NT
-
 2012 Intellectual Property Rights Award Ceremony Held
The 2012 Intellectual Property Rights Award Ceremony was held at Seoul KAIST Campus.
Recipients of the award included former congressmen Kim Young Sun and Lee Jeong Hyuk, and Kim Boo Kyung researcher at Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute also representing Vooz Ltd. that created the character POOCA.
The Intellectual Property Rights Award is given to an individual or a group that succeeded in utilizing, protecting, creating, and establishment of its foundation including patent, copyright, and brand. Intellectual Property Rights is viewed as of importance for future national competitiveness.
The Award is organized by the Korea Patent Attorneys Association, the Korea Association of Intellectual Property Services, and KAIST and are respectively core institutions in the training of Intellectual Property Rights Experts and the creation, utilization, and the protection of intellectual property.
In addition the Award is also co-organized by the KAIST Graduate School of Intellectual Property Rights (established in cooperation with KAIST and the Korean Intellectual Property Office) and the total 20 million Won of prize money is funded by Korea Institute of Intellectual Strategy and Kim Ok Lan Foundation.
The Award Ceremony was held with a special lecture by the recipients.
It was stressed that the evaluation process was carried out with that the decision is a silent message to the society and is also a type of market signal.
Director Ko Gi Seok (Presidential Council on Intellectual Property) revealed that the candidates’ impact on the strength of national intellectual property rights was thoroughly scrutinized.
In the criteria of Creation of Intellectual Property, ETRI received the award in recognition of the institution’s successful patenting and commercializing of products of Korean R&D.
ETRI created a total of 251 International Patents in cooperation with ITU, ISO, IEE, etc. and also participated in a total of 9 International Standard Patent Pool, showing its active Intellectual Property management.
Such efforts ranked ETRI 1st in the United States Patent Evaluation performed by the US Patent Board in 2011 out of 237 institutions.
In addition Recipient of the Intellectual Property Utilization criteria, VOOZ ltd.’s Kim Boo Kyung promised the free use of their character POOCA in ETRI’s automated Korean-English translator. Researcher Kim Boo Kyung was rewarded with the award in recognition of his contribution to the domestic economy and realization of the commercialization of a copy right through licensing.
Former congressman Kim Young Son received an Award in the Foundation criteria in recognition of his efforts in the establishment of the Presidential Council on Intellectual Property and the Basic Blueprints for the Intellectual Property Law.
Former congressman Lee Jeong Hyuk received the same award in recognition of standardization and streamlining Intellectual Property Rights Policies. His realization and pursuit of the establishment of a balanced growth based on law for the competitiveness of businesses was the driving force behind his accomplishments.
2012.10.16 View 13977
2012 Intellectual Property Rights Award Ceremony Held
The 2012 Intellectual Property Rights Award Ceremony was held at Seoul KAIST Campus.
Recipients of the award included former congressmen Kim Young Sun and Lee Jeong Hyuk, and Kim Boo Kyung researcher at Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute also representing Vooz Ltd. that created the character POOCA.
The Intellectual Property Rights Award is given to an individual or a group that succeeded in utilizing, protecting, creating, and establishment of its foundation including patent, copyright, and brand. Intellectual Property Rights is viewed as of importance for future national competitiveness.
The Award is organized by the Korea Patent Attorneys Association, the Korea Association of Intellectual Property Services, and KAIST and are respectively core institutions in the training of Intellectual Property Rights Experts and the creation, utilization, and the protection of intellectual property.
In addition the Award is also co-organized by the KAIST Graduate School of Intellectual Property Rights (established in cooperation with KAIST and the Korean Intellectual Property Office) and the total 20 million Won of prize money is funded by Korea Institute of Intellectual Strategy and Kim Ok Lan Foundation.
The Award Ceremony was held with a special lecture by the recipients.
It was stressed that the evaluation process was carried out with that the decision is a silent message to the society and is also a type of market signal.
Director Ko Gi Seok (Presidential Council on Intellectual Property) revealed that the candidates’ impact on the strength of national intellectual property rights was thoroughly scrutinized.
In the criteria of Creation of Intellectual Property, ETRI received the award in recognition of the institution’s successful patenting and commercializing of products of Korean R&D.
ETRI created a total of 251 International Patents in cooperation with ITU, ISO, IEE, etc. and also participated in a total of 9 International Standard Patent Pool, showing its active Intellectual Property management.
Such efforts ranked ETRI 1st in the United States Patent Evaluation performed by the US Patent Board in 2011 out of 237 institutions.
In addition Recipient of the Intellectual Property Utilization criteria, VOOZ ltd.’s Kim Boo Kyung promised the free use of their character POOCA in ETRI’s automated Korean-English translator. Researcher Kim Boo Kyung was rewarded with the award in recognition of his contribution to the domestic economy and realization of the commercialization of a copy right through licensing.
Former congressman Kim Young Son received an Award in the Foundation criteria in recognition of his efforts in the establishment of the Presidential Council on Intellectual Property and the Basic Blueprints for the Intellectual Property Law.
Former congressman Lee Jeong Hyuk received the same award in recognition of standardization and streamlining Intellectual Property Rights Policies. His realization and pursuit of the establishment of a balanced growth based on law for the competitiveness of businesses was the driving force behind his accomplishments.
2012.10.16 View 13977 -
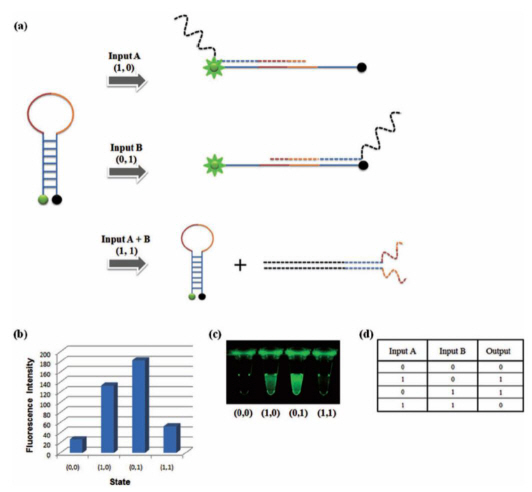 DNA based semiconductor technology developed
Professor Park Hyun Gyu’s research team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has successfully implemented all logic gates using DNA, a feat that led the research to be published as the cover paper for the international nanotechnology paper "Small".
Even with the latest technology, it was impossible to create a silicon based semiconductor smaller than 10nm, but because DNA has a thickness of only 2nm, this could lead to the creation of semiconductors with groundbreaking degrees of integration.
A 2 nm semiconductor will be able to store 10,000 HD movies within a size of a postage stamp, at least 100 times more than the current 20nm semiconductors.
DNAs are comprised of 4 bases which are continually connected: Adenine (A) with Thymine (T), and Guanine (G) with Cytosine (C).
For this research, the team used the specific binding properties of DNA, which forms its helix-shape, and a circular molecular beacon that has fluorescent signaling properties under structural changes.
The research team used input signals to open and close the circular DNA, the same principle that is applied to logic gates in digital circuits.
The output signal was measured using the increase and decrease of the fluorescent signal from the molecular beacon due to the opening and closing of the circular DNA respectively.
The team overcame the limited system problems of the existing logic gates and managed to implement all 8 logic gates (AND, OR, XOR, INHIBIT, NAND, NOR, XNOR, IMPlCATION). A multilevel circuit that connects different logic gates was also tested to show its regenerative properties.
Professor Park said that “cheap bio-electric devices with high degrees of integration will be made possible by this research” and that “there will be a large difference in the field of molecular level electronic research”
Mr. Park Gi Su, a doctoral candidate and the 1st author of this research, said that “a DNA sequence of 10 bases is only 3.4nm long and 2nm thick, which can be used to effectively increase the degree of integration of electronic devices” and that “a bio computer could materialize in the near future through DNA semiconductors with accurate logic gates”.
XOR Gate: The output signal 1 comes through the open circular DNA when either input DNA A or input DNA B is present. When both inputs are not present, the flourescent signal does not come through
2012.09.27 View 11691
DNA based semiconductor technology developed
Professor Park Hyun Gyu’s research team from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering at KAIST has successfully implemented all logic gates using DNA, a feat that led the research to be published as the cover paper for the international nanotechnology paper "Small".
Even with the latest technology, it was impossible to create a silicon based semiconductor smaller than 10nm, but because DNA has a thickness of only 2nm, this could lead to the creation of semiconductors with groundbreaking degrees of integration.
A 2 nm semiconductor will be able to store 10,000 HD movies within a size of a postage stamp, at least 100 times more than the current 20nm semiconductors.
DNAs are comprised of 4 bases which are continually connected: Adenine (A) with Thymine (T), and Guanine (G) with Cytosine (C).
For this research, the team used the specific binding properties of DNA, which forms its helix-shape, and a circular molecular beacon that has fluorescent signaling properties under structural changes.
The research team used input signals to open and close the circular DNA, the same principle that is applied to logic gates in digital circuits.
The output signal was measured using the increase and decrease of the fluorescent signal from the molecular beacon due to the opening and closing of the circular DNA respectively.
The team overcame the limited system problems of the existing logic gates and managed to implement all 8 logic gates (AND, OR, XOR, INHIBIT, NAND, NOR, XNOR, IMPlCATION). A multilevel circuit that connects different logic gates was also tested to show its regenerative properties.
Professor Park said that “cheap bio-electric devices with high degrees of integration will be made possible by this research” and that “there will be a large difference in the field of molecular level electronic research”
Mr. Park Gi Su, a doctoral candidate and the 1st author of this research, said that “a DNA sequence of 10 bases is only 3.4nm long and 2nm thick, which can be used to effectively increase the degree of integration of electronic devices” and that “a bio computer could materialize in the near future through DNA semiconductors with accurate logic gates”.
XOR Gate: The output signal 1 comes through the open circular DNA when either input DNA A or input DNA B is present. When both inputs are not present, the flourescent signal does not come through
2012.09.27 View 11691 -
 Professor Moon Song Chun appointed representative director of European IT society
Professor Moon Song Chun from the College of business at KAIST was appointed as the representative director of Asia for the European IR society EUROMICRO at its 35th general meeting in Lille, France.
Professor Moon is highly regarded in his work in popularization of IT in 3rd world countries and has published the largest number of papers in the history of EUROMICRO. For the next two years, Professor Moon will work to introduce Asia’s IT capabilities to the world and to increase the recognition of the society in the region.
Professor Moon, who is also known as the first Computer Science Doctor (PhD) in Korea, has worked to popularize IT by initiating IT volunteer services in Africa, the Middle East, Central and South America, South East Asia and Eastern Europe. He has also helped in the recognition of Korea’s IT capacity, working as a Korean Delegate for the UN International Y2K Cooperation Center, a Distinguished Scholar at Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and a Visiting Scholar at Cambridge University.
2012.09.25 View 10329
Professor Moon Song Chun appointed representative director of European IT society
Professor Moon Song Chun from the College of business at KAIST was appointed as the representative director of Asia for the European IR society EUROMICRO at its 35th general meeting in Lille, France.
Professor Moon is highly regarded in his work in popularization of IT in 3rd world countries and has published the largest number of papers in the history of EUROMICRO. For the next two years, Professor Moon will work to introduce Asia’s IT capabilities to the world and to increase the recognition of the society in the region.
Professor Moon, who is also known as the first Computer Science Doctor (PhD) in Korea, has worked to popularize IT by initiating IT volunteer services in Africa, the Middle East, Central and South America, South East Asia and Eastern Europe. He has also helped in the recognition of Korea’s IT capacity, working as a Korean Delegate for the UN International Y2K Cooperation Center, a Distinguished Scholar at Hungarian Academy of Sciences, and a Visiting Scholar at Cambridge University.
2012.09.25 View 10329 -
 Anonymous philanthropist donates 5.5 billion won to KAIST
An unnamed philanthropist donated a large sum of money to KAIST to be used as funds for the school"s development.
On September 6th, the donor met with President Suh to donate a sum of 5.5 billion won to the school for the development of science and technology.
A KAIST representative announced that the donor did not want to be named and that he was greatly impressed by President Suh"s and KAIST"s efforts towards reformation. The philanthropist wanted the donation to be used for research funds and financial aid.
President Suh said that "KAIST was deeply thankful and that it would work harder to show fulfill the donor"s wishes" and that the money would indeed be used for research and the students.
This was the 6th largest donation since the start of President Suh"s post in July 2006. Since 2006, the accumulated KAIST development fund has increased 30 times, from 5.9 billion won at the end of 2006 to 180 billion won in September 2012.
2012.09.24 View 7911
Anonymous philanthropist donates 5.5 billion won to KAIST
An unnamed philanthropist donated a large sum of money to KAIST to be used as funds for the school"s development.
On September 6th, the donor met with President Suh to donate a sum of 5.5 billion won to the school for the development of science and technology.
A KAIST representative announced that the donor did not want to be named and that he was greatly impressed by President Suh"s and KAIST"s efforts towards reformation. The philanthropist wanted the donation to be used for research funds and financial aid.
President Suh said that "KAIST was deeply thankful and that it would work harder to show fulfill the donor"s wishes" and that the money would indeed be used for research and the students.
This was the 6th largest donation since the start of President Suh"s post in July 2006. Since 2006, the accumulated KAIST development fund has increased 30 times, from 5.9 billion won at the end of 2006 to 180 billion won in September 2012.
2012.09.24 View 7911 -
 Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yeop Appointed as Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences) has become the first Korea Scientist to be appointed as the Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers was founded in 1908 and boasts a 100 year history. It is composed of 43,000 members over 90 countries and is the largest international Academic Institute in the field of Chemical Engineering.
The Institute appoints Fellows after a rigorous procedure of recommendation and evaluation and Professor Lee is the first Korean to become a Fellow.
Professor Lee’s expertise is the field of Metabolic Engineering and successfully applied the system design method and optimization strategy of chemical engineering to biological systems thereby developing numerous core technologies for the biology based chemical industries.
Professor Lee is the founder of the System Metabolic Engineering and enabled the medical application of microorganisms by manipulating the metabolic pathways on a systems level in addition to making great progress in synthesizing various oil originated chemical materials using biology based, environmentally friends methods.
Professor Lee received the Marvin J. Johnson Award, Charles Thom Award, and has been appointed by the first Chairman of the Biotech Global Agenda Counsel of the World Economic Forum.
2012.09.22 View 11444
Distinguished Professor Lee Sang Yeop Appointed as Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers
Professor Lee Sang Yeop (Dean of the Department of Biological Sciences) has become the first Korea Scientist to be appointed as the Fellow of the American Institute of Chemical Engineers.
The American Institute of Chemical Engineers was founded in 1908 and boasts a 100 year history. It is composed of 43,000 members over 90 countries and is the largest international Academic Institute in the field of Chemical Engineering.
The Institute appoints Fellows after a rigorous procedure of recommendation and evaluation and Professor Lee is the first Korean to become a Fellow.
Professor Lee’s expertise is the field of Metabolic Engineering and successfully applied the system design method and optimization strategy of chemical engineering to biological systems thereby developing numerous core technologies for the biology based chemical industries.
Professor Lee is the founder of the System Metabolic Engineering and enabled the medical application of microorganisms by manipulating the metabolic pathways on a systems level in addition to making great progress in synthesizing various oil originated chemical materials using biology based, environmentally friends methods.
Professor Lee received the Marvin J. Johnson Award, Charles Thom Award, and has been appointed by the first Chairman of the Biotech Global Agenda Counsel of the World Economic Forum.
2012.09.22 View 11444 -
 KAIST Alumni Association Hosts 1st Annual Mentoring Concert
KAIST Alums begin the management of a mentoring program for the benefit of worrying KAIST students.
President of KAIST Alumni Association will host on the 22nd of September the 1st Annual Mentoring Concert from 2pm to 8pm.
The Mentoring Concert was hosted in response to the Student Government Survey that enquired to the students of KAIST the type of help they’d like from Alumni.
The Alumni Association expanded its Goodwill Café program into the Mentoring Concert in order to improve the connection between the students and the alumni.
The Concert is composed of eight sessions (Academia, Industry, Government Institute, Consulting, Finance, Venture I, Venture II) and will involve 40 mentors and 400 mentees.
Each session will be attended by 5 mentors and 50 mentees and each mentor will give a ten minute presentation on the value of life, work experience, and their catalysis for choice of vocation.
KAIST Alumni Association stated that the Online Mentor System is under construction which will allow KAIST students to directly email mentors.
2012.09.22 View 7343
KAIST Alumni Association Hosts 1st Annual Mentoring Concert
KAIST Alums begin the management of a mentoring program for the benefit of worrying KAIST students.
President of KAIST Alumni Association will host on the 22nd of September the 1st Annual Mentoring Concert from 2pm to 8pm.
The Mentoring Concert was hosted in response to the Student Government Survey that enquired to the students of KAIST the type of help they’d like from Alumni.
The Alumni Association expanded its Goodwill Café program into the Mentoring Concert in order to improve the connection between the students and the alumni.
The Concert is composed of eight sessions (Academia, Industry, Government Institute, Consulting, Finance, Venture I, Venture II) and will involve 40 mentors and 400 mentees.
Each session will be attended by 5 mentors and 50 mentees and each mentor will give a ten minute presentation on the value of life, work experience, and their catalysis for choice of vocation.
KAIST Alumni Association stated that the Online Mentor System is under construction which will allow KAIST students to directly email mentors.
2012.09.22 View 7343 -
 Lee Su Young President of Gwang Won Industries Donates Real Estate worth 7 Million USD
On the 14th of September Lee Su Young President of Gwang Won Industries (since 1988) donated her entire personal real estate in Los Angeles worth 7 million USD.
President Lee commented that “the strength of Science and Technology is the strength behind the development of Korea and I am certain that KAIST is the driving force” and the she “wishes to help out on the nurture of excellent intellectuals”.
“I have led a frugal life, working hard and buying real estate in America. Wealth is not something that you can take beyond death so I always spent rationally in order to return my accumulated wealth back to society. I pondered what would be best for the development of Korea and without a moment’s hesitation I chose KAIST.”
President Lee was touched by the drive for innovation by President Seo and the members of KAIST working day and night for the development of KAIST.
“It was very moving to see a world renowned scholar like President Seo working tirelessly for the past six years to resurrect and develop KAIST. If KAIST continues to develop at such a pace then I am sure that KAIST will become a world class university. Donating to KAIST was sure to be equivalent to donating the Korea.”
President Lee led a life more frugal and most and yet she did not have even a moment’s hesitation in donating her entire fortune.
“My only wish is to see my donation help the students of KAIST with their studies. What more could I expect from them if they become outstanding servants of Korea.”
President Lee graduated from Gyungi Girl’s High School and majored Law in Seoul National University and worked as a newspaper reporter from 1963 to 1980.
She is the President of Gwang Won Industries which began as Gwang Won Ranch in 1971, and is also the Head Board Member at Seoul National University’s Scholarship Foundation for the College of Law.
The donation will be used to fund the ‘KAIST-Lee Su Young International Education Program’ which encompasses the currently under test Education 3.0 program which will allow for the next generation student led education system using multimedia services.
2012.09.22 View 9039
Lee Su Young President of Gwang Won Industries Donates Real Estate worth 7 Million USD
On the 14th of September Lee Su Young President of Gwang Won Industries (since 1988) donated her entire personal real estate in Los Angeles worth 7 million USD.
President Lee commented that “the strength of Science and Technology is the strength behind the development of Korea and I am certain that KAIST is the driving force” and the she “wishes to help out on the nurture of excellent intellectuals”.
“I have led a frugal life, working hard and buying real estate in America. Wealth is not something that you can take beyond death so I always spent rationally in order to return my accumulated wealth back to society. I pondered what would be best for the development of Korea and without a moment’s hesitation I chose KAIST.”
President Lee was touched by the drive for innovation by President Seo and the members of KAIST working day and night for the development of KAIST.
“It was very moving to see a world renowned scholar like President Seo working tirelessly for the past six years to resurrect and develop KAIST. If KAIST continues to develop at such a pace then I am sure that KAIST will become a world class university. Donating to KAIST was sure to be equivalent to donating the Korea.”
President Lee led a life more frugal and most and yet she did not have even a moment’s hesitation in donating her entire fortune.
“My only wish is to see my donation help the students of KAIST with their studies. What more could I expect from them if they become outstanding servants of Korea.”
President Lee graduated from Gyungi Girl’s High School and majored Law in Seoul National University and worked as a newspaper reporter from 1963 to 1980.
She is the President of Gwang Won Industries which began as Gwang Won Ranch in 1971, and is also the Head Board Member at Seoul National University’s Scholarship Foundation for the College of Law.
The donation will be used to fund the ‘KAIST-Lee Su Young International Education Program’ which encompasses the currently under test Education 3.0 program which will allow for the next generation student led education system using multimedia services.
2012.09.22 View 9039 -
 Professor Yoon Dong Ki becomes first Korean to Receive the Michi Nakata Prize
Professor Yoon Dong Ki (Graduate School of Nano Science and Technology) became the first Korean to receive the Michi Nakata Prize from the International Liquid Crystal Society.
The Awards Ceremony was held on the 23rd of August in Mainz, Germany in the 24th Annual International Liquid Crystal Conference.
The Michi Nakata Prize was initiated in 2008 and is rewarded every two years to a young scientist that made a ground breaking discovery or experimental result in the field of liquid crystal. Professor Yoon is the first Korean recipient of the Michi Nakata Prize.
Professor Yoon is the founder of the patterning field that utilizes the defect structure formed by smectic displays. He succeeded in large scale patterning complex chiral nano structures that make up bent-core molecules.
Professor Yoon’s experimental accomplishment was published in the Advanced Materials magazine and the Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. and also as the cover dissertation of Liquid Crystals magazine.
Professor Yoon is currently working on Three Dimensional Nano Patterning of Supermolecular Liquid Crystal and is part of the World Class University organization.
2012.09.11 View 15161
Professor Yoon Dong Ki becomes first Korean to Receive the Michi Nakata Prize
Professor Yoon Dong Ki (Graduate School of Nano Science and Technology) became the first Korean to receive the Michi Nakata Prize from the International Liquid Crystal Society.
The Awards Ceremony was held on the 23rd of August in Mainz, Germany in the 24th Annual International Liquid Crystal Conference.
The Michi Nakata Prize was initiated in 2008 and is rewarded every two years to a young scientist that made a ground breaking discovery or experimental result in the field of liquid crystal. Professor Yoon is the first Korean recipient of the Michi Nakata Prize.
Professor Yoon is the founder of the patterning field that utilizes the defect structure formed by smectic displays. He succeeded in large scale patterning complex chiral nano structures that make up bent-core molecules.
Professor Yoon’s experimental accomplishment was published in the Advanced Materials magazine and the Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. and also as the cover dissertation of Liquid Crystals magazine.
Professor Yoon is currently working on Three Dimensional Nano Patterning of Supermolecular Liquid Crystal and is part of the World Class University organization.
2012.09.11 View 15161 -
 First Annual CanSat Idea Exhibition held
The Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology held the ‘CanSat’ Exhibition in order to increase interest and understanding of satellites in primary, secondary, and high school level students.
The exhibition, hosted by KAIST Satellite Research Center and funded by Korea Aerospace Institute, was held in SaeJeong City.
90 primary, secondary school teams, 57 high school teams, and 14 university teams submitted their applications for participation. Of these teams 20 primary, secondary school teams, 5 high school teams, and 5 university teams were selected after thorough document valuation and presentation assessment.
The 20 primary, secondary school teams participated in the science camp to gain firsthand experience in the construction and launch of a simple satellite system.
The high school and university teams were evaluated by the level of completion of the task given and the level of creativity involved.
The CanSat Exhibition has been held in aerospace powerhouses and this was the first time such an exhibition was held in Korea.
2012.08.21 View 11472
First Annual CanSat Idea Exhibition held
The Ministry of Education, Science, and Technology held the ‘CanSat’ Exhibition in order to increase interest and understanding of satellites in primary, secondary, and high school level students.
The exhibition, hosted by KAIST Satellite Research Center and funded by Korea Aerospace Institute, was held in SaeJeong City.
90 primary, secondary school teams, 57 high school teams, and 14 university teams submitted their applications for participation. Of these teams 20 primary, secondary school teams, 5 high school teams, and 5 university teams were selected after thorough document valuation and presentation assessment.
The 20 primary, secondary school teams participated in the science camp to gain firsthand experience in the construction and launch of a simple satellite system.
The high school and university teams were evaluated by the level of completion of the task given and the level of creativity involved.
The CanSat Exhibition has been held in aerospace powerhouses and this was the first time such an exhibition was held in Korea.
2012.08.21 View 11472 -
 Hosting of Third Annual 2012 Social Web International Workshop
KAIST Department of WebScience Engineering hosted the 2012 Social Web International Workshop in JaeJu Ramada Hotel.
The 3rd Annual International Workshop involves the coming together of domestic and international experts on various fields like sociology, journalism, electronics, economics, and etc. to introduce and discuss the direction of social web’s numerous factions.
Dr. Krishna Gummadi (Max Plank Research Institute), Professor Irwin King (Chinese University of Hong Kong), Dr. Winter Mason (Stevens Technology Research Institute), and Professor Daniele Quercia (Cambridge University) made up the international participants of the workshop.
Professor Kim Yong Chan (Yonsei University), Professor Kim Ye Ran (KwangWoon University), Professor Park Ju Yong (Kyung Hee University), Professor Oh Hae Yeon and Professor Lee Won Jae (KAIST) made up the domestic participants to the workshop.
The workshop was a place for free discussion of social networks and apps and the research direction of social sciences.
2012.08.21 View 8774
Hosting of Third Annual 2012 Social Web International Workshop
KAIST Department of WebScience Engineering hosted the 2012 Social Web International Workshop in JaeJu Ramada Hotel.
The 3rd Annual International Workshop involves the coming together of domestic and international experts on various fields like sociology, journalism, electronics, economics, and etc. to introduce and discuss the direction of social web’s numerous factions.
Dr. Krishna Gummadi (Max Plank Research Institute), Professor Irwin King (Chinese University of Hong Kong), Dr. Winter Mason (Stevens Technology Research Institute), and Professor Daniele Quercia (Cambridge University) made up the international participants of the workshop.
Professor Kim Yong Chan (Yonsei University), Professor Kim Ye Ran (KwangWoon University), Professor Park Ju Yong (Kyung Hee University), Professor Oh Hae Yeon and Professor Lee Won Jae (KAIST) made up the domestic participants to the workshop.
The workshop was a place for free discussion of social networks and apps and the research direction of social sciences.
2012.08.21 View 8774 -
 Graduate School of Culture and Technology Begins Mobile Science Classroom
KAIST Graduate School of Culture and Technology plans visits to elementary schools without the facilities to facilitate hands on science education.
The Graduate School of Culture and Technology planned the ‘STEAM Creative Camp’ involving three elementary schools during the summer holidays.
The ‘STEAM Creative Camp’ involves increasing interest and artistic sensitivity through experience based science education.
The program is composed of two separate programs in consideration to the level of participating students.
The beginner level program includes: code making, writing secret letters, sticker decorating program and the moderate level program includes: making wipers using complex pulley system, catapult design using elasticity, and puppet show using joints to animate.
The programs will be taught by masters and doctorate program candidates from the KAIST Youth Culture and Technology Experience Center.
*STEAM: And integrated education system including Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics.
2012.07.26 View 10643
Graduate School of Culture and Technology Begins Mobile Science Classroom
KAIST Graduate School of Culture and Technology plans visits to elementary schools without the facilities to facilitate hands on science education.
The Graduate School of Culture and Technology planned the ‘STEAM Creative Camp’ involving three elementary schools during the summer holidays.
The ‘STEAM Creative Camp’ involves increasing interest and artistic sensitivity through experience based science education.
The program is composed of two separate programs in consideration to the level of participating students.
The beginner level program includes: code making, writing secret letters, sticker decorating program and the moderate level program includes: making wipers using complex pulley system, catapult design using elasticity, and puppet show using joints to animate.
The programs will be taught by masters and doctorate program candidates from the KAIST Youth Culture and Technology Experience Center.
*STEAM: And integrated education system including Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics.
2012.07.26 View 10643 -
 Professor Bae Sang Min Wins Multiple Prestigious Design Awards
Summer is perfect for many outdoor activities, but it is also the season for mosquitoes, an annoying pest that makes outdoor experiences unpleasant and sometimes even dangerous. An easy-to-use and environmentally-friendly spray, “Sound Spray” (http://idsa.org/soundspray-self-generating-non-toxic-ultrasonic-anti-mosquito-spray), which repels mosquitoes by setting off ultrasonic waves, has been developed by a research team at KAIST. The spray produces sounds similar to those of mosquitoes’ natural predators.
Sound Spray made the list of finalists in the category of "Social Impact Design" from the 2012 International Design Excellence Awards (IDEA). The IDEA is one of the most renowned design competitions in the world, which has been held annually by the Industrial Designers Society of America (IDSA).
Inside Sound Spray is a battery that generates electricity when a user shakes the spray bottle. Electrical energy produced by the battery creates an ultrasonic sound that mosquitoes dislike, thereby discouraging their contact with human skin. Professor Sangmin Bae from the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST explains,
“In regions such as Africa or Southeast Asia, mosquitoes are still posing a big threat to public health. Unlike Freon-based, disposable insect repellents on the market, Sound Spray is eco-friendly, easy to carry around, reusable, and affordable. I plan to commercialize and distribute it to nations in Africa or Southeast Asia to help them combat against malaria, an infectious disease that patients contract through mosquito bites.”
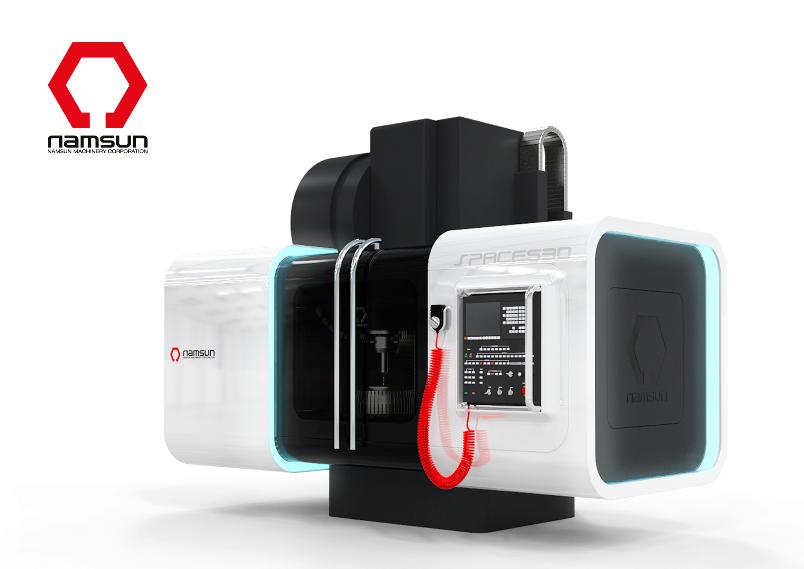
Professor Bae also received another award from the 2012 IDEA in the area of Commercial and Industrial Products: a bronze medal for a milling machine, the Namsun Milling Machine (http://www.idsa.org/namsunnew-innovative-milling-machine-design). The machine has large windows on each side of its main body that display a transparent workflow so that users easily understand the machine’s operation status. Curved lines are actively used for the exterior design of the machine to create a more friendly work environment.
In addition to the 2012 IDEA, Professor Bae has participated in other major international design awards, including the Red Dot Award, the If Design Award Japan, and the Good Design Award, from which his research team has received a total of 41 prizes.
Professor Bae initiated a campaign in 2005 called “Philanthropy Design,” through which he has donated many of his designs to help people in need. For more on his research, please visit http://www.coroflot.com/frame29/Portfolio1.
2012.07.26 View 14232
Professor Bae Sang Min Wins Multiple Prestigious Design Awards
Summer is perfect for many outdoor activities, but it is also the season for mosquitoes, an annoying pest that makes outdoor experiences unpleasant and sometimes even dangerous. An easy-to-use and environmentally-friendly spray, “Sound Spray” (http://idsa.org/soundspray-self-generating-non-toxic-ultrasonic-anti-mosquito-spray), which repels mosquitoes by setting off ultrasonic waves, has been developed by a research team at KAIST. The spray produces sounds similar to those of mosquitoes’ natural predators.
Sound Spray made the list of finalists in the category of "Social Impact Design" from the 2012 International Design Excellence Awards (IDEA). The IDEA is one of the most renowned design competitions in the world, which has been held annually by the Industrial Designers Society of America (IDSA).
Inside Sound Spray is a battery that generates electricity when a user shakes the spray bottle. Electrical energy produced by the battery creates an ultrasonic sound that mosquitoes dislike, thereby discouraging their contact with human skin. Professor Sangmin Bae from the Department of Industrial Design at KAIST explains,
“In regions such as Africa or Southeast Asia, mosquitoes are still posing a big threat to public health. Unlike Freon-based, disposable insect repellents on the market, Sound Spray is eco-friendly, easy to carry around, reusable, and affordable. I plan to commercialize and distribute it to nations in Africa or Southeast Asia to help them combat against malaria, an infectious disease that patients contract through mosquito bites.”
Professor Bae also received another award from the 2012 IDEA in the area of Commercial and Industrial Products: a bronze medal for a milling machine, the Namsun Milling Machine (http://www.idsa.org/namsunnew-innovative-milling-machine-design). The machine has large windows on each side of its main body that display a transparent workflow so that users easily understand the machine’s operation status. Curved lines are actively used for the exterior design of the machine to create a more friendly work environment.
In addition to the 2012 IDEA, Professor Bae has participated in other major international design awards, including the Red Dot Award, the If Design Award Japan, and the Good Design Award, from which his research team has received a total of 41 prizes.
Professor Bae initiated a campaign in 2005 called “Philanthropy Design,” through which he has donated many of his designs to help people in need. For more on his research, please visit http://www.coroflot.com/frame29/Portfolio1.
2012.07.26 View 14232