 immune checkpoint inhibitor.
< Figure 1. Study results on improved survival rate due to increased antitumor activity of anti-PD-1 treatment in inhibitory Fc gamma receptor(Fcgr2b) ablation mice with murine glioblastoma. >
Their findings showed that deleting FcγRIIB induced the increase of tumor antigen-specific memory T cells, which helps to suppress exhaustion, enhances stem-like qualities, and reactivates T cell-mediated antitumor immunity, particularly in response to anti-PD-1 treatment. Furthermore, FcγRIIB deletion led to an increase in antigen-specific memory T cells that maintained continuous infiltration into the tumor tissue.
This study presents a new therapeutic target for tumors unresponsive to immune checkpoint inhibitors and demonstrates that combining FcγRIIB inhibition with anti-PD-1 treatment can produce synergistic effects, potentially improving therapeutic outcomes for tumors like glioblastoma, which typically show resistance to anti-PD-1 therapy.
< Figure 2. Overview of the study on the enhanced response to anti-PD-1 therapy for glioblastoma brain tumors upon deletion of the inhibitory Fc gamma receptor (FcγRIIB) in tumor microenvironment. When the inhibitory Fc gamma receptor (FcγRIIB) of cytotoxic T cells is deleted, an increase in tumor-specific memory T cells (Ttsms) was observed. In addition, this T cell subset is identified as originating from the tumor-draining lymph nodes(TdLNs) and leads to persistent infiltration into the tumor tissue. Anti-PD-1 therapy leads to an increased anti-tumor immune response via Ttsms, which is confirmed by increased tumor cell toxicity and increased cell division and decreased cell de-migration indices. Ultimately, the increased cytotoxic T cell immune response leads to an increase in the survival rate of glioblastoma. >
Professor Heung Kyu Lee explained, "This study offers a way to overcome clinical failures in treating brain tumors with immune checkpoint therapy and opens possibilities for broader applications to other intractable cancers. It also highlights the potential of utilizing cytotoxic T cells for tumor cell therapy."
The study, led by Dr. Keun Bon Ku of KAIST (currently a senior researcher at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology's Center for Infectious Disease Diagnosis and Prevention), along with Chae Won Kim, Yumin Kim, Byeong Hoon Kang, Jeongwoo La, In Kang, Won Hyung Park, Stephen Ahn, and Sung Ki Lee, was published online on October 26 in the Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer, an international journal in tumor immunology and therapy from the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer. (Paper title: “Inhibitory Fcγ receptor deletion enhances CD8 T cell stemness increasing anti-PD-1 therapy responsiveness against glioblastoma,” http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/jitc-2024-009449).
This research received support from the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Bio & Medical Technology Development Program, and the Samsung Science & Technology Foundation.
2024.11.15 View 4753 -
 KAIST Professor Uichin Lee Receives Distinguished Paper Award from ACM
< Photo. Professor Uichin Lee (left) receiving the award >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of October that Professor Uichin Lee’s research team from the School of Computing received the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and International Symposium on Wearable Computing (Ubicomp / ISWC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in Melbourne, Australia on October 8.
The ACM Ubiquitous Computing Conference is the most prestigious international conference where leading universities and global companies from around the world present the latest research results on ubiquitous computing and wearable technologies in the field of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The main conference program is composed of invited papers published in the Proceedings of the ACM (PACM) on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), which covers the latest research in the field of ubiquitous and wearable computing.
The Distinguished Paper Award Selection Committee selected eight papers among 205 papers published in Vol. 7 of the ACM Proceedings (PACM IMWUT) that made outstanding and exemplary contributions to the research community. The committee consists of 16 prominent experts who are current and former members of the journal's editorial board which made the selection after a rigorous review of all papers for a period that stretched over a month.
< Figure 1. BeActive mobile app to promote physical activity to form active lifestyle habits >
The research that won the Distinguished Paper Award was conducted by Dr. Junyoung Park, a graduate of the KAIST Graduate School of Data Science, as the 1st author, and was titled “Understanding Disengagement in Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions”
Professor Uichin Lee’s research team explored user engagement of ‘Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions’ that actively provide interventions in opportune situations by utilizing sensor data collected from health management apps, based on the premise that these apps are aptly in use to ensure effectiveness.
< Figure 2. Traditional user-requested digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) delivery (Pull) vs. Automatic transmission (Push) for Just-in-Time (JIT) mobile DBCI using smartphone sensing technologies >
The research team conducted a systematic analysis of user disengagement or the decline in user engagement in digital behavior change interventions. They developed the BeActive system, an app that promotes physical activities designed to help forming active lifestyle habits, and systematically analyzed the effects of users’ self-control ability and boredom-proneness on compliance with behavioral interventions over time.
The results of an 8-week field trial revealed that even if just-in-time interventions are provided according to the user’s situation, it is impossible to avoid a decline in participation. However, for users with high self-control and low boredom tendency, the compliance with just-in-time interventions delivered through the app was significantly higher than that of users in other groups.
In particular, users with high boredom proneness easily got tired of the repeated push interventions, and their compliance with the app decreased more quickly than in other groups.
< Figure 3. Just-in-time Mobile Health Intervention: a demonstrative case of the BeActive system: When a user is identified to be sitting for more than 50 mins, an automatic push notification is sent to recommend a short active break to complete for reward points. >
Professor Uichin Lee explained, “As the first study on user engagement in digital therapeutics and wellness services utilizing mobile just-in-time health interventions, this research provides a foundation for exploring ways to empower user engagement.” He further added, “By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and comprehensive context-aware technologies, it will be possible to develop user-centered AI technologies that can significantly boost engagement."
< Figure 4. A conceptual illustration of user engagement in digital health apps. Engagement in digital health apps consists of (1) engagement in using digital health apps and (2) engagement in behavioral interventions provided by digital health apps, i.e., compliance with behavioral interventions. Repeated adherences to behavioral interventions recommended by digital health apps can help achieve the distal health goals. >
This study was conducted with the support of the 2021 Biomedical Technology Development Program and the 2022 Basic Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 5. A conceptual illustration of user disengagement and engagement of digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) apps. In general, user engagement of digital health intervention apps consists of two components: engagement in digital health apps and engagement in behavioral interventions recommended by such apps (known as behavioral compliance or intervention adherence). The distinctive stages of user can be divided into adoption, abandonment, and attrition. >
< Figure 6. Trends of changes in frequency of app usage and adherence to behavioral intervention over 8 weeks, ● SC: Self-Control Ability (High-SC: user group with high self-control, Low-SC: user group with low self-control) ● BD: Boredom-Proneness (High-BD: user group with high boredom-proneness, Low-BD: user group with low boredom-proneness). The app usage frequencies were declined over time, but the adherence rates of those participants with High-SC and Low-BD were significantly higher than other groups. >
2024.10.25 View 6979
KAIST Professor Uichin Lee Receives Distinguished Paper Award from ACM
< Photo. Professor Uichin Lee (left) receiving the award >
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 25th of October that Professor Uichin Lee’s research team from the School of Computing received the Distinguished Paper Award at the International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing and International Symposium on Wearable Computing (Ubicomp / ISWC) hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) in Melbourne, Australia on October 8.
The ACM Ubiquitous Computing Conference is the most prestigious international conference where leading universities and global companies from around the world present the latest research results on ubiquitous computing and wearable technologies in the field of human-computer interaction (HCI).
The main conference program is composed of invited papers published in the Proceedings of the ACM (PACM) on Interactive, Mobile, Wearable and Ubiquitous Technologies (IMWUT), which covers the latest research in the field of ubiquitous and wearable computing.
The Distinguished Paper Award Selection Committee selected eight papers among 205 papers published in Vol. 7 of the ACM Proceedings (PACM IMWUT) that made outstanding and exemplary contributions to the research community. The committee consists of 16 prominent experts who are current and former members of the journal's editorial board which made the selection after a rigorous review of all papers for a period that stretched over a month.
< Figure 1. BeActive mobile app to promote physical activity to form active lifestyle habits >
The research that won the Distinguished Paper Award was conducted by Dr. Junyoung Park, a graduate of the KAIST Graduate School of Data Science, as the 1st author, and was titled “Understanding Disengagement in Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions”
Professor Uichin Lee’s research team explored user engagement of ‘Just-in-Time Mobile Health Interventions’ that actively provide interventions in opportune situations by utilizing sensor data collected from health management apps, based on the premise that these apps are aptly in use to ensure effectiveness.
< Figure 2. Traditional user-requested digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) delivery (Pull) vs. Automatic transmission (Push) for Just-in-Time (JIT) mobile DBCI using smartphone sensing technologies >
The research team conducted a systematic analysis of user disengagement or the decline in user engagement in digital behavior change interventions. They developed the BeActive system, an app that promotes physical activities designed to help forming active lifestyle habits, and systematically analyzed the effects of users’ self-control ability and boredom-proneness on compliance with behavioral interventions over time.
The results of an 8-week field trial revealed that even if just-in-time interventions are provided according to the user’s situation, it is impossible to avoid a decline in participation. However, for users with high self-control and low boredom tendency, the compliance with just-in-time interventions delivered through the app was significantly higher than that of users in other groups.
In particular, users with high boredom proneness easily got tired of the repeated push interventions, and their compliance with the app decreased more quickly than in other groups.
< Figure 3. Just-in-time Mobile Health Intervention: a demonstrative case of the BeActive system: When a user is identified to be sitting for more than 50 mins, an automatic push notification is sent to recommend a short active break to complete for reward points. >
Professor Uichin Lee explained, “As the first study on user engagement in digital therapeutics and wellness services utilizing mobile just-in-time health interventions, this research provides a foundation for exploring ways to empower user engagement.” He further added, “By leveraging large language models (LLMs) and comprehensive context-aware technologies, it will be possible to develop user-centered AI technologies that can significantly boost engagement."
< Figure 4. A conceptual illustration of user engagement in digital health apps. Engagement in digital health apps consists of (1) engagement in using digital health apps and (2) engagement in behavioral interventions provided by digital health apps, i.e., compliance with behavioral interventions. Repeated adherences to behavioral interventions recommended by digital health apps can help achieve the distal health goals. >
This study was conducted with the support of the 2021 Biomedical Technology Development Program and the 2022 Basic Research and Development Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
< Figure 5. A conceptual illustration of user disengagement and engagement of digital behavior change intervention (DBCI) apps. In general, user engagement of digital health intervention apps consists of two components: engagement in digital health apps and engagement in behavioral interventions recommended by such apps (known as behavioral compliance or intervention adherence). The distinctive stages of user can be divided into adoption, abandonment, and attrition. >
< Figure 6. Trends of changes in frequency of app usage and adherence to behavioral intervention over 8 weeks, ● SC: Self-Control Ability (High-SC: user group with high self-control, Low-SC: user group with low self-control) ● BD: Boredom-Proneness (High-BD: user group with high boredom-proneness, Low-BD: user group with low boredom-proneness). The app usage frequencies were declined over time, but the adherence rates of those participants with High-SC and Low-BD were significantly higher than other groups. >
2024.10.25 View 6979 -
 KAIST Develops a Fire-risk Free Self-Powered Hydrogen Production System
KAIST researchers have developed a new hydrogen production system that overcomes the current limitations of green hydrogen production. By using a water-splitting system with an aqueous electrolyte, this system is expected to block fire risks and enable stable hydrogen production.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd of October that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a self-powered hydrogen production system based on a high-performance zinc-air battery*.
*Zinc-air battery: A primary battery that absorbs oxygen from the air and uses it as an oxidant. Its advantage is long life, but its low electromotive force is a disadvantage.
Hydrogen (H₂) is a key raw material for synthesizing high-value-added substances, and it is gaining attention as a clean fuel with an energy density (142 MJ/kg) more than three times higher than traditional fossil fuels (gasoline, diesel, etc.). However, most current hydrogen production methods impose environmental burden as they emit carbon dioxide (CO₂).
While green hydrogen can be produced by splitting water using renewable energy sources such as solar cells and wind power, these sources are subject to irregular power generation due to weather and temperature fluctuations, leading to low water-splitting efficiency.
To overcome this, air batteries that can emit sufficient voltage (greater than 1.23V) for water splitting have been gaining attention. However, achieving sufficient capacity requires expensive precious metal catalysts and the performance of the catalyst materials becomes significantly degraded during prolonged charge and discharge cycles. Thus, it is essential to develop catalysts that are effective for the water-splitting reactions (oxygen and hydrogen evolution) and materials that can stabilize the repeated charge and discharge reactions (oxygen reduction and evolution) in zinc-air battery electrodes.
In response, Professor Kang's research team proposed a method to synthesize a non-precious metal catalyst material (G-SHELL) that is effective for three different catalytic reactions (oxygen evolution, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen reduction) by growing nano-sized, metal-organic frameworks on graphene oxide.
The team incorporated the developed catalyst material into the air cathode of a zinc-air battery, confirming that it achieved approximately five times higher energy density (797Wh/kg), high power characteristics (275.8mW/cm²), and long-term stability even under repeated charge and discharge conditions compared to conventional batteries.
Additionally, the zinc-air battery, which operates using an aqueous electrolyte, is safe from fire risks. It is expected that this system can be applied as a next-generation energy storage device when linked with water electrolysis systems, offering an environmentally friendly method for hydrogen production.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of a trifunctional graphene-sandwiched heterojunction-embedded layered lattice (G-SHELL) structure. Schematic representation of a) synthesis procedures of G-SHELL from a zeolitic imidazole framework, b) hollow core-layered shell structure with trifunctional sites for oxygen reduction evolution (ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and c) heterojunctions, eterojunction-induced internal electric fields, and the corresponding band structure. >
Professor Kang explained, "By developing a catalyst material with high activity and durability for three different electrochemical catalytic reactions at low temperatures using simple methods, the self-powered hydrogen production system we implemented based on zinc-air batteries presents a new breakthrough to overcome the current limitations of green hydrogen production."
<Figure 2. Electrochemical performance of a ZAB-driven water-splitting cell with G-SHELL. Diagram of a self-driven water-splitting cell integrated by combining a ZAB with an alkaline water electrolyzer.>
PhD candidate Dong Won Kim and Jihoon Kim, a master's student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, were co-first authors of this research, which was published in the international journal Advanced Science on September 17th in the multidisciplinary field of materials science. (Paper Title: “Trifunctional Graphene-Sandwiched Heterojunction-Embedded Layered Lattice Electrocatalyst for High Performance in Zn-Air Battery-Driven Water Splitting”)
This research was supported by the Nano and Material Technology Development Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Future Technology Research Laboratory.
2024.10.22 View 5296
KAIST Develops a Fire-risk Free Self-Powered Hydrogen Production System
KAIST researchers have developed a new hydrogen production system that overcomes the current limitations of green hydrogen production. By using a water-splitting system with an aqueous electrolyte, this system is expected to block fire risks and enable stable hydrogen production.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 22nd of October that a research team led by Professor Jeung Ku Kang from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering developed a self-powered hydrogen production system based on a high-performance zinc-air battery*.
*Zinc-air battery: A primary battery that absorbs oxygen from the air and uses it as an oxidant. Its advantage is long life, but its low electromotive force is a disadvantage.
Hydrogen (H₂) is a key raw material for synthesizing high-value-added substances, and it is gaining attention as a clean fuel with an energy density (142 MJ/kg) more than three times higher than traditional fossil fuels (gasoline, diesel, etc.). However, most current hydrogen production methods impose environmental burden as they emit carbon dioxide (CO₂).
While green hydrogen can be produced by splitting water using renewable energy sources such as solar cells and wind power, these sources are subject to irregular power generation due to weather and temperature fluctuations, leading to low water-splitting efficiency.
To overcome this, air batteries that can emit sufficient voltage (greater than 1.23V) for water splitting have been gaining attention. However, achieving sufficient capacity requires expensive precious metal catalysts and the performance of the catalyst materials becomes significantly degraded during prolonged charge and discharge cycles. Thus, it is essential to develop catalysts that are effective for the water-splitting reactions (oxygen and hydrogen evolution) and materials that can stabilize the repeated charge and discharge reactions (oxygen reduction and evolution) in zinc-air battery electrodes.
In response, Professor Kang's research team proposed a method to synthesize a non-precious metal catalyst material (G-SHELL) that is effective for three different catalytic reactions (oxygen evolution, hydrogen evolution, and oxygen reduction) by growing nano-sized, metal-organic frameworks on graphene oxide.
The team incorporated the developed catalyst material into the air cathode of a zinc-air battery, confirming that it achieved approximately five times higher energy density (797Wh/kg), high power characteristics (275.8mW/cm²), and long-term stability even under repeated charge and discharge conditions compared to conventional batteries.
Additionally, the zinc-air battery, which operates using an aqueous electrolyte, is safe from fire risks. It is expected that this system can be applied as a next-generation energy storage device when linked with water electrolysis systems, offering an environmentally friendly method for hydrogen production.
< Figure 1. Illustrations of a trifunctional graphene-sandwiched heterojunction-embedded layered lattice (G-SHELL) structure. Schematic representation of a) synthesis procedures of G-SHELL from a zeolitic imidazole framework, b) hollow core-layered shell structure with trifunctional sites for oxygen reduction evolution (ORR), oxygen evolution reaction (OER), and hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), and c) heterojunctions, eterojunction-induced internal electric fields, and the corresponding band structure. >
Professor Kang explained, "By developing a catalyst material with high activity and durability for three different electrochemical catalytic reactions at low temperatures using simple methods, the self-powered hydrogen production system we implemented based on zinc-air batteries presents a new breakthrough to overcome the current limitations of green hydrogen production."
<Figure 2. Electrochemical performance of a ZAB-driven water-splitting cell with G-SHELL. Diagram of a self-driven water-splitting cell integrated by combining a ZAB with an alkaline water electrolyzer.>
PhD candidate Dong Won Kim and Jihoon Kim, a master's student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST, were co-first authors of this research, which was published in the international journal Advanced Science on September 17th in the multidisciplinary field of materials science. (Paper Title: “Trifunctional Graphene-Sandwiched Heterojunction-Embedded Layered Lattice Electrocatalyst for High Performance in Zn-Air Battery-Driven Water Splitting”)
This research was supported by the Nano and Material Technology Development Program of the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Future Technology Research Laboratory.
2024.10.22 View 5296 -
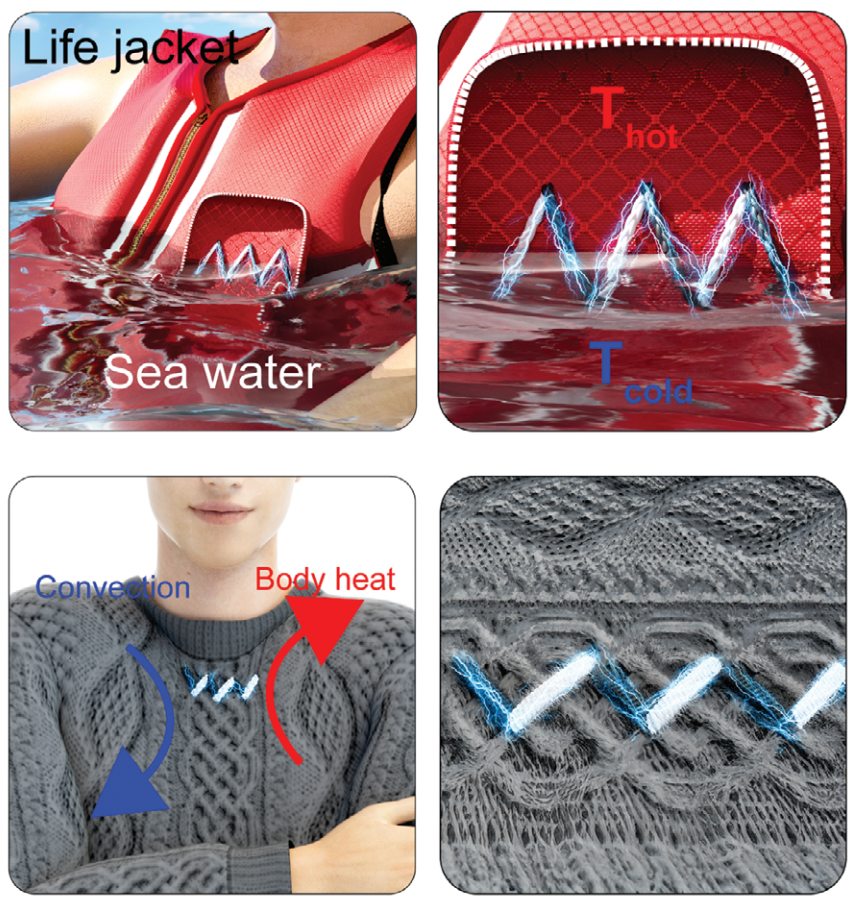 KAIST Develops Thread-like, Flexible Thermoelectric Materials Applicable in Extreme Environments
A team of Korean researchers developed a thermoelectric material that can be used in wearable devices, such as smart clothing, and while maintaining stable thermal energy performance even in extreme environments. It has dramatically resolved the dilemma of striking the balance between achieving good performance and the mechanical flexibility of thermoelectric materials, which has been a long-standing challenge in the field of thermoelectric materials, and has also proven the possibility of commercialization.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 21st that a joint research team of Professor Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Inkyu Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with the research teams of Professor Min-Wook Oh of Hanbat National University (President Yong Jun Oh) and Dr. Jun-Ho Jeong of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Seoghyun Ryu), have successfully developed ‘bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) thermoelectric fibers,’ an innovative energy harvesting solution for next-generation flexible electronic devices.
Thermoelectric materials are materials that generate voltage when there is a temperature difference and convert thermal energy into electrical energy. Currently, about 70% of energy being lost as wasted heat, so due attention is being given to research on these as sustainable energy materials that can recover and harvesting energy from this waste heat.
Most of the heat sources around us are curved, such as the human body, vehicle exhaust pipes, and cooling fins. Inorganic thermoelectric materials based on ceramic materials boast high thermoelectric performance, but they are fragile and difficult to produce in curved shapes. On the other hand, flexible thermoelectric materials using existing polymer binders can be applied to surfaces of various shapes, but their performance was limited due to the low electrical conductivity and high thermal resistance of the polymer.
Existing flexible thermoelectric materials contain polymer additives, but the inorganic thermoelectric material developed by the research team is not flexible, so they overcame these limitations by twisting nano ribbons instead of additives to produce a thread-shaped thermoelectric material. Inspired by the flexibility of inorganic nano ribbons, the research team used a nanomold-based electron beam deposition technique to continuously deposit nano ribbons and then twisted them into a thread shape to create bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) inorganic thermoelectric fibers.
These inorganic thermoelectric fibers have higher bending strength than existing thermoelectric materials, and showed almost no change in electrical properties even after repeated bending and tensile tests of more than 1,000 times. The thermoelectric device created by the research team generates electricity using temperature differences, and if clothes are made with fiber-type thermoelectric devices, electricity can be generated from body temperature to operate other electronic devices.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram and actual image of the all-inorganic flexible thermoelectric yarn made without polymer additives >
In fact, the possibility of commercialization was proven through a demonstration of collecting energy by embedding thermoelectric fibers in life jackets or clothing. In addition, it opened up the possibility of building a high-efficiency energy harvesting system that recycles waste heat by utilizing the temperature difference between the hot fluid inside a pipe and the cold air outside in industrial settings.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung said, "The inorganic flexible thermoelectric material developed in this study can be used in wearable devices such as smart clothing, and it can maintain stable performance even in extreme environments, so it has a high possibility of being commercialized through additional research in the future." Professor Inkyu Park also emphasized, "This technology will become the core of next-generation energy harvesting technology, and it is expected to play an important role in various fields from waste heat utilization in industrial sites to personal wearable self-power generation devices."
This study, in which Hanhwi Jang, a Ph.D. student at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Junseong Ahn of Korea University, Sejong Campus, and Dr. Yongrok Jeong of Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute contributed equally as joint first authors, was published in the online edition of the international academic journal Advanced Materials on September 17, and was selected as the back-cover paper in recognition of its excellence. (Paper title: Flexible All-Inorganic Thermoelectric Yarns)
Meanwhile, this study was conducted through the Mid-career Researcher Support Program and the Future Materials Discovery Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the support from the Global Bio-Integrated Materials Center, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology Evaluation and Planning (KEIT) upon the support by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2024.10.21 View 4147
KAIST Develops Thread-like, Flexible Thermoelectric Materials Applicable in Extreme Environments
A team of Korean researchers developed a thermoelectric material that can be used in wearable devices, such as smart clothing, and while maintaining stable thermal energy performance even in extreme environments. It has dramatically resolved the dilemma of striking the balance between achieving good performance and the mechanical flexibility of thermoelectric materials, which has been a long-standing challenge in the field of thermoelectric materials, and has also proven the possibility of commercialization.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 21st that a joint research team of Professor Yeon Sik Jung of the Department of Materials Science and Engineering and Professor Inkyu Park of the Department of Mechanical Engineering, in collaboration with the research teams of Professor Min-Wook Oh of Hanbat National University (President Yong Jun Oh) and Dr. Jun-Ho Jeong of the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials (President Seoghyun Ryu), have successfully developed ‘bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) thermoelectric fibers,’ an innovative energy harvesting solution for next-generation flexible electronic devices.
Thermoelectric materials are materials that generate voltage when there is a temperature difference and convert thermal energy into electrical energy. Currently, about 70% of energy being lost as wasted heat, so due attention is being given to research on these as sustainable energy materials that can recover and harvesting energy from this waste heat.
Most of the heat sources around us are curved, such as the human body, vehicle exhaust pipes, and cooling fins. Inorganic thermoelectric materials based on ceramic materials boast high thermoelectric performance, but they are fragile and difficult to produce in curved shapes. On the other hand, flexible thermoelectric materials using existing polymer binders can be applied to surfaces of various shapes, but their performance was limited due to the low electrical conductivity and high thermal resistance of the polymer.
Existing flexible thermoelectric materials contain polymer additives, but the inorganic thermoelectric material developed by the research team is not flexible, so they overcame these limitations by twisting nano ribbons instead of additives to produce a thread-shaped thermoelectric material. Inspired by the flexibility of inorganic nano ribbons, the research team used a nanomold-based electron beam deposition technique to continuously deposit nano ribbons and then twisted them into a thread shape to create bismuth telluride (Bi2Te3) inorganic thermoelectric fibers.
These inorganic thermoelectric fibers have higher bending strength than existing thermoelectric materials, and showed almost no change in electrical properties even after repeated bending and tensile tests of more than 1,000 times. The thermoelectric device created by the research team generates electricity using temperature differences, and if clothes are made with fiber-type thermoelectric devices, electricity can be generated from body temperature to operate other electronic devices.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram and actual image of the all-inorganic flexible thermoelectric yarn made without polymer additives >
In fact, the possibility of commercialization was proven through a demonstration of collecting energy by embedding thermoelectric fibers in life jackets or clothing. In addition, it opened up the possibility of building a high-efficiency energy harvesting system that recycles waste heat by utilizing the temperature difference between the hot fluid inside a pipe and the cold air outside in industrial settings.
Professor Yeon Sik Jung said, "The inorganic flexible thermoelectric material developed in this study can be used in wearable devices such as smart clothing, and it can maintain stable performance even in extreme environments, so it has a high possibility of being commercialized through additional research in the future." Professor Inkyu Park also emphasized, "This technology will become the core of next-generation energy harvesting technology, and it is expected to play an important role in various fields from waste heat utilization in industrial sites to personal wearable self-power generation devices."
This study, in which Hanhwi Jang, a Ph.D. student at KAIST's Department of Materials Science and Engineering, Professor Junseong Ahn of Korea University, Sejong Campus, and Dr. Yongrok Jeong of Korea Atomic Energy Research Institute contributed equally as joint first authors, was published in the online edition of the international academic journal Advanced Materials on September 17, and was selected as the back-cover paper in recognition of its excellence. (Paper title: Flexible All-Inorganic Thermoelectric Yarns)
Meanwhile, this study was conducted through the Mid-career Researcher Support Program and the Future Materials Discovery Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, and the support from the Global Bio-Integrated Materials Center, the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy, and the Korea Institute of Industrial Technology Evaluation and Planning (KEIT) upon the support by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
2024.10.21 View 4147 -
 KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 5689
KAIST Develops Technology for the Precise Diagnosis of Electric Vehicle Batteries Using Small Currents
Accurately diagnosing the state of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is essential for their efficient management and safe use. KAIST researchers have developed a new technology that can diagnose and monitor the state of batteries with high precision using only small amounts of current, which is expected to maximize the batteries’ long-term stability and efficiency.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 17th of October that a research team led by Professors Kyeongha Kwon and Sang-Gug Lee from the School of Electrical Engineering had developed electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) technology that can be used to improve the stability and performance of high-capacity batteries in electric vehicles.
EIS is a powerful tool that measures the impedance* magnitude and changes in a battery, allowing the evaluation of battery efficiency and loss. It is considered an important tool for assessing the state of charge (SOC) and state of health (SOH) of batteries. Additionally, it can be used to identify thermal characteristics, chemical/physical changes, predict battery life, and determine the causes of failures. *Battery Impedance: A measure of the resistance to current flow within the battery that is used to assess battery performance and condition.
However, traditional EIS equipment is expensive and complex, making it difficult to install, operate, and maintain. Moreover, due to sensitivity and precision limitations, applying current disturbances of several amperes (A) to a battery can cause significant electrical stress, increasing the risk of battery failure or fire and making it difficult to use in practice.
< Figure 1. Flow chart for diagnosis and prevention of unexpected combustion via the use of the electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) for the batteries for electric vehicles. >
To address this, the KAIST research team developed and validated a low-current EIS system for diagnosing the condition and health of high-capacity EV batteries. This EIS system can precisely measure battery impedance with low current disturbances (10mA), minimizing thermal effects and safety issues during the measurement process.
In addition, the system minimizes bulky and costly components, making it easy to integrate into vehicles. The system was proven effective in identifying the electrochemical properties of batteries under various operating conditions, including different temperatures and SOC levels.
Professor Kyeongha Kwon (the corresponding author) explained, “This system can be easily integrated into the battery management system (BMS) of electric vehicles and has demonstrated high measurement accuracy while significantly reducing the cost and complexity compared to traditional high-current EIS methods. It can contribute to battery diagnosis and performance improvements not only for electric vehicles but also for energy storage systems (ESS).”
This research, in which Young-Nam Lee, a doctoral student in the School of Electrical Engineering at KAIST participated as the first author, was published in the prestigious international journal IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics (top 2% in the field; IF 7.5) on September 5th. (Paper Title: Small-Perturbation Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy System With High Accuracy for High-Capacity Batteries in Electric Vehicles, Link: https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/10666864)
< Figure 2. Impedance measurement results of large-capacity batteries for electric vehicles. ZEW (commercial EW; MP10, Wonatech) versus ZMEAS (proposed system) >
This research was supported by the Basic Research Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, the Next-Generation Intelligent Semiconductor Technology Development Program of the Korea Evaluation Institute of Industrial Technology, and the AI Semiconductor Graduate Program of the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation.
2024.10.17 View 5689 -
 KAIST Develops Janus-like Metasurface Technology that Acts According to the Direction of Light
Metasurface technology is an advanced optical technology that is thinner, lighter, and capable of precisely controlling light through nanometer-sized artificial structures compared to conventional technologies. KAIST researchers have overcome the limitations of existing metasurface technologies and successfully designed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission. By applying this technology, they also proposed an innovative method to significantly enhance security by only decoding information under specific conditions.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of October that a research team led by Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission.
Asymmetric properties, which react differently depending on the direction, play a crucial role in various fields of science and engineering. The Janus metasurface developed by the research team implements an optical system capable of performing different functions in both directions.
Like the Roman god Janus with two faces, this metasurface shows entirely different optical responses depending on the direction of incoming light, effectively operating two independent optical systems with a single device (for example, a metasurface that acts as a magnifying lens in one direction and as a polarized camera in the other). In other words, by using this technology, it's possible to operate two different optical systems (e.g., a lens and a hologram) depending on the direction of the light.
This achievement addresses a challenge that existing metasurface technologies had not resolved. Conventional metasurface technology had limitations in selectively controlling the three properties of light—intensity, phase, and polarization—based on the direction of incidence.
The research team proposed a solution based on mathematical and physical principles, and succeeded in experimentally implementing different vector holograms in both directions. Through this achievement, they showcased a complete asymmetric light transmission control technology.
< Figure 1. Schematics of a device featuring asymmetric transmission. a) Device operating as a magnifying lens for back-side illumination. b) Device operating as a polarization camera for front-side illumination. >
Additionally, the research team developed a new optical encryption technology based on this metasurface technology. By using the Janus metasurface, they implemented a vector hologram that generates different images depending on the direction and polarization state of incoming light, showcasing an optical encryption system that significantly enhances security by allowing information to be decoded only under specific conditions.
This technology is expected to serve as a next-generation security solution, applicable in various fields such as quantum communication and secure data transmission.
Furthermore, the ultra-thin structure of the metasurface is expected to significantly reduce the volume and weight of traditional optical devices, contributing greatly to the miniaturization and lightweight design of next-generation devices.
< Figure 2. Experimental demonstration of Janus vectorial holograms. With front illuminations, vector images of the butterfly and the grasshopper are created, and with the back-side illuminations, vector images of the ladybug and the beetle are created. >
Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST stated, "This research has enabled the complete asymmetric transmission control of light’s intensity, phase, and polarization, which has been a long-standing challenge in optics. It has opened up the possibility of developing various applied optical devices." He added, "We plan to continue developing optical devices that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR), holographic displays, and LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles, utilizing the full potential of metasurface technology."
This research, in which Hyeonhee Kim (a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST) and Joonkyo Jung participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal Advanced Materials and is scheduled to be published in the October 31 issue. (Title of the paper: "Bidirectional Vectorial Holography Using Bi-Layer Metasurfaces and Its Application to Optical Encryption")
The research was supported by the Nano Materials Technology Development Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.15 View 3631
KAIST Develops Janus-like Metasurface Technology that Acts According to the Direction of Light
Metasurface technology is an advanced optical technology that is thinner, lighter, and capable of precisely controlling light through nanometer-sized artificial structures compared to conventional technologies. KAIST researchers have overcome the limitations of existing metasurface technologies and successfully designed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission. By applying this technology, they also proposed an innovative method to significantly enhance security by only decoding information under specific conditions.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 15th of October that a research team led by Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering had developed a Janus metasurface capable of perfectly controlling asymmetric light transmission.
Asymmetric properties, which react differently depending on the direction, play a crucial role in various fields of science and engineering. The Janus metasurface developed by the research team implements an optical system capable of performing different functions in both directions.
Like the Roman god Janus with two faces, this metasurface shows entirely different optical responses depending on the direction of incoming light, effectively operating two independent optical systems with a single device (for example, a metasurface that acts as a magnifying lens in one direction and as a polarized camera in the other). In other words, by using this technology, it's possible to operate two different optical systems (e.g., a lens and a hologram) depending on the direction of the light.
This achievement addresses a challenge that existing metasurface technologies had not resolved. Conventional metasurface technology had limitations in selectively controlling the three properties of light—intensity, phase, and polarization—based on the direction of incidence.
The research team proposed a solution based on mathematical and physical principles, and succeeded in experimentally implementing different vector holograms in both directions. Through this achievement, they showcased a complete asymmetric light transmission control technology.
< Figure 1. Schematics of a device featuring asymmetric transmission. a) Device operating as a magnifying lens for back-side illumination. b) Device operating as a polarization camera for front-side illumination. >
Additionally, the research team developed a new optical encryption technology based on this metasurface technology. By using the Janus metasurface, they implemented a vector hologram that generates different images depending on the direction and polarization state of incoming light, showcasing an optical encryption system that significantly enhances security by allowing information to be decoded only under specific conditions.
This technology is expected to serve as a next-generation security solution, applicable in various fields such as quantum communication and secure data transmission.
Furthermore, the ultra-thin structure of the metasurface is expected to significantly reduce the volume and weight of traditional optical devices, contributing greatly to the miniaturization and lightweight design of next-generation devices.
< Figure 2. Experimental demonstration of Janus vectorial holograms. With front illuminations, vector images of the butterfly and the grasshopper are created, and with the back-side illuminations, vector images of the ladybug and the beetle are created. >
Professor Jonghwa Shin from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST stated, "This research has enabled the complete asymmetric transmission control of light’s intensity, phase, and polarization, which has been a long-standing challenge in optics. It has opened up the possibility of developing various applied optical devices." He added, "We plan to continue developing optical devices that can be applied to various fields such as augmented reality (AR), holographic displays, and LiDAR systems for autonomous vehicles, utilizing the full potential of metasurface technology."
This research, in which Hyeonhee Kim (a doctoral student in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering at KAIST) and Joonkyo Jung participated as co-first authors, was published online in the international journal Advanced Materials and is scheduled to be published in the October 31 issue. (Title of the paper: "Bidirectional Vectorial Holography Using Bi-Layer Metasurfaces and Its Application to Optical Encryption")
The research was supported by the Nano Materials Technology Development Program and the Mid-Career Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2024.10.15 View 3631 -
 KAIST Succeeds in the Real-time Observation of Organoids using Holotomography
Organoids, which are 3D miniature organs that mimic the structure and function of human organs, play an essential role in disease research and drug development. A Korean research team has overcome the limitations of existing imaging technologies, succeeding in the real-time, high-resolution observation of living organoids.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 14th of October that Professor YongKeun Park’s research team from the Department of Physics, in collaboration with the Genome Editing Research Center (Director Bon-Kyoung Koo) of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS President Do-Young Noh) and Tomocube Inc., has developed an imaging technology using holotomography to observe live, small intestinal organoids in real time at a high resolution.
Existing imaging techniques have struggled to observe living organoids in high resolution over extended periods and often required additional treatments like fluorescent staining.
< Figure 1. Overview of the low-coherence HT workflow. Using holotomography, 3D morphological restoration and quantitative analysis of organoids can be performed. In order to improve the limited field of view, which is a limitation of the microscope, our research team utilized a large-area field of view combination algorithm and made a 3D restoration by acquiring multi-focus holographic images for 3D measurements. After that, the organoids were compartmentalized to divide the parts necessary for analysis and quantitatively evaluated the protein concentration measurable from the refractive index and the survival rate of the organoids. >
The research team introduced holotomography technology to address these issues, which provides high-resolution images without the need for fluorescent staining and allows for the long-term observation of dynamic changes in real time without causing cell damage.
The team validated this technology using small intestinal organoids from experimental mice and were able to observe various cell structures inside the organoids in detail. They also captured dynamic changes such as growth processes, cell division, and cell death in real time using holotomography.
Additionally, the technology allowed for the precise analysis of the organoids' responses to drug treatments, verifying the survival of the cells.
The researchers believe that this breakthrough will open new horizons in organoid research, enabling the greater utilization of organoids in drug development, personalized medicine, and regenerative medicine.
Future research is expected to more accurately replicate the in vivo environment of organoids, contributing significantly to a more detailed understanding of various life phenomena at the cellular level through more precise 3D imaging.
< Figure 2. Real-time organoid morphology analysis. Using holotomography, it is possible to observe the lumen and villus development process of intestinal organoids in real time, which was difficult to observe with a conventional microscope. In addition, various information about intestinal organoids can be obtained by quantifying the size and protein amount of intestinal organoids through image analysis. >
Dr. Mahn Jae Lee, a graduate of KAIST's Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, currently at Chungnam National University Hospital and the first author of the paper, commented, "This research represents a new imaging technology that surpasses previous limitations and is expected to make a major contribution to disease modeling, personalized treatments, and drug development research using organoids."
The research results were published online in the international journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine on October 1, 2024, and the technology has been recognized for its applicability in various fields of life sciences. (Paper title: “Long-term three-dimensional high-resolution imaging of live unlabeled small intestinal organoids via low-coherence holotomography”)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, KAIST Institutes, and the Institute for Basic Science.
2024.10.14 View 4501
KAIST Succeeds in the Real-time Observation of Organoids using Holotomography
Organoids, which are 3D miniature organs that mimic the structure and function of human organs, play an essential role in disease research and drug development. A Korean research team has overcome the limitations of existing imaging technologies, succeeding in the real-time, high-resolution observation of living organoids.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 14th of October that Professor YongKeun Park’s research team from the Department of Physics, in collaboration with the Genome Editing Research Center (Director Bon-Kyoung Koo) of the Institute for Basic Science (IBS President Do-Young Noh) and Tomocube Inc., has developed an imaging technology using holotomography to observe live, small intestinal organoids in real time at a high resolution.
Existing imaging techniques have struggled to observe living organoids in high resolution over extended periods and often required additional treatments like fluorescent staining.
< Figure 1. Overview of the low-coherence HT workflow. Using holotomography, 3D morphological restoration and quantitative analysis of organoids can be performed. In order to improve the limited field of view, which is a limitation of the microscope, our research team utilized a large-area field of view combination algorithm and made a 3D restoration by acquiring multi-focus holographic images for 3D measurements. After that, the organoids were compartmentalized to divide the parts necessary for analysis and quantitatively evaluated the protein concentration measurable from the refractive index and the survival rate of the organoids. >
The research team introduced holotomography technology to address these issues, which provides high-resolution images without the need for fluorescent staining and allows for the long-term observation of dynamic changes in real time without causing cell damage.
The team validated this technology using small intestinal organoids from experimental mice and were able to observe various cell structures inside the organoids in detail. They also captured dynamic changes such as growth processes, cell division, and cell death in real time using holotomography.
Additionally, the technology allowed for the precise analysis of the organoids' responses to drug treatments, verifying the survival of the cells.
The researchers believe that this breakthrough will open new horizons in organoid research, enabling the greater utilization of organoids in drug development, personalized medicine, and regenerative medicine.
Future research is expected to more accurately replicate the in vivo environment of organoids, contributing significantly to a more detailed understanding of various life phenomena at the cellular level through more precise 3D imaging.
< Figure 2. Real-time organoid morphology analysis. Using holotomography, it is possible to observe the lumen and villus development process of intestinal organoids in real time, which was difficult to observe with a conventional microscope. In addition, various information about intestinal organoids can be obtained by quantifying the size and protein amount of intestinal organoids through image analysis. >
Dr. Mahn Jae Lee, a graduate of KAIST's Graduate School of Medical Science and Engineering, currently at Chungnam National University Hospital and the first author of the paper, commented, "This research represents a new imaging technology that surpasses previous limitations and is expected to make a major contribution to disease modeling, personalized treatments, and drug development research using organoids."
The research results were published online in the international journal Experimental & Molecular Medicine on October 1, 2024, and the technology has been recognized for its applicability in various fields of life sciences. (Paper title: “Long-term three-dimensional high-resolution imaging of live unlabeled small intestinal organoids via low-coherence holotomography”)
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea, KAIST Institutes, and the Institute for Basic Science.
2024.10.14 View 4501 -
 KAIST Changes the Paradigm of Drug Discovery with World's First Atomic Editing
In pioneering drug development, the new technology that enables the easy and rapid editing of key atoms responsible for drug efficacy has been regarded as a fundamental and "dream" technology, revolutionizing the process of discovering potential drug candidates. KAIST researchers have become the first in the world to successfully develop single-atom editing technology that maximizes drug efficacy.
On October 8th, KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that Professor Yoonsu Park’s research team from the Department of Chemistry successfully developed technology that enables the easy editing and correction of oxygen atoms in furan compounds into nitrogen atoms, directly converting them into pyrrole frameworks, which are widely used in pharmaceuticals.
< Image. Conceptual image illustrating the main idea of the research >
This research was published in the prestigious scientific journal Science on October 3rd under the title "Photocatalytic Furan-to-Pyrrole Conversion."
Many drugs have complex chemical structures, but their efficacy is often determined by a single critical atom. Atoms like oxygen and nitrogen play a central role in enhancing the pharmacological effects of these drugs, particularly against viruses.
This phenomenon, where the introduction of specific atoms into a drug molecule dramatically affects its efficacy, is known as the "Single Atom Effect." In leading-edge drug development, discovering atoms that maximize drug efficacy is key.
However, evaluating the Single Atom Effect has traditionally required multi-step, costly synthesis processes, as it has been difficult to selectively edit single atoms within stable ring structures containing oxygen or nitrogen.
Professor Park’s team overcame this challenge by introducing a photocatalyst that uses light energy. They developed a photocatalyst that acts as a “molecular scissor,” freely cutting and attaching five-membered rings, enabling single-atom editing at room temperature and atmospheric pressure—a world first.
The team discovered a new reaction mechanism in which the excited molecular scissor removes oxygen from furan via single-electron oxidation and then sequentially adds a nitrogen atom.
Donghyeon Kim and Jaehyun You, the study's first authors and candidates in KAIST’s integrated master's and doctoral program in the Department of Chemistry, explained that this technique offers high versatility by utilizing light energy to replace harsh conditions. They further noted that the technology enables selective editing, even when applied to complex natural products or pharmaceuticals. Professor Yoonsu Park, who led the research, remarked, "This breakthrough, which allows for the selective editing of five-membered organic ring structures, will open new doors for building libraries of drug candidates, a key challenge in pharmaceuticals. I hope this foundational technology will be used to revolutionize the drug development process."
The significance of this research was highlighted in the Perspective section of Science, a feature where a peer scientist of prominence outside of the project group provides commentary on an impactful research.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Creative Research Program, the Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab Project at KAIST, and the POSCO Science Fellowship of the POSCO TJ Park Foundation.
2024.10.11 View 5099
KAIST Changes the Paradigm of Drug Discovery with World's First Atomic Editing
In pioneering drug development, the new technology that enables the easy and rapid editing of key atoms responsible for drug efficacy has been regarded as a fundamental and "dream" technology, revolutionizing the process of discovering potential drug candidates. KAIST researchers have become the first in the world to successfully develop single-atom editing technology that maximizes drug efficacy.
On October 8th, KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced that Professor Yoonsu Park’s research team from the Department of Chemistry successfully developed technology that enables the easy editing and correction of oxygen atoms in furan compounds into nitrogen atoms, directly converting them into pyrrole frameworks, which are widely used in pharmaceuticals.
< Image. Conceptual image illustrating the main idea of the research >
This research was published in the prestigious scientific journal Science on October 3rd under the title "Photocatalytic Furan-to-Pyrrole Conversion."
Many drugs have complex chemical structures, but their efficacy is often determined by a single critical atom. Atoms like oxygen and nitrogen play a central role in enhancing the pharmacological effects of these drugs, particularly against viruses.
This phenomenon, where the introduction of specific atoms into a drug molecule dramatically affects its efficacy, is known as the "Single Atom Effect." In leading-edge drug development, discovering atoms that maximize drug efficacy is key.
However, evaluating the Single Atom Effect has traditionally required multi-step, costly synthesis processes, as it has been difficult to selectively edit single atoms within stable ring structures containing oxygen or nitrogen.
Professor Park’s team overcame this challenge by introducing a photocatalyst that uses light energy. They developed a photocatalyst that acts as a “molecular scissor,” freely cutting and attaching five-membered rings, enabling single-atom editing at room temperature and atmospheric pressure—a world first.
The team discovered a new reaction mechanism in which the excited molecular scissor removes oxygen from furan via single-electron oxidation and then sequentially adds a nitrogen atom.
Donghyeon Kim and Jaehyun You, the study's first authors and candidates in KAIST’s integrated master's and doctoral program in the Department of Chemistry, explained that this technique offers high versatility by utilizing light energy to replace harsh conditions. They further noted that the technology enables selective editing, even when applied to complex natural products or pharmaceuticals. Professor Yoonsu Park, who led the research, remarked, "This breakthrough, which allows for the selective editing of five-membered organic ring structures, will open new doors for building libraries of drug candidates, a key challenge in pharmaceuticals. I hope this foundational technology will be used to revolutionize the drug development process."
The significance of this research was highlighted in the Perspective section of Science, a feature where a peer scientist of prominence outside of the project group provides commentary on an impactful research.
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea’s Creative Research Program, the Cross-Generation Collaborative Lab Project at KAIST, and the POSCO Science Fellowship of the POSCO TJ Park Foundation.
2024.10.11 View 5099