KI
-
 Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 12711
Team Geumo Wins Consecutive Victories in K-Cyber Security Challenge
< Professor Sang Kil Cha >
< Masters Candidate Kangsu Kim and Researcher Corentin Soulet >
Team Geumo, led by Professor Sang Kil Cha from the Graduate School of Information Security, won the K-Cyber Security Challenge in the AI-based automatic vulnerability detection division for two consecutive years in 2018 and 2019.
The K-Cyber Security Challenge is an inter-machine hacking competition. Participants develop and operate AI-based systems that are capable of independently identifying software vulnerabilities and gaining operating rights through hacking. The K-Cyber Security Challenge, inspired by the US Cyber Grand Challenge launched by the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA), is hosted by the Ministry of Science and ICT and organized by the Korea Internet and Security Agency.
Researcher Corentin Soulet of the School of Computing and master’s student Kangsu Kim of the Graduate School of Information Security teamed up for the competition. Professor Cha, who has led the research on software and systems security since his days at Carnegie Mellon University, succeeded in establishing a world-class system using domestic technology.
In a recent collaboration with the Cyber Security Research Center, Professor Cha achieved a ten-fold increase in the speed of binary analysis engines, a key component of AI-based hacking systems. For this accomplishment, he received the Best Paper Award at the 2019 Network and Distributed System Security Workshop on Binary Analysis Research (NDSS BAR).
Kangsu Kim said, "It is a great honor to win the competition two years in a row. I will continue to work hard and apply my knowledge to serve society.”
(END)
2019.12.20 View 12711 -
 Two Professors Receive Awards from the Korea Robotics Society
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu and Professor Ayoung Kim >
The Korea Robotics Society (KROS) conferred awards onto two KAIST professors from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in recognition of their achievements and contributions to the development of the robotics industry in 2019. Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu has been actively engaged in researching the field of teleoperation, and this led him to win the KROS Robotics Innovation (KRI) Award. The KRI Award was newly established in 2019 by the KROS, in order to encourage researchers who have made innovative achievements in robotics. Professor Ryu shared the honor of being the first winner of this award with Professor Jaeheung Park of Seoul National University. Professor Ayoung Kim, from the same department, received the Young Investigator Award presented to emerging robitics researchers under 40 years of age. (END)
2019.12.19 View 13518
Two Professors Receive Awards from the Korea Robotics Society
< Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu and Professor Ayoung Kim >
The Korea Robotics Society (KROS) conferred awards onto two KAIST professors from the Department of Civil and Environmental Engineering in recognition of their achievements and contributions to the development of the robotics industry in 2019. Professor Jee-Hwan Ryu has been actively engaged in researching the field of teleoperation, and this led him to win the KROS Robotics Innovation (KRI) Award. The KRI Award was newly established in 2019 by the KROS, in order to encourage researchers who have made innovative achievements in robotics. Professor Ryu shared the honor of being the first winner of this award with Professor Jaeheung Park of Seoul National University. Professor Ayoung Kim, from the same department, received the Young Investigator Award presented to emerging robitics researchers under 40 years of age. (END)
2019.12.19 View 13518 -
 New Members of KAST 2020
< Professor Zong-Tae Bae (Left) and Professor Sang Ouk Kim (Right) >
Professor Zong-Tae Bae from the School of Management Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering became new fellows of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) along with 22 other scientists in Korea.
On November 22, KAST announced 24 new members for the year 2020. This includes seven scientists from the field of natural sciences, six from engineering, four from medical sciences, another four from policy research, and three from agriculture and fishery.
The new fellows will begin their term from January next year, and their fellowships wll be conferred during the KAST’s New Year Reception to be held on January 14 in Seoul.
(END)
2019.12.09 View 15655
New Members of KAST 2020
< Professor Zong-Tae Bae (Left) and Professor Sang Ouk Kim (Right) >
Professor Zong-Tae Bae from the School of Management Engineering and Professor Sang Ouk Kim from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering became new fellows of the Korean Academy of Science and Technology (KAST) along with 22 other scientists in Korea.
On November 22, KAST announced 24 new members for the year 2020. This includes seven scientists from the field of natural sciences, six from engineering, four from medical sciences, another four from policy research, and three from agriculture and fishery.
The new fellows will begin their term from January next year, and their fellowships wll be conferred during the KAST’s New Year Reception to be held on January 14 in Seoul.
(END)
2019.12.09 View 15655 -
 ‘Carrier-Resolved Photo-Hall’ to Push Semiconductor Advances
(Professor Shin and Dr. Gunawan (left))
An IBM-KAIST research team described a breakthrough in a 140-year-old mystery in physics. The research reported in Nature last month unlocks the physical characteristics of semiconductors in much greater detail and aids in the development of new and improved semiconductor materials.
Research team under Professor Byungha Shin at the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering and Dr. Oki Gunawan at IBM discovered a new formula and technique that enables the simultaneous extraction of both majority and minority carrier information such as their density and mobility, as well as gain additional insights about carrier lifetimes, diffusion lengths, and the recombination process. This new discovery and technology will help push semiconductor advances in both existing and emerging technologies.
Semiconductors are the basic building blocks of today’s digital electronics age, providing us with a multitude of devices that benefit our modern life. To truly appreciate the physics of semiconductors, it is very important to understand the fundamental properties of the charge carriers inside the materials, whether those particles are positive or negative, their speed under an applied electric field, and how densely they are packed into the material.
Physicist Edwin Hall found a way to determine those properties in 1879, when he discovered that a magnetic field will deflect the movement of electronic charges inside a conductor and that the amount of deflection can be measured as a voltage perpendicular to the flow of the charge. Decades after Hall’s discovery, researchers also recognized that they can measure the Hall effect with light via “photo-Hall experiments”. During such experiments, the light generates multiple carriers or electron–hole pairs in the semiconductors.
Unfortunately, the basic Hall effect only provided insights into the dominant charge carrier (or majority carrier). Researchers were unable to extract the properties of both carriers (the majority and minority carriers) simultaneously. The property information of both carriers is crucial for many applications that involve light such as solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
In the photo-Hall experiment by the KAIST-IBM team, both carriers contribute to changes in conductivity and the Hall coefficient. The key insight comes from measuring the conductivity and Hall coefficient as a function of light intensity. Hidden in the trajectory of the conductivity, the Hall coefficient curve reveals crucial new information: the difference in the mobility of both carriers. As discussed in the paper, this relationship can be expressed elegantly as: Δµ = d (σ²H)/dσ
The research team solved for both majority and minority carrier mobility and density as a function of light intensity, naming the new technique Carrier-Resolved Photo Hall (CRPH) measurement. With known light illumination intensity, the carrier lifetime can be established in a similar way.
Beyond advances in theoretical understanding, advances in experimental techniques were also critical for enabling this breakthrough. The technique requires a clean Hall signal measurement, which can be challenging for materials where the Hall signal is weak due to low mobility or when extra unwanted signals are present, such as under strong light illumination.
The newly developed photo-Hall technique allows the extraction of an astonishing amount of information from semiconductors. In contrast to only three parameters obtained in the classic Hall measurements, this new technique yields up to seven parameters at every tested level of light intensity. These include the mobility of both the electron and hole; their carrier density under light; the recombination lifetime; and the diffusion lengths for electrons, holes, and ambipolar types. All of these can be repeated N times (i.e. the number of light intensity settings used in the experiment).
Professor Shin said, “This novel technology sheds new light on understanding the physical characteristics of semiconductor materials in great detail.” Dr. Gunawan added, “This will will help accelerate the development of next-generation semiconductor technology such as better solar cells, better optoelectronics devices, and new materials and devices for artificial intelligence technology.”
Profile:
Professor Byungha Shin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
2019.11.18 View 16693
‘Carrier-Resolved Photo-Hall’ to Push Semiconductor Advances
(Professor Shin and Dr. Gunawan (left))
An IBM-KAIST research team described a breakthrough in a 140-year-old mystery in physics. The research reported in Nature last month unlocks the physical characteristics of semiconductors in much greater detail and aids in the development of new and improved semiconductor materials.
Research team under Professor Byungha Shin at the Department of Material Sciences and Engineering and Dr. Oki Gunawan at IBM discovered a new formula and technique that enables the simultaneous extraction of both majority and minority carrier information such as their density and mobility, as well as gain additional insights about carrier lifetimes, diffusion lengths, and the recombination process. This new discovery and technology will help push semiconductor advances in both existing and emerging technologies.
Semiconductors are the basic building blocks of today’s digital electronics age, providing us with a multitude of devices that benefit our modern life. To truly appreciate the physics of semiconductors, it is very important to understand the fundamental properties of the charge carriers inside the materials, whether those particles are positive or negative, their speed under an applied electric field, and how densely they are packed into the material.
Physicist Edwin Hall found a way to determine those properties in 1879, when he discovered that a magnetic field will deflect the movement of electronic charges inside a conductor and that the amount of deflection can be measured as a voltage perpendicular to the flow of the charge. Decades after Hall’s discovery, researchers also recognized that they can measure the Hall effect with light via “photo-Hall experiments”. During such experiments, the light generates multiple carriers or electron–hole pairs in the semiconductors.
Unfortunately, the basic Hall effect only provided insights into the dominant charge carrier (or majority carrier). Researchers were unable to extract the properties of both carriers (the majority and minority carriers) simultaneously. The property information of both carriers is crucial for many applications that involve light such as solar cells and other optoelectronic devices.
In the photo-Hall experiment by the KAIST-IBM team, both carriers contribute to changes in conductivity and the Hall coefficient. The key insight comes from measuring the conductivity and Hall coefficient as a function of light intensity. Hidden in the trajectory of the conductivity, the Hall coefficient curve reveals crucial new information: the difference in the mobility of both carriers. As discussed in the paper, this relationship can be expressed elegantly as: Δµ = d (σ²H)/dσ
The research team solved for both majority and minority carrier mobility and density as a function of light intensity, naming the new technique Carrier-Resolved Photo Hall (CRPH) measurement. With known light illumination intensity, the carrier lifetime can be established in a similar way.
Beyond advances in theoretical understanding, advances in experimental techniques were also critical for enabling this breakthrough. The technique requires a clean Hall signal measurement, which can be challenging for materials where the Hall signal is weak due to low mobility or when extra unwanted signals are present, such as under strong light illumination.
The newly developed photo-Hall technique allows the extraction of an astonishing amount of information from semiconductors. In contrast to only three parameters obtained in the classic Hall measurements, this new technique yields up to seven parameters at every tested level of light intensity. These include the mobility of both the electron and hole; their carrier density under light; the recombination lifetime; and the diffusion lengths for electrons, holes, and ambipolar types. All of these can be repeated N times (i.e. the number of light intensity settings used in the experiment).
Professor Shin said, “This novel technology sheds new light on understanding the physical characteristics of semiconductor materials in great detail.” Dr. Gunawan added, “This will will help accelerate the development of next-generation semiconductor technology such as better solar cells, better optoelectronics devices, and new materials and devices for artificial intelligence technology.”
Profile:
Professor Byungha Shin
Department of Materials Science and Engineering
KAIST
byungha@kaist.ac.kr
http://energymatlab.kaist.ac.kr/
2019.11.18 View 16693 -
 Gallium-Based Solvating Agent Efficiently Analyzes Optically Active Alcohols
A KAIST research team has developed a gallium-based metal complex enabling the rapid chiral analysis of alcohols. A team working under Professor Hyunwoo Kim reported the efficient new alcohol analysis method using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in iScience.
Enantiopure chiral alcohols are ubiquitous in nature and widely utilized as pharmaceuticals. This importance of chirality in synthetic and medicinal chemistry has advanced the search for rapid and facile methods to determine the enantiomeric purities of compounds. To date, chiral analysis has been performed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with chiral columns.
Along with the HPLC technique, chiral analysis using NMR spectroscopy has gained tremendous attention as an alternative to traditionally employed chromatographic methods due to its simplicity and rapid detection for real-time measurement. However, this method carries drawbacks such as line-broadening, narrow substrate scope, and poor resolution. Thus, compared with popular methods of chromatographic analysis, NMR spectroscopy is infrequently used for chiral analysis.
In principle, a chiral solvating agent is additionally required for the NMR measurement of chiral alcohols to obtain two distinct signals. However, NMR analysis of chiral alcohols has been challenging due to weak binding interactions with chiral solvating agents. To overcome the intrinsic difficulty of relatively weak molecular interactions that are common for alcohols, many researchers have used multifunctional alcohols to enhance interactions with solvating agents.
Instead, the KAIST team successfully varied the physical properties of metal complexes to induce stronger interactions with alcohols rather than the strategy of using multifunctional analytes, in the hopes of developing a universal chiral solvating agent for alcohols. Compared to the current method of chiral analysis used in the pharmaceutical industry, alcohols that do not possess chromophores can also be directly analyzed with the gallium complexes.
Professor Kim said that this method could be a complementary chiral analysis technique at the industry level in the near future. He added that since the developed gallium complex can determine enantiomeric excess within minutes, it can be further utilized to monitor asymmetric synthesis. This feature will benefit a large number of researchers in the organic chemistry community, as well as the pharmaceutical industry.
(Figure: Schematic view of the in-situ direct 1H NMR chiral analysis.)
-Profile:
Professor Hyunwoo Kim
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
http://mdos.kaist.ac.kr
hwk34@kaist.ac.kr
For more on this article,
please go to https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci2019.07051
2019.11.14 View 13152
Gallium-Based Solvating Agent Efficiently Analyzes Optically Active Alcohols
A KAIST research team has developed a gallium-based metal complex enabling the rapid chiral analysis of alcohols. A team working under Professor Hyunwoo Kim reported the efficient new alcohol analysis method using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in iScience.
Enantiopure chiral alcohols are ubiquitous in nature and widely utilized as pharmaceuticals. This importance of chirality in synthetic and medicinal chemistry has advanced the search for rapid and facile methods to determine the enantiomeric purities of compounds. To date, chiral analysis has been performed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with chiral columns.
Along with the HPLC technique, chiral analysis using NMR spectroscopy has gained tremendous attention as an alternative to traditionally employed chromatographic methods due to its simplicity and rapid detection for real-time measurement. However, this method carries drawbacks such as line-broadening, narrow substrate scope, and poor resolution. Thus, compared with popular methods of chromatographic analysis, NMR spectroscopy is infrequently used for chiral analysis.
In principle, a chiral solvating agent is additionally required for the NMR measurement of chiral alcohols to obtain two distinct signals. However, NMR analysis of chiral alcohols has been challenging due to weak binding interactions with chiral solvating agents. To overcome the intrinsic difficulty of relatively weak molecular interactions that are common for alcohols, many researchers have used multifunctional alcohols to enhance interactions with solvating agents.
Instead, the KAIST team successfully varied the physical properties of metal complexes to induce stronger interactions with alcohols rather than the strategy of using multifunctional analytes, in the hopes of developing a universal chiral solvating agent for alcohols. Compared to the current method of chiral analysis used in the pharmaceutical industry, alcohols that do not possess chromophores can also be directly analyzed with the gallium complexes.
Professor Kim said that this method could be a complementary chiral analysis technique at the industry level in the near future. He added that since the developed gallium complex can determine enantiomeric excess within minutes, it can be further utilized to monitor asymmetric synthesis. This feature will benefit a large number of researchers in the organic chemistry community, as well as the pharmaceutical industry.
(Figure: Schematic view of the in-situ direct 1H NMR chiral analysis.)
-Profile:
Professor Hyunwoo Kim
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
http://mdos.kaist.ac.kr
hwk34@kaist.ac.kr
For more on this article,
please go to https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci2019.07051
2019.11.14 View 13152 -
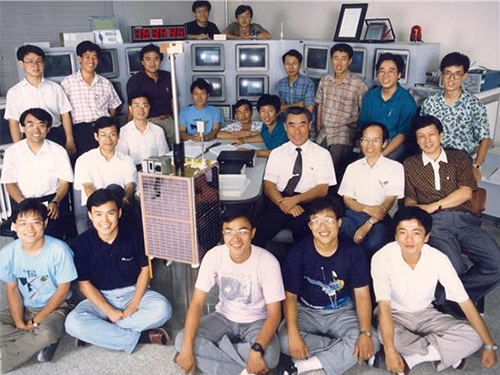 SaTReC, Birthplace of Korea’s First Satellite, Celebrates 30th Anniversary
< SaTReC researchers who developed Korea's first satellite, KITSAT-1 >
The Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, which launched the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1, celebrated 30 years in operation last week. A ceremony in honor of this milestone was held on campus on October 30. With the launching of KITSAT-1 in 1992, SaTReC paved the way for space research in Korea, and helped the nation achieve technological independence and strengthen competitiveness in the field.
The ceremony was attended by over 100 affiliates from academia and industry, including the family of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, the first director of SaTReC also known as the father of the first Korean satellite KITSAT-1 (nicknamed “Our Star” in Korean). His family members traveled all the way from the US to Korea for the event. A plaque of appreciation was posthumously awarded to the family of former Director Choi in memory of his pioneering Korean satellite research.
Right after the establishment of SaTReC in 1989, Dr.Choi dispatched five KAIST students to the University of Surrey in the UK to develop the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1 under a bilateral agreement for a joint research program.
KITSAT-1, completed in collaboration with Surrey researchers, was successfully launched from the Guiana Space Center in August 1992. Through this launch, Korea became the 22nd nation to own a satellite, and launched the domestically produced follow-up satellite KITSAT-2 in September 1993.
Since then, SaTReC has developed a total of nine satellites, including three in the KITSAT series in the 1990s as well as five STSATs and one Next-Generation Small Satellite in the 2000s. These satellites are still in operation today, thanks to SaTReC’s constant maintenance.
SaTReC is still contributing to the verification of core space technologies and Earth and space observation technologies using small satellites. It is also training specialized personnel in national space research and development.
Most significantly, STSAT-2C, also commonly known as the Naro Science Satellite, was launched on January 30, 2013 and served an important role in allowing the first Korean launch vehicle Naro-1 (KSLV-1) to enter into orbit.
SaTReC researchers are now working on developing a Next-Generation Small Satellite named NEXTSat-2 that boasts a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system developed with domestic technology. NEXTSat-2 will be launched in 2022 from Korean soil, carried by a Korean launch vehicle developed with local technology.
Director of SaTReC Sejin Kwon said, “We will follow the noble spirit of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, who dedicated his entire life to the nation’s satellite research and bolstered our commitment to the development of Korea’s future space technology.” He added, “We will pursue our dreams of space exploration with a sense of social responsibility to pay back to society the benefits reaped from space technology.”
The ceremony was followed by a Future Space Technology Workshop, where eight KAIST professors participated as speakers.
< Timeline of Korea's Satellite Research and Development >
(END)
2019.11.05 View 8285
SaTReC, Birthplace of Korea’s First Satellite, Celebrates 30th Anniversary
< SaTReC researchers who developed Korea's first satellite, KITSAT-1 >
The Satellite Technology Research Center (SaTReC) at KAIST, which launched the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1, celebrated 30 years in operation last week. A ceremony in honor of this milestone was held on campus on October 30. With the launching of KITSAT-1 in 1992, SaTReC paved the way for space research in Korea, and helped the nation achieve technological independence and strengthen competitiveness in the field.
The ceremony was attended by over 100 affiliates from academia and industry, including the family of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, the first director of SaTReC also known as the father of the first Korean satellite KITSAT-1 (nicknamed “Our Star” in Korean). His family members traveled all the way from the US to Korea for the event. A plaque of appreciation was posthumously awarded to the family of former Director Choi in memory of his pioneering Korean satellite research.
Right after the establishment of SaTReC in 1989, Dr.Choi dispatched five KAIST students to the University of Surrey in the UK to develop the Korea’s first satellite KITSAT-1 under a bilateral agreement for a joint research program.
KITSAT-1, completed in collaboration with Surrey researchers, was successfully launched from the Guiana Space Center in August 1992. Through this launch, Korea became the 22nd nation to own a satellite, and launched the domestically produced follow-up satellite KITSAT-2 in September 1993.
Since then, SaTReC has developed a total of nine satellites, including three in the KITSAT series in the 1990s as well as five STSATs and one Next-Generation Small Satellite in the 2000s. These satellites are still in operation today, thanks to SaTReC’s constant maintenance.
SaTReC is still contributing to the verification of core space technologies and Earth and space observation technologies using small satellites. It is also training specialized personnel in national space research and development.
Most significantly, STSAT-2C, also commonly known as the Naro Science Satellite, was launched on January 30, 2013 and served an important role in allowing the first Korean launch vehicle Naro-1 (KSLV-1) to enter into orbit.
SaTReC researchers are now working on developing a Next-Generation Small Satellite named NEXTSat-2 that boasts a Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) system developed with domestic technology. NEXTSat-2 will be launched in 2022 from Korean soil, carried by a Korean launch vehicle developed with local technology.
Director of SaTReC Sejin Kwon said, “We will follow the noble spirit of the late Dr. Soon-dal Choi, who dedicated his entire life to the nation’s satellite research and bolstered our commitment to the development of Korea’s future space technology.” He added, “We will pursue our dreams of space exploration with a sense of social responsibility to pay back to society the benefits reaped from space technology.”
The ceremony was followed by a Future Space Technology Workshop, where eight KAIST professors participated as speakers.
< Timeline of Korea's Satellite Research and Development >
(END)
2019.11.05 View 8285 -
 Object Identification and Interaction with a Smartphone Knock
(Professor Lee (far right) demonstrate 'Knocker' with his students.)
A KAIST team has featured a new technology, “Knocker”, which identifies objects and executes actions just by knocking on it with the smartphone. Software powered by machine learning of sounds, vibrations, and other reactions will perform the users’ directions.
What separates Knocker from existing technology is the sensor fusion of sound and motion. Previously, object identification used either computer vision technology with cameras or hardware such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags. These solutions all have their limitations. For computer vision technology, users need to take pictures of every item. Even worse, the technology will not work well in poor lighting situations. Using hardware leads to additional costs and labor burdens.
Knocker, on the other hand, can identify objects even in dark environments only with a smartphone, without requiring any specialized hardware or using a camera. Knocker utilizes the smartphone’s built-in sensors such as a microphone, an accelerometer, and a gyroscope to capture a unique set of responses generated when a smartphone is knocked against an object. Machine learning is used to analyze these responses and classify and identify objects.
The research team under Professor Sung-Ju Lee from the School of Computing confirmed the applicability of Knocker technology using 23 everyday objects such as books, laptop computers, water bottles, and bicycles. In noisy environments such as a busy café or on the side of a road, it achieved 83% identification accuracy. In a quiet indoor environment, the accuracy rose to 98%.
The team believes Knocker will open a new paradigm of object interaction. For instance, by knocking on an empty water bottle, a smartphone can automatically order new water bottles from a merchant app. When integrated with IoT devices, knocking on a bed’s headboard before going to sleep could turn off the lights and set an alarm. The team suggested and implemented 15 application cases in the paper, presented during the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2019) held in London last month.
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “This new technology does not require any specialized sensor or hardware. It simply uses the built-in sensors on smartphones and takes advantage of the power of machine learning. It’s a software solution that everyday smartphone users could immediately benefit from.” He continued, “This technology enables users to conveniently interact with their favorite objects.”
The research was supported in part by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure: An example knock on a bottle. Knocker identifies the object by analyzing a unique set of responses from the knock, and automatically launches a proper application or service.
2019.10.02 View 31433
Object Identification and Interaction with a Smartphone Knock
(Professor Lee (far right) demonstrate 'Knocker' with his students.)
A KAIST team has featured a new technology, “Knocker”, which identifies objects and executes actions just by knocking on it with the smartphone. Software powered by machine learning of sounds, vibrations, and other reactions will perform the users’ directions.
What separates Knocker from existing technology is the sensor fusion of sound and motion. Previously, object identification used either computer vision technology with cameras or hardware such as RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags. These solutions all have their limitations. For computer vision technology, users need to take pictures of every item. Even worse, the technology will not work well in poor lighting situations. Using hardware leads to additional costs and labor burdens.
Knocker, on the other hand, can identify objects even in dark environments only with a smartphone, without requiring any specialized hardware or using a camera. Knocker utilizes the smartphone’s built-in sensors such as a microphone, an accelerometer, and a gyroscope to capture a unique set of responses generated when a smartphone is knocked against an object. Machine learning is used to analyze these responses and classify and identify objects.
The research team under Professor Sung-Ju Lee from the School of Computing confirmed the applicability of Knocker technology using 23 everyday objects such as books, laptop computers, water bottles, and bicycles. In noisy environments such as a busy café or on the side of a road, it achieved 83% identification accuracy. In a quiet indoor environment, the accuracy rose to 98%.
The team believes Knocker will open a new paradigm of object interaction. For instance, by knocking on an empty water bottle, a smartphone can automatically order new water bottles from a merchant app. When integrated with IoT devices, knocking on a bed’s headboard before going to sleep could turn off the lights and set an alarm. The team suggested and implemented 15 application cases in the paper, presented during the 2019 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (UbiComp 2019) held in London last month.
Professor Sung-Ju Lee said, “This new technology does not require any specialized sensor or hardware. It simply uses the built-in sensors on smartphones and takes advantage of the power of machine learning. It’s a software solution that everyday smartphone users could immediately benefit from.” He continued, “This technology enables users to conveniently interact with their favorite objects.”
The research was supported in part by the Next-Generation Information Computing Development Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and an Institute for Information & Communications Technology Promotion (IITP) grant funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Figure: An example knock on a bottle. Knocker identifies the object by analyzing a unique set of responses from the knock, and automatically launches a proper application or service.
2019.10.02 View 31433 -
 School of Transdisciplinary Studies Aims to Attract New Talents
KAIST opened the School of Transdisciplinary Studies to foster ‘convergent talents’ who can create new knowledge through a transdisciplinary approach. The new department will officially start classes in the spring semester of 2020 while recruiting its first cohorts during the fall semester among current freshmen.
President Sung-Chul Shin, the Head of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies Jong Duk Kim, and other prominent members of KAIST’s administration celebrated the opening of the new department during a ceremony on September 18. Students who will declare their major this semester and many parents showed strong interests in this new department while attending the ceremony. They all toured the new facilities together and attended the special lecture sessions.
The School of Transdisciplinary Studies is designed to empower students to create new solutions to emerging complex technologies and rapidly evolving global issues. This is one of the education innovation initiatives under Vision 2031, the plan President Sung-Chul Shin has launched to nurture creative young convergent leaders, and the first single transdisciplinary department that will be introduced in a Korean university.
The new faculty aims to educate students who will have a deeper understanding of the humanities, scientific creativity, the ability to conceive new ideas, complex problem-solving skills, and global leadership. The curriculum boasts a strong foundation of basic science and humanities over six required courses in physics, chemistry, molecular biology, applied mathematics modeling, data structure, and economics. Then, students will explore their academic depth by choosing one of eight emerging fields. The eight concentration majors encompass data and AI, smart cities and media, healthcare, culture and media, management and startups, materials and matter, energy and environment, and machinery and precision. In their third and fourth years, students can customize their study course based on their career path and academic interest after consultation with a faculty mentor and an internship. Upon graduation, they will earn a bachelor’s degree in convergent science or a bachelor of convergent engineering degree. They may also elect to receive a bachelor’s degree in science or engineering.
“This faculty offers deep knowledge in basic science and humanities to help students explore their specialties more creatively. Specialties built upon strong theory and creative applicability will be the key to solving the global challenges in an era of volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity,” said Professor Kim, the head of the school, at the ceremony.
President Shin also stressed the importance of convergence education during his special lecture, saying, “We will continue to strive to foster new talents who will create new convergent knowledge in emerging technologies such as IoT, big data, 5G, and AI. By fostering such young convergent talents, we will take the lead in national development and work for the prosperity of humanity.”
(END)
2019.09.19 View 6525
School of Transdisciplinary Studies Aims to Attract New Talents
KAIST opened the School of Transdisciplinary Studies to foster ‘convergent talents’ who can create new knowledge through a transdisciplinary approach. The new department will officially start classes in the spring semester of 2020 while recruiting its first cohorts during the fall semester among current freshmen.
President Sung-Chul Shin, the Head of the School of Transdisciplinary Studies Jong Duk Kim, and other prominent members of KAIST’s administration celebrated the opening of the new department during a ceremony on September 18. Students who will declare their major this semester and many parents showed strong interests in this new department while attending the ceremony. They all toured the new facilities together and attended the special lecture sessions.
The School of Transdisciplinary Studies is designed to empower students to create new solutions to emerging complex technologies and rapidly evolving global issues. This is one of the education innovation initiatives under Vision 2031, the plan President Sung-Chul Shin has launched to nurture creative young convergent leaders, and the first single transdisciplinary department that will be introduced in a Korean university.
The new faculty aims to educate students who will have a deeper understanding of the humanities, scientific creativity, the ability to conceive new ideas, complex problem-solving skills, and global leadership. The curriculum boasts a strong foundation of basic science and humanities over six required courses in physics, chemistry, molecular biology, applied mathematics modeling, data structure, and economics. Then, students will explore their academic depth by choosing one of eight emerging fields. The eight concentration majors encompass data and AI, smart cities and media, healthcare, culture and media, management and startups, materials and matter, energy and environment, and machinery and precision. In their third and fourth years, students can customize their study course based on their career path and academic interest after consultation with a faculty mentor and an internship. Upon graduation, they will earn a bachelor’s degree in convergent science or a bachelor of convergent engineering degree. They may also elect to receive a bachelor’s degree in science or engineering.
“This faculty offers deep knowledge in basic science and humanities to help students explore their specialties more creatively. Specialties built upon strong theory and creative applicability will be the key to solving the global challenges in an era of volatility, uncertainty, complexity, and ambiguity,” said Professor Kim, the head of the school, at the ceremony.
President Shin also stressed the importance of convergence education during his special lecture, saying, “We will continue to strive to foster new talents who will create new convergent knowledge in emerging technologies such as IoT, big data, 5G, and AI. By fostering such young convergent talents, we will take the lead in national development and work for the prosperity of humanity.”
(END)
2019.09.19 View 6525 -
 Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 13074
Two More Cross-generation Collaborative Labs Open
< President Sung-Chul Shin (sixth from the left) and Professor Sun Chang Kim (seventh from the left) at the signboard ceremony of KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory >
KAIST opened two more cross-generation collaborative labs last month. KAIST BioDesigneering Laboratory headed by Professor Sun Chang Kim from the Department of Biological Sciences and Nanophotonics Laboratory led by Professor Yong-Hee Lee from the Department of Physics have been selected to receive 500 million KRW funding for five years.
A four-member selection committee including the former President of ETH Zürich Professor Emeritus Ralph Eichler and Professor Kwang-Soo Kim of Harvard Medical School conducted a three-month review and evaluation for this selection to be made. With these two new labs onboard, a total of six cross-generation collaborative labs will be operated on campus.
The operation of cross-generation collaborative labs has been in trial since March last year, as one of the KAIST’s Vision 2031 research innovation initiatives. This novel approach is to pair up senior and junior faculty members for sustaining research and academic achievements even after the senior researcher retires, so that the spectrum of knowledge and research competitiveness can be extended to future generations. The selected labs will be funded for five years, and the funding will be extended if necessary. KAIST will continue to select new labs every year.
One of this year’s selectees Professor Sun Chang Kim will be teamed up with Professor Byung-Kwan Cho from the same department and Professor Jung Kyoon Choi from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering to collaborate in the fields of synthetic biology, systems biology, and genetic engineering. This group mainly aims at designing and synthesizing optimal genomes that can efficiently manufacture protein drug and biomedical active materials. They will also strive to secure large amounts of high-functioning natural active substances, new adhesive antibacterial peptides, and eco-friendly ecological restoration materials. It is expected that collaboration between these three multigenerational professors will help innovate their bio-convergence technology and further strengthen their international competitiveness in the global bio-market.
Another world-renowned scholar Professor Yong-Hee Lee of photonic crystal laser study will be joined by Professor Minkyo Seo from the same department and Professor Hansuek Lee from the Graduate School of Nanoscience and Technology. They will explore the extreme limits of light-material interaction based on optical micro/nano resonators, with the goal of developing future nonlinear optoelectronic and quantum optical devices. The knowledge and technology newly gained from the research are expected to provide an important platform for a diverse range of fields from quantum communications to biophysics.
(END)
2019.09.06 View 13074 -
 FIRIC-EU JRC Joint Workshop on Smart Specialization
The Fourth Industrial Revolution Intelligence Center (FIRIC) at KAIST discussed ‘Smart Specialization’ for regional innovation and economic growth in the wake of the Fourth Industrial Revolution during the workshop with the EU Joint Research Center (EU-JRC) in Seville, Spain last week. The two sides also agreed to sign an MOU to expand mutual collaboration.
KAIST’s FIRIC was founded in cooperation with the World Economic Forum in July 2017 to carry out policy research for the promotion of science and technology-based inclusive growth and innovation and to lead related global efforts. The EU-JRC has committed to developing cohesive policies that aim to narrow regional gaps within the European Union. Founded in 1958 in Brussels, the EU-JRC has long been in charge of EU strategies for regional innovation based on emerging technologies.
The workshop also covered issues related to public-private partnerships and innovation clusters from the perspective of the EU and Asia, such as the global value chain and the implementation of industrial clusters policy amid the changes in the industrial ecosystem due to digitalization, automation, and the utilization of robotics during the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In addition, the session included discussions on inclusive growth and job market changes in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, addressing how Smart Specialization and the outcomes of the 4IR will shift the paradigm of current job and technology capabilities, as well as employment issues in many relevant industries. In particular, the actual case studies and their related policies and regulatory trends regarding the potential risks and ethical issues of artificial intelligence were introduced.
Regarding the financial services that utilize blockchain technologies and the establishment of public sector governance for such technologies, the participating experts noted difficulties in the diffusion of blockchain-based local currencies or public services, which call for a sophisticated analytical and practical framework for innovative and transparent governance.
Dr. Mark Boden, the Team Leader of the EU-JRC, introduced the EU’s initiatives to promote Smart Specialization, such as its policy process, governance design, vision sharing, and priority setting, with particular emphasis on targeted support for Smart Specialization in lagging regions. Professor So Young Kim, who is the dean of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy and FIRIC’s Deputy Director said, “KAIST’s global role regarding the Fourth Industrial Revolution will be expanded in the process of exploring and developing innovative models of technology-policy governance while working jointly with the EU-JRC.”
2019.08.02 View 8964
FIRIC-EU JRC Joint Workshop on Smart Specialization
The Fourth Industrial Revolution Intelligence Center (FIRIC) at KAIST discussed ‘Smart Specialization’ for regional innovation and economic growth in the wake of the Fourth Industrial Revolution during the workshop with the EU Joint Research Center (EU-JRC) in Seville, Spain last week. The two sides also agreed to sign an MOU to expand mutual collaboration.
KAIST’s FIRIC was founded in cooperation with the World Economic Forum in July 2017 to carry out policy research for the promotion of science and technology-based inclusive growth and innovation and to lead related global efforts. The EU-JRC has committed to developing cohesive policies that aim to narrow regional gaps within the European Union. Founded in 1958 in Brussels, the EU-JRC has long been in charge of EU strategies for regional innovation based on emerging technologies.
The workshop also covered issues related to public-private partnerships and innovation clusters from the perspective of the EU and Asia, such as the global value chain and the implementation of industrial clusters policy amid the changes in the industrial ecosystem due to digitalization, automation, and the utilization of robotics during the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
In addition, the session included discussions on inclusive growth and job market changes in the era of the Fourth Industrial Revolution, addressing how Smart Specialization and the outcomes of the 4IR will shift the paradigm of current job and technology capabilities, as well as employment issues in many relevant industries. In particular, the actual case studies and their related policies and regulatory trends regarding the potential risks and ethical issues of artificial intelligence were introduced.
Regarding the financial services that utilize blockchain technologies and the establishment of public sector governance for such technologies, the participating experts noted difficulties in the diffusion of blockchain-based local currencies or public services, which call for a sophisticated analytical and practical framework for innovative and transparent governance.
Dr. Mark Boden, the Team Leader of the EU-JRC, introduced the EU’s initiatives to promote Smart Specialization, such as its policy process, governance design, vision sharing, and priority setting, with particular emphasis on targeted support for Smart Specialization in lagging regions. Professor So Young Kim, who is the dean of the Graduate School of Science and Technology Policy and FIRIC’s Deputy Director said, “KAIST’s global role regarding the Fourth Industrial Revolution will be expanded in the process of exploring and developing innovative models of technology-policy governance while working jointly with the EU-JRC.”
2019.08.02 View 8964 -
 Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-Device Interaction
< Research Group of Professor Insik Shin (center) >
KAIST researchers have developed mobile software platform technology that allows a mobile application (app) to be executed simultaneously and more dynamically on multiple smart devices. Its high flexibility and broad applicability can help accelerate a shift from the current single-device paradigm to a multiple one, which enables users to utilize mobile apps in ways previously unthinkable.
Recent trends in mobile and IoT technologies in this era of 5G high-speed wireless communication have been hallmarked by the emergence of new display hardware and smart devices such as dual screens, foldable screens, smart watches, smart TVs, and smart cars. However, the current mobile app ecosystem is still confined to the conventional single-device paradigm in which users can employ only one screen on one device at a time. Due to this limitation, the real potential of multi-device environments has not been fully explored.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing, in collaboration with Professor Steve Ko’s group from the State University of New York at Buffalo, has developed mobile software platform technology named FLUID that can flexibly distribute the user interfaces (UIs) of an app to a number of other devices in real time without needing any modifications. The proposed technology provides single-device virtualization, and ensures that the interactions between the distributed UI elements across multiple devices remain intact.
This flexible multimodal interaction can be realized in diverse ubiquitous user experiences (UX), such as using live video steaming and chatting apps including YouTube, LiveMe, and AfreecaTV. FLUID can ensure that the video is not obscured by the chat window by distributing and displaying them separately on different devices respectively, which lets users enjoy the chat function while watching the video at the same time.
In addition, the UI for the destination input on a navigation app can be migrated into the passenger’s device with the help of FLUID, so that the destination can be easily and safely entered by the passenger while the driver is at the wheel.
FLUID can also support 5G multi-view apps – the latest service that allows sports or games to be viewed from various angles on a single device. With FLUID, the user can watch the event simultaneously from different viewpoints on multiple devices without switching between viewpoints on a single screen.
PhD candidate Sangeun Oh, who is the first author, and his team implemented the prototype of FLUID on the leading open-source mobile operating system, Android, and confirmed that it can successfully deliver the new UX to 20 existing legacy apps.
“This new technology can be applied to next-generation products from South Korean companies such as LG’s dual screen phone and Samsung’s foldable phone and is expected to embolden their competitiveness by giving them a head-start in the global market.” said Professor Shin.
This study will be presented at the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019) October 21 through 25 in Los Cabos, Mexico. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) (CNS-1350883 (CAREER) and CNS-1618531).
Figure 1. Live video streaming and chatting app scenario
Figure 2. Navigation app scenario
Figure 3. 5G multi-view app scenario
Publication: Sangeun Oh, Ahyeon Kim, Sunjae Lee, Kilho Lee, Dae R. Jeong, Steven Y. Ko, and Insik Shin. 2019. FLUID: Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-device Interaction. To be published in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019). ACM, New York, NY, USA. Article Number and DOI Name TBD.
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/lGO4GwH4enA
Profile: Prof. Insik Shin, MS, PhD
ishin@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/~ishin
Professor
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangeun Oh, PhD Candidate
ohsang1213@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/
PhD Candidate
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Steve Ko, PhD
stevko@buffalo.edu
https://nsr.cse.buffalo.edu/?page_id=272
Associate Professor
Networked Systems Research Group
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
State University of New York at Buffalo
http://www.buffalo.edu/ Buffalo 14260, USA
(END)
2019.07.20 View 42579
Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-Device Interaction
< Research Group of Professor Insik Shin (center) >
KAIST researchers have developed mobile software platform technology that allows a mobile application (app) to be executed simultaneously and more dynamically on multiple smart devices. Its high flexibility and broad applicability can help accelerate a shift from the current single-device paradigm to a multiple one, which enables users to utilize mobile apps in ways previously unthinkable.
Recent trends in mobile and IoT technologies in this era of 5G high-speed wireless communication have been hallmarked by the emergence of new display hardware and smart devices such as dual screens, foldable screens, smart watches, smart TVs, and smart cars. However, the current mobile app ecosystem is still confined to the conventional single-device paradigm in which users can employ only one screen on one device at a time. Due to this limitation, the real potential of multi-device environments has not been fully explored.
A KAIST research team led by Professor Insik Shin from the School of Computing, in collaboration with Professor Steve Ko’s group from the State University of New York at Buffalo, has developed mobile software platform technology named FLUID that can flexibly distribute the user interfaces (UIs) of an app to a number of other devices in real time without needing any modifications. The proposed technology provides single-device virtualization, and ensures that the interactions between the distributed UI elements across multiple devices remain intact.
This flexible multimodal interaction can be realized in diverse ubiquitous user experiences (UX), such as using live video steaming and chatting apps including YouTube, LiveMe, and AfreecaTV. FLUID can ensure that the video is not obscured by the chat window by distributing and displaying them separately on different devices respectively, which lets users enjoy the chat function while watching the video at the same time.
In addition, the UI for the destination input on a navigation app can be migrated into the passenger’s device with the help of FLUID, so that the destination can be easily and safely entered by the passenger while the driver is at the wheel.
FLUID can also support 5G multi-view apps – the latest service that allows sports or games to be viewed from various angles on a single device. With FLUID, the user can watch the event simultaneously from different viewpoints on multiple devices without switching between viewpoints on a single screen.
PhD candidate Sangeun Oh, who is the first author, and his team implemented the prototype of FLUID on the leading open-source mobile operating system, Android, and confirmed that it can successfully deliver the new UX to 20 existing legacy apps.
“This new technology can be applied to next-generation products from South Korean companies such as LG’s dual screen phone and Samsung’s foldable phone and is expected to embolden their competitiveness by giving them a head-start in the global market.” said Professor Shin.
This study will be presented at the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019) October 21 through 25 in Los Cabos, Mexico. The research was supported by the National Science Foundation (NSF) (CNS-1350883 (CAREER) and CNS-1618531).
Figure 1. Live video streaming and chatting app scenario
Figure 2. Navigation app scenario
Figure 3. 5G multi-view app scenario
Publication: Sangeun Oh, Ahyeon Kim, Sunjae Lee, Kilho Lee, Dae R. Jeong, Steven Y. Ko, and Insik Shin. 2019. FLUID: Flexible User Interface Distribution for Ubiquitous Multi-device Interaction. To be published in Proceedings of the 25th Annual International Conference on Mobile Computing and Networking (ACM MobiCom 2019). ACM, New York, NY, USA. Article Number and DOI Name TBD.
Video Material:
https://youtu.be/lGO4GwH4enA
Profile: Prof. Insik Shin, MS, PhD
ishin@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/~ishin
Professor
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Sangeun Oh, PhD Candidate
ohsang1213@kaist.ac.kr
https://cps.kaist.ac.kr/
PhD Candidate
Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS) Lab
School of Computing
Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST)
http://kaist.ac.kr Daejeon 34141, Korea
Profile: Prof. Steve Ko, PhD
stevko@buffalo.edu
https://nsr.cse.buffalo.edu/?page_id=272
Associate Professor
Networked Systems Research Group
Department of Computer Science and Engineering
State University of New York at Buffalo
http://www.buffalo.edu/ Buffalo 14260, USA
(END)
2019.07.20 View 42579 -
 Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 15245
Two Alumni Win the Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards
Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim (Left) and Distinguished Professor Sukbok Chang (Right)
<ⓒ Photo by MSIT and KOFST>
Distinguished KAIST Professor Sukbok Chang from the Department of Chemistry and Vice Chairman Ki-Nam Kim of Samsung Electronics were selected as the winners of the “2019 Korea Best Scientist and Technologist Awards” by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) and the Korean Federation of Science and Technology Societies (KOFST). The awards, which were first handed out in 2003, are the highest honor bestowed to the two most outstanding scientists in Korea every year, and this year’s awardees are of greater significance as they are both KAIST alumni.
Professor Chang was recognized for his pioneering achievements and lifetime contributions to the development of carbon-hydrogen activation strategies, especially for carbon-carbon, carbon-nitrogen, and carbon-oxygen formations. His research group has also been actively involved in the development of highly selective catalytic systems allowing the controlled defunctionalization of bio-derived platform substrates under mild conditions, and opening a new avenue for the utilization of biomass-derived platform chemicals. The results of his study have been introduced worldwide through many prestigious journals including Science, Nature Chemistry, and Nature Catalysis, making him one of the world's top 1% researchers by the number of references made to his papers by his peers over four consecutive years from 2015 to 2018.
Vice Chairman Kim, who received his M.E. degree from KAIST’s School of Electrical Engineering in 1983, has been credited with playing a leading role in the development of system semiconductors.
The awards were conferred on July 4 at the opening ceremony of the 2019 Korea Science and Technology Annual Meeting.
(END)
2019.07.09 View 15245