UCL
-
 KAIST Uses AI to Discover Optimal New Material for Removing Radioactive Iodine Contamination
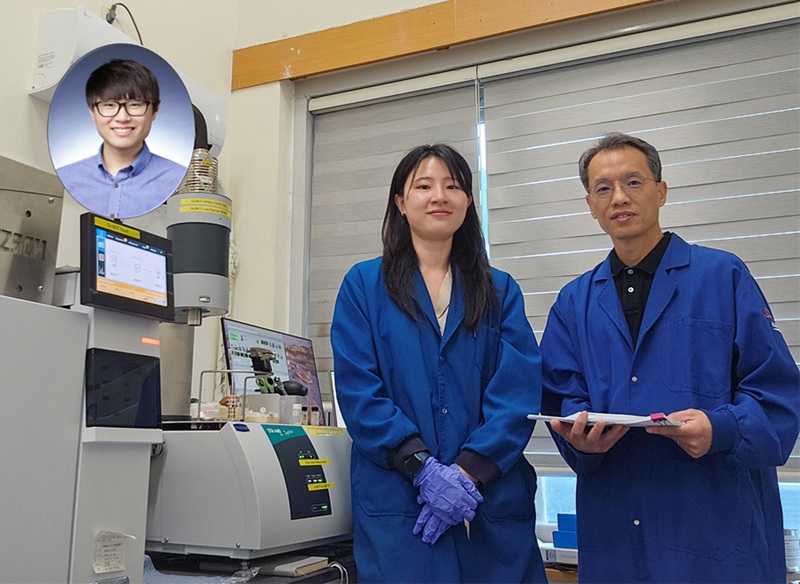
<(From the Right) Professor Ho Jin Ryu, Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, Dr. Sujeong Lee, a graduate of the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dr. Juhwan Noh of KRICT’s Digital Chemistry Research Center>
Managing radioactive waste is one of the core challenges in the use of nuclear energy. In particular, radioactive iodine poses serious environmental and health risks due to its long half-life (15.7 million years in the case of I-129), high mobility, and toxicity to living organisms. A Korean research team has successfully used artificial intelligence to discover a new material that can remove iodine for nuclear environmental remediation. The team plans to push forward with commercialization through various industry-academia collaborations, from iodine-adsorbing powders to contaminated water treatment filters.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 2of July that Professor Ho Jin Ryu's research team from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Juhwan Noh of the Digital Chemistry Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young Kook Lee), which operates under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Youngsik Kim), developed a technique using AI to discover new materials that effectively remove radioactive iodine contaminants.
Recent studies show that radioactive iodine primarily exists in aqueous environments in the form of iodate (IO₃⁻). However, existing silver-based adsorbents have weak chemical adsorption strength for iodate, making them inefficient. Therefore, it is imperative to develop new adsorbent materials that can effectively remove iodate.
Professor Ho Jin Ryu’s team used a machine learning-based experimental strategy to identify optimal iodate adsorbents among compounds called Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs), which contain various metal elements.
The multi-metal LDH developed in this study – Cu₃(CrFeAl), based on copper, chromium, iron, and aluminum—showed exceptional adsorption performance, removing over 90% of iodate. This achievement was made possible by efficiently exploring a vast compositional space using AI-driven active learning, which would be difficult to search through conventional trial-and-error experiments.
<Picture2. Concept of Developed AI-Based Technology for Exploring New Materials for Radioactive Contamination Removal>
The research team focused on the fact that LDHs, like high-entropy materials, can incorporate a wide range of metal compositions and possess structures favorable for anion adsorption. However, due to the overwhelming number of possible metal combinations in multi-metal LDHs, identifying the optimal composition through traditional experimental methods has been nearly impossible.
To overcome this, the team employed AI (machine learning). Starting with experimental data from 24 binary and 96 ternary LDH compositions, they expanded their search to include quaternary and quinary candidates. As a result, they were able to discover the optimal material for iodate removal by testing only 16% of the total candidate materials.
Professor Ho Jin Ryu stated, “This study shows the potential of using artificial intelligence to efficiently identify radioactive decontamination materials from a vast pool of new material candidates, which is expected to accelerate research for developing new materials for nuclear environmental cleanup.”
The research team has filed a domestic patent application for the developed powder technology and is currently proceeding with an international patent application. They plan to enhance the material’s performance under various conditions and pursue commercialization through industry-academia cooperation in the development of filters for treating contaminated water.
Dr. Sujeong Lee, a graduate of the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dr. Juhwan Noh of KRICT’s Digital Chemistry Research Center, participated as the co-first authors of the study. The results were published online on May 26 in the internationally renowned environmental publication Journal of Hazardous Materials.
※ Paper title: Discovery of multi-metal-layered double hydroxides for decontamination of iodate by machine learning-assisted experiments ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138735
This research was supported by the Nuclear Energy Research Infrastructure Program and the Nano-Materials Technology Development Program funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.07.03 View 1212
KAIST Uses AI to Discover Optimal New Material for Removing Radioactive Iodine Contamination
<(From the Right) Professor Ho Jin Ryu, Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, Dr. Sujeong Lee, a graduate of the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dr. Juhwan Noh of KRICT’s Digital Chemistry Research Center>
Managing radioactive waste is one of the core challenges in the use of nuclear energy. In particular, radioactive iodine poses serious environmental and health risks due to its long half-life (15.7 million years in the case of I-129), high mobility, and toxicity to living organisms. A Korean research team has successfully used artificial intelligence to discover a new material that can remove iodine for nuclear environmental remediation. The team plans to push forward with commercialization through various industry-academia collaborations, from iodine-adsorbing powders to contaminated water treatment filters.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 2of July that Professor Ho Jin Ryu's research team from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering, in collaboration with Dr. Juhwan Noh of the Digital Chemistry Research Center at the Korea Research Institute of Chemical Technology (KRICT, President Young Kook Lee), which operates under the National Research Council of Science & Technology (NST, Chairman Youngsik Kim), developed a technique using AI to discover new materials that effectively remove radioactive iodine contaminants.
Recent studies show that radioactive iodine primarily exists in aqueous environments in the form of iodate (IO₃⁻). However, existing silver-based adsorbents have weak chemical adsorption strength for iodate, making them inefficient. Therefore, it is imperative to develop new adsorbent materials that can effectively remove iodate.
Professor Ho Jin Ryu’s team used a machine learning-based experimental strategy to identify optimal iodate adsorbents among compounds called Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs), which contain various metal elements.
The multi-metal LDH developed in this study – Cu₃(CrFeAl), based on copper, chromium, iron, and aluminum—showed exceptional adsorption performance, removing over 90% of iodate. This achievement was made possible by efficiently exploring a vast compositional space using AI-driven active learning, which would be difficult to search through conventional trial-and-error experiments.
<Picture2. Concept of Developed AI-Based Technology for Exploring New Materials for Radioactive Contamination Removal>
The research team focused on the fact that LDHs, like high-entropy materials, can incorporate a wide range of metal compositions and possess structures favorable for anion adsorption. However, due to the overwhelming number of possible metal combinations in multi-metal LDHs, identifying the optimal composition through traditional experimental methods has been nearly impossible.
To overcome this, the team employed AI (machine learning). Starting with experimental data from 24 binary and 96 ternary LDH compositions, they expanded their search to include quaternary and quinary candidates. As a result, they were able to discover the optimal material for iodate removal by testing only 16% of the total candidate materials.
Professor Ho Jin Ryu stated, “This study shows the potential of using artificial intelligence to efficiently identify radioactive decontamination materials from a vast pool of new material candidates, which is expected to accelerate research for developing new materials for nuclear environmental cleanup.”
The research team has filed a domestic patent application for the developed powder technology and is currently proceeding with an international patent application. They plan to enhance the material’s performance under various conditions and pursue commercialization through industry-academia cooperation in the development of filters for treating contaminated water.
Dr. Sujeong Lee, a graduate of the KAIST Department of Materials Science and Engineering, and Dr. Juhwan Noh of KRICT’s Digital Chemistry Research Center, participated as the co-first authors of the study. The results were published online on May 26 in the internationally renowned environmental publication Journal of Hazardous Materials.
※ Paper title: Discovery of multi-metal-layered double hydroxides for decontamination of iodate by machine learning-assisted experiments ※ DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2025.138735
This research was supported by the Nuclear Energy Research Infrastructure Program and the Nano-Materials Technology Development Program funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea.
2025.07.03 View 1212 -
 Simultaneous Analysis of 21 Chemical Reactions... AI to Transform New Drug Development
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hyunwoo Kim and students Donghun Kim and Gyeongseon Choi in the Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program of the Department of Chemistry >
Thalidomide, a drug once used to alleviate morning sickness in pregnant women, exhibits distinct properties due to its optical isomers* in the body: one isomer has a sedative effect, while the other causes severe side effects like birth defects. As this example illustrates, precise organic synthesis techniques, which selectively synthesize only the desired optical isomer, are crucial in new drug development. Overcoming the traditional methods that struggled with simultaneously analyzing multiple reactants, our research team has developed the world's first technology to precisely analyze 21 types of reactants simultaneously. This breakthrough is expected to make a significant contribution to new drug development utilizing AI and robots.
*Optical Isomers: A pair of molecules with the same chemical formula that are mirror images of each other and cannot be superimposed due to their asymmetric structure. This is analogous to a left and right hand, which are similar in form but cannot be perfectly overlaid.
KAIST's Professor Hyunwoo Kim's research team in the Department of Chemistry announced on the 16th that they have developed an innovative optical isomer analysis technology suitable for the era of AI-driven autonomous synthesis*. This research is the world's first technology to precisely analyze asymmetric catalytic reactions involving multiple reactants simultaneously using high-resolution fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (19F NMR). It is expected to make groundbreaking contributions to various fields, including new drug development and catalyst optimization.
*AI-driven Autonomous Synthesis: An advanced technology that automates and optimizes chemical substance synthesis processes using artificial intelligence (AI). It is gaining attention as a core element for realizing automated and intelligent research environments in future laboratories. AI predicts and adjusts experimental conditions, interprets results, and designs subsequent experiments independently, minimizing human intervention in repetitive experiments and significantly increasing research efficiency and innovativeness.
Currently, while autonomous synthesis systems can automate everything from reaction design to execution, reaction analysis still relies on individual processing using traditional equipment. This leads to slower speeds and bottlenecks, making it unsuitable for high-speed repetitive experiments.
Furthermore, multi-substrate simultaneous screening techniques proposed in the 1990s garnered attention as a strategy to maximize reaction analysis efficiency. However, limitations of existing chromatography-based analysis methods restricted the number of applicable substrates. In asymmetric synthesis reactions, which selectively synthesize only the desired optical isomer, simultaneously analyzing more than 10 types of substrates was nearly impossible.
< Figure 1. Conventional organic reaction evaluation methods follow a process of deriving optimal reaction conditions using a single substrate, then expanding the substrate scope one by one under those conditions, leaving potential reaction areas unexplored. To overcome this, high-throughput screening is introduced to broadly explore catalyst reactivity for various substrates. When combined with multi-substrate screening, this approach allows for a much broader and more systematic understanding of reaction scope and trends. >
To overcome these limitations, the research team developed a 19F NMR-based multi-substrate simultaneous screening technology. This method involves performing asymmetric catalytic reactions with multiple reactants in a single reaction vessel, introducing a fluorine functional group into the products, and then applying their self-developed chiral cobalt reagent to clearly quantify all optical isomers using 19F NMR.
Utilizing the excellent resolution and sensitivity of 19F NMR, the research team successfully performed asymmetric synthesis reactions of 21 substrates simultaneously in a single reaction vessel and quantitatively measured the product yield and optical isomer ratio without any separate purification steps.
Professor Hyunwoo Kim stated, "While anyone can perform asymmetric synthesis reactions with multiple substrates in one reactor, accurately analyzing all the products has been a challenging problem to solve until now. We expect that achieving world-class multi-substrate screening analysis technology will greatly contribute to enhancing the analytical capabilities of AI-driven autonomous synthesis platforms."
< Figure 2. A method for analyzing multi-substrate asymmetric catalytic reactions, where different substrates react simultaneously in a single reactor, using fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance has been implemented. By utilizing the characteristics of fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance, which has a clean background signal and a wide chemical shift range, the reactivity of each substrate can be quantitatively analyzed. It is also shown that the optical activity of all reactants can be simultaneously measured using a cobalt metal complex. >
He further added, "This research provides a technology that can rapidly verify the efficiency and selectivity of asymmetric catalytic reactions essential for new drug development, and it is expected to be utilized as a core analytical tool for AI-driven autonomous research."
< Figure 3. It can be seen that in a multi-substrate reductive amination reaction using a total of 21 substrates, the yield and optical activity of the reactants according to the catalyst system were simultaneously measured using a fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance-based analysis platform. The yield of each reactant is indicated by color saturation, and the optical activity by numbers. >
Donghun Kim (first author, Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program) and Gyeongseon Choi (second author, Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program) from the KAIST Department of Chemistry participated in this research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on May 27, 2025.※ Paper Title: One-pot Multisubstrate Screening for Asymmetric Catalysis Enabled by 19F NMR-based Simultaneous Chiral Analysis※ DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03446
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-Career Researcher Program, the Asymmetric Catalytic Reaction Design Center, and the KAIST KC30 Project.
< Figure 4. Conceptual diagram of performing multi-substrate screening reactions and utilizing fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. >
2025.06.16 View 2763
Simultaneous Analysis of 21 Chemical Reactions... AI to Transform New Drug Development
< Photo 1. (From left) Professor Hyunwoo Kim and students Donghun Kim and Gyeongseon Choi in the Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program of the Department of Chemistry >
Thalidomide, a drug once used to alleviate morning sickness in pregnant women, exhibits distinct properties due to its optical isomers* in the body: one isomer has a sedative effect, while the other causes severe side effects like birth defects. As this example illustrates, precise organic synthesis techniques, which selectively synthesize only the desired optical isomer, are crucial in new drug development. Overcoming the traditional methods that struggled with simultaneously analyzing multiple reactants, our research team has developed the world's first technology to precisely analyze 21 types of reactants simultaneously. This breakthrough is expected to make a significant contribution to new drug development utilizing AI and robots.
*Optical Isomers: A pair of molecules with the same chemical formula that are mirror images of each other and cannot be superimposed due to their asymmetric structure. This is analogous to a left and right hand, which are similar in form but cannot be perfectly overlaid.
KAIST's Professor Hyunwoo Kim's research team in the Department of Chemistry announced on the 16th that they have developed an innovative optical isomer analysis technology suitable for the era of AI-driven autonomous synthesis*. This research is the world's first technology to precisely analyze asymmetric catalytic reactions involving multiple reactants simultaneously using high-resolution fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (19F NMR). It is expected to make groundbreaking contributions to various fields, including new drug development and catalyst optimization.
*AI-driven Autonomous Synthesis: An advanced technology that automates and optimizes chemical substance synthesis processes using artificial intelligence (AI). It is gaining attention as a core element for realizing automated and intelligent research environments in future laboratories. AI predicts and adjusts experimental conditions, interprets results, and designs subsequent experiments independently, minimizing human intervention in repetitive experiments and significantly increasing research efficiency and innovativeness.
Currently, while autonomous synthesis systems can automate everything from reaction design to execution, reaction analysis still relies on individual processing using traditional equipment. This leads to slower speeds and bottlenecks, making it unsuitable for high-speed repetitive experiments.
Furthermore, multi-substrate simultaneous screening techniques proposed in the 1990s garnered attention as a strategy to maximize reaction analysis efficiency. However, limitations of existing chromatography-based analysis methods restricted the number of applicable substrates. In asymmetric synthesis reactions, which selectively synthesize only the desired optical isomer, simultaneously analyzing more than 10 types of substrates was nearly impossible.
< Figure 1. Conventional organic reaction evaluation methods follow a process of deriving optimal reaction conditions using a single substrate, then expanding the substrate scope one by one under those conditions, leaving potential reaction areas unexplored. To overcome this, high-throughput screening is introduced to broadly explore catalyst reactivity for various substrates. When combined with multi-substrate screening, this approach allows for a much broader and more systematic understanding of reaction scope and trends. >
To overcome these limitations, the research team developed a 19F NMR-based multi-substrate simultaneous screening technology. This method involves performing asymmetric catalytic reactions with multiple reactants in a single reaction vessel, introducing a fluorine functional group into the products, and then applying their self-developed chiral cobalt reagent to clearly quantify all optical isomers using 19F NMR.
Utilizing the excellent resolution and sensitivity of 19F NMR, the research team successfully performed asymmetric synthesis reactions of 21 substrates simultaneously in a single reaction vessel and quantitatively measured the product yield and optical isomer ratio without any separate purification steps.
Professor Hyunwoo Kim stated, "While anyone can perform asymmetric synthesis reactions with multiple substrates in one reactor, accurately analyzing all the products has been a challenging problem to solve until now. We expect that achieving world-class multi-substrate screening analysis technology will greatly contribute to enhancing the analytical capabilities of AI-driven autonomous synthesis platforms."
< Figure 2. A method for analyzing multi-substrate asymmetric catalytic reactions, where different substrates react simultaneously in a single reactor, using fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance has been implemented. By utilizing the characteristics of fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance, which has a clean background signal and a wide chemical shift range, the reactivity of each substrate can be quantitatively analyzed. It is also shown that the optical activity of all reactants can be simultaneously measured using a cobalt metal complex. >
He further added, "This research provides a technology that can rapidly verify the efficiency and selectivity of asymmetric catalytic reactions essential for new drug development, and it is expected to be utilized as a core analytical tool for AI-driven autonomous research."
< Figure 3. It can be seen that in a multi-substrate reductive amination reaction using a total of 21 substrates, the yield and optical activity of the reactants according to the catalyst system were simultaneously measured using a fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance-based analysis platform. The yield of each reactant is indicated by color saturation, and the optical activity by numbers. >
Donghun Kim (first author, Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program) and Gyeongseon Choi (second author, Integrated M.S./Ph.D. program) from the KAIST Department of Chemistry participated in this research. The study was published online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society on May 27, 2025.※ Paper Title: One-pot Multisubstrate Screening for Asymmetric Catalysis Enabled by 19F NMR-based Simultaneous Chiral Analysis※ DOI: 10.1021/jacs.5c03446
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-Career Researcher Program, the Asymmetric Catalytic Reaction Design Center, and the KAIST KC30 Project.
< Figure 4. Conceptual diagram of performing multi-substrate screening reactions and utilizing fluorine nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. >
2025.06.16 View 2763 -
 Decoding Fear: KAIST Identifies An Affective Brain Circuit Crucial for Fear Memory Formation by Non-nociceptive Threat Stimulus
Fear memories can form in the brain following exposure to threatening situations such as natural disasters, accidents, or violence. When these memories become excessive or distorted, they can lead to severe mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying fear memory formation triggered by affective pain rather than direct physical pain have remained largely unexplored – until now.
A KAIST research team has identified, for the first time, a brain circuit specifically responsible for forming fear memories in the absence of physical pain, marking a significant advance in understanding how psychological distress is processed and drives fear memory formation in the brain. This discovery opens the door to the development of targeted treatments for trauma-related conditions by addressing the underlying neural pathways.
< Photo 1. (from left) Professor Jin-Hee Han, Dr. Junho Han and Ph.D. Candidate Boin Suh of the Department of Biological Sciences >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 15th that the research team led by Professor Jin-Hee Han in the Department of Biological Sciences has identified the pIC-PBN circuit*, a key neural pathway involved in forming fear memories triggered by psychological threats in the absence of sensory pain. This groundbreaking work was conducted through experiments with mice.*pIC–PBN circuit: A newly identified descending neural pathway from the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to the parabrachial nucleus (PBN), specialized for transmitting psychological threat information.
Traditionally, the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) has been recognized as a critical part of the ascending pain pathway, receiving pain signals from the spinal cord. However, this study reveals a previously unknown role for the PBN in processing fear induced by non-painful psychological stimuli, fundamentally changing our understanding of its function in the brain.
This work is considered the first experimental evidence that 'emotional distress' and 'physical pain' are processed through different neural circuits to form fear memories, making it a significant contribution to the field of neuroscience. It clearly demonstrates the existence of a dedicated pathway (pIC-PBN) for transmitting emotional distress.
The study's first author, Dr. Junho Han, shared the personal motivation behind this research: “Our dog, Lego, is afraid of motorcycles. He never actually crashed into one, but ever since having a traumatizing event of having a motorbike almost run into him, just hearing the sound now triggers a fearful response. Humans react similarly – even if you didn’t have a personal experience of being involved in an accident, a near-miss or exposure to alarming media can create lasting fear memories, which may eventually lead to PTSD.”
He continued, “Until now, fear memory research has mainly relied on experimental models involving physical pain. However, much of real-world human fears arise from psychological threats, rather than from direct physical harm. Despite this, little was known about the brain circuits responsible for processing these psychological threats that can drive fear memory formation.”
To investigate this, the research team developed a novel fear conditioning model that utilizes visual threat stimuli instead of electrical shocks. In this model, mice were exposed to a rapidly expanding visual disk on a ceiling screen, simulating the threat of an approaching predator. This approach allowed the team to demonstrate that fear memories can form in response to a non-nociceptive, psychological threat alone, without the need for physical pain.
< Figure 1. Artificial activation of the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) neural circuit induces anxiety-like behaviors and fear memory formation in mice. >
Using advanced chemogenetic and optogenetic techniques, the team precisely controlled neuronal activity, revealing that the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) is essential to form fear memories in response to visual threats. They further traced the origin of these signals to the posterior insular cortex (pIC), a region known to process negative emotions and pain, confirming a direct connection between the two areas.
The study also showed that inhibiting the pIC–PBN circuit significantly reduced fear memory formation in response to visual threats, without affecting innate fear responses or physical pain-based learning. Conversely, artificially activating this circuit alone was sufficient to drive fear memory formation, confirming its role as a key pathway for processing psychological threat information.
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram of brain neural circuits transmitting emotional & physical pain threat signals. Visual threat stimuli do not involve physical pain but can create an anxious state and form fear memory through the affective pain signaling pathway. >
Professor Jin-Hee Han commented, “This study lays an important foundation for understanding how emotional distress-based mental disorders, such as PTSD, panic disorder, and anxiety disorder, develop, and opens new possibilities for targeted treatment approaches.”
The findings, authored by Dr. Junho Han (first author), Ph.D. candidate Boin Suh (second author), and Dr. Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author) of the Department of Biological Sciences, were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 9, 2025.※ Paper Title: A top-down insular cortex circuit crucial for non-nociceptive fear learning. Science Advances (https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.14.618356)※ Author Information: Junho Han (first author), Boin Suh (second author), and Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author)
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022M3E5E8081183 and NRF-2017M3C7A1031322).
2025.05.15 View 4289
Decoding Fear: KAIST Identifies An Affective Brain Circuit Crucial for Fear Memory Formation by Non-nociceptive Threat Stimulus
Fear memories can form in the brain following exposure to threatening situations such as natural disasters, accidents, or violence. When these memories become excessive or distorted, they can lead to severe mental health disorders, including post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), anxiety disorders, and depression. However, the mechanisms underlying fear memory formation triggered by affective pain rather than direct physical pain have remained largely unexplored – until now.
A KAIST research team has identified, for the first time, a brain circuit specifically responsible for forming fear memories in the absence of physical pain, marking a significant advance in understanding how psychological distress is processed and drives fear memory formation in the brain. This discovery opens the door to the development of targeted treatments for trauma-related conditions by addressing the underlying neural pathways.
< Photo 1. (from left) Professor Jin-Hee Han, Dr. Junho Han and Ph.D. Candidate Boin Suh of the Department of Biological Sciences >
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 15th that the research team led by Professor Jin-Hee Han in the Department of Biological Sciences has identified the pIC-PBN circuit*, a key neural pathway involved in forming fear memories triggered by psychological threats in the absence of sensory pain. This groundbreaking work was conducted through experiments with mice.*pIC–PBN circuit: A newly identified descending neural pathway from the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to the parabrachial nucleus (PBN), specialized for transmitting psychological threat information.
Traditionally, the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) has been recognized as a critical part of the ascending pain pathway, receiving pain signals from the spinal cord. However, this study reveals a previously unknown role for the PBN in processing fear induced by non-painful psychological stimuli, fundamentally changing our understanding of its function in the brain.
This work is considered the first experimental evidence that 'emotional distress' and 'physical pain' are processed through different neural circuits to form fear memories, making it a significant contribution to the field of neuroscience. It clearly demonstrates the existence of a dedicated pathway (pIC-PBN) for transmitting emotional distress.
The study's first author, Dr. Junho Han, shared the personal motivation behind this research: “Our dog, Lego, is afraid of motorcycles. He never actually crashed into one, but ever since having a traumatizing event of having a motorbike almost run into him, just hearing the sound now triggers a fearful response. Humans react similarly – even if you didn’t have a personal experience of being involved in an accident, a near-miss or exposure to alarming media can create lasting fear memories, which may eventually lead to PTSD.”
He continued, “Until now, fear memory research has mainly relied on experimental models involving physical pain. However, much of real-world human fears arise from psychological threats, rather than from direct physical harm. Despite this, little was known about the brain circuits responsible for processing these psychological threats that can drive fear memory formation.”
To investigate this, the research team developed a novel fear conditioning model that utilizes visual threat stimuli instead of electrical shocks. In this model, mice were exposed to a rapidly expanding visual disk on a ceiling screen, simulating the threat of an approaching predator. This approach allowed the team to demonstrate that fear memories can form in response to a non-nociceptive, psychological threat alone, without the need for physical pain.
< Figure 1. Artificial activation of the posterior insular cortex (pIC) to lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) neural circuit induces anxiety-like behaviors and fear memory formation in mice. >
Using advanced chemogenetic and optogenetic techniques, the team precisely controlled neuronal activity, revealing that the lateral parabrachial nucleus (PBN) is essential to form fear memories in response to visual threats. They further traced the origin of these signals to the posterior insular cortex (pIC), a region known to process negative emotions and pain, confirming a direct connection between the two areas.
The study also showed that inhibiting the pIC–PBN circuit significantly reduced fear memory formation in response to visual threats, without affecting innate fear responses or physical pain-based learning. Conversely, artificially activating this circuit alone was sufficient to drive fear memory formation, confirming its role as a key pathway for processing psychological threat information.
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram of brain neural circuits transmitting emotional & physical pain threat signals. Visual threat stimuli do not involve physical pain but can create an anxious state and form fear memory through the affective pain signaling pathway. >
Professor Jin-Hee Han commented, “This study lays an important foundation for understanding how emotional distress-based mental disorders, such as PTSD, panic disorder, and anxiety disorder, develop, and opens new possibilities for targeted treatment approaches.”
The findings, authored by Dr. Junho Han (first author), Ph.D. candidate Boin Suh (second author), and Dr. Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author) of the Department of Biological Sciences, were published online in the international journal Science Advances on May 9, 2025.※ Paper Title: A top-down insular cortex circuit crucial for non-nociceptive fear learning. Science Advances (https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.10.14.618356)※ Author Information: Junho Han (first author), Boin Suh (second author), and Jin-Hee Han (corresponding author)
This research was supported by grants from the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF-2022M3E5E8081183 and NRF-2017M3C7A1031322).
2025.05.15 View 4289 -
 KAIST's Pioneering VR Precision Technology & Choreography Tool Receive Spotlights at CHI 2025
Accurate pointing in virtual spaces is essential for seamless interaction. If pointing is not precise, selecting the desired object becomes challenging, breaking user immersion and reducing overall experience quality. KAIST researchers have developed a technology that offers a vivid, lifelike experience in virtual space, alongside a new tool that assists choreographers throughout the creative process.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 13th that a research team led by Professor Sang Ho Yoon of the Graduate School of Culture Technology, in collaboration with Professor Yang Zhang of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), has developed the ‘T2IRay’ technology and the ‘ChoreoCraft’ platform, which enables choreographers to work more freely and creatively in virtual reality. These technologies received two Honorable Mention awards, recognizing the top 5% of papers, at CHI 2025*, the best international conference in the field of human-computer interaction, hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) from April 25 to May 1.
< (From left) PhD candidates Jina Kim and Kyungeun Jung along with Master's candidate, Hyunyoung Han and Professor Sang Ho Yoon of KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology and Professor Yang Zhang (top) of UCLA >
T2IRay: Enabling Virtual Input with Precision
T2IRay introduces a novel input method that allows for precise object pointing in virtual environments by expanding traditional thumb-to-index gestures. This approach overcomes previous limitations, such as interruptions or reduced accuracy due to changes in hand position or orientation.
The technology uses a local coordinate system based on finger relationships, ensuring continuous input even as hand positions shift. It accurately captures subtle thumb movements within this coordinate system, integrating natural head movements to allow fluid, intuitive control across a wide range.
< Figure 1. T2IRay framework utilizing the delicate movements of the thumb and index fingers for AR/VR pointing >
Professor Sang Ho Yoon explained, “T2IRay can significantly enhance the user experience in AR/VR by enabling smooth, stable control even when the user’s hands are in motion.”
This study, led by first author Jina Kim, was supported by the Excellent New Researcher Support Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT, as well as the University ICT Research Center (ITRC) Support Project of the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP).
▴ Paper title: T2IRay: Design of Thumb-to-Index Based Indirect Pointing for Continuous and Robust AR/VR Input▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713442
▴ T2IRay demo video: https://youtu.be/ElJlcJbkJPY
ChoreoCraft: Creativity Support through VR for Choreographers
In addition, Professor Yoon’s team developed ‘ChoreoCraft,’ a virtual reality tool designed to support choreographers by addressing the unique challenges they face, such as memorizing complex movements, overcoming creative blocks, and managing subjective feedback.
ChoreoCraft reduces reliance on memory by allowing choreographers to save and refine movements directly within a VR space, using a motion-capture avatar for real-time interaction. It also enhances creativity by suggesting movements that naturally fit with prior choreography and musical elements. Furthermore, the system provides quantitative feedback by analyzing kinematic factors like motion stability and engagement, helping choreographers make data-driven creative decisions.
< Figure 2. ChoreoCraft's approaches to encourage creative process >
Professor Yoon noted, “ChoreoCraft is a tool designed to address the core challenges faced by choreographers, enhancing both creativity and efficiency. In user tests with professional choreographers, it received high marks for its ability to spark creative ideas and provide valuable quantitative feedback.”
This research was conducted in collaboration with doctoral candidate Kyungeun Jung and master’s candidate Hyunyoung Han, alongside the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and One Million Co., Ltd. (CEO Hye-rang Kim), with support from the Cultural and Arts Immersive Service Development Project by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism.
▴ Paper title: ChoreoCraft: In-situ Crafting of Choreography in Virtual Reality through Creativity Support Tools▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3714220
▴ ChoreoCraft demo video: https://youtu.be/Ms1fwiSBjjw
*CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems): The premier international conference on human-computer interaction, organized by the ACM, was held this year from April 25 to May 1, 2025.
2025.05.13 View 5120
KAIST's Pioneering VR Precision Technology & Choreography Tool Receive Spotlights at CHI 2025
Accurate pointing in virtual spaces is essential for seamless interaction. If pointing is not precise, selecting the desired object becomes challenging, breaking user immersion and reducing overall experience quality. KAIST researchers have developed a technology that offers a vivid, lifelike experience in virtual space, alongside a new tool that assists choreographers throughout the creative process.
KAIST (President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on May 13th that a research team led by Professor Sang Ho Yoon of the Graduate School of Culture Technology, in collaboration with Professor Yang Zhang of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), has developed the ‘T2IRay’ technology and the ‘ChoreoCraft’ platform, which enables choreographers to work more freely and creatively in virtual reality. These technologies received two Honorable Mention awards, recognizing the top 5% of papers, at CHI 2025*, the best international conference in the field of human-computer interaction, hosted by the Association for Computing Machinery (ACM) from April 25 to May 1.
< (From left) PhD candidates Jina Kim and Kyungeun Jung along with Master's candidate, Hyunyoung Han and Professor Sang Ho Yoon of KAIST Graduate School of Culture Technology and Professor Yang Zhang (top) of UCLA >
T2IRay: Enabling Virtual Input with Precision
T2IRay introduces a novel input method that allows for precise object pointing in virtual environments by expanding traditional thumb-to-index gestures. This approach overcomes previous limitations, such as interruptions or reduced accuracy due to changes in hand position or orientation.
The technology uses a local coordinate system based on finger relationships, ensuring continuous input even as hand positions shift. It accurately captures subtle thumb movements within this coordinate system, integrating natural head movements to allow fluid, intuitive control across a wide range.
< Figure 1. T2IRay framework utilizing the delicate movements of the thumb and index fingers for AR/VR pointing >
Professor Sang Ho Yoon explained, “T2IRay can significantly enhance the user experience in AR/VR by enabling smooth, stable control even when the user’s hands are in motion.”
This study, led by first author Jina Kim, was supported by the Excellent New Researcher Support Project of the National Research Foundation of Korea under the Ministry of Science and ICT, as well as the University ICT Research Center (ITRC) Support Project of the Institute of Information and Communications Technology Planning and Evaluation (IITP).
▴ Paper title: T2IRay: Design of Thumb-to-Index Based Indirect Pointing for Continuous and Robust AR/VR Input▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3713442
▴ T2IRay demo video: https://youtu.be/ElJlcJbkJPY
ChoreoCraft: Creativity Support through VR for Choreographers
In addition, Professor Yoon’s team developed ‘ChoreoCraft,’ a virtual reality tool designed to support choreographers by addressing the unique challenges they face, such as memorizing complex movements, overcoming creative blocks, and managing subjective feedback.
ChoreoCraft reduces reliance on memory by allowing choreographers to save and refine movements directly within a VR space, using a motion-capture avatar for real-time interaction. It also enhances creativity by suggesting movements that naturally fit with prior choreography and musical elements. Furthermore, the system provides quantitative feedback by analyzing kinematic factors like motion stability and engagement, helping choreographers make data-driven creative decisions.
< Figure 2. ChoreoCraft's approaches to encourage creative process >
Professor Yoon noted, “ChoreoCraft is a tool designed to address the core challenges faced by choreographers, enhancing both creativity and efficiency. In user tests with professional choreographers, it received high marks for its ability to spark creative ideas and provide valuable quantitative feedback.”
This research was conducted in collaboration with doctoral candidate Kyungeun Jung and master’s candidate Hyunyoung Han, alongside the Electronics and Telecommunications Research Institute (ETRI) and One Million Co., Ltd. (CEO Hye-rang Kim), with support from the Cultural and Arts Immersive Service Development Project by the Ministry of Culture, Sports and Tourism.
▴ Paper title: ChoreoCraft: In-situ Crafting of Choreography in Virtual Reality through Creativity Support Tools▴ Paper link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3706598.3714220
▴ ChoreoCraft demo video: https://youtu.be/Ms1fwiSBjjw
*CHI (Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems): The premier international conference on human-computer interaction, organized by the ACM, was held this year from April 25 to May 1, 2025.
2025.05.13 View 5120 -
 Editing Parkinson's Disease – KAIST Makes World's First Discovery of an Inflammatory RNA Editing Enzyme through Co-work with UCL Researchers
< Professor Minee Choi of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences (top left). Professor Sonia Gandhi (top right) and Professor Klenerman of the University College London (bottom right) >
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder in which the α-synuclein protein abnormally aggregates within brain cells, causing neuronal damage. Through international collaboration, researchers at KAIST have revealed that RNA editing plays a crucial role in regulating neuroinflammation, a key pathology of Parkinson's disease.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th of April that a research team led by Professor Minee L. Choi from the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, in collaboration with University College London (UCL) and the Francis Crick Institute, discovered that the RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 plays an important role in controlling immune responses in astrocytes, glial cells that trigger protective reactions in the brain, and demonstrated that this mechanism is critically involved in the progression of Parkinson’s disease.
Professor Choi's research team created a co-culture model composed of astrocytes and neurons derived from stem cells originating from Parkinson's disease patients, in order to study the inflammatory responses of brain immune cells. They then treated the model with α-synuclein aggregates, which are known to cause Parkinson’s disease, and analyzed how the immune cells' inflammatory responses changed.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the inflammatory RNA editing model in Parkinson's disease >
As a result, it was found that early pathological forms of α-synuclein, known as oligomers, activated the Toll-like receptor pathway, which acts as a danger sensor in astrocytes, as well as the interferon response pathway, an immune signaling network that combats viruses and pathogens. During this process, the RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 was expressed and transformed into an isoform with an altered protein structure and function.
Notably, the RNA editing activity of ADAR1, which normally functions to regulate immune responses during viral infections by converting adenosine (A) to inosine (I) through a process known as A-to-I RNA editing, was found to be abnormally focused on genes that cause inflammation rather than operating under normal conditions. This phenomenon was observed not only in the patient-derived neuron models but also in postmortem brain tissues from actual Parkinson’s disease patients.
< Figure 2. Experimental design and inflammatory response induction in astrocytes following treatment with α-synuclein oligomers (abnormally folded protein fragments) >
This directly proves that the dysregulation of RNA editing induces chronic inflammatory responses in astrocytes, ultimately leading to neuronal toxicity and pathological progression.
This study is significant in that it newly identified the regulation of RNA editing within astrocytes as a key mechanism behind neuroinflammatory responses. In particular, it suggests that ADAR1 could serve as a novel genetic target for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.
It is also noteworthy that the study reflected actual pathological characteristics of patients by utilizing patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-based precision models for brain diseases.
Professor Minee L. Choi stated, “This study demonstrates that the regulator of inflammation caused by protein aggregation operates at the new layer of RNA editing, offering a completely different therapeutic strategy from existing approaches to Parkinson's disease treatment." She further emphasized, “RNA editing technology could become an important turning point in the development of therapeutics for neuroinflammation.”
< Figure 3. When treated with α-synuclein oligomers, the causative agent of Parkinson's disease, A-to-I RNA editing is induced to change genetic information by ADAR in patient-derived stem cell-differentiated glial cells, confirming that α-synuclein is likely to be associated with the progression of Parkinson's disease through RNA editing >
This study was published in Science Advances on April 11, with Professor Choi listed as a co-first author.
Paper Title: Astrocytic RNA editing regulates the host immune response to alpha-synuclein, Science Advances Vol.11, Issue 15. (DOI:10.1126/sciadv.adp8504)
Lead Authors: Karishma D’Sa (UCL, Co-First Author), Minee L. Choi (KAIST, Co-First Author), Mina Ryten (UCL, Corresponding Author), Sonia Gandhi (Francis Crick Institute, University of Cambridge, Corresponding Author)
This research was supported by the Brain Research Program and the Excellent Young Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, as well as KAIST’s Daekyo Cognitive Enhancement Program.
2025.05.02 View 5065
Editing Parkinson's Disease – KAIST Makes World's First Discovery of an Inflammatory RNA Editing Enzyme through Co-work with UCL Researchers
< Professor Minee Choi of the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences (top left). Professor Sonia Gandhi (top right) and Professor Klenerman of the University College London (bottom right) >
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder in which the α-synuclein protein abnormally aggregates within brain cells, causing neuronal damage. Through international collaboration, researchers at KAIST have revealed that RNA editing plays a crucial role in regulating neuroinflammation, a key pathology of Parkinson's disease.
KAIST (represented by President Kwang-Hyung Lee) announced on the 27th of April that a research team led by Professor Minee L. Choi from the Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences, in collaboration with University College London (UCL) and the Francis Crick Institute, discovered that the RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 plays an important role in controlling immune responses in astrocytes, glial cells that trigger protective reactions in the brain, and demonstrated that this mechanism is critically involved in the progression of Parkinson’s disease.
Professor Choi's research team created a co-culture model composed of astrocytes and neurons derived from stem cells originating from Parkinson's disease patients, in order to study the inflammatory responses of brain immune cells. They then treated the model with α-synuclein aggregates, which are known to cause Parkinson’s disease, and analyzed how the immune cells' inflammatory responses changed.
< Figure 1. Schematic diagram of the inflammatory RNA editing model in Parkinson's disease >
As a result, it was found that early pathological forms of α-synuclein, known as oligomers, activated the Toll-like receptor pathway, which acts as a danger sensor in astrocytes, as well as the interferon response pathway, an immune signaling network that combats viruses and pathogens. During this process, the RNA editing enzyme ADAR1 was expressed and transformed into an isoform with an altered protein structure and function.
Notably, the RNA editing activity of ADAR1, which normally functions to regulate immune responses during viral infections by converting adenosine (A) to inosine (I) through a process known as A-to-I RNA editing, was found to be abnormally focused on genes that cause inflammation rather than operating under normal conditions. This phenomenon was observed not only in the patient-derived neuron models but also in postmortem brain tissues from actual Parkinson’s disease patients.
< Figure 2. Experimental design and inflammatory response induction in astrocytes following treatment with α-synuclein oligomers (abnormally folded protein fragments) >
This directly proves that the dysregulation of RNA editing induces chronic inflammatory responses in astrocytes, ultimately leading to neuronal toxicity and pathological progression.
This study is significant in that it newly identified the regulation of RNA editing within astrocytes as a key mechanism behind neuroinflammatory responses. In particular, it suggests that ADAR1 could serve as a novel genetic target for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease.
It is also noteworthy that the study reflected actual pathological characteristics of patients by utilizing patient-specific induced pluripotent stem cell-based precision models for brain diseases.
Professor Minee L. Choi stated, “This study demonstrates that the regulator of inflammation caused by protein aggregation operates at the new layer of RNA editing, offering a completely different therapeutic strategy from existing approaches to Parkinson's disease treatment." She further emphasized, “RNA editing technology could become an important turning point in the development of therapeutics for neuroinflammation.”
< Figure 3. When treated with α-synuclein oligomers, the causative agent of Parkinson's disease, A-to-I RNA editing is induced to change genetic information by ADAR in patient-derived stem cell-differentiated glial cells, confirming that α-synuclein is likely to be associated with the progression of Parkinson's disease through RNA editing >
This study was published in Science Advances on April 11, with Professor Choi listed as a co-first author.
Paper Title: Astrocytic RNA editing regulates the host immune response to alpha-synuclein, Science Advances Vol.11, Issue 15. (DOI:10.1126/sciadv.adp8504)
Lead Authors: Karishma D’Sa (UCL, Co-First Author), Minee L. Choi (KAIST, Co-First Author), Mina Ryten (UCL, Corresponding Author), Sonia Gandhi (Francis Crick Institute, University of Cambridge, Corresponding Author)
This research was supported by the Brain Research Program and the Excellent Young Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, as well as KAIST’s Daekyo Cognitive Enhancement Program.
2025.05.02 View 5065 -
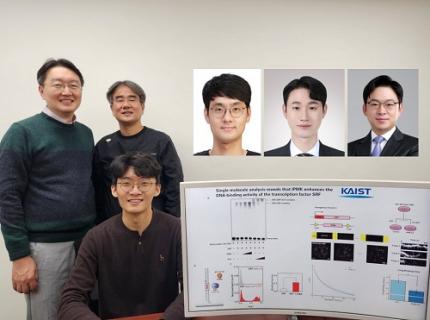 KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 11982
KAIST Uncovers the Principles of Gene Expression Regulation in Cancer and Cellular Functions
< (From left) Professor Seyun Kim, Professor Gwangrog Lee, Dr. Hyoungjoon Ahn, Dr. Jeongmin Yu, Professor Won-Ki Cho, and (below) PhD candidate Kwangmin Ryu of the Department of Biological Sciences>
A research team at KAIST has identified the core gene expression networks regulated by key proteins that fundamentally drive phenomena such as cancer development, metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation processes. This discovery lays the foundation for developing innovative therapeutic technologies.
On the 22nd of January, KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced that the joint research team led by Professors Seyun Kim, Gwangrog Lee, and Won-Ki Cho from the Department of Biological Sciences had uncovered essential mechanisms controlling gene expression in animal cells.
Inositol phosphate metabolites produced by inositol metabolism enzymes serve as vital secondary messengers in eukaryotic cell signaling systems and are broadly implicated in cancer, obesity, diabetes, and neurological disorders.
The research team demonstrated that the inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme, a key player in the inositol metabolism system, acts as a critical transcriptional activator within the core gene expression networks of animal cells. Notably, although IPMK was previously reported to play an important role in the transcription process governed by serum response factor (SRF), a representative transcription factor in animal cells, the precise mechanism of its action was unclear.
SRF is a transcription factor directly controlling the expression of at least 200–300 genes, regulating cell growth, proliferation, apoptosis, and motility, and is indispensable for organ development, such as in the heart.
The team discovered that IPMK binds directly to SRF, altering the three-dimensional structure of the SRF protein. This interaction facilitates the transcriptional activity of various genes through the SRF activated by IPMK, demonstrating that IPMK acts as a critical regulatory switch to enhance SRF's protein activity.
< Figure 1. The serum response factor (SRF) protein, a key transcription factor in animal cells, directly binds to inositol polyphosphate multikinase (IPMK) enzyme and undergoes structural change to acquire DNA binding ability, and precisely regulates growth and differentiation of animal cells through transcriptional activation. >
The team further verified that disruptions in the direct interaction between IPMK and SRF lead to the reduced functionality and activity of SRF, causing severe impairments in gene expression.
By highlighting the significance of the intrinsically disordered region (IDR) in SRF, the researchers underscored the biological importance of intrinsically disordered proteins (IDPs). Unlike most proteins that adopt distinct structures through folding, IDPs, including those with IDRs, do not exhibit specific structures but play crucial biological roles, attracting significant attention in the scientific community.
Professor Seyun Kim commented, "This study provides a vital mechanism proving that IPMK, a key enzyme in the inositol metabolism system, is a major transcriptional activator in the core gene expression network of animal cells. By understanding fundamental processes such as cancer development and metastasis, tissue differentiation from stem cells, and neural activation through SRF, we hope this discovery will lead to the broad application of innovative therapeutic technologies."
The findings were published on January 7th in the international journal Nucleic Acids Research (IF=16.7, top 1.8% in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology), under the title “Single-molecule analysis reveals that IPMK enhances the DNA-binding activity of the transcription factor SRF" (DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkae1281).
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea's Mid-career Research Program, Leading Research Center Program, and Global Research Laboratory Program, as well as by the Suh Kyungbae Science Foundation and the Samsung Future Technology Development Program.
2025.01.24 View 11982 -
 'Jumping Genes' Found to Alter Human Colon Genomes, Offering Insights into Aging and Tumorigenesis
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and their collaborators have conducted a groundbreaking study targeting 'jumping genes' in the entire genomes of the human large intestine. Published in Nature on May 18 2023, the research unveils the surprising activity of 'Long interspersed nuclear element-1 (L1),' a type of jumping gene previously thought to be mostly dormant in human genomes. The study shows that L1 genes can become activated and disrupt genomic functions throughout an individual's lifetime, particularly in the colorectal epithelium.
(Paper Title: Widespread somatic L1 retrotransposition in normal colorectal epithelium, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06046-z)
With approximately 500,000 L1 jumping genes, accounting for 17% of the human genome, they have long been recognized for their contribution to the evolution of the human species by introducing 'disruptive innovation' to genome sequences. Until now, it was believed that most L1 elements had lost their ability to jump in normal tissues of modern humans. However, this study reveals that some L1 jumping genes can be widely activated in normal cells, leading to the accumulation of genomic mutations over an individual's lifetime. The rate of L1 jumping and resulting genomic changes vary among different cell types, with a notable concentration observed in aged colon epithelial cells. The study illustrates that every colonic epithelial cell experiences an L1 jumping event by the age of 40 on average.
The research, led by co-first authors Chang Hyun Nam (a graduate student at KAIST) and Dr. Jeonghwan Youk (former graduate student at KAIST and assistant clinical professor at Seoul National University Hospital), involved the analysis of whole-genome sequences from 899 single cells obtained from skin (fibroblasts), blood, and colon epithelial tissues collected from 28 individuals. The study uncovers the activation of L1 jumping genes in normal cells, resulting in the gradual accumulation of genomic mutations over time. Additionally, the team explored epigenomic (DNA methylation) sequences to understand the mechanism behind L1 jumping gene activation. They found that cells with activated L1 jumping genes exhibit epigenetic instability, suggesting the critical role of epigenetic changes in regulating L1 jumping gene activity. Most of these epigenomic instabilities were found to arise during the early stages of embryogenesis. The study provides valuable insights into the aging process and the development of diseases in human colorectal tissues.
"This study illustrates that genomic damage in normal cells is acquired not only through exposure to carcinogens but also through the activity of endogenous components whose impact was previously unclear. Genomes of apparently healthy aged cells, particularly in the colorectal epithelium, become mosaic due to the activity of L1 jumping genes," said Prof. Young Seok Ju at KAIST.
"We emphasize the essential and ongoing collaboration among researchers in clinical medicine and basic medical sciences," said Prof. Min Jung Kim of the Department of Surgery at Seoul National University Hospital. "This case highlights the critical role of systematically collected human tissues from clinical settings in unraveling the complex process of disease development in humans."
"I am delighted that the research team's advancements in single-cell genome technology have come to fruition. We will persistently strive to lead in single-cell genome technology," said Prof. Hyun Woo Kwon of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at Korea University School of Medicine.
The research team received support from the Research Leader Program and the Young Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, a grant from the MD-PhD/Medical Scientist Training Program through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Suh Kyungbae Foundation.
< Figure 1. Experimental design of the study >
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram illustrating factors influencing the soL1R landscape. >
Genetic composition of rc-L1s is inherited from the parents. The methylation landscape of rc-L1 promoters is predominantly determined by global DNA demethylation, followed by remethylation processes in the developmental stages. Then, when an rc-L1 is promoter demethylated in a specific cell lineage, the source expresses L1 transcripts thus making possible the induction of soL1Rs.
2023.05.22 View 10633
'Jumping Genes' Found to Alter Human Colon Genomes, Offering Insights into Aging and Tumorigenesis
The Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) and their collaborators have conducted a groundbreaking study targeting 'jumping genes' in the entire genomes of the human large intestine. Published in Nature on May 18 2023, the research unveils the surprising activity of 'Long interspersed nuclear element-1 (L1),' a type of jumping gene previously thought to be mostly dormant in human genomes. The study shows that L1 genes can become activated and disrupt genomic functions throughout an individual's lifetime, particularly in the colorectal epithelium.
(Paper Title: Widespread somatic L1 retrotransposition in normal colorectal epithelium, https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06046-z)
With approximately 500,000 L1 jumping genes, accounting for 17% of the human genome, they have long been recognized for their contribution to the evolution of the human species by introducing 'disruptive innovation' to genome sequences. Until now, it was believed that most L1 elements had lost their ability to jump in normal tissues of modern humans. However, this study reveals that some L1 jumping genes can be widely activated in normal cells, leading to the accumulation of genomic mutations over an individual's lifetime. The rate of L1 jumping and resulting genomic changes vary among different cell types, with a notable concentration observed in aged colon epithelial cells. The study illustrates that every colonic epithelial cell experiences an L1 jumping event by the age of 40 on average.
The research, led by co-first authors Chang Hyun Nam (a graduate student at KAIST) and Dr. Jeonghwan Youk (former graduate student at KAIST and assistant clinical professor at Seoul National University Hospital), involved the analysis of whole-genome sequences from 899 single cells obtained from skin (fibroblasts), blood, and colon epithelial tissues collected from 28 individuals. The study uncovers the activation of L1 jumping genes in normal cells, resulting in the gradual accumulation of genomic mutations over time. Additionally, the team explored epigenomic (DNA methylation) sequences to understand the mechanism behind L1 jumping gene activation. They found that cells with activated L1 jumping genes exhibit epigenetic instability, suggesting the critical role of epigenetic changes in regulating L1 jumping gene activity. Most of these epigenomic instabilities were found to arise during the early stages of embryogenesis. The study provides valuable insights into the aging process and the development of diseases in human colorectal tissues.
"This study illustrates that genomic damage in normal cells is acquired not only through exposure to carcinogens but also through the activity of endogenous components whose impact was previously unclear. Genomes of apparently healthy aged cells, particularly in the colorectal epithelium, become mosaic due to the activity of L1 jumping genes," said Prof. Young Seok Ju at KAIST.
"We emphasize the essential and ongoing collaboration among researchers in clinical medicine and basic medical sciences," said Prof. Min Jung Kim of the Department of Surgery at Seoul National University Hospital. "This case highlights the critical role of systematically collected human tissues from clinical settings in unraveling the complex process of disease development in humans."
"I am delighted that the research team's advancements in single-cell genome technology have come to fruition. We will persistently strive to lead in single-cell genome technology," said Prof. Hyun Woo Kwon of the Department of Nuclear Medicine at Korea University School of Medicine.
The research team received support from the Research Leader Program and the Young Researcher Program of the National Research Foundation of Korea, a grant from the MD-PhD/Medical Scientist Training Program through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute, and the Suh Kyungbae Foundation.
< Figure 1. Experimental design of the study >
< Figure 2. Schematic diagram illustrating factors influencing the soL1R landscape. >
Genetic composition of rc-L1s is inherited from the parents. The methylation landscape of rc-L1 promoters is predominantly determined by global DNA demethylation, followed by remethylation processes in the developmental stages. Then, when an rc-L1 is promoter demethylated in a specific cell lineage, the source expresses L1 transcripts thus making possible the induction of soL1Rs.
2023.05.22 View 10633 -
 Professor Poong Hyun Seong Elected INSC Chair
Professor Emeritus Poong Hyun Seong from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering was elected as the Chairman of the International Nuclear Societies Council (INSC). His two-year term began on January 1.
The INSC is an organization made up of nuclear societies all over the world, representing more than 80,000 nuclear professionals. The INSC founded in 1990 acts as a global forum to establish common goals of nuclear power usage, delivering the views and ideas of professionals throughout their regional societies.
The INSC has advocated for nuclear power to be deemed an indispensable clean energy resources that can mitigate the climate change. The council has engaged in public awareness and publicity activities promoting the advantages of nuclear energy for developing next-generation power plants such as small nuclear reactors, local heating system, seawater desalination, and fair production of energy.
Professor Seong is a globally renowned scholar in the fields of nuclear instrumentation control and human factor engineering. He retired last year after 30-year career at KAIST. He took on leadership roles in the Korea Nuclear Society and served as a member of the Korea Nuclear Safety and Security Commission as well as Atomic Energy Commission. A fellow at the America Nuclear Society, Professor Seong served as the first vice chair of the INSC and he received the Don Miller Award in 2019. The award established in 2009 by the American Nuclear Society in honor of former ANS President Don Miller is given to an individual who has made a significant contribution to the advancement of nuclear instrumentation and control of human-machine interfaces.
He led the leadership role to help the Korean government steered into efficient and reasonable energy policymaking. More recently, as the Korean government decided to abandon nuclear energy, he actively opposed the government’s pivot. Professor Seong said, “Advanced countries like the US, UK, France, and Japan push forward the production of renewable energy by driving nuclear power plant under their pledges toward carbon neutrality by 2050. However, we are very concerned about the government’s policy shift to decrease the number of nuclear power plants while increasing the fossil fuel usage. I don’t think we can realize carbon neutrality by 2050 with the current policy.”
(END)
2021.01.13 View 8357
Professor Poong Hyun Seong Elected INSC Chair
Professor Emeritus Poong Hyun Seong from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering was elected as the Chairman of the International Nuclear Societies Council (INSC). His two-year term began on January 1.
The INSC is an organization made up of nuclear societies all over the world, representing more than 80,000 nuclear professionals. The INSC founded in 1990 acts as a global forum to establish common goals of nuclear power usage, delivering the views and ideas of professionals throughout their regional societies.
The INSC has advocated for nuclear power to be deemed an indispensable clean energy resources that can mitigate the climate change. The council has engaged in public awareness and publicity activities promoting the advantages of nuclear energy for developing next-generation power plants such as small nuclear reactors, local heating system, seawater desalination, and fair production of energy.
Professor Seong is a globally renowned scholar in the fields of nuclear instrumentation control and human factor engineering. He retired last year after 30-year career at KAIST. He took on leadership roles in the Korea Nuclear Society and served as a member of the Korea Nuclear Safety and Security Commission as well as Atomic Energy Commission. A fellow at the America Nuclear Society, Professor Seong served as the first vice chair of the INSC and he received the Don Miller Award in 2019. The award established in 2009 by the American Nuclear Society in honor of former ANS President Don Miller is given to an individual who has made a significant contribution to the advancement of nuclear instrumentation and control of human-machine interfaces.
He led the leadership role to help the Korean government steered into efficient and reasonable energy policymaking. More recently, as the Korean government decided to abandon nuclear energy, he actively opposed the government’s pivot. Professor Seong said, “Advanced countries like the US, UK, France, and Japan push forward the production of renewable energy by driving nuclear power plant under their pledges toward carbon neutrality by 2050. However, we are very concerned about the government’s policy shift to decrease the number of nuclear power plants while increasing the fossil fuel usage. I don’t think we can realize carbon neutrality by 2050 with the current policy.”
(END)
2021.01.13 View 8357 -
 Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano.
Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journals including ACS Nano, Nano Energy, and Energy Storage Materials made Zoom presentations in three main categories: 1) nanostructures for next-generation applications, 2) chemistry and biotechnology for applications in the fields of environment and industry, and 3) material innovation for technological applications.
During Session I, speakers including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University and Professor Zhenan Bao of Stanford University led the session on Emerging Soft Electronics and 3D printing.
In later sessions, other globally recognized scholars gave talks titled Advanced Nanostructuring for Emerging Materials, Frontiers in Emerging Materials Research, Advanced Energy Materials and Functional Nanomaterials, and Latest Advances in Nanomaterials Research.
These included 2010 Nobel Prize laureate and professor at Manchester University Andre Geim, editor-in-chief of ACS Nano and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss, Professor Paul Alivisatos of UC Berkeley, Professor William Chueh of Stanford University, and Professor Mircea Dinca of MIT.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a materials physicist, said in his opening address, “Innovation in materials science will become an important driving force to change our way of life. All the breakthroughs in materials have extended a new paradigm that has transformed our lives.”
“Creative research projects alongside global collaborators like all of you will allow the breakthroughs that will deliver us from these crises,” he added.
(END)
2020.10.06 View 18503
Big Ideas on Emerging Materials Explored at EMS
Renowned scholars and editors from academic journals joined the Emerging Materials e-Symposium (EMS) held at KAIST and shared the latest breakthroughs and big ideas in new material development last month. This e-symposium was organized by Professor Il-Doo Kim from the KAIST Department of Materials Sciences and Engineering over five days from September 21 through 25 via Zoom and YouTube. Professor Kim also serves as an associate editor of ACS Nano.
Esteemed scholars and editors of academic journals including ACS Nano, Nano Energy, and Energy Storage Materials made Zoom presentations in three main categories: 1) nanostructures for next-generation applications, 2) chemistry and biotechnology for applications in the fields of environment and industry, and 3) material innovation for technological applications.
During Session I, speakers including Professor John A. Rogers of Northwestern University and Professor Zhenan Bao of Stanford University led the session on Emerging Soft Electronics and 3D printing.
In later sessions, other globally recognized scholars gave talks titled Advanced Nanostructuring for Emerging Materials, Frontiers in Emerging Materials Research, Advanced Energy Materials and Functional Nanomaterials, and Latest Advances in Nanomaterials Research.
These included 2010 Nobel Prize laureate and professor at Manchester University Andre Geim, editor-in-chief of ACS Nano and professor at UCLA Paul S. Weiss, Professor Paul Alivisatos of UC Berkeley, Professor William Chueh of Stanford University, and Professor Mircea Dinca of MIT.
KAIST President Sung-Chul Shin, who is also a materials physicist, said in his opening address, “Innovation in materials science will become an important driving force to change our way of life. All the breakthroughs in materials have extended a new paradigm that has transformed our lives.”
“Creative research projects alongside global collaborators like all of you will allow the breakthroughs that will deliver us from these crises,” he added.
(END)
2020.10.06 View 18503 -
 Professor Sungyeol Choi Receives Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation
< Professor Sungyeol Choi >
Professor Sungyeol Choi from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering received the Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation on the 9th Annual Nuclear Safety and Promotion Day last month, in recognition of his contributions to the promotion of nuclear energy through the safe management of spent nuclear fuel and radioactive waste.
Professor Choi developed high-precision, multi-physics codes that can predict and prevent abnormal power fluctuations caused by boron hideout within nuclear fuel in a pressurized water reactor, solving the problem that has caused economic losses of tens of billions of won every year from industrial sites.
He is now developing a new technology that can reduce high-level waste by recycling spent nuclear fuel, while preventing nuclear material from being used for nuclear weapons, which is one of the biggest challenges faced by the nuclear industry.
In 2017, his first year in office as a KAIST professor, Professor Choi was selected as the youngest and the only member under 50 of the Standing Scientific Advisory Committee at the Information Exchange Meeting on Partitioning and Transmutation (IEMPT), an authoritative association on the disposal of high-level nuclear waste.
The following year, he became the first Korean to receive the Early Career Award, which is given to one person every two years by the International Youth Nuclear Congress.
2020.01.15 View 6534
Professor Sungyeol Choi Receives Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation
< Professor Sungyeol Choi >
Professor Sungyeol Choi from the Department of Nuclear and Quantum Engineering received the Science and ICT Ministerial Commendation on the 9th Annual Nuclear Safety and Promotion Day last month, in recognition of his contributions to the promotion of nuclear energy through the safe management of spent nuclear fuel and radioactive waste.
Professor Choi developed high-precision, multi-physics codes that can predict and prevent abnormal power fluctuations caused by boron hideout within nuclear fuel in a pressurized water reactor, solving the problem that has caused economic losses of tens of billions of won every year from industrial sites.
He is now developing a new technology that can reduce high-level waste by recycling spent nuclear fuel, while preventing nuclear material from being used for nuclear weapons, which is one of the biggest challenges faced by the nuclear industry.
In 2017, his first year in office as a KAIST professor, Professor Choi was selected as the youngest and the only member under 50 of the Standing Scientific Advisory Committee at the Information Exchange Meeting on Partitioning and Transmutation (IEMPT), an authoritative association on the disposal of high-level nuclear waste.
The following year, he became the first Korean to receive the Early Career Award, which is given to one person every two years by the International Youth Nuclear Congress.
2020.01.15 View 6534 -
 Gallium-Based Solvating Agent Efficiently Analyzes Optically Active Alcohols
A KAIST research team has developed a gallium-based metal complex enabling the rapid chiral analysis of alcohols. A team working under Professor Hyunwoo Kim reported the efficient new alcohol analysis method using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in iScience.
Enantiopure chiral alcohols are ubiquitous in nature and widely utilized as pharmaceuticals. This importance of chirality in synthetic and medicinal chemistry has advanced the search for rapid and facile methods to determine the enantiomeric purities of compounds. To date, chiral analysis has been performed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with chiral columns.
Along with the HPLC technique, chiral analysis using NMR spectroscopy has gained tremendous attention as an alternative to traditionally employed chromatographic methods due to its simplicity and rapid detection for real-time measurement. However, this method carries drawbacks such as line-broadening, narrow substrate scope, and poor resolution. Thus, compared with popular methods of chromatographic analysis, NMR spectroscopy is infrequently used for chiral analysis.
In principle, a chiral solvating agent is additionally required for the NMR measurement of chiral alcohols to obtain two distinct signals. However, NMR analysis of chiral alcohols has been challenging due to weak binding interactions with chiral solvating agents. To overcome the intrinsic difficulty of relatively weak molecular interactions that are common for alcohols, many researchers have used multifunctional alcohols to enhance interactions with solvating agents.
Instead, the KAIST team successfully varied the physical properties of metal complexes to induce stronger interactions with alcohols rather than the strategy of using multifunctional analytes, in the hopes of developing a universal chiral solvating agent for alcohols. Compared to the current method of chiral analysis used in the pharmaceutical industry, alcohols that do not possess chromophores can also be directly analyzed with the gallium complexes.
Professor Kim said that this method could be a complementary chiral analysis technique at the industry level in the near future. He added that since the developed gallium complex can determine enantiomeric excess within minutes, it can be further utilized to monitor asymmetric synthesis. This feature will benefit a large number of researchers in the organic chemistry community, as well as the pharmaceutical industry.
(Figure: Schematic view of the in-situ direct 1H NMR chiral analysis.)
-Profile:
Professor Hyunwoo Kim
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
http://mdos.kaist.ac.kr
hwk34@kaist.ac.kr
For more on this article,
please go to https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci2019.07051
2019.11.14 View 13054
Gallium-Based Solvating Agent Efficiently Analyzes Optically Active Alcohols
A KAIST research team has developed a gallium-based metal complex enabling the rapid chiral analysis of alcohols. A team working under Professor Hyunwoo Kim reported the efficient new alcohol analysis method using nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy in iScience.
Enantiopure chiral alcohols are ubiquitous in nature and widely utilized as pharmaceuticals. This importance of chirality in synthetic and medicinal chemistry has advanced the search for rapid and facile methods to determine the enantiomeric purities of compounds. To date, chiral analysis has been performed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) with chiral columns.
Along with the HPLC technique, chiral analysis using NMR spectroscopy has gained tremendous attention as an alternative to traditionally employed chromatographic methods due to its simplicity and rapid detection for real-time measurement. However, this method carries drawbacks such as line-broadening, narrow substrate scope, and poor resolution. Thus, compared with popular methods of chromatographic analysis, NMR spectroscopy is infrequently used for chiral analysis.
In principle, a chiral solvating agent is additionally required for the NMR measurement of chiral alcohols to obtain two distinct signals. However, NMR analysis of chiral alcohols has been challenging due to weak binding interactions with chiral solvating agents. To overcome the intrinsic difficulty of relatively weak molecular interactions that are common for alcohols, many researchers have used multifunctional alcohols to enhance interactions with solvating agents.
Instead, the KAIST team successfully varied the physical properties of metal complexes to induce stronger interactions with alcohols rather than the strategy of using multifunctional analytes, in the hopes of developing a universal chiral solvating agent for alcohols. Compared to the current method of chiral analysis used in the pharmaceutical industry, alcohols that do not possess chromophores can also be directly analyzed with the gallium complexes.
Professor Kim said that this method could be a complementary chiral analysis technique at the industry level in the near future. He added that since the developed gallium complex can determine enantiomeric excess within minutes, it can be further utilized to monitor asymmetric synthesis. This feature will benefit a large number of researchers in the organic chemistry community, as well as the pharmaceutical industry.
(Figure: Schematic view of the in-situ direct 1H NMR chiral analysis.)
-Profile:
Professor Hyunwoo Kim
Department of Chemistry
KAIST
http://mdos.kaist.ac.kr
hwk34@kaist.ac.kr
For more on this article,
please go to https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci2019.07051
2019.11.14 View 13054 -
 Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 9519
Professor Hyun Gyu Park Appointed as Associate Editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics
Professor Hyun Gyu Park from the Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering was appointed as an associate editor for Biosensors and Bioelectronics, an international journal published by Elsevier.
Biosensors and Bioelectronics is one of the top SCI journals in the fields of chemistry and analytical science (IF 9.518 as of 2018). Professor Park was recognized and appointed as the associate editor for this journal due to his outstanding research achievements in the fields of nucleic acid engineering, biosensors, and nanobiotechnology.
Professor Park will serve as the associate editor from this October until December 2021.
(END)
2019.10.01 View 9519