reconstruction
-
 KAIST Develops AI ‘MARIOH’ to Uncover and Reconstruct Hidden Multi-Entity Relationships
<(From Left) Professor Kijung Shin, Ph.D candidate Kyuhan Lee, and Ph.D candidate Geon Lee>
Just like when multiple people gather simultaneously in a meeting room, higher-order interactions—where many entities interact at once—occur across various fields and reflect the complexity of real-world relationships. However, due to technical limitations, in many fields, only low-order pairwise interactions between entities can be observed and collected, which results in the loss of full context and restricts practical use. KAIST researchers have developed the AI model “MARIOH,” which can accurately reconstruct* higher-order interactions from such low-order information, opening up innovative analytical possibilities in fields like social network analysis, neuroscience, and life sciences.
*Reconstruction: Estimating/reconstructing the original structure that has disappeared or was not observed.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that Professor Kijung Shin’s research team at the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI has developed an AI technology called “MARIOH” (Multiplicity-Aware Hypergraph Reconstruction), which can reconstruct higher-order interaction structures with high accuracy using only low-order interaction data.
Reconstructing higher-order interactions is challenging because a vast number of higher-order interactions can arise from the same low-order structure.
The key idea behind MARIOH, developed by the research team, is to utilize multiplicity information of low-order interactions to drastically reduce the number of candidate higher-order interactions that could stem from a given structure.
In addition, by employing efficient search techniques, MARIOH quickly identifies promising interaction candidates and uses multiplicity-based deep learning to accurately predict the likelihood that each candidate represents an actual higher-order interaction.
<Figure 1. An example of recovering high-dimensional relationships (right) from low-dimensional paper co-authorship relationships (left) with 100% accuracy, using MARIOH technology.>
Through experiments on ten diverse real-world datasets, the research team showed that MARIOH reconstructed higher-order interactions with up to 74% greater accuracy compared to existing methods.
For instance, in a dataset on co-authorship relations (source: DBLP), MARIOH achieved a reconstruction accuracy of over 98%, significantly outperforming existing methods, which reached only about 86%. Furthermore, leveraging the reconstructed higher-order structures led to improved performance in downstream tasks, including prediction and classification.
According to Kijung, “MARIOH moves beyond existing approaches that rely solely on simplified connection information, enabling precise analysis of the complex interconnections found in the real world.” Furthermore, “it has broad potential applications in fields such as social network analysis for group chats or collaborative networks, life sciences for studying protein complexes or gene interactions, and neuroscience for tracking simultaneous activity across multiple brain regions.”
The research was conducted by Kyuhan Lee (Integrated M.S.–Ph.D. program at the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST; currently a software engineer at GraphAI), Geon Lee (Integrated M.S.–Ph.D. program at KAIST), and Professor Kijung Shin. It was presented at the 41st IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (IEEE ICDE), held in Hong Kong this past May.
※ Paper title: MARIOH: Multiplicity-Aware Hypergraph Reconstruction ※ DOI: https://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/ICDE65448.2025.00233
<Figure 2. An example of the process of recovering high-dimensional relationships using MARIOH technology>
This research was supported by the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) through the project “EntireDB2AI: Foundational technologies and software for deep representation learning and prediction using complete relational databases,” as well as by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the project “Graph Foundation Model: Graph-based machine learning applicable across various modalities and domains.”
2025.08.05 View 287
KAIST Develops AI ‘MARIOH’ to Uncover and Reconstruct Hidden Multi-Entity Relationships
<(From Left) Professor Kijung Shin, Ph.D candidate Kyuhan Lee, and Ph.D candidate Geon Lee>
Just like when multiple people gather simultaneously in a meeting room, higher-order interactions—where many entities interact at once—occur across various fields and reflect the complexity of real-world relationships. However, due to technical limitations, in many fields, only low-order pairwise interactions between entities can be observed and collected, which results in the loss of full context and restricts practical use. KAIST researchers have developed the AI model “MARIOH,” which can accurately reconstruct* higher-order interactions from such low-order information, opening up innovative analytical possibilities in fields like social network analysis, neuroscience, and life sciences.
*Reconstruction: Estimating/reconstructing the original structure that has disappeared or was not observed.
KAIST (President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 5th that Professor Kijung Shin’s research team at the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI has developed an AI technology called “MARIOH” (Multiplicity-Aware Hypergraph Reconstruction), which can reconstruct higher-order interaction structures with high accuracy using only low-order interaction data.
Reconstructing higher-order interactions is challenging because a vast number of higher-order interactions can arise from the same low-order structure.
The key idea behind MARIOH, developed by the research team, is to utilize multiplicity information of low-order interactions to drastically reduce the number of candidate higher-order interactions that could stem from a given structure.
In addition, by employing efficient search techniques, MARIOH quickly identifies promising interaction candidates and uses multiplicity-based deep learning to accurately predict the likelihood that each candidate represents an actual higher-order interaction.
<Figure 1. An example of recovering high-dimensional relationships (right) from low-dimensional paper co-authorship relationships (left) with 100% accuracy, using MARIOH technology.>
Through experiments on ten diverse real-world datasets, the research team showed that MARIOH reconstructed higher-order interactions with up to 74% greater accuracy compared to existing methods.
For instance, in a dataset on co-authorship relations (source: DBLP), MARIOH achieved a reconstruction accuracy of over 98%, significantly outperforming existing methods, which reached only about 86%. Furthermore, leveraging the reconstructed higher-order structures led to improved performance in downstream tasks, including prediction and classification.
According to Kijung, “MARIOH moves beyond existing approaches that rely solely on simplified connection information, enabling precise analysis of the complex interconnections found in the real world.” Furthermore, “it has broad potential applications in fields such as social network analysis for group chats or collaborative networks, life sciences for studying protein complexes or gene interactions, and neuroscience for tracking simultaneous activity across multiple brain regions.”
The research was conducted by Kyuhan Lee (Integrated M.S.–Ph.D. program at the Kim Jaechul Graduate School of AI at KAIST; currently a software engineer at GraphAI), Geon Lee (Integrated M.S.–Ph.D. program at KAIST), and Professor Kijung Shin. It was presented at the 41st IEEE International Conference on Data Engineering (IEEE ICDE), held in Hong Kong this past May.
※ Paper title: MARIOH: Multiplicity-Aware Hypergraph Reconstruction ※ DOI: https://doi.ieeecomputersociety.org/10.1109/ICDE65448.2025.00233
<Figure 2. An example of the process of recovering high-dimensional relationships using MARIOH technology>
This research was supported by the Institute of Information & Communications Technology Planning & Evaluation (IITP) through the project “EntireDB2AI: Foundational technologies and software for deep representation learning and prediction using complete relational databases,” as well as by the National Research Foundation of Korea through the project “Graph Foundation Model: Graph-based machine learning applicable across various modalities and domains.”
2025.08.05 View 287 -
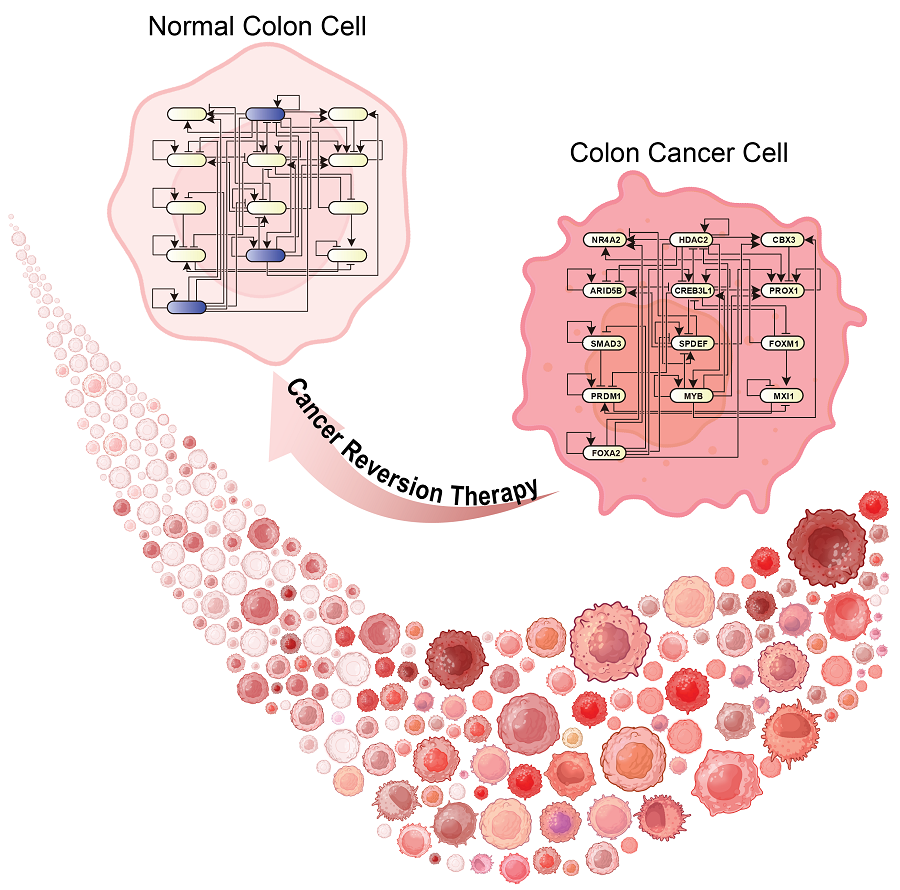 KAIST Develops Foundational Technology to Revert Cancer Cells to Normal Cells
Despite the development of numerous cancer treatment technologies, the common goal of current cancer therapies is to eliminate cancer cells. This approach, however, faces fundamental limitations, including cancer cells developing resistance and returning, as well as severe side effects from the destruction of healthy cells.
< (From top left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD candidates Juhee Kim, Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, and Hoon-Min Kim posed for a group photo with Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of December that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed a groundbreaking technology that can treat colon cancer by converting cancer cells into a state resembling normal colon cells without killing them, thus avoiding side effects.
The research team focused on the observation that during the oncogenesis process, normal cells regress along their differentiation trajectory. Building on this insight, they developed a technology to create a digital twin of the gene network associated with the differentiation trajectory of normal cells.
< Figure 1. Technology for creating a digital twin of a gene network from single-cell transcriptome data of a normal cell differentiation trajectory. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a digital twin creation technology that precisely observes the dynamics of gene regulatory relationships during the process of normal cells differentiating along a differentiation trajectory and analyzes the relationships among key genes to build a mathematical model that can be simulated (A-F). In addition, they developed a technology to discover key regulatory factors that control the differentiation trajectory of normal cells by simulating and analyzing this digital twin. >
< Figure 2. Digital twin simulation simulating the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells. The dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data for the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells were analyzed (A) and a digital twin of the gene network was developed representing the regulatory relationships of key genes in this differentiation trajectory (B). The simulation results of the digital twin confirm that it readily reproduces the dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data (C, D). >
Through simulation analysis, the team systematically identified master molecular switches that induce normal cell differentiation. When these switches were applied to colon cancer cells, the cancer cells reverted to a normal-like state, a result confirmed through molecular and cellular experiments as well as animal studies.
< Figure 3. Discovery of top-level key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells. By applying control factor discovery technology to the digital twin model, three genes, HDAC2, FOXA2, and MYB, were discovered as key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells (A, B). The results of simulation analysis of the regulatory effects of the discovered control factors through the digital twin confirmed that they could induce complete differentiation of colon cells (C). >
< Figure 4. Verification of the effect of the key control factors discovered using colon cancer cells and animal experiments on the reversibility of colon cancer. The key control factors of the normal colon cell differentiation trajectory discovered through digital twin simulation analysis were applied to actual colon cancer cells and colon cancer mouse animal models to experimentally verify the effect of cancer reversibility. The key control factors significantly reduced the proliferation of three colon cancer cell lines (A), and this was confirmed in the same way in animal models (B-D). >
This research demonstrates that cancer cell reversion can be systematically achieved by analyzing and utilizing the digital twin of the cancer cell gene network, rather than relying on serendipitous discoveries. The findings hold significant promise for developing reversible cancer therapies that can be applied to various types of cancer.
< Figure 5. The change in overall gene expression was confirmed through the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors, which converted the state of colon cancer cells to that of normal colon cells. The transcriptomes of colon cancer tissues and normal colon tissues from more than 400 colon cancer patients were compared with the transcriptomes of colon cancer cell lines and reversible colon cancer cell lines, respectively. The comparison results confirmed that the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors converted all three colon cancer cell lines to a state similar to the transcriptome expression of normal colon tissues. >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho remarked, "The fact that cancer cells can be converted back to normal cells is an astonishing phenomenon. This study proves that such reversion can be systematically induced."
He further emphasized, "This research introduces the novel concept of reversible cancer therapy by reverting cancer cells to normal cells. It also develops foundational technology for identifying targets for cancer reversion through the systematic analysis of normal cell differentiation trajectories."
This research included contributions from Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, Hoon-Min Kim, Juhee Kim, and Jaeog Jeon, and was published in the online edition of the international journal Advanced Science by Wiley on December 11. (Title: “Control of Cellular Differentiation Trajectories for Cancer Reversion”) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202402132
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a source technology to systematically discover key control factors that can induce reversibility of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach and a digital twin simulation analysis of the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells, and verified the effects of reversion on actual colon cancer through molecular cell experiments and animal experiments. >
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program. The research findings have been transferred to BioRevert Inc., where they will be used for the development of practical cancer reversion therapies.
2024.12.23 View 107553
KAIST Develops Foundational Technology to Revert Cancer Cells to Normal Cells
Despite the development of numerous cancer treatment technologies, the common goal of current cancer therapies is to eliminate cancer cells. This approach, however, faces fundamental limitations, including cancer cells developing resistance and returning, as well as severe side effects from the destruction of healthy cells.
< (From top left) Bio and Brain Engineering PhD candidates Juhee Kim, Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, and Hoon-Min Kim posed for a group photo with Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho >
KAIST (represented by President Kwang Hyung Lee) announced on the 20th of December that a research team led by Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho from the Department of Bio and Brain Engineering has developed a groundbreaking technology that can treat colon cancer by converting cancer cells into a state resembling normal colon cells without killing them, thus avoiding side effects.
The research team focused on the observation that during the oncogenesis process, normal cells regress along their differentiation trajectory. Building on this insight, they developed a technology to create a digital twin of the gene network associated with the differentiation trajectory of normal cells.
< Figure 1. Technology for creating a digital twin of a gene network from single-cell transcriptome data of a normal cell differentiation trajectory. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a digital twin creation technology that precisely observes the dynamics of gene regulatory relationships during the process of normal cells differentiating along a differentiation trajectory and analyzes the relationships among key genes to build a mathematical model that can be simulated (A-F). In addition, they developed a technology to discover key regulatory factors that control the differentiation trajectory of normal cells by simulating and analyzing this digital twin. >
< Figure 2. Digital twin simulation simulating the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells. The dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data for the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells were analyzed (A) and a digital twin of the gene network was developed representing the regulatory relationships of key genes in this differentiation trajectory (B). The simulation results of the digital twin confirm that it readily reproduces the dynamics of single-cell transcriptome data (C, D). >
Through simulation analysis, the team systematically identified master molecular switches that induce normal cell differentiation. When these switches were applied to colon cancer cells, the cancer cells reverted to a normal-like state, a result confirmed through molecular and cellular experiments as well as animal studies.
< Figure 3. Discovery of top-level key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells. By applying control factor discovery technology to the digital twin model, three genes, HDAC2, FOXA2, and MYB, were discovered as key control factors that induce differentiation of normal colon cells (A, B). The results of simulation analysis of the regulatory effects of the discovered control factors through the digital twin confirmed that they could induce complete differentiation of colon cells (C). >
< Figure 4. Verification of the effect of the key control factors discovered using colon cancer cells and animal experiments on the reversibility of colon cancer. The key control factors of the normal colon cell differentiation trajectory discovered through digital twin simulation analysis were applied to actual colon cancer cells and colon cancer mouse animal models to experimentally verify the effect of cancer reversibility. The key control factors significantly reduced the proliferation of three colon cancer cell lines (A), and this was confirmed in the same way in animal models (B-D). >
This research demonstrates that cancer cell reversion can be systematically achieved by analyzing and utilizing the digital twin of the cancer cell gene network, rather than relying on serendipitous discoveries. The findings hold significant promise for developing reversible cancer therapies that can be applied to various types of cancer.
< Figure 5. The change in overall gene expression was confirmed through the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors, which converted the state of colon cancer cells to that of normal colon cells. The transcriptomes of colon cancer tissues and normal colon tissues from more than 400 colon cancer patients were compared with the transcriptomes of colon cancer cell lines and reversible colon cancer cell lines, respectively. The comparison results confirmed that the regulation of the identified key regulatory factors converted all three colon cancer cell lines to a state similar to the transcriptome expression of normal colon tissues. >
Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho remarked, "The fact that cancer cells can be converted back to normal cells is an astonishing phenomenon. This study proves that such reversion can be systematically induced."
He further emphasized, "This research introduces the novel concept of reversible cancer therapy by reverting cancer cells to normal cells. It also develops foundational technology for identifying targets for cancer reversion through the systematic analysis of normal cell differentiation trajectories."
This research included contributions from Jeong-Ryeol Gong, Chun-Kyung Lee, Hoon-Min Kim, Juhee Kim, and Jaeog Jeon, and was published in the online edition of the international journal Advanced Science by Wiley on December 11. (Title: “Control of Cellular Differentiation Trajectories for Cancer Reversion”) DOI: https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202402132
< Figure 6. Schematic diagram of the research results. Professor Kwang-Hyun Cho's research team developed a source technology to systematically discover key control factors that can induce reversibility of colon cancer cells through a systems biology approach and a digital twin simulation analysis of the differentiation trajectory of normal colon cells, and verified the effects of reversion on actual colon cancer through molecular cell experiments and animal experiments. >
The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and ICT and the National Research Foundation of Korea through the Mid-Career Researcher Program and Basic Research Laboratory Program. The research findings have been transferred to BioRevert Inc., where they will be used for the development of practical cancer reversion therapies.
2024.12.23 View 107553